Tsoliclone is a monoclonal antibody produced by genetic engineering. Most often, mice are used to obtain it - a special antigen is injected into the animal, and then rodent ascites fluid is obtained, which contains the indicated antibodies. Morphologically, they belong to class M immunoglobulins, i.e. acute phase antibodies. Their mechanism of action is due to the formation of an antigen-antibody complex, where some molecules (in this situation, proteins that determine the blood group and its Rh) located on the cell membrane act as antigens.
Why is the analysis carried out?
Group and Rh factor are genetically determined blood characteristics that are inherited from parents and remain unchanged throughout a person’s life.
. The classification of blood groups is carried out based on a certain set of biochemical parameters and the composition of antigens, and has 4 main groups. Transfusing a patient with blood of an incompatible group or with a different Rh factor carries with it a mortal danger - the immune system begins to produce antibodies against foreign cells that attack and destroy them. It is for this reason that in situations that carry the risk of extensive blood loss, it is necessary to accurately determine the blood identity and Rh factor of both the donor and the recipient.
What are zoliclones?
Tsoliklon is a saline solution of monoclonal antigens to human erythrocyte antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies are used to determine blood group. To obtain them, hybridoma technology is used. Anti-A and anti-B zoliclones were created to determine human blood groups of the ABO system instead of standard isohem agglutinating sera.
Absolutely all people develop their own special circulatory system in the womb. Being aware of your blood type is, of course, important, but not enough. Read more in the article: “Blood group 1, Rh negative.”
Coliclones anti-A and anti-B are hybridoma products of cell lines acquired as a result of the fusion of mouse antibody-producing B lymphocytes with mouse tumor cells (bone marrow myeloma). Personal hybridomas produce bands of homogeneous antibodies only of the 1st class, which, immunoglobulins, are entirely similar in structure and bio Antibodies. The activities produced by cells of the 1st clone (offspring of one cell) are monoclonal.
In antibodies, cells of the same specificity, originating from the 1st form, lymphocyte cells of the 1st clone. The main thing is that you need to: then get special antibodies from one cell and develop them in huge quantities. The difficulty lies in overcoming two tasks: firstly, ordinary cells die after several divisions; secondly, only cancer cells are capable of multiplying indefinitely. To solve these two incomparable problems, G. Köhler and K. Milstein made cell modifications or hybridomas in 1975. Hybridomas are the fusion of ordinary lymphocytes in a nutrient medium with lymphocyte cells. myelomas do not die in this environment, and from the myeloma they receive a partner the opportunity to endlessly reproduce. In a similar hybridoma way, the clan multiplies, and as a result of this process, monoclonal antibodies are formed.
Chlamydia in women is a urogenital venereal disease caused by chlamydia. More than half of the cases are asymptomatic. During the manifest course or relapse, patients may complain of itching in the vagina, pain during urination, mucous or purulent-mucous leucorrhoea, pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, and groin area. Read more in the article: “how chlamydia manifests itself in women.”
How is the research conducted?
To determine a blood group using cyclones, you need a flat, even surface (plate) moistened with water, a set of chemical reagents and biological fluid samples, and a specialist can use any blood: capillary, venous, frozen, etc.
- The sides of the tablet are marked so as not to confuse which of them will be applied to one or another type of zoliclones.
- One drop of reagents (usually anti-A and anti-B cyclones) and blood are dropped onto the surface, and the volume of chemicals should be 8-10 times greater than the volume of the biomaterial.
- Wait 3-5 minutes, gently rocking the plate so that the liquids are well mixed and red blood cells do not settle around the edges of the samples.
After a few minutes, a reaction will occur, by which it is possible to determine with high accuracy whether the blood belongs to a certain group.
Test tube determination technique
- Prepare a 5% suspension of washed red blood cells in saline solution.
- Add 0.1 ml of Anti-D-Super (Anti-D IgM) coliclone and one drop of red blood cells to the test tube.
- Stir the contents.
- Incubate the tube for half an hour. The reaction rate increases when the test tube is heated to 37 °C using a water bath or thermostat.
- Centrifuge the tube at 1500 - 2000 rpm at room temperature for half a minute.
- Shake the test tube lightly to separate the sediment from the bottom.
- Visually assess for the presence of agglutination. When antigen D is detected, one or more clearly visible agglutinates are formed against the background of a clear NaCl solution. Otherwise, the sediment is easily broken up and becomes an opaque homogeneous suspension.
incubation in a thermostat
centrifugation
pronounced agglutinates
opaque suspension
Decoding the results
Determination of the group of erythrocyte antigens and the Rh factor has long become one of the mandatory studies for most patients admitted for hospital treatment. It can be carried out at any level of medical care, provided that the necessary reagents and instruments are available.
Typically, group determination is carried out using standard sera, although it is competed by another method, similar in methodology to the reference one, using zoliclones.
Advertising:
Coliclone is a monoclonal antibody produced by genetic engineering. Most often, to obtain it, mice are used; a special antigen is injected into the animal, and then rodent ascites fluid is obtained, which contains the indicated antibodies.
Morphologically, they belong to class M immunoglobulins, i.e. acute phase antibodies. Their mechanism of action is due to the formation of an antigen-antibody complex, where some molecules (in this situation, proteins that determine the blood group and its Rh) located on the cell membrane act as antigens.
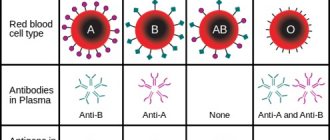
Table. Reactions of different blood groups with anti-A and anti-B zoliclone.
| Blood type | Reaction with zoliclone anti-A | Reaction with zoliclone anti-B |
| Group I | Absent | Absent |
| Group II | Positive | Absent |
| III group | Absent | Positive |
| IV group | Positive | Positive |
Coliclone anti-D IgG
Anti-D IgG zolicone is used to detect all types of red blood cell D antigen. Allows detection of weak Du antigen and variants DI - DVII. It is used in the indirect antiglobulin test and in the conglutination reaction with gelatin.
The reagent is used:
- as a clarifying diagnostic tool for identifying partial variants of the DI - DVII antigen in samples of donor erythrocytes, which, in reaction with monoclonal anti-D IgM reagents, were initially determined to be D-negative;
- as an independent reagent for identifying all types of antigen D: D, Du, DI - DVII.
The active principle of the diagnosticum is human monoclonal IgG antibodies. Produced by a human-mouse heterohybridoma cell line.
What should you consider when conducting your analysis?
In order for the analysis result to be as reliable as possible, a number of conditions must be met during the procedure:
Advertising:
- reagents should be stored in a cool place at a temperature of +2-8 degrees in bottles with a tightly screwed cap (if storage rules are violated, they quickly lose their properties);
- For analysis, you cannot use cyclones that have expired (about 30 days) or liquids that contain sediment, flakes or debris;
- the study is performed in a well-lit room at an air temperature of no lower than +15 and no higher than +25 degrees, and there should be no dirt, dust or other factors that can distort the result;
- when applying biomaterial and reagents to the surface of the tablet, the proportions must be strictly observed - if there is too much blood, the reaction is more difficult to track, and in the opposite case (with a small volume) it will be too slow;
- Drops of blood mixed with different types of zoliclones should not be allowed to merge together - if this happens, the test is carried out again; for the same reason, different sticks should be used to mix reagents with biomaterial.
The reaction duration should be at least 3 minutes, and if the result is questionable, the observation time for biomaterial samples should be extended to 5 minutes. However, after 10 minutes, the biomaterial may dry out and red blood cells may naturally precipitate, so you should not trust such a study.
Typing on a plane
- Label the plate: indicate the patient’s name and the name of the reagent.
- Apply one drop (approximately 0.1 ml) of Anti-D-Super reagent to the surface.
- Place one small drop (0.01 - 0.05 ml) of red blood cells nearby.
- Using a clean glass or plastic rod, mix two drops.
- Wait 10 – 15 seconds.
- Gently rock the record for 20 to 30 seconds.
- Evaluate the result in 3 minutes.
Typically, characteristic large-lobed hemagglutination is observed after 30–60 seconds, but in the presence of Du antigen, the reaction time increases. Warming the plate to 37 °C increases the reaction rate.
Why is analysis necessary?
Advertising:
Currently, zoliclones are used primarily to determine blood group and Rh factor. The study can be carried out as planned, as prescribed by a local physician, or for emergency indications when a blood transfusion is required (massive blood loss occurred during the operation or the patient was delivered with extensive trauma and massive bleeding). In the clinic, group determination is carried out mainly through the use of sera.
Blood group based on cyclones is most often determined in a hospital or specialized laboratories. The use of zoliclones is usually resorted to when it is impossible to use serums. The speed of obtaining results is somewhat faster than when testing with standard sera, which makes the technique more universal. Many laboratories are trying to switch to using this method.