Without electrolytes, not a single vital process occurs in the human body. They determine the acid-base balance, maintain osmotic pressure in the blood plasma, and perform other important functions. Without electrolytes, cells will stop interacting, muscles will stop contracting, and nerve fibers will stop transmitting signals. Everything will stop. The balance of sodium, potassium and chlorine is a significant indicator of human health, especially the functioning of the heart and kidneys. Program 116 “Electrolyte balance in the body” allows you to determine the general state of health and diagnose electrolyte metabolism disorders that lead to serious consequences - shock, respiratory and heart failure, arrhythmia and cardiac arrest.
The composition of the program is designed in such a way as to determine the main indicators of electrolyte and acid-base balance:
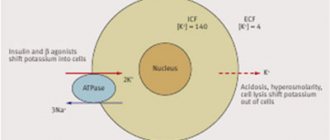
- Potassium (K+) is clinically important for assessing renal function, the cardiovascular system, diagnosing arrhythmias, hypertension, and adrenal insufficiency.
- Sodium (Na+) reflects the health of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Chlorine (Cl-). Used for monitoring and dynamic observation of acid-base balance disorders, diagnosis of kidney diseases, diabetes insipidus.
- Calcium (Ca2+) . Determining its concentration is important in diagnosing patients with chronic renal failure, in determining hyperthyroidism caused by phosphate retention in the body, and also for monitoring treatment results.
- Phosphorus . It is used in the diagnosis of various pathological conditions that cause disturbances in phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
- Blood pH – determination of acid-base balance for the diagnosis of acidosis and alkalosis.
Since electrolyte and acid-base imbalances accompany a wide range of acute and chronic diseases, Program 116 “Electrolyte Balance in the Body” can be prescribed to both patients who are already hospitalized and those who have just presented to emergency departments.
Basic electrolytes
Potassium
- an important component of most cells. Together with other electrolytes, potassium ions are responsible for the functioning of muscles and nerves, normal acid-base balance, and water metabolism. The blood contains only a small amount of the macronutrient; even minor fluctuations in its level lead to serious consequences. Significant deviations from the norm can lead to life-threatening conditions (shock, cardiac dysfunction, respiratory failure, etc.). Normal potassium concentration is 3.5-5.1 mmol/liter.
Magnesium
participates in energy production, enzyme synthesis, muscle contraction and other vital processes. It is absorbed from food into the gastrointestinal tract and excreted by the kidneys. A deficiency of this electrolyte can be caused by poor nutrition, problems with its absorption, or excessive loss in urine. Elevated levels may indicate kidney pathologies. Significant electrolyte deficiency leads to symptoms such as weakness, confusion, loss of appetite, and muscle spasms. Its excess manifests itself in a similar way. Heart rhythm disturbances and nausea may also be added to the symptoms.
Sodium
present in all tissues and fluids of the body. It is necessary for muscle contraction and maintaining water-salt balance. The macroelement is absorbed in the intestines from ordinary table salt. Deviations of its normal level are associated with a violation of one of the mechanisms of its maintenance. For example, normal sodium concentrations are disrupted if antidiuretic hormone, which prevents fluid loss through urine, is produced in abnormal amounts. A violation of the amount of this electrolyte leads to the appearance of edema or dehydration, as the amount of fluid in the tissues changes. Sodium testing is used in the diagnosis of many diseases (for example, pathologies of the kidneys, lungs, brain).
Chlorine
It is part of many biologically active substances and performs a number of physiological functions. Its level is normally relatively stable (a slight decrease in levels is observed after eating). A test for the amount of chlorine is often prescribed in conjunction with other studies to identify various pathologies. Its results are also used to determine the cause of weakness, prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, and breathing problems.
What are electrolytes and why are they needed?
If we do not consider the issue from the point of view of biochemistry and physiology, electrolytes are substances that conduct electric current: when performing any exercise, we send a signal to our muscles to contract, and electrolytes are necessary for this signal to be transmitted to its destination.
During training, we move the body from a comfort zone to a zone of extreme stress. Moreover, even training at the so-called “low heart rate” (about 120 beats per minute) represents stress for the body. Depending on the level of training, this stress will be of medium or extreme level. During exercise, body temperature begins to rise. The body immediately turns on its cooling mechanisms, and we begin to sweat. The cooling system in the body is a so-called “open” type system. And this is the main problem: we cool ourselves due to the loss of fluid. Sweat evaporates and this physical process cools our skin.
When you lose beneficial minerals
The causes of loss of electrolytes in the body can be divided into natural and pathological. I will give the most common reasons.
Meager diet
If you eat few vegetables, fruits, greens and nuts, you will constantly face a deficiency of electrolytes. Popular foods such as baked goods, sweets and processed foods contain virtually no minerals.
Sports, hard physical work, heat
To lower body temperature, the body intensively secretes sweat. Sodium and potassium usually leave with the fluid. This is why sports drinks are so popular among those who go to the gym or run.
Lack of fluid
As I wrote above, minerals become electrolytes in the body only in an aqueous solution. If there is little moisture, they only clog the internal organs, especially the kidneys.
Taking medications
The process of mineral absorption can be disrupted by the following drugs: diuretics, NSAIDs, antibiotics. After stopping the course of treatment, the balance of electrolytes in the body is restored.
Tip: drink 1.5–2 liters of water per day and don’t forget about vegetables and fruits. Do not get carried away with laxatives and diuretics.
Pathological causes of electrolyte deficiency are acute and chronic diseases. Thus, food poisoning causes vomiting and diarrhea. Minerals leave along with the liquid, which only aggravates the problem. Therefore, to restore the balance of electrolytes in the body after poisoning, doctors recommend taking a salt preparation, for example, Regidron.
The following diseases often lead to improper absorption of micro and macroelements:
- stomach (gastritis, ulcer);
- kidney;
- endocrine system (especially pathologies of the thyroid gland - thyroiditis, hypothyroidism);
- cystic fibrosis;
- gout;
- dysbacteriosis or intestinal infection with worms.
In such situations, drinking sports drinks and taking dietary supplements is useless. First you need to cure the underlying disease. Then the exchange of electrolytes in the body will gradually return to normal.
Are electrolytes needed for excessive sweating?
When you sweat, you lose water and electrolytes, especially sodium and chlorine. As a result, long periods of exercise or activity, especially when the body heats up, can lead to significant loss of electrolytes. It is estimated that sweat contains on average about 40-60 mmol sodium per liter ().
But the actual amount of electrolytes lost through sweat can vary from person to person (, ).
In the US, the maximum recommended sodium intake is 2,300 mg per day, which is equivalent to 6 g or 1 teaspoon of table salt ().
Since about 90% of American adults consume more than this, most people do not need to replace the sodium lost through sweat ().
However, some people, such as athletes who exercise for more than two hours or those who exercise in high temperature environments, may want to consider drinking sports drinks fortified with electrolytes to replenish electrolyte losses ().
For everyone else, getting a normal amount of sodium from foods and drinking water is enough to stay hydrated.
You lose water and electrolytes, especially sodium, when you sweat. However, the sodium consumed through your diet is usually enough to cover any losses.
General analysis
It is one of the basic tests required when visiting many specialists.
General analysis among specialists may also be referred to as “clinical”, or bear the abbreviation KLA. It is a whole set of tests aimed at determining both the quantity and parameters (size, etc.) of various blood cells.
The test allows blood sampling from both a vein and a finger (capillary).
Indications for use, preparation for the study
This is one of the most common laboratory tests performed to assess the general health of a patient. Prescribed for routine medical examinations, preparation for surgery, and included in the medical commission.
Symptoms for which a doctor may prescribe OAC: complaints of fatigue, weakness, apathy, signs of an infectious disease or inflammation, and elevated body temperature. A timely test allows you to diagnose and promptly treat a whole range of serious diseases.
The results of your analysis will be as reliable as possible if, before taking it, you:
- the day before your visit to the clinic, exclude alcohol and medications from your diet (in consultation with your doctor);
- You will not take it for 8 hours before the test (you can drink still water);
- Half an hour before donating blood, it is advisable not to overexert yourself physically and emotionally. Try not to smoke either.
General blood test indicators
The blood test includes a number of parameters. First of all, this is the calculation of the number of red blood cells (oxygen transport), leukocytes (ensure the fight against bacteria and viruses), platelets (blood clotting) per microliter or liter of blood. This also includes other indicators that describe the shape, volume and other characteristics of the cells being studied.
The basic table with blood sampling results includes:
- hemoglobin level
- hematocrit
- average red blood cell volume
- average hemoglobin content in an erythrocyte
- average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes
- platelets
- white blood cell count
- red blood cell count
In addition to basic indicators, the doctor may prescribe a leukocyte formula (the ratio of different forms of leukocytes as a percentage) and a calculation of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Professionals call such a comprehensive study a “clinical blood test.”
Stock
Antibody test for coronavirus (COVID-19)
2000a
Rapid test for coronavirus (COVID-19)
Results within 25 minutes from the moment the biomaterial is submitted
1600a
Coronavirus (COVID-19) antibody test at home
from 4000 a
Coronavirus (COVID-19) test at home
from 4200 a
Coronavirus (COVID-19) test
2200a
What foods are rich in electrolytes?
The answer to this question will sound like this: all food is more or less saturated with electrolytes. However, there are a number of products whose salt levels are simply off the charts. It is this food that will quickly replenish the deficiency of calcium, potassium, magnesium, chlorine or sodium in the blood. All that remains is to properly prepare these products (or better yet, consume them raw) in order to get the maximum benefit. So, the most electrolytes are in:
- Leguminous plants . The leader in salt content is white beans. It contains the greatest amount of potassium.
- Plain beets , loaded with sodium. Eating beets in moderation has a beneficial effect on the functioning of all organs of the human body.
- Nutritious seeds and nuts . Sesame and sunflower seeds are rich in magnesium. The presence of these products in the diet will help improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Before going on a diet, it is recommended to consult with a specialist about what components your body is missing and what products will help fill this deficiency.
Analysis for tumor markers
Today, comprehensive cancer screening is not possible without laboratory tests, in particular, blood tests for tumor markers. Regular testing allows you to detect a serious disease at an early stage.
Indications for passing
The test is prescribed by a doctor both during a course of treatment to assess its effectiveness and to prevent relapses.
If you conduct an examination yourself, without a doctor’s prescription, its results should be provided to specialists for correct interpretation!
Analysis results
It is important to understand that diagnosing cancer cannot be based solely on the results of laboratory blood tests, since benign neoplasms and inflammatory processes can also provoke an increase in the level of tumor markers.
Only a comprehensive study under the supervision of experienced doctors will help you reliably identify a malignant tumor at an early stage.
Our clinic specialists will provide you with a sufficient set of examinations to monitor your health.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
Children and newborns are most susceptible to electrolyte imbalance. The concentration of electrolytes in the blood can change significantly when various diseases occur. If the level of electrolytes is elevated, they are removed by dialysis or using special resins; if the level is low, medications are prescribed.
How to replenish lost electrolytes?
There are specialized supplements such as isotonics, but they do not fully compensate for the loss of salts.
Based on my own experience, I can confidently say that I have not tried a better electrolyte complex than Electrolytes Plus. One tablet contains a unique combination of four essential salts: sodium, calcium, potassium and magnesium. A similar additive is available in the form of electrolyte powder. Personally, I find it more convenient to use the supplement in tablet form. The ratio of salts in this supplement was not chosen by chance: as a result of research, scientists developed a formula for the complex that, in its chemical composition, is as close as possible to the composition of electrolytes lost through sweat.
I first started taking this electrolyte complex last summer. At this time, I actively included intense interval training, combining CrossFit complexes with weights and running at the stadium. I ran long cross-country races and did tempo work. All this happened in the heat, the temperature reached 35 degrees. And under these conditions, the Electrolytes Plus supplement coped with the task one hundred percent: there were no signs of heat stroke, muscle spasms or cramps, and no loss of strength.
Play a vital role for the body
Electrolytes are critical to keeping your nervous system and muscles healthy and your internal environment balanced.
Nervous system
Your brain sends electrical signals through nerve cells to communicate with cells throughout your body.
These signals are called nerve impulses, and they are generated by changes in the electrical charge of the nerve cell membrane ().
The changes occur due to the movement of sodium electrolyte across the membrane of nerve cells.
When this happens, it sets up a chain reaction, moving more sodium ions (and a change in charge) along the length of the nerve cell's axon.
Muscle work
Calcium as an electrolyte is necessary for muscle contraction ().
Related articles:
- Symptoms of anemia in women: external signs, risk factors
- How to treat food poisoning at home
It allows muscle fibers to move simultaneously and move over each other as the muscle contracts and contracts.
Magnesium is also needed in this process so that muscle fibers can tense and relax after contraction.
The role of electrolytes in the body is enormous. Electrolytes are especially important during sports
Hydration
Water must be stored in the correct amount both inside and outside every cell of your body ().
Electrolytes, especially sodium, help maintain fluid balance through osmosis. This is one of the main roles of electrolytes in the body.
Osmosis is the process where water moves through the cell membrane wall from a dilute solution (more water and less electrolytes) towards a more concentrated solution (less water and more electrolytes).
This prevents cells from rupturing from too much water and vice versa due to dehydration ().
Internal pH levels
To stay healthy, your body must regulate its internal pH ().
pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is. In your body, it is regulated by chemical buffers, or weak acids and bases, that help minimize changes in the internal environment.
For example, the blood constantly renews itself to remain at a pH level of approximately 7.35-7.45. If it deviates from this, the body will not be able to function properly and you will become ill.
Having the correct balance of electrolytes is fundamental to maintaining pH levels in the body and blood in particular ().
Electrolytes are necessary to maintain the functioning of the nervous system and muscles. They also ensure that your body's internal environment is optimal by maintaining proper hydration levels and helping regulate your internal pH.