Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Cardiovascular diseases — How to quickly lower blood pressure at home
Consistently high blood pressure is a pathological condition indicating the development of a dangerous disease - hypertension. Arterial hypertension is the most common disease in the world. Without timely treatment, hypertension causes complications such as diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidney failure, and loss of vision.
The importance of high blood pressure as a risk factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases increases with age.
Normal blood pressure numbers
The movement of blood through a closed circulatory system is the joint work of the heart and blood vessels.
There are two indicators of blood pressure:
- Systolic (upper) pressure is formed during the period of myocardial contraction, when blood from the left ventricle is ejected into the vascular bed.
- Diastolic (lower) pressure is maintained in the vessels during the diastole phase - the period of relaxation of the heart after contraction.
The unit of measurement for blood pressure is the millimeter of mercury (mmHg). This is due to the fact that the first device in history to measure blood pressure was mercury, and the result was determined by the level of the mercury column. The International Association of Cardiology has determined the norm for blood pressure to be no higher than 130/80 mmHg.
In a healthy person, blood pressure changes during the day under the influence of external and internal factors: physical activity, stressful situations. This is a normal adaptive reaction. The body contains mechanisms of nervous and humoral regulation that return blood pressure to its original level after the cessation of the action of provoking factors.
Classification of antihypertensive drugs
Blood pressure is maintained by several physiological mechanisms: peripheral vascular resistance, heart rate and circulating blood volume. Antihypertensives usually affect one or more mechanisms of blood pressure maintenance.
Drugs that reduce the activity of the sympathetic nervous system
- Central type of action (clonidine, methyldopa, guanfacine, moxonidine)
- Beta-blockers (metoprolol, nebivolol, bisoprolol, atenolol, betaxolol, talinolol, carvedilol)
- Alpha blockers (prazosin, doxazazin, terazosin)
- Gagnlioblockers (hexamethonium benzosulfonate, azamethonium bromide, etc.)
Peripheral vasodilators (peripheral vasodilators)
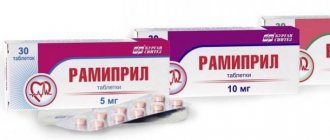
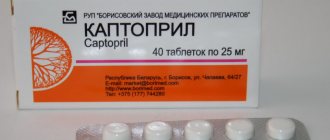
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril, captopril, perindopril, moexipril, spirapril)
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (valsartan, irbesartan, losartan, telmisartan, eprosartan)
- Calcium ion antagonists (nifedipine, amlodipine, lacidipine, isradipine, verapamil, diltiazem)
- Antispasmodics of myotropic type of action (papverine, bendazole)
Agents affecting water and electrolyte balance
- Diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, torsemide, chlorthalidone, spironolactone)
In addition to the drugs listed in the classification, blood pressure can be lowered by drugs that reduce psycho-emotional stress. For example, sedatives or tranquilizers.
What pressure is considered high
Provoking factors that cause increased blood pressure include:
- At a young age: smoking, addiction to alcohol, drug use, congenital anomaly of the renal vessels, vegetative-vascular dystonia, pathology of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- With age, the role of obesity, endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism), diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and in women - hormonal imbalance during menopause, and neuropsychic overload increases in the development of hypertension.
- In old and senile age, atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels come to the fore.
Arterial hypertension is diagnosed when systolic and diastolic pressure levels are equal to or greater than 140/90 mmHg. Art.
A persistent increase in systolic and diastolic pressure by 5-10 mmHg. Art. increases the incidence of strokes by 30-40%, and heart attacks by 25-30%.
When can you not do without a doctor?
In the treatment of arterial hypertension, other drugs are traditionally used, which, in general, do not have pronounced features inherent in any specific group of antihypertensives. For example, the same dibazole or, say, magnesium sulfate (magnesia), which is successfully used by emergency doctors to relieve a hypertensive crisis.
Magnesium sulfate injected into a vein has an antispasmodic, sedative, anticonvulsant and slightly hypnotic effect. A very good drug, however, it is not easy to administer: it must be done very slowly, so the work lasts for about 10 minutes (the patient becomes unbearably hot - the doctor stops and waits).
For the treatment of hypertension, in particular, in severe hypertensive crises, pentamine-N (an anticholinergic blocker of the sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia, which reduces the tone of arterial and venous vessels), benzohexonium, similar to pentamine, arfonad (ganglioblocker), and aminazine (phenothiazine derivatives) are sometimes prescribed. These drugs are intended for emergency care or intensive care, and therefore can only be used by a doctor who is well aware of their characteristics!
Ways to lower blood pressure permanently
In the initial stages of hypertension, the first step is to prescribe therapy with non-drug methods associated with changing the patient’s lifestyle:
- To give up smoking. Tobacco smoking is recognized as one of the main risk factors for the development of arterial hypertension. One cigarette smoked leads to a sharp increase in blood pressure and increased heart rate.
- Normalization of body weight. Numerous studies have proven that losing weight in overweight or obese patients leads to stabilization of blood pressure.
- Increasing physical activity. Regular dynamic physical exercises in the air for 50-40 minutes at least 4 times a week are recommended.
- Reducing salt intake to 5 g/day.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Compliance with the work and rest regime.
- Balanced diet. Increasing the proportion of plant foods and low-fat dairy products in the diet.
While blood pressure is slightly elevated, following the principles of a healthy lifestyle can stabilize blood pressure at a normal level with minimal drug support or even without drugs at all.
As the disease progresses, hypertension is treated using medications from various pharmacological groups to achieve a reduction in blood pressure to normal levels.
First aid at home for symptoms of high blood pressure:
- It is necessary to reassure the patient and create conditions for physical and emotional peace.
- Provide a flow of fresh air into the room.
- Breathing exercises help to quickly reduce pressure: take a deep breath, hold your breath for 10 seconds, exhale noisily through your mouth, then take short breaths in and out through your mouth for 2 minutes.
- Give the patient Corvalol to drink: dissolve 30 drops in 100 ml of water.
If attacks recur repeatedly, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause of the increase in pressure.
How to measure pressure correctly
Rules for measuring blood pressure (BP):
Blood pressure is measured when a person is at rest: no earlier than 1.5–2 hours after eating, smoking, drinking coffee and other tonic drinks.
The best position for measuring pressure is when the person is sitting on a chair and the hand on which the pressure is supposed to be measured is placed on the table. The part of the arm on which the cuff is applied must be freed from pressure clothing and the muscles relaxed, as muscle contractions can lead to incorrect results.
The cuff, depending on the type of tonometer, is applied either to the lower third of the shoulder, not reaching 2.5 cm to the upper edge of the cubital fossa, or to the wrist.
While the tonometer is operating, it is important to maintain a motionless posture, do not move your hand, do not talk, or worry.
For the first time, the pressure is measured on both hands. If the difference between the readings does not exceed 10 mm Hg. Art., then subsequent measurements are usually performed on the non-working hand - for right-handers on the left, for left-handers - on the right. If the indicators differ by more than 10 mm Hg. Art. it is necessary to measure the pressure on the arm, where large numbers are recorded.
It is necessary to measure blood pressure, especially for people who have already been diagnosed with hypertension, twice a day: in the morning an hour after waking up and in the evening before going to bed. The number of measurements during the day varies depending on how you feel, if alarming symptoms appear indicating increased blood pressure.
Patients measuring blood pressure at home are advised to record the results in a special diary. Such blood pressure monitoring allows you to monitor blood pressure levels and evaluate the effectiveness of medications used to reduce blood pressure.
Blood pressure is measured using a special tonometer device.
Two modifications of tonometers are used:
- Mechanical
- Semi-automatic
Mechanical aneroid sphygmomanometers are used mainly in medical institutions, since their use requires certain knowledge and skills. The cuff is placed on the shoulder, air is pumped into its chamber using a rubber bulb, and tones are listened to using a phonendoscope.
For home use, it is better to use automatic or semi-automatic models of tonometers.
A semi-automatic tonometer works on the following principle: a cuff is fastened on the wrist, air is pumped into it with a bulb, which soon comes out automatically. At the end of the measurement, the results appear on the display.
To operate the automatic blood pressure monitor, simply place the cuff on your wrist and press the start button. All other actions occur automatically. Various types of automatic tonometers have been developed: with a shoulder cuff, wrist, finger.
Calcium antagonists
By blocking the penetration of calcium ions into cells, these drugs cause a reflex relaxation of the muscle walls of blood vessels, reducing their tone. As a result of the expansion of the lumen of the arteries, the blood pressure decreases. Side effects of such drugs include: tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances, dizziness. Popular tablets of this group:
- Dialtiazem;
- Verapamil;
- Norvasc.
The drugs effectively reduce blood pressure in various forms of hypertension, but do not combine well with other groups of antihypertensive drugs and have many contraindications.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
Very often, the increase in pressure does not manifest itself for a long time. This is the insidiousness of hypertension. It is not for nothing that the disease is called the “silent killer” - for many years the pathological process progresses in the body: the heart, blood vessels, kidneys are destroyed, but the person feels well, so he does not go to the doctor.
Over time, the patient develops fatigue, headaches of varying degrees of intensity, decreased performance, and sleep disturbances. Damage to target organs causes pain in the heart, blurred vision, irritability, and decreased performance.
Signs of high blood pressure:
- Hypertensive crisis is a dangerous condition caused by a sharp increase in blood pressure to high numbers (190/120 mm Hg).
- Symptoms of a hypertensive crisis:
- A sharp headache, mainly in the occipital region.
- Tachycardia, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Visual impairment.
- Dizziness.
Trying to lower your blood pressure on your own can lead to myocardial infarction or stroke. If symptoms indicating high blood pressure appear, you should immediately call an ambulance and urgently take measures to reduce the pressure.
Before the medical team arrives:
- Sit the patient down and place pillows under his back.
- Check pressure every 15 minutes.
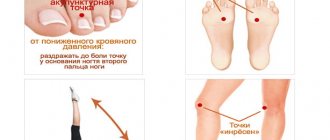
- Hot foot bath for blood flow to the lower extremities. For this purpose, mustard plasters are also applied to the calves of the legs.
- An antihypertensive tablet under the tongue - Andipal, Capoten, Captopril.
New drugs are the safest
New generation medications for hypertension cause fewer side effects and are the safest.
Advantages:
- The composition includes active ingredients that reduce the negative effects on the body. At the same time, they do not lose their effectiveness.
- The effect of one tablet is enough for at least a day, because new generation drugs have a cumulative effect.
- The medications contain substances that have a positive effect on all organs and vital systems.