Sex hormones regulate not only reproductive function, they influence organs and tissues, mucous membranes. The coordinated work of all systems and organs in a healthy woman does not lead to noticeable changes during one cycle. often various disturbances in the balance of sex hormones , especially obvious symptoms in the cardiovascular system. Fluctuations in the level of estrogens, gestagens and androgens lead to various changes - spasms and, conversely, dilation of blood vessels, which affects blood pressure.
On the eve of critical days, many women note a slight increase in blood pressure and a deterioration in their health. And in the presence of arterial hypertension, its course can become poorly controlled. Causes of increased blood pressure:
- Manifestations of PMS. An increase in circulating blood volume leads to an increase in heart function and blood pressure. You should start taking diuretics (at least herbs, herbs), follow a diet and take sedatives in advance.
- Premenopausal period. Estrogen receptors, which are located in the vascular endothelium, do not receive the required dose of the hormone, resulting in their spasm. The result of this action is an increase in blood pressure. These may be fluctuations or a persistent increase in numbers.
- Stress, psycho-emotional lability. In the second phase of the cycle, women are more susceptible to external influences. Stress, overwork, physical strain, domestic and family disagreements lead to disruption of blood pressure regulation at the level of the cerebral cortex
A decrease in pressure on the eve of critical days is more typical for young girls prone to hypotension. Most often they are of asthenic build, melancholic, and prone to depression. A decrease in blood pressure may be associated with the action of progesterone, taking analogue drugs - Utrozhestan, Duphaston and others. A decrease in blood pressure may be one of the manifestations of premenstrual syndrome.
In many ways, a woman’s condition is influenced by the nature of her menstruation; blood pressure can increase, but more often it tends to decrease. High blood pressure numbers are associated with ongoing symptoms of PMS due to the accumulation of fluid in the body and emotional lability. A decrease in blood pressure during menstruation is due to the following: heavy discharge, severe pain, taking medications, diet.
In healthy women, the numbers do not exceed 130/80 mmHg. Correcting your lifestyle, nutrition, and taking medications will help you cope with hesitation. If the readings are higher than indicated or lower than 90/60 mmHg, you should consult a doctor for a detailed examination and to exclude serious diseases.
Read more in our article about the reasons for changes in blood pressure during menstruation.
The relationship between the cardiovascular and reproductive systems in women
Hormones responsible for the proper development of a woman’s menstrual cycle are always present in her body. They have a significant impact on reproductive processes and also help in the regular retreat of the uterine endometrium. The ratio of these sex hormones in a woman’s body changes throughout the entire cycle: before, during and even after menstruation.
Sex hormones depend on the influence of the brain and adrenal hormones, and vice versa. This is due to the fact that adrenaline, aldosterone and glucocorticoids produced by the endocrine system affect the tone of blood vessels and are actively involved in regulating blood pressure. For this reason, many women notice a drop or increase in blood pressure not only during menstruation, but also before it begins.
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the body if the indicator rises for the first time during menstruation. Hypotension or hypertension can be suspected if pressure surges during menstruation persist on the 4th-5th day of the cycle.
You should consult a doctor immediately if you experience the following accompanying symptoms:
- vomit;
- confusion of consciousness and speech;
- intense bleeding;
- severe pain.
Before menstruation
With the onset of menstruation, progesterone always increases. This is a physiologically active substance produced by the endocrine system, which creates favorable conditions for the hatching of the embryo in the uterus. It relaxes its internal mucous membrane, preparing it to receive a fertilized egg, and also improves blood circulation in the pelvic organs, dilating blood vessels and participating in the formation of new branches necessary for the successful development of the unborn child.
Vasodilation leads to increased blood pressure. Normally, its value should be 120/80 mmHg. Art., but for many women it is much higher or lower.
What to do if your blood pressure rises before your period
If the indicator regularly rises, you must stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. For accompanying headaches, you can apply cold compresses and rub essential oils of eucalyptus, lavender or rosemary into the temple area. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- chocolate;
- potato;
- pork;
- sausages and smoked meats.
If the indicator increases, antispasmodics are taken, which promote vasodilation.
Important! Medications are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the data of the anamnesis and examination.
Why does the pressure rise?
High blood pressure can be caused by the following reasons:
- Violation of the water-salt balance of the body, stagnation of fluid in the tissues and resulting tension in the blood vessels;
- constant changes in blood vessels and the active pulsation of blood they cause;
- Significant decrease in serotonin levels in the body.
In the first case, the woman begins to swell greatly, in the second her heartbeat quickens and she feels slight pain behind the sternum, in the third she becomes the subject of frequent emotional outbursts, and sometimes even falls into hysterics.
Is blood pressure related to the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a periodic fluctuation in the concentration of female sex hormones, which repeats every 28-33 days. There are two main phases, depending on the most characteristic changes in the girl’s body:
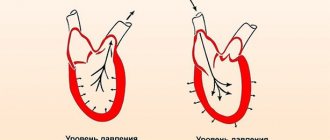
- follicular - from the first day of regula (bloody discharge) to 12-14 days of the cycle. During this period, a large amount of estrogens are synthesized, which cause swelling (infiltration) of the inner layer of the vascular wall. The latter effect contributes to an increase in indicators: a maximum increase in pressure is recorded before menstruation;
- luteal - occurs after ovulation and is characterized by high levels of progesterone (synthesized by the corpus luteum in the ovaries). The latter relaxes the smooth muscle fibers in the vessels and causes a decrease in pressure.
Decreased performance
A sharp jump in blood pressure just before menstruation is associated with the maximum amount of estrogen in the blood, the accumulation of salt and water in the soft tissues of the body. However, after the start of discharge, most women experience a decrease in values. The drop in indicators is associated with a gradual decrease in biologically active substances and fluid loss with menstruation.
Characteristic symptoms may appear:
increased heart rate (heart rate) up to 90-100 per minute;- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness (more often in young thin girls with vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- weakness, fatigue;
- swelling in the lower extremities;
- with heavy bleeding - pale skin and thirst.
On average, systolic blood pressure decreases by 5-10 mmHg, diastolic by 2-5 mmHg. Lower values during menstruation are a reason to consult a doctor.
If blood pressure rises, what contributes to this?
Increased blood pressure often occurs due to narrowing of blood vessels caused by decreased serotonin levels. In addition, fluid in the body puts pressure on the walls of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure.
According to doctors, other reasons can cause high blood pressure:
- changes associated with the processes of distribution, absorption and excretion of water and mineral salts in the body;
- dystrophic disorders of cartilaginous joints and intestinal diseases;
- existing heart and vascular diseases;
- hereditary factor.
Causes of low blood pressure before menstruation
A decrease in pressure on the eve of critical days is more typical for young girls prone to hypotension. Most often they are of asthenic build, melancholic, and prone to depressive moods.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
A decrease in blood pressure may be associated with the action of progesterone. The same effect is achieved by taking analogue drugs, Utrozhestan, Duphaston and others. Its level increases in the second phase. As you know, it relaxes smooth muscles - the intestines, blood vessels and, of course, the uterus. This is a physiological process aimed at maintaining pregnancy if conception occurs during ovulation.
Also, a decrease in blood pressure may be one of the manifestations of premenstrual syndrome.
What causes the drop in blood pressure?
Low blood pressure is most often noticed by women of reproductive age. Most of them perceive menstruation as a serious illness and have difficulty getting out of bed during it.
The reasons for the decline in numbers may be:
- Diseases of the genital organs - endometriosis of the uterus, polyps or benign neoplasms in the uterine cavity. They are accompanied by increased hematopoiesis, decreased hemoglobin levels and insufficient saturation of tissues with nutrients. All this reduces vitality.
- Hormonal imbalance is an abnormal ratio of estrogen and progesterone in the body. The predominance of the first hormone is dangerous for a woman who has reduced glucose production, dilated blood vessels and low blood pressure.
- Algodysmenorrhea, which occurs against the background of increased pain sensitivity and an excess of hormone-like substances - prostaglandins. As well as the excessive use of painkillers against it, which dilate blood vessels.
- Poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency, leading to the development of hormonal disorders and sexual dysfunction. As well as a lack of red blood cells and, as a result, a decrease in vascular tone.
Useful video
Watch this video about whether pressure surges are associated with menstruation:
Similar articles
- Menstruation or bleeding - how not to confuse the dangerous...
It can be very difficult to independently understand whether it is heavy periods or bleeding. However, there are clear signs of menstruation and bleeding, as well as additional symptoms for which it is important to see a doctor. Read more - Toilet and menstruation: features, why it hurts
If a painful toilet and menstruation coincide, then the reasons may be hidden diseases, non-compliance with the diet, the presence of hemorrhoids and others. You can get rid of them if you identify and treat the pathology, as well as carry out prevention. Read more
- Increase in temperature before menstruation...
An increase in temperature occurs before menstruation due to a number of natural reasons (conception, PMS and others), as well as due to the presence of certain diseases. Read more
- Anovulatory menstrual cycle: could it be...
Sometimes there may be menstruation without ovulation. Doctors call this an anovulatory menstrual cycle. If this happens once or twice a year, then there is no need to panic. But if menstrual bleeding occurs without ovulation when planning a pregnancy, then this is a reason to visit a doctor. Read more
Vessels after menstruation
When the “red” days pass, the woman’s well-being improves significantly. However, even after this, high or low blood pressure may persist for several days.
If this phenomenon occurs after the cessation of menstruation, for a fairly long period of time, then the woman should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Otherwise, there is a risk of serious abnormalities in the cardiovascular system.
For high blood pressure
The occurrence of high blood pressure after menstruation is due to the fact that after the end of the menstrual cycle, the woman’s reproductive system still depends on hormones, and reproductive processes in the body continue.
Progesterone creates a new layer of the uterine mucosa and actively participates in the formation of new blood vessels, increases blood flow in them and quickly leads to a change in blood pressure to higher levels.
At low pressure
A decrease in indicators is observed after menstruation no less often than an increase. The reason for this is also the cyclical processes occurring in a woman’s body. The norm is considered to be the time interval in which it is observed, lasting 2-3 days.
Prevention of high blood pressure before menstruation
An increase or decrease in blood pressure on the 2-3rd day of menstruation is observed in most representatives of the fair sex. Therapy is prescribed if the indicator rises constantly and shows high values.
Preventive measures include:
- reducing the amount of salt consumed to 5 g per day;
- physical activity, such as yoga, Pilates or breathing exercises;
- exclusion of coffee;
- organizing a regular and balanced diet, in particular, avoiding fried and spicy foods;
- good sleep;
- prevention of stress.
Prevention methods help if the indicator increases during menstruation. If you have persistent hypertension, you need to visit a specialist.
Treatment
Incorrect pressure must be corrected. In case of painful critical days, it is better to try not to get out of bed unnecessarily. These changes may make you feel dizzy, very drowsy, or even lose consciousness.
Drug treatment
If blood pressure rises during menstruation, it is worth taking medications aimed at relieving pain caused by spasms, as well as dilation of blood vessels. These include: “No-shpa”, “Trigan” or “Papaverine”. It is best to consult your doctor before using these medications. This will avoid side effects.
If the pressure, on the contrary, decreases, then instead of antispasmodics you should take painkillers. Medicines from this group help normalize blood pressure. These include: Coldrex, Analgin, Paracetamol, Theraflu, etc.
Traditional methods
To normalize blood pressure, you can use traditional methods that are no less effective than popular drugs.
An empty glass of mineral water with lemon juice and a teaspoon of honey every day for a week or ready-made cranberry infusion can be used to normalize blood pressure. To prepare the latter, you will need 100 g of sugar and 2 cups of cranberries. These ingredients should be poured with a small amount of water, boiled, then cooled and taken one glass before meals, depending on your needs.
If you have low blood pressure, you can brew St. John's wort or ginger tea.
St. John's wort infusion recipe
Pour a tablespoon of dried St. John's wort into a glass of boiled water, leave for half an hour, and then filter thoroughly. Take 1/4 cup daily before meals as needed.
Ginger tea recipe
Brew tea with sugar. Add half a teaspoon of chopped ginger to the finished drink. Drink three times a day for a week. Do not exceed the indicated dose!
Menstrual irregularities
Iron deficiency
Menopause
Climax
Uterine cancer
Cervical cancer
12089 02 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Menstrual irregularities: causes of occurrence, what diseases cause them, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Menstrual cycle disorders (MCI) are not a pathology, but only a symptom of problems in the female body. A physiologically normal manifestation of the ongoing ovarian-menstrual cycle is the occurrence of menstruation with an individual frequency and duration for each woman. Menstruation is the name given to repeated uterine bleeding, during which an unfertilized egg, endometrial particles and mucous secretions from the cervix are released from the body along with menstrual blood. Normally, they are not accompanied by significant blood loss due to rapid contraction of blood vessels, and their volume is about 150 ml.
The menstrual cycle is not only menstruation, but also the maturation of the egg in the ovary, ovulation and the growth of the endometrium for the potential introduction of a fertilized egg into it.
A healthy woman of reproductive age may experience anovulatory menstrual cycles, during which fertilization does not occur due to the lack of release of the egg. With age, the number of such cycles increases.
Menarche (first menstruation) usually develops by the age of 11-15 and indicates the readiness of the woman’s reproductive system for fertilization. The time at which menarche appears varies from person to person and depends on many factors, such as weight, diet with sufficient fat, heredity, etc.
Types of menstrual irregularities
The menstrual cycle depends on the coordinated functioning of the endocrine system, so the most common cause of its disorders is hormonal imbalance.
- Disorders associated with pathology of the brain (hypothalamic-pituitary structures), which entail a failure of the neuroendocrine regulation of sexual function.
- Pathology of the uterus and/or ovaries.
- Congenital pathologies, including chromosomal ones.
- Diseases of other endocrine organs, for example, hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
Menstrual irregularities after 40 years of age may be associated with the decline of the reproductive function of the female body, while the amount of estrogen naturally decreases, the number of anovulatory cycles increases, and dysfunctional uterine bleeding may occur.
The unevenness of the menstrual cycle in girls of puberty is explained both by the incomplete formation of the reproductive system and by the widespread obsession with diets at this age, in which the body does not receive enough fats necessary for the synthesis of sex hormones.
Symptoms of menstrual irregularities
:
- Changing the duration of the cycle towards decreasing (less than 21 days) or increasing (more than 35 days).
- Delayed menstruation with normal frequency of previous ones.
- Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation in a woman of reproductive age for more than 6 months (can be primary and secondary; secondary is typical for girls of puberty).
- Change in the volume of menstrual blood loss towards increase or decrease.
- Change in the duration of menstruation towards a decrease or increase.
- The appearance of intermenstrual discharge of varying degrees of severity.
- Clinically pronounced pain syndrome (algomenorrhea, algomenorrhea).
With an increase in the volume and duration of menstrual bleeding and the appearance of acyclic bleeding, there is a risk of developing iron deficiency anemia.
For many women, infertility is associated with menstrual irregularities - the absence of pregnancy within 1 year of regular sexual activity without the use of contraception. At the same time, the presence of anovulatory cycles often does not manifest itself in anything other than the absence of conception, so the woman considers herself reproductively healthy.
Menstrual cycle disorders at different age periods of a woman’s life
Juvenile period (up to 21 years). Characterized by delayed menstruation, pubertal bleeding, hair loss, insufficiency or excess body weight. Stress and changes in the sleep-wake cycle can be a provoking factor.
Reproductive period (up to 45–50 years). It is necessary to distinguish between pathological causes of menstrual irregularities and physiological ones.
Physiological reasons include changes in the menstrual cycle due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, and the use of intrauterine contraceptives.
One of the common pathological causes is the formation of a follicular cyst: the egg is not fertilized, excessive growth of the follicle is noted, which leads to the growth of the endometrium. This process can last up to 6–8 weeks, resembling the development of pregnancy, but then heavy menstruation follows, which is dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Pathological bleeding can develop during the ovulatory period, which is associated with insufficiency of the luteal phase (that is, hormonal imbalance). Increased changes in the menstrual cycle should be expected after an abortion (spontaneous (miscarriage) or medical, including medicinal). Restoring the menstrual cycle usually takes about three months; if there are complications, the process becomes protracted.
Menopause and premenopause. During premenopause, changes in hormonal levels in conditions of declining reproductive function lead to disruption of cyclicity and heavy menstruation. In addition, women complain of unexplained mood swings and autonomic disorders (the so-called menopausal syndrome).
Uterine bleeding during menopause is an alarming symptom and requires immediate medical attention.
Pregnancy with an irregular menstrual cycle is possible, but its occurrence depends on the severity of the disorder. Often, menstrual irregularities lead to spontaneous abortion in the early stages.
Which doctors should I contact if I have menstrual irregularities?
Any irregularity in the menstrual cycle requires contacting a gynecologist. In most cases, these disorders have a favorable outcome, but about 10% are gynecological cancers. If necessary, the gynecologist can prescribe a consultation with an endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of menstrual cycle disorders
The leading role in the diagnostic search is played by collecting anamnesis with the obligatory clarification of many factors: the presence of pregnancies and the characteristics of their course, methods of contraception, previous diseases, surgical interventions, determination of body mass index.
To exclude inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, most often caused by infections such as gonococcus, genital herpes, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia, gardnerella, spirochete pallidum, trichomonas, cytomegalovirus, a smear is taken on the microflora to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antimicrobial drugs.
Prevention
To eliminate the pressure from the future, follow the diet, nutrition and use preventive measures accordingly:
- reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your daily diet;
- Limiting the strength of training, preferring equally effective exercises for women: Pilates, yoga or breathing exercises;
- Replace coffee drinks with herbal infusions;
- Quit smoking and drinking alcohol.
Don't forget that every woman's body is a separate system. They must be carefully analyzed to find out how to overcome pressure surges or avoid them. If necessary, please contact specialists.
What to do about blood pressure changes?
If abdominal pain is accompanied by other alarming symptoms: headaches, nausea, weakness, dizziness, then they cannot be ignored. You should know how to give yourself first aid in case of severe pressure surges during menstruation. It is undesirable to use antispasmodics for low blood pressure, as they can provoke a worsening of the condition. They can be replaced with other painkillers - analgesics (Citramon). To lower blood pressure, medications that relieve spasms will be effective, as they dilate blood vessels.
During menstruation, you should refrain from bad habits, avoid eating spicy and fatty foods, and reduce stress when playing sports. Hormonal levels are disrupted during this period, so you need to carefully monitor your body and not overstrain it. Most of the time should be spent in a state of peace and relaxation.
If you feel severe pain and weakness, you should stay at home and take time off from work until your condition returns to normal. For headaches, cold compresses can help, as can breathing or rubbing with essential oils.