Type 2 diabetes mellitus imposes certain restrictions on the patient’s lifestyle. This is especially true for nutrition - you should eat small, varied and balanced, healthy foods, giving preference to fruits, vegetables and whole grains, lean meat, fish and dairy products. Endocrinologists have also developed a special diet that divides all foods into recommended, acceptable and undesirable. Let's take a closer look at each category in our article.
Three basic rules for choosing products
All products, including grains and cereals, for the diabetic menu are selected according to three main criteria:
- Glycemic index (GI). Allowed food, indexed from 0 to 30 units. Limited products are products with GI from 30 to 70 units. A higher glycemic index is not acceptable for diabetics.
- Energy value. The diet of diabetics should not contain high-calorie foods. This is especially true for patients with type 2 diabetes who are obese.
- Content of nutrients in a dish (product). Simple carbohydrates (confectionery and other sweets) are eliminated from the menu. The emphasis in nutrition is on protein foods, slow carbohydrates and fiber.
Diabetics should control portion sizes. Overeating leads to gaining extra pounds. In addition, an important parameter for type 1 diabetes is the number of bread units (XU) contained in products. Based on XE, the correct dose of insulin is calculated.
Millet
Millet is a cereal that is also recommended for diabetes; it will not only saturate the body with useful minerals and vitamins, but will also help fight the manifestations of the disease.
It has been studied that with regular consumption of millet porridge, a person loses excess weight. A decrease in cholesterol was also noted. And as you know, with diabetes, especially type 2, patients often suffer from obesity and atherosclerosis.
This cereal is also useful for the cardiovascular system, as it contains potassium and magnesium in large quantities.
Millet also helps reduce sugar levels, as it has the ability to improve insulin production. There are even traditional methods of treating diabetes using millet. To do this, washed and dried cereals are ground into flour. Take 1 tablespoon of powder in the morning on an empty stomach, washed down with milk. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Therefore, to the question whether it is possible to eat millet porridge if you have diabetes, the answer is unequivocal, you should!
Despite the enormous benefits, for some people it is still better to limit millet. This applies to people with constipation and low acidity of gastric juice. Also, the substances contained in it interfere with the absorption of iodine, so it is not advisable to use millet if you have hypothyroidism.
Prerogative aspects of eating cereals for patients with diabetes
For diabetics, porridge is an integral part of the diet. Firstly, cereals are complex carbohydrates. They are slowly processed by the body, without causing a forced rise in blood sugar levels. Prolonged digestion of porridge does not cause a feeling of hunger for several hours.
This is a prevention of overeating and, as a result, excess weight gain. Secondly, many cereals and grains contain a sufficient amount of dietary fiber, which helps normalize digestive processes. Thirdly, cereals contain those useful elements that are prescribed to diabetics in the form of vitamin and mineral complexes.
Almost all cereals contain the vital group of B vitamins:
- B2 (riboflavin) - normalizes the metabolism of fats and proteins, helps improve vision;
- B1 (thiamine) - has a positive effect on the blood supply to organs and tissues of the body, participates in metabolic processes;
- B5 (pantothenic acid) - takes part in the restoration of damaged cells and tissues;
- B3 (niacin) – responsible for memory and attention, regulates heart function;
- B6 (pyridoxine) - activates the conduction of nerve impulses, increases blood circulation in brain cells, stabilizes the functioning of the nervous system;
- B4 (choline) – prevents the development of visceral obesity;
- B12 (cyanocobalamin) – normalizes the activity of the psycho-emotional state and the activity of the nervous system.
- B9 (folic acid) – eliminates sleep disorders.
Cereals contain minerals, essential amino acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Barley grits
This cereal is a relative of pearl barley; pearl barley is simply polished barley, and barley groats are obtained by crushing unpolished grain. For this reason, barley contains more fiber - this is a huge plus. The porridge is digested slowly and creates a feeling of fullness for a long time.
Barley porridge has the same great benefits as pearl barley: it reduces sugar and cholesterol levels.
Cereals are contraindicated in cases of exacerbation of colitis, chronic constipation, and hyperantocidal gastritis.
Cereals on the menu for diabetics
Before you start developing a daily menu, you need to find out what kind of cereals a person with diabetes can eat. Only cereals that meet the criteria of the diabetic food basket are allowed in the diabetic diet. In addition, cereals come in different varieties, which also needs to be taken into account when choosing.
Reference! During the cooking process, any cereal absorbs water, which reduces its energy value by 2-3 times.
Buckwheat
Buckwheat comes in two types: crushed and whole grain. In case of diabetes, preference should be given to the kernel. It contains a higher percentage of B vitamins, as well as the following micro- and macroelements:
- potassium and magnesium – are responsible for stable heart function;
- iron – prevents the development of anemia (anemia);
- calcium and phosphorus – support healthy bone tissue;
- zinc and manganese – promote the synthesis of natural insulin.
Buckwheat contains lysine, tryptophan, leucine, and arginine. These are essential amino acids that the body urgently needs, but is unable to produce on its own. The energy value of the kernel is 308 kcal/100 g. Buckwheat boiled in water without seasonings and salt contains 98 kcal/100 g.
In 100 gr. crumbly buckwheat porridge contains 17.1 g. carbohydrates or 1.4 XE. The glycemic index of buckwheat is 55 units, which is beyond the acceptable GI for diabetes. Therefore, it belongs to the category of restricted foods, that is, diabetics should not indulge in buckwheat.
It would be optimal to eat buckwheat twice a week. Buckwheat compares favorably with other grain crops with its high content of vegetable protein (13 g/100 g) and fiber (12 g/100 g).
Buckwheat is good for diabetics
Barley and egg
Pearl barley and barley groats are made from a common cereal crop, barley. Yachka is unpolished crushed grains, pearl barley is peeled grain, devoid of shell. Just like buckwheat, pearl barley and barley are rich in B-group vitamins and contain tocopherol acetate, otherwise known as vitamin E. Its direct purpose is:
- strengthening the immune system;
- increasing the strength of the walls of capillaries and large vessels;
- normalization of blood glucose levels;
- maintaining the skin's regenerative capabilities.
Since cereals are made from the same raw materials, their mineral composition is the same. The difference lies in the quantitative content of micro- and macroelements.
| Microelements | Macronutrients |
| iron, manganese, copper, selenium, zinc fluorine, molybdenum | potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, sulfur |
The calorie content of the egg is 313 kcal/100 g. Porridge with water contains 76 kcal/100g. The glycemic index of the product is 40 units. The energy value of raw barley is 324 kcal/100g, boiled - 109 kcal/100g. GI is 30 units.
Regarding bread units, per 100 gr. ready-made pearl barley or barley porridge in water accounts for approximately 1.83 XE. Regular consumption of barley cereals helps cleanse the digestive tract of toxins and the body as a whole of toxic deposits.
Semolina and corn
Semolina is a derivative of wheat. Compared to other cereal crops, semolina contains a minimum of dietary fiber and a maximum of carbohydrates. Semolina porridge is quickly processed by the body and causes a rise in blood sugar levels in diabetics.
The calorie content of cereal is 333 kcal/100 g, ready-made porridge – 99 cal/100 g. The glycemic index of porridge without sugar is 75 units. For diabetics, semolina belongs to the prohibited category of food products.
Semolina porridge contains phytin, a substance that interferes with the absorption of calcium and iron.
Corn porridge, otherwise known as hominy, is a filling and low-calorie dish. Raw cereal contains 328 kcal/100 g. In mamalyga – 92 kcal/100 g. Corn grits are rich in beta-carotene, vitamins B3, B5, B6, potassium and phosphorus. Contains arachidonic, linolenic and linoleic amino acids.
The disadvantage of hominy is its high glycemic index – 75 units. For diabetes mellitus, the product is not recommended. Corn flakes are not allowed in the diet. Their GI is 85 units, energy value ranges from 360 to 380 kcal/100 g. (depending on the manufacturer).
Linen
Flaxseed porridge is a dish with a unique chemical composition. It contains a large amount of Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. There is no need to add butter or sour cream to the porridge. The total fat content is 40 g/100 g.
The flax product is rich in proteins and has a significantly lower carbohydrate component than other cereals. In addition, flaxseed porridge is a leader in dietary fiber content. The vitamin complex is represented by:
- group of vitamins B;
- vitamin E;
- ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is a powerful antioxidant for strengthening the immune system and cleansing blood vessels of cholesterol.
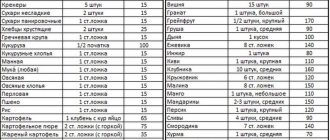
Table of bread units for diabetics
Amount of micro- and macroelements (mg per 100g):
- potassium – 819.6;
- phosphorus – 647.4;
- magnesium - 395;
- calcium 257;
- iron 5.76;
- manganese – 2.52;
- zinc – 4.38.
The composition of nutrients determines the calorie content of the product - 298 kcal/100 g. But the glycemic index does not exceed 35 units. 2 tablespoons (heaped) contain 1 XE.
Oats
Oatmeal is prepared from whole grains or flakes - peeled oats. The vitamin and mineral composition of oatmeal is similar to buckwheat. During industrial processing of grains, cereals lose most of their valuable substances. For example, in terms of the amount of dietary fiber, Hercules oatmeal is inferior even to buckwheat.
In addition, the cereal contains increased carbohydrate content, therefore higher calorie content. Therefore, diabetic patients are recommended to cook porridge from unpeeled oats or the coarsest flakes. The glycemic index of cereals cooked in water is 40 units; when cooked in milk, the figure increases 1.5 times.
Important! Muesli is contraindicated for diabetes; its GI is 80-85 units.
Millet and wheat
These are two different products and should not be confused. Wheat groats are made from durum wheat, millet groats are made from purified millet grains. Wheat contains a large amount of fiber, vitamins B1, B2, B4, B5, B6, B9, potassium, magnesium and phosphorus.
The energy value of raw cereals is 341 kcal/100 g, ready-made wheat porridge is 111 kcal/100 g. The glycemic index of cereal does not exceed 45 units. One unit of bread contains 50-60 grams. cereals (depending on the variety). Considering that wheat boils a lot, a serving of porridge is 100 grams. does not exceed 1.3 XE.
Wheat dishes are available for diabetics due to their low glycemic index
Millet cereal is higher in calories - 378 kcal/100 g. The useful components of the product are vitamins A, E, B-vitamin complex, iron, magnesium, potassium, sulfur, calcium, fluorine, manganese, etc. The main valuable property of millet porridge is its ability to stimulate the production of natural insulin and regulate metabolic processes.
Endocrinologists recommend consuming millet porridge on a regular basis for prediabetes and diabetes. The glycemic index of cereals is 40-50 units. Millet can be cooked in water and 1.5% milk.
Rice
Diabetics need to be extremely careful with rice cereal. Plain white rice has a high glycemic index because it contains a lot of starch and simple carbohydrates. White grains should be avoided. For people with diabetes, brown (brown) and black varieties of rice with a GI of 50 units are allowed on the menu. In 100 gr. Ready-made rice porridge in water contains 2 XE and 110 kcal.
More information about peas and lentils
Peas and lentils are legumes recommended for consumption in diabetes mellitus. Legumes are rich in fiber, a healthy plant protein. Lentils and peas contain vitamins, amino acids, and minerals. Dishes made from legumes make you feel full for a long time.
According to the glycemic index, products belong to the permitted category (GI = 30 units). In terms of energy value, pea porridge contains 84.5 kcal/100 g, lentil porridge – 93 kcal/100 g. For bread units, the approximate content is 1 XE = 60g. ready dish.
Buckwheat
This cereal can be found in every home; since childhood, everyone has heard about its beneficial properties and not without reason. Of all the cereals, it is the most valuable for the body.
Buckwheat is rich in choline. This is a substance that improves the functioning of the central nervous system.
This cereal also helps fight anemia due to its high iron content.
The most important qualities for diabetics are:
- Improving immunity and strengthening blood vessels thanks to the rutin in this cereal.
- A positive effect on heart function, which is achieved with the help of selenium, folic acid, potassium and magnesium.
- Low calorie content (308 kcal in 100 grams of cereal and 132 kcal in buckwheat porridge with water). Although buckwheat contains a lot of carbohydrates, it does not contribute to weight gain because it is digested slowly.
- Regular consumption of buckwheat porridge helps lower cholesterol, thus reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
This cereal should only be limited to people prone to the formation of blood clots; there are no other obvious contraindications.
Diabetic rules for cooking and eating porridge
In order not to provoke an attack of hyperglycemia (increased glucose levels in the blood), porridges for diabetics are prepared in compliance with certain conditions:
- the basis is water or milk with a fat content of no more than 1.5%;
- It is prohibited to add sugar; it is replaced with fresh or frozen berries, dried fruits (except raisins), and nuts;
- it is necessary to wash the cereal to remove excess starch;
- butter is allowed in the compensated stage of the disease, no more than 5 grams. per serving (diabetologists recommend replacing tea oil with 10% sour cream);
- It is better to eat viscous porridge for breakfast;
- It is not recommended to cook oatmeal; they should be brewed with boiling water and left to infuse;
- the volume of the dish cannot be exceeded (a single serving for type 2 diabetes is 200 grams, for type 1 diabetes it is calculated according to XE):
- cereals with a glycemic index of more than 40 are allowed only with stable glycemic compensation (you can lower the GI of the finished dish if you pre-soak the cereal, cook it al dente and cook it until ready, wrapped in a blanket);
- semolina porridge and hominy are excluded from the diet;
- you should choose whole buckwheat grains, unrefined oat grains or coarse oat flakes for cooking;
- Instant porridges should be eliminated from the menu.
As a side dish, cereal dishes go well with boiled (baked) chicken, turkey, and fish. Buckwheat and pearl barley go well with mushrooms. Recipes for making viscous porridges for diabetics differ from traditional recipes in the absence of sugar.
From boyar-style buckwheat porridge, you should exclude the brisket; do not fry vegetables (onions and carrots), but only simmer a little in olive oil. Millet porridge with pumpkin should be avoided, since the dish has a high GI.
On a note! Diabetologists recommend adding a tablespoon of bran to a serving of viscous porridge. This will help speed up metabolism and enrich the dish with minerals and vitamins.
What do you eat them with?
It is also important what to combine the permitted side dishes with. For diabetes, these should be foods rich in fiber that can lower the GI:
- fresh herbs;
- salads from raw vegetables (without mayonnaise);
- mild, unsweetened and low-fat sauces.
Your doctor can recommend a recipe for a healthy salad or addition to your porridge. The patient’s task is to eat fractionally (small portions, but often), monitor blood sugar levels and follow other recommendations of the endocrinologist.
Results
Porridges are healthy and satisfying dishes, the presence of which is necessary in the diabetic menu. When choosing cereals, you need to be guided by the glycemic index value. Diabetics are prohibited from eating semolina porridge, hominy and cereal dishes made from white rice.
The most useful options would be buckwheat, pearl barley, barley, oatmeal, and flaxseed porridge. It is recommended to prepare water-based porridge; replace butter with 10% sour cream. Dishes made from legumes (pea and lentil porridge) can dilute the cereal diet.
Pearl barley
This cereal is also very healthy and has a low glycemic index, so it is not only possible, but also necessary to consume it if you have diabetes.
According to some reports, this cereal has an antibacterial effect, and it is also necessary for allergy sufferers during exacerbation of the disease.
Thanks to its good vitamin and mineral composition, this cereal is good for the skin and eyesight.
The most important qualities for diabetic patients is the ability of pearl barley to reduce cholesterol and glucose levels.
In order to bring maximum benefits, this cereal can be consumed about three times a week.
Barley is contraindicated for chronic constipation and increased acidity of gastric juice.
Adverse reactions
Gluten is able to cross both the intestinal and blood-brain barriers, which has been demonstrated in rodent studies. Modern wheat, which is the most widely used and produces the best bread from a functional point of view, has greater cytotoxic and immunogenic capacity.
Neurogluten is the term used to describe various neurological disorders caused by gluten consumption, that is, those that affect any organ or tissue of the nervous system. Patients may develop serious neurological disorders due to consumption of neurogluten.
Rice
Not all rice grains are good. White polished rice is pure carbohydrate, without vitamins or fiber. It acts on the body like semolina porridge or a white bun: it rapidly increases glucose levels and brings nothing but a mass of empty calories.
Another thing is brown, long-grain rice. It is a storehouse of fiber and B vitamins. Despite the high percentage of starches, it is considered a dietary product. Fiber from the rough shell reduces the intensity of glucose absorption into the blood.