Cholesterol is a fat-like organic compound found in the cell membranes of the body. Cholesterol plays an important role in the body and ensures the stability of the cell membrane. The production of vitamin D, testosterone and estrogen, progesterone would not be possible without this organic compound.
Cholesterol is produced to a greater extent by the liver, kidneys, and adrenal glands. The remaining percentage of the organic compound enters the body from food. High cholesterol during pregnancy is a natural process caused by the development of a new life.
What causes cholesterol levels to increase?
A healthy woman's body contains approximately 4.138 mmol/L cholesterol. This indicator indicates the normal functioning of organs and systems and the absence of serious health problems. Why does the level of the substance increase? During pregnancy, cholesterol may rise slightly above the permissible norm.
This occurs against the background of the fact that the kidneys and liver begin to work harder due to hormonal changes. The adrenal glands are not able to cope with the elimination of excess and when taking tests, you can see an increase in a fat-like organic compound. During the period of bearing a baby, the normal cholesterol level is considered to be 3.20 - 14 mmol/l.
The organic compound indicator may increase depending on the age category of the pregnant woman. An organic fat-like compound plays an important role for the body of a woman carrying a child. Cholesterol is involved in the formation of the placenta, where the baby grows and develops. Cholesterol takes an active part in the synthesis of hormones.
Very often, the cholesterol level of the expectant mother increases by 1.5-2 times.
If a woman feels well and does not experience any symptoms, then a decreased or increased indicator in this case will not indicate a pathological condition. The amount of cholesterol affects the health of the expectant mother and is responsible for the intrauterine development of the baby.
To lower cholesterol you will need to follow a special diet
Delivery with ICP
For ICP, prenatal hospitalization is indicated at 36 weeks. in order to resolve the issue of time and method of delivery, including induction of labor. There is no evidence of the need for early delivery in ICP, but there is a practice of induction of labor in severe forms of cholestasis with severe hyperfermentemia and bile acid concentrations >40 µmol/l [5, 7]. When discussing the issue of delivery, it is necessary to warn about the impossibility of accurately predicting perinatal complications in ICP and the advisability of early delivery in order to reduce the risk of stillbirth. It is also necessary to warn about the risks of intensive care for newborns. Thus, the frequency of hospitalization in the neonatal intensive care unit for early induction of labor at 37 weeks. is 7–11%, at 38 weeks - 6% and at 39 weeks - 1.5%. The decision to deliver should be based not only on laboratory results, but also on other risk factors, since a strong correlation between liver enzyme levels and fetal outcome has not been identified. Making a final decision on the time and method of delivery is possible only after the pregnant woman has been fully informed about the risks to the fetus during induction of labor and the possible deterioration of the fetal condition when pregnancy is prolonged [5].
Norms during pregnancy
The main indicators of cholesterol levels in the body during pregnancy include:
- total cholesterol indicator (3.08-13.8 mmol/l);
- the level of the atherogenic coefficient, reflecting the ratio of bad and good cholesterol (0.4-2.5 units);
- fatty acid content indicator (0.4-2.2 mmol/l).
A wide range of cholesterol levels during pregnancy may be due to a number of reasons. The indicator is influenced not only by the age category of the pregnant woman, but also by the duration of pregnancy. Below is a table with norms in the first, second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Normal cholesterol levels in pregnant women
| Age category | First months of pregnancy | 2-3 trimester of pregnancy |
| 17-20 years old | 3.07 - 5.19 mmol/l | 3.07 - 10.38 mmol/l |
| 20-25 years | 3.17 - 5.6 mmol/l | 3.17 - 11.2 mmol/l |
| 25-30 years | 3.3 - 5.8 mmol/l | 3.3 - 11.6 mmol/l |
| 30-40 years | 3.4 - 5.97 mmol/l | 3.7 - 12.6 mmol/l |
| 35-45 years | 3.9 - 6.9 mmol/l | 3.9 - 13.8 mmol/l |
During pregnancy, part of the diagnosis is in the range of cholesterol 7 mmol/l or cholesterol 9 mmol/l. Both indicators are normal!
We fight cholesterol. How to save your heart and blood vessels?
About a quarter of the population is overweight. More than 18 million people worldwide die from cardiovascular diseases. At least 2 million people have diabetes. The common cause of all these ailments is high cholesterol, which affects about 147 million people around the world.
The problem has already been called a “national catastrophe”, but, unfortunately, not everyone takes it seriously. How to prevent severe vascular disorders?
Cholesterol: myths and reality
Cholesterol is one of the main building materials of the body. It is part of cell membranes, hormones, vitamin D, and nervous tissue.
The body really needs cholesterol, since the membrane of our cells consists of it. Therefore, no matter what we eat, the body will produce it and distribute it to create new cells and restore the membrane of old ones.
The main purpose of cholesterol compounds is to insulate nerve tissue and protect the cell membrane. Cholesterol promotes the production of hormones by the adrenal glands and sex glands. 80% of the substance is produced by it itself, the rest enters the body with the products we eat.
There are two types of cholesterol; in everyday life they are called “good” and “bad”. The substance itself is homogeneous and has neutral characteristics.
And the usefulness of the substance depends on how cholesterol is transported, what substances pick it up, and which lipoproteins it interacts with. It contains about 200 g in organs, mainly in nerve tissues and the brain.
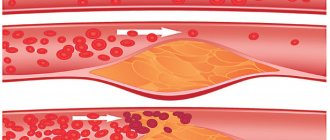
The first type is represented by high-density lipoproteins, which prevent contamination of blood vessels with foreign deposits. “Bad cholesterol” to low-density lipoproteins that can settle in the vascular bed and create health problems.
There is also a type of very low density lipoprotein. Increased bad cholesterol in the blood, what does this mean? Once formed, a plaque does not disappear from the body. By clogging the arteries, it prevents the passage of blood and oxygen to the internal organs.
Gradually, the lumens of blood vessels narrow, and atherosclerosis is often diagnosed at a young age.
A life-threatening plaque is a plaque that turns into a paste of calcium and clogs the vascular bed by 75%. “bad” creates these problems , although its properties are often attributed to cholesterol in general.
Why do we need cholesterol?
- If cholesterol is within normal limits, it only has a positive effect on the body. In addition to creating a cell membrane that protects it from an aggressive environment, it also performs many other functions:
- Plays the role of a filter that recognizes molecules that need to be allowed into the cell and those whose access needs to be blocked;
- Controls the level of carbon crystallization;
- Serves as a stimulating substance in the production of bile acids;
- Helps synthesize vitamin D, which is essential for normal skin condition, using solar energy;
- Its optimal level improves metabolism, including fat-soluble vitamins;
- As part of the myelin sheath, it covers nerve endings;
- Normalizes hormonal levels (testosterone contains 50% cholesterol);
- Responsible for the degree of membrane survival;
- Protects red blood cells from the aggressive effects of hemolytic toxins;
- Helps the liver synthesize fatty acids necessary for processing fats;
- Activates serotonin receptors, eliminating depression.
But the body needs a tiny fraction of the cholesterol produced. Excess amounts pose a fatal risk to the heart.
Reasons for the increase in “bad” cholesterol – who is at risk?
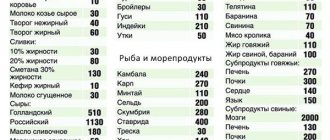
The main prerequisite that contributes to the accumulation of excess cholesterol is an unbalanced diet, when an excess amount of fat enters the body (margarine (spread), mayonnaise, butter, fatty meat, crabs, shrimp, baked goods, high-fat fermented milk products).
By the way, the amount of cholesterol in lard is lower than in butter. According to nutritionists, you should consume 1g of fat per 1 kg of body weight per day.
Provoke an increase in “bad” cholesterol:
- Alcohol and smoking abuse, which have a toxic effect on the liver, where cholesterol is synthesized;
- Cardiac pathologies in the form of heart attack and angina;
- Diabetes mellitus – high blood glucose levels are an additional provoking factor for the production of “bad” cholesterol;
- Kidney failure;
- Extrahepatic jaundice;
- Hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver;
- Pregnancy;
- Lack of growth hormone;
- Uncontrolled use of a group of drugs disrupts the metabolic balance;
- Frequent stressful situations increase the production of the hormone cortisol in the blood, which destroys protein tissue and increases the level of glucose in the blood;
- Excess body weight.
Men with large bellies are also at risk. Fat envelops internal organs, disrupting their function, increases intra-abdominal pressure, and negatively affects the function of the liver, which synthesizes cholesterol. This list also includes women during menopause, who have reduced reproductive function and the synthesis of female sex hormones.
Fans of low-fat diets are also at risk. Why do people need cholesterol when losing weight, and why should it come from food? When 20% of the required cholesterol does not come from food, the body begins to produce more of it.
Concentration camp prisoners had constantly high levels of cholesterol in their blood. In addition to the stressful situation, the cause was constant malnutrition with a complete lack of fat in the diet.
Other causes also influence the production of high cholesterol: hormonal medications, oral contraceptives, diuretics and B-blockers. Age will also be a risk factor, since over time the normal functioning of the body becomes more difficult.
Blood cholesterol level
In healthy people, cholesterol levels are quite high: normal levels do not exceed 1.0 mmol/l. A deficiency will create additional problems for the body.
The cholesterol limit for healthy people does not exceed 3.5 mmol/l.
In hypertensive patients and diabetics, this figure should be less than 1.8 mmol/l. Exceeding this norm can provoke the development of atherosclerosis. For total cholesterol, normal values should not exceed 5.2 mmol/l.
The most accessible way to determine your concentration of all types of cholesterol, which can be done in any clinic, is a blood test called a “lipid profile.”
Healthy people over 35 years old need to monitor whether their indicators are within the normal range at least once every 2 years. Patients at risk, as well as those who have (or have had) patients with vascular pathologies in their family, should be examined annually.
If levels are below 3.5 mmol/l, it is also recommended to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
Cholesterol is called the “gentle killer” because the desire to eat a cake or ham does not provoke pain, like a bad tooth. The accumulation of harmful substances is often asymptomatic.
When cholesterol concentrations increase, atherosclerotic plaques form in the body, which lead to cardiovascular and other health problems.
A number of nonspecific signs indicate elevated cholesterol in the blood:
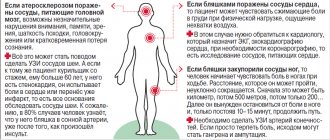
- Cardiac pathologies. Coronary artery disease is a consequence of narrowing of the coronary arteries;
- The appearance of clots with significant bleeding;
- Chest and joint pain;
- Fat granulomas are painful inflammation of the skin;
- Yellow spots of fat on the skin under the eyes, small fatty spots in the corners of the eyes;
- Pain and heaviness in the legs even with minor exertion.
These are just the main signs, if identified, you need to undergo an examination. Signs of the disease often appear only when cholesterol levels have already reached critical levels.
What are the dangers of high cholesterol?
High cholesterol concentrations over a long period of time create conditions for the formation of severe pathologies:
- Coronary heart diseases caused by difficulties with blood saturation with oxygen;
- Vascular thrombosis;
- Brain stroke;
- Myocardial infarction;
- IHD;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Alzheimer's diseases.
Excessive cholesterol content provokes the development of hypertension. Damage to the walls of blood vessels creates the preconditions for leg diseases - varicose veins, thrombophlebitis.
Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by dyslipidemia - a change in the proportions of different types of lipoproteins. As a result, diabetics have an increased chance of developing heart and vascular diseases.
Patients often find out about high cholesterol only after some complication occurs - coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke. In men, a strict cholesterol-free diet reduces sexual activity; in women, amenorrhea may develop.
As you can see, high cholesterol significantly increases the chances of serious vascular diseases; it can literally kill a person, so our main task is to prevent its significant fluctuations.
Atherosclerosis in the first stages can be stopped, and nutrition in this matter serves as a powerful preventive measure. If high cholesterol is detected, you should try to reduce the level of the problem substance through nutritional correction.
10 simple rules for maintaining normal cholesterol:
- Vegetable oil (linseed, sunflower, olive, corn) with polyunsaturated fatty acids in small quantities (up to 30g/day) helps the synthesis of high-density lipoproteins. Excess oil thickens the blood.
- Lean meats and eggs. For a long time, eggs were considered a harmful product because they contain a lot of cholesterol. But they also contain a substance that helps dissolve it in the body.
But you still shouldn’t overeat: the norm for an adult is 1 egg per day. Dishes where they are in a semi-liquid state are useful, since the yolk is also an excellent choleretic agent. (You can also get rid of excess cholesterol through the bile ducts).
- Honey, cabbage, grated carrots are also on the list of recommended products. In general, you need to add a lot of fiber and dietary fiber to your diet, which contains vegetables and fruits. It removes 15% of cholesterol from the intestines, preventing its absorption. Due to the lack of fiber, canned foods are also included in the “black list”.
- Whole grain cereals contain a lot of magnesium, an anti-atherosclerotic agent that normalizes the production of healthy cholesterol.
- Thins the blood and restores blood flow and fish oil from northern fish species, rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 group, promoting the production of high-density lipoproteins. Fish should be consumed 2-3 times a week. Rich in iodine, which lowers “bad” cholesterol, seaweed, cod liver, perch, and shrimp.
- Among the nuts, pistachios are the leader: if you eat them regularly (20-30g/day), cholesterol levels are reduced several times! Good results can be obtained from almonds or walnuts, which also contain useful acids. Nuts are added to salad, cottage cheese, porridge, dosing their consumption.
- Cranberries, tea, peppers, raspberries, blueberries and cherries with a high content of manganese, which reduces cholesterol levels, have proven themselves well in the fight against excess cholesterol. If blueberries should only be fresh, then cherries can be used after heat treatment.
- A very useful product is mushrooms, which, in addition to fiber, contain a special statin substance that blocks the production of low-density lipoproteins. In general, mushrooms are a difficult food for the stomach, so moderation is important.
- Beans absorb and eliminate excess cholesterol. It is enough to eat 200 g of legumes per day (boiled) so as not to think about excess cholesterol. It is useful to include artichoke or its extract in the menu.
- Citrus fruits, which contain pectins that bind “bad” cholesterol in the gastrointestinal tract, also reduce cholesterol. In this case, grapefruit must be eaten with a white film. Baked apples also contain a lot of pectin.
Nutritional Features
With high cholesterol, modifying your diet for the rest of your life is one of the main factors in the fight against such disorders. The main principle of a healthy diet is that fats in the menu should not exceed 30%.
Moreover, these should mainly be unsaturated types - those that contain fish or nuts. If you adhere to these rules, you can not only reduce the concentration of unwanted cholesterol, but also increase the percentage of useful cholesterol.
A healthy diet involves avoiding the use of trans fats, from which margarine or spread is made. Freak molecules are also present in confectionery products made on its basis.
Liver is a good source of vitamin A, but it also contains a lot of cholesterol, as does fish roe. If you limit these foods in your diet, “bad” cholesterol can be reduced by half. The ban also applies to red meat, instead of which lean chicken is recommended.
Boiling foods, as opposed to frying them, reduces cholesterol levels by 20%.
Drug cholesterol lowering
Modifying dietary habits is not enough to normalize high cholesterol levels, because it depends not only on what we eat: it is largely produced by the liver.
If its levels are very high or there is a serious cardiovascular risk, doctors recommend taking medications that lower high cholesterol for life. The most commonly prescribed drugs are statins, which block the synthesis of a substance in the liver.
Cholesterol and pregnancy
The lipid profile during pregnancy changes significantly in the 2nd and 3rd trimester. In this case, the content of lipoproteins can increase by one and a half to two times. But such indicators should not be a cause for concern, since the intensive work of the liver is aimed at the needs of the developing fetus.
And one last little secret: be more happy. Endorphins (hormones of happiness), which the body produces at this moment, help reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol and related health problems.
Be healthy!
Kuzmich Tatyana Nikolaevna,
Head of the regional cardiology department
How can you reduce cholesterol?
By following your doctor's recommendations, monitoring your diet, undergoing tests and donating blood to control cholesterol levels, you can quickly reduce the high level of fat-like organic compounds in pregnant women. When reducing high cholesterol concentrations, it is important not to forget about the safety of the mother and her baby.
During this period, it is highly undesirable to use medications. An increased level of an organic compound can only cause harm if it is in excess. The use of medicines and folk remedies should be moderate so as not to cause severe stress to the body during a difficult period.
Is it possible to normalize the level without medications?
To reduce cholesterol, experts advise eliminating from the diet:
- fatty foods;
- fried foods and pickles;
- sweets (cakes, sweets, pastries, croissants and buns);
- butter;
- Palm oil;
- fast foods;
- sausages and pates;
- semi-finished products;
- pork
Physical exercise can help balance the balance of bad and good cholesterol. During pregnancy you can do:
- aerobics;
- fitness;
- yoga;
- special gymnastics;
- swimming.
If any unpleasant symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor
Physical activity will help normalize lipid metabolism and reduce weight. Green tea, freshly squeezed fruit juice, fruits, and vegetable juice can have a beneficial effect on the metabolic process and reduce the level of fat-like organic compounds.
Very often, during a difficult pregnancy, severe toxicosis and weakness, a woman least of all thinks about the recommendations of specialists. Snacking on your favorite food on the go, it involuntarily increases cholesterol in the blood even more. And this causes an increase in the frequency of vomiting and unpleasant painful sensations in the abdominal area.
The main part of cholesterol in a pregnant woman is synthesized independently in the body. Excess compounds come precisely from eating junk food. While carrying a baby, it is unacceptable to eat too much. It is best to eat in small, fractional portions.
The basis of the diet should be foods containing omega-3 and omega-6. Such foods include sea fish, flax seeds, and flaxseed oil. By following simple rules, you can prevent the development of pathologies when carrying a child, keep your weight and cholesterol levels under control.
Painful attacks during hepatosis
In the most difficult cases of hepatosis, the patient sometimes experiences attacks characterized by severe pain in the right hypochondrium. Often the pain is felt in the abdomen, at the level of the navel and is mistaken for an exacerbation of gastritis. Such attacks may be accompanied by continuous and painful vomiting without relief, headache, tinnitus, rapid heartbeat, darkening of the eyes and shortness of breath. They are very similar to severe poisoning syndrome, only in this case the stool practically does not change, and the food eaten is vomited.
Most often, such attacks are caused by eating harmful foods (fried, spicy, fatty, alcohol) and begin 40-60 minutes after eating or by a sudden movement, for example, a quick turn, bend or fall. Painful attacks can last up to 20-40 minutes, they begin suddenly and recede just as sharply. Often after an attack, quite severe residual pain remains in the right hypochondrium for several days. A big mistake during such attacks is taking paracetamol, because it only aggravates the situation, negatively affecting liver activity. It is allowed to take antispasmodic drugs such as No-Shpa.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Why is control needed?
It is important to keep serum cholesterol levels under control. The increase in the level of the compound should be within reasonable limits so as not to provoke the development of complications.
An excessive increase in the fat-like organic compound can cause a decrease in the strength of the expectant mother’s blood vessels and an increase in blood viscosity. As a result, the baby develops heart defects and liver and kidney diseases. Therefore, it is so important to keep cholesterol levels under control and record their dynamics.
You should immediately seek help from your doctor if:
Deciphering a blood test for cholesterol
- a sharp increase in the percentage of fat-like organic compounds by more than 2 times;
- deterioration of health;
- frequent migraines;
- systematic prolonged attacks of nausea in the last months of pregnancy;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in the neck, heart and collarbone.
A specialist will help you find out the reason for the increase in the substance in the blood and take measures to reduce cholesterol. If you ignore unpleasant symptoms, a pregnant woman may experience complications such as the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the development of varicose veins, difficulties in bearing a child, the risk of premature birth or termination of pregnancy.
The right snack – nuts and sunflower seeds
Changes in coagulogram and clinical blood test parameters
Changes in the coagulogram of a pregnant woman are a natural physiological process associated with the appearance of the uteroplacental circulation. It is due to the fact that the pregnant woman’s body prepares for an increase in blood volume during pregnancy and for possible blood loss during childbirth.
During normal pregnancy, the activity of the blood coagulation system increases. This means that already in the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen increases, which reaches its maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (once per trimester, if there are deviations in these indicators, more often, once a week).
Simultaneously with the increase in fibrinogen, the activity of the internal blood coagulation mechanism also increases, while the analysis shows a shortening of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Other parts of the blood coagulation system, such as the coagulation blocker antithrombin III, also change during pregnancy. But as pregnancy progresses, there is a gradual decrease in the activity of this indicator.
But lupus anticoagulant should not be produced normally in a pregnant woman.
Pregnancy also affects the results of a general blood test. Indicators such as hemoglobin and hematocrit may decrease in the second half of pregnancy, and leukocytes, on the contrary, may increase.
Prevention and treatment
As a preventative measure, experts recommend paying attention to your own diet, which should be based on seasonal fresh fruits and vegetables. For prevention purposes, it is better to completely avoid coffee drinks and minimize the consumption of eggs, fried foods and sweets.
If proper nutrition does not help reduce the level of fat-like organic compounds, you should consult with your doctor, who will select special medications and prescribe a course of therapy.
High cholesterol during pregnancy requires careful attention, although it is the norm. As soon as unpleasant symptoms begin to bother you, you should immediately take measures to normalize the concentration level of this substance, which will help avoid unpleasant consequences for both the expectant mother and the child.
Management in the postpartum period
A decrease in hyperenzymemia after childbirth confirms the diagnosis of ICP. Postpartum women with ICP need a biochemical blood test within 7–10 days after birth to confirm the diagnosis, and to assess the dynamics of the decrease in the concentration of liver enzymes and/or bile acids - after 6 and 8 weeks. after childbirth [5, 16]. If after childbirth the symptoms do not stop (or progress), it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with other chronic liver diseases, including primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis C, in which itchy skin may appear in the last weeks of pregnancy.
It is advisable for postpartum women with ICP to avoid estrogen-containing methods of contraception, which provoke the appearance of itching in 10% of women.