The safest way to check vessels for the presence of cholesterol plaques is to undergo an ultrasound examination of the IMT of the carotid artery. Measuring the intima-media thickness (IMT) of the carotid artery in the neck is useful for accurately checking the extent of blockage of blood vessels by cholesterol plaques. There is no need to irradiate the body for this procedure.
Research shows that 90% of the time, cholesterol plaques grow at the same rate in the carotid arteries, coronary arteries, and even in the arteries of the legs. Therefore, the thickness of cholesterol plaques in the carotid artery reflects their amount throughout the body, including the coronary vessels (which supply blood to the heart). Measuring carotid artery IMT makes it possible to make reliable predictions of the risks of strokes and heart attacks.
See also:
Cholesterol plaques on the heart
Plaque in a brain vessel
Where do they look for cholesterol plaques in blood vessels?
During the IMT study, cholesterol plaques are looked for in the carotid artery, with angiography - in the coronary vessels of the heart (the procedure is invasive), with computed tomography of the thoracic region - in the coronary vessels (without internal intervention, but using x-rays).
With traditional ultrasound - in blood vessels (possibly the carotid artery). Indirect methods, such as, for example, measuring pressure under load, do not involve searching for atherosclerotic plaques at all, but provide an assessment of indirect signs. This also includes monitoring heart rate after exercise and assessing energy consumption during physical work.
See also:
Is it possible to play sports with vascular atherosclerosis?
How to determine cholesterol plaques in blood vessels by measuring carotid artery IMT
To determine cholesterol plaques in the carotid artery (which is incomparably easier to reach than the coronary vessels), the patient only needs to lie quietly on the couch for 10 to 12 minutes. The procedure itself boils down to an ultrasound examination of the carotid artery: a special gel is applied to the neck, and the doctor takes about 12 photographs of the right and left arteries from different angles.
The resulting images are processed on a computer. The measurement accuracy is several hundredths of a millimeter. The obtained values are compared with the average statistical values - and from this comparison one can, for example, estimate the age of the circulatory system. The procedure for high blood cholesterol levels should be repeated every 1 to 2 years (to assess changes in plaque size).
Regular observations make it possible to predict the risks of complications and adjust diet and lifestyle to the needs of the cardiovascular system. An alternative to changing IMT in terms of accuracy is only invasive (internal) angiography procedures.
Check your blood vessels
Atherosclerosis is a disease that develops gradually. How to know in time that the process of atherosclerosis development has started?
High cholesterol levels are not the only factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Laboratory tests can help monitor this and other indicators of cardiovascular disease risk.
everything about cholesterol. Lipid profile, extended.
Total cholesterol will show whether there is an excess of this substance in the blood. The level of total cholesterol in patients who have had a heart attack is a sign of the need to prescribe cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low- and very-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL and VLDL) is what is colloquially referred to as “bad cholesterol.” Their excess indicates lipid metabolism disorders. If the increase is not very large, then to correct the situation it is enough to reduce weight, move more, and remove excess fats and carbohydrates from the diet. Significant excesses of the norm require the prescription of appropriate medications.
Triglycerides are another type of fat present in the blood. Normally, triglycerides are the source of energy for cells and are present in the blood only “on the way” from the intestines to the cells. Triglyceride levels fluctuate throughout the day: after the first meal, their concentration in the blood increases rapidly and remains at this level for 9-12 hours. Therefore, a blood test for triglycerides (including the lipid profile) should be taken no earlier than 12 hours after eating.
The extended lipid profile also includes the following parameters:
Apolipoprotein A1 is a representative of “good cholesterol” (high-density lipoprotein, HDL). It prevents cholesterol from being deposited in plaques, protecting, among other things, the blood vessels of the heart and brain. This test shows how well the vascular protection system works.
Apolipoprotein B is the main protein of LDL. One of the accurate markers of atherosclerosis. With its help, it is possible to identify the initial stage of this disease even with normal LDL levels.
Lipoprotein (a) shows how high the hereditary risk of atherosclerosis of the heart and brain vessels is.
A set of tests is recommended for all people over 50 years of age, as well as for those who are at risk of developing atherosclerosis due to heredity, lifestyle, and poor nutrition.
Independent and dangerous
The homocysteine test helps assess the risk of thrombosis. Homocysteine is an amino acid that is produced in the body from the essential amino acid methionine. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the entire metabolism and is a donor of the methyl group. However, if the body does not have enough vitamins B6, B9 (folate) and B12 or there is a genetic defect, the level of homocysteine in the blood increases. Then it can damage the walls of blood vessels.
The test can be done as an additional test to the lipid profile. It is important to remember that smokers and heavy coffee drinkers should have their homocysteine levels determined annually, along with a cholesterol test or lipid profile.
How else can you identify cholesterol plaques in blood vessels?
Standard ultrasound procedures are not as accurate as IMT tests and can only detect cases of restricted blood flow. A simple ultrasound can lead to incorrect conclusions and recommendations, for example, vascular blockage of less than 70% is considered insignificant, even with a large amount of cholesterol plaque in the arteries.
Angiography is another alternative method for diagnosing cholesterol plaques in the vessels of the circulatory system. During it, a thin flexible casing is inserted into the artery in the groin and pushed through the blood vessels into the pelvis, abdominal cavity, chest, and coronary vessels. Vascular angiography is positioned as a simple and painless way to diagnose cholesterol plaques.
However, this method has a big drawback: there is - albeit an extremely low - risk of damage to existing cholesterol plaques, even to the point of rupture or chipping of one of them. This potentially threatens to block blood vessels in the brain (stroke) or in the coronary vessels of the heart (heart attack). Therefore, whenever there is an alternative to angiography, the alternative must be used.
A fairly painless and completely safe method is to take a blood test for total cholesterol levels and get a comparison of the ratio of the total level to the level of high-density lipoproteins (“good” cholesterol). Indicator values below 3 are considered excellent; a ratio of no higher than 3.5 is considered normal. A parameter of 5 means a very high level rate of cholesterol plaques.
How to detect cholesterol plaques using computed tomography?
When performing a computed tomography scan of the chest (CT coronography), a detailed image of the heart and coronary vessels is obtained (by irradiating the patient with X-rays). At the output, the calcium index of the arteries is calculated - the higher it is, the higher the degree of calcification (calcium deposits on the walls of blood vessels).
Calcification is an indicator of the amount of fossilized (hardened) atherosclerotic plaques. However, soft plaques will not be detected during CT. In addition, X-ray radiation can provoke the development of cancer in the future. Therefore, the procedure can be performed extremely rarely. And it's more expensive in terms of money.
How do I know if I have atherosclerotic plaques? Cardiologist answers
“Mayak” opens a new section. Medical. Or more precisely, preventive and educational. Our “Cardio Page” will, as you might guess, have a cardiological focus. About the heart and blood vessels, which set the main tone of our entire life. What questions you will have on this topic depends on you, our dear readers. What would you like to ask the doctor? Send your questions by email, indicating “Cardio Page” in the subject line, or in private messages to the Mayak group on VKontakte. And together we will find out the answers to long-plagued health concerns.
How do I know if I have atherosclerotic plaques?
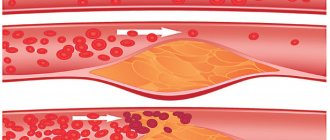
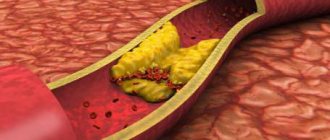
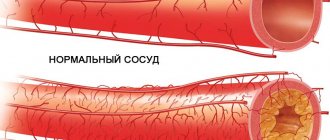
A cardiologist answers. A disease that manifests itself by the formation of plaques in the lumen of the arteries is called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic plaque is primarily composed of cholesterol, but may contain calcium inclusions. As the plaque grows, it narrows the lumen of the artery. Restriction of blood flow through the artery leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients for the heart, brain, and internal organs.
For a long time, atherosclerotic plaques do not manifest themselves in any way. The danger lies in their unexpected rupture and the formation of a blood clot on their surface. This is the main cause for diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene.
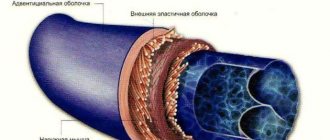
Large vessels, such as the arteries of the neck and legs, can be “looked into” using ultrasound. The study will show whether there is thickening of the vascular wall. Wall thickening occurs in the first stage, when cholesterol is deposited under the inner lining of the artery. In a more serious case, the atherosclerotic plaque itself will be visible, which can be “examined” using ultrasound. Diagnostics allows you to determine the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the artery, to see whether it is “dangerous” by breaking off small particles that can rush into the brain with the bloodstream and cause a stroke.
The modern standard for early detection of atherosclerosis includes ultrasound examination of blood vessels and, if atherosclerotic plaques are detected, therapy is prescribed to reduce their growth. If plaques critically narrow the lumen of the main arteries, then surgical intervention may be necessary.
“Vascular check-up” involves examining all accessible arteries using ultrasound. This is the safest and most accessible way to identify atherosclerotic plaques. In more complex cases, the doctor will order tests with a contrast agent, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ultrasound is not suitable for heart vessels, since the arteries are much smaller in diameter and the heart is constantly contracting.
I will talk about how to find out whether there are atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the heart in the next issue.
Ekaterina Borisova,
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Chief Physician of CardioClinic JSC
Telephone
Website: https://kardioklinika.ru/
License to carry out medical activities No. LO-78-01-011261 dated November 11, 2020. There are contraindications. You should consult your doctor.
How to detect cholesterol plaques yourself
How to detect cholesterol plaques at home? The methods, of course, are not at all effective, because... There are no symptoms of high cholesterol levels in the blood and the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, but if it is not possible to undergo a carotid IMT study, CT coronography or even angiography, you can monitor your condition:
- level of physical endurance (the higher the better);
- amount of fiber consumed (more is better);
- frequency of fish consumption (more is better);
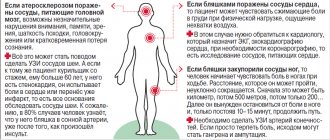
- systolic (upper) pressure (ideal - around 120, and always no more than 140);
- body mass index and excess body fat (less is better, BMI should be no more than 24).
Energy expenditure as a way to independently measure the number of cholesterol plaques
In the gym (gym) or at home, but on sports equipment, you can assess the level of physical fitness by energy expenditure (calorie consumption) during physical exercise. For example, race walking burns about 240 - 300 kcal per hour under normal conditions, if much more is burned, this is already a reason to think about studying the condition of the blood vessels.
The methodology for assessing the level of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels based on measuring the body's energy expenditure is based on the concept of metabolic equivalent (MET). 1 MET corresponds to the amount of oxygen burned that is consumed at rest, lying down.
- 1.5 - 4 MET is spent on work in the garden or around the house.
- For construction and installation work - 4 - 8 MET.
- When jogging (up to 5.4 km/h or 1.5 m/s) and walking uphill (with an incline of no more than 14%) - 8 - 8.3 MET.
- When exercising on a treadmill (depending on speed) – 5 – 18 MET.
The MET scale is used in stress texts. Extremely poor fitness is when a person is unable to reach the 4 MET level of exercise. The norm is considered to be the unimpeded achievement of a value of 10 - 12 METs, 15 is a good result. People who are able to achieve 15 METs almost never perform poorly on IMT.
Monitoring blood pressure is another indirect sign of the level of atherosclerotic plaques
Normal pressure, as indicated above, is 120/80, excellent - 110/70, however, after physical activity, the upper pressure can increase to 150, 160 and even 170. The lower pressure is 10 - 20 points less (in trained people - by 40 or more). Those. a trained person with intense training can have a blood pressure of 170/40! And it will be normal.
If the resting pressure is elevated (between 120/80 and 140/90), then during training the systolic pressure can reach 180 - 200, and the diastolic (lower) pressure can increase by 5 - 9 points or remain unchanged. High blood pressure itself is one of the reasons that accelerates the growth of atherosclerotic plaques. But the conditional norm in the described case will be its value under load up to 190/85.
If the resting pressure exceeds 140/90 mmHg. Art., then under load the systolic pressure can exceed 200, and the diastolic pressure increases by 10 points or more. This causes the blood vessels to contract, which is an undesirable reaction. Blood pressure can reach 200/105.