negative Rh factor, pixabay.com Human blood is divided into 4 groups and 2 types of Rh factor. The most common group is No. 2, and Rh is positive. Moreover, such information was discovered not so long ago - 120 years ago. In 1900, the Austrian doctor K. Landsteiner learned about the existence of different types of blood, for which he received the Nobel Prize in 1930. Now this discovery saves millions of lives every day.
Let's get back to the main point. While most people still have at least some understanding of blood groups, not everyone knows about the Rh factor. In fact, even scientists have not been able to fully figure out why the factor is needed. But doctors say that knowing the group and Rh is vitally important. This is true. Because such knowledge allows doctors to transfuse blood to patients, saving their lives.
We propose to consider 4 main issues using the material in our article. The information will be useful for people with a negative Rh factor, since their body has certain features that are worth knowing about.
What does Rh negative mean?
Which Rh factor is better?
- How dangerous is negative Rh and what should people with this type know?
- Features of negative Rh in women?
- Interesting facts about negative Rh factor blood.
“As statistics show: 40% of people of the white race have a positive blood type, while Asian people are characterized by negative Rh. Only 27% of Asians live with a positive blood type, the remaining 73% live with a negative blood type.”
Support the publication
- Join the CLAN
Or
“The first trial of blood transfusion was carried out in 1600. It failed. Not surprising, because scientists took liquid from animals in an attempt to save their patients. But, as Blundell, a British gynecologist, later found out, such treatment is only permissible with the help of human blood. Although four of his 10 patients who received blood transfusions survived, he did not stop and carried out further research.
Who discovered the human blood type
{banner_banstat0}
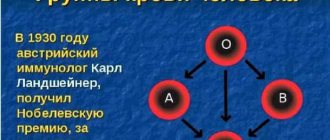
The Austrian immunologist Karl Landsteiner succeeded in identifying the class of human biological material in 1900. At this time, only 3 types of antigen were identified in the membranes of erythrocytes - A, B and C. In 1902, it was possible to identify the 4th class of erythrocytes.
Karl Landsteiner was able to make another important achievement in medicine. In 1930, the scientist, in tandem with Alexander Wiener, discovered the Rh factor of blood (negative and positive).
Classification and characteristics of blood groups and Rh factor
Group antigens are classified according to a single AB0 system (a, b, zero). The established concept divides the composition of blood cells into 4 main types. Their differences are in alpha and beta agglutinins in plasma, as well as the presence of specific antigens on the membrane of red blood cells, which are designated by the letters A and B.
Table "Characteristics of blood classes"
| Variety | Description |
| 1 group or zero | There are no antigens in blood cells. Plasma contains alpha and beta agglutinins |
| Group 2 (A) – the most common | Group A antibodies are present in the membrane of blood cells, and only beta-agglutinin is present in the plasma itself |
| Group 3 (B) | Red blood cells contain B antigen, but plasma contains only alpha antibody |
| Group 4 (AB) | Blood cells in their membrane contain antigens of both groups (A and B), but there are no agglutinins in the plasma |
People's nationality or race does not affect group membership.
Rh factor
{banner_banstat1}
In addition to the AB0 system, biological material is classified according to the blood phenotype - the presence or absence of a specific antigen D, which is called the Rh factor (Rh). In addition to protein D, the Rh system covers 5 more main antigens - C, c, d, E, e. They are contained in the outer membrane of red blood cells.
The Rh factor and the class of blood cells are formed in the child in the womb and are passed on to him from his parents for life.
Method for determining blood group and Rh factor
To calculate group affiliation and Rh factor, it is enough to provide biological material from a vein or finger. The analysis is carried out in the laboratory. Results can be seen within 5–10 minutes.
Methods for identifying group affiliation
{banner_banstat2}
Several methods are used to detect specific antigens in erythrocytes:
- simple reaction - standard serum of classes 1, 2 and 3 is taken, with which the patient’s biological material is compared;
- double reaction - a feature of the method is the use of not only standard sera (compared with the blood cells being studied), but also standard erythrocytes (compared with the patient’s serum), which are pre-prepared in blood transfusion centers;
- monoclonal antibodies - anti-A and anti-B cyclones are used (prepared using genetic engineering from the blood of sterile mice), with which the biological material under study is compared.
The very specificity of studying plasma for its group affiliation lies in comparing a sample of the patient’s biological material with standard serum or standard red blood cells.
The sequence of this process is as follows:
- collection of venous fluid on an empty stomach in the amount of 5 ml;
- distribution of standard samples on a glass slide or special plate (each class is signed);
- The patient’s blood is placed parallel to the samples (the amount of material should be several times less than the volume of drops of standard serum);
- blood fluid is mixed with prepared samples (simple or double reaction) or with cyclones (monoclinal antibodies);
- after 2.5 minutes, a special saline solution is added to those drops where agglutination has occurred (proteins of group A, B or AB have been formed).
The presence of agglutination (sticking and precipitation of red blood cells with corresponding antigens) in biological material makes it possible to classify red blood cells into one class or another (2, 3, 4). But the absence of such a process indicates a zero (1) form.
How to determine the Rh factor
{banner_banstat3}
There are several methods for detecting Rh-relatedness - the use of anti-Rhesus sera and a monoclinal reagent (group D proteins).
In the first case, the procedure is as follows:
- the material is collected from a finger (canned blood or red blood cells themselves, which were formed after settling of the serum, are allowed);
- 1 drop of anti-Rhesus sample is placed in a test tube;
- a drop of the plasma being studied is poured into the prepared material;
- a little shaking allows the serum to be evenly distributed in the glass container;
- after 3 minutes, a sodium chloride solution is added to the container with the serum and blood cells being tested.
After several inversions of the test tube, the specialist deciphers it. If agglutinins appear against the background of clarified liquid, we are talking about Rh+ - a positive Rh factor. The absence of changes in the color and consistency of the serum indicates negative Rh.
The study of Rhesus using a monoclinal reagent involves the use of coliclon anti-D super (special solution). The analysis procedure includes several stages.
- The reagent (0.1 ml) is applied to the prepared surface (plate, glass).
- A drop of the patient’s blood (no more than 0.01 ml) is placed next to the solution.
- Two drops of material are mixed.
- Decoding takes place 3 minutes after the start of the study.
Most people on the planet have an agglutinogen of the Rh system in their red blood cells. If we look at percentages, then 85% of recipients have protein D and are Rh positive, and 15% do not have it - this is a Rh negative factor.
Compatibility
{banner_banstat4}
Blood compatibility is a match by group and Rh factor. This criterion is very important when transfusing vital fluid, as well as during pregnancy planning and gestation.
What blood type will the child have?
The science of genetics provides for the inheritance of group affiliation and rhesus by children from their parents. Genes transmit information about the composition of blood cells (agglutinin alpha and beta, antigens A, B), as well as Rh.
Table "Inheritance of blood groups"
{banner_banstat5}
| Parents | Child | |||
| Blood groups, % | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1+1 | 100 | |||
| 1+2 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 1+3 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 1+4 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 2+2 | 25 | 75 | ||
| 2+3 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| 2+4 | 50 | 25 | 25 | |
| 3+3 | 25 | 75 | ||
| 3+4 | 25 | 50 | 25 | |
| 4+4 | 25 | 25 | 50 | |
Mixing groups of erythrocytes with different Rh leads to the fact that the child’s Rh factor can be either “plus” or “minus”.
- If Rh is the same between spouses (group D antibodies are present), 75% of children will inherit the dominant protein, and 25% will be absent.
- In the absence of specific protein D in the membranes of the mother’s and father’s red blood cells, the child will also be Rh negative.
- In a woman Rh-, and in a man Rh+ - the combination suggests the presence or absence of Rh in the child in a 50 to 50 ratio, with a possible conflict between the antigen of mother and baby.
- If the mother has Rh+ and the father does not have anti-D, there is a 50/50 chance that Rh will be passed on to the baby, but there is no risk of antibody conflict.
Important! It is important to understand that the Rh factor is transmitted at the genetic level. Therefore, if the parents are Rh-positive, and the child was born with Rh-, men should not rush to question their paternity. Such people simply have a person in their family without the dominant protein D in their red blood cells, which is what the baby inherited.
Blood type for transfusion
{banner_banstat6}
When performing blood transfusion (blood transfusion), it is important to maintain the compatibility of antigen and rhesus groups. Experts are guided by the Ottenberg rule, which states that the donor’s blood cells should not stick together with the recipient’s plasma. In small doses, they dissolve in a large volume of the patient’s biological material and do not precipitate. This principle applies to transfusions of vital fluid up to 500 ml and is not suitable when a person has severe blood loss.
People with group zero are considered universal donors. Their blood suits everyone.
Representatives of the rare 4th class are suitable for blood transfusion of 1st, 2nd and 3rd types of blood fluid. They are considered universal recipients (people who receive blood infusions).
For patients with 1 (0) positive, class 1 (Rh+/-) is suitable for transfusion, while a person with negative Rh can only be given a zero with Rh-.
For people who have 2 positive, 1 (+/-) and 2 (+/-) are suitable. Patients with Rh- can only use 1 (-) and 2 (-). The situation is similar with 3rd grade. If Rh+ – you can pour in 1 and 3, both positive and negative. In the case of Rh-, only 1 and 3 without anti-D are suitable.
Compatibility at conception
{banner_banstat7}
When planning a pregnancy, the combination of the Rh factor of a man and a woman is of great importance. This is done to avoid Rh conflict. This happens when the mother has Rh-, and the child inherits Rh+ from the father. When a dominant protein enters a person’s blood where it is not present, an immunological reaction and the production of agglutinins may occur. This condition provokes the adhesion of the resulting red blood cells and their further destruction.
Incompatibility of Rhesus of mother and child during the first pregnancy does not pose any danger, but before the second conception it is better to interrupt the production of anti-Rhesus bodies. The woman is injected with a special globulin, which destroys immunological chains. If this is not done, Rh conflict can provoke termination of pregnancy.
Disadvantages of having type 1 negative blood
Advertising:
In the event of an emergency and the need for immediate blood transfusion, a person with type 1 negative blood will need a donor with similar biological blood characteristics.
In case of unforeseen emergencies, it is necessary to have a relative or friend with the same biological blood characteristics on hand.
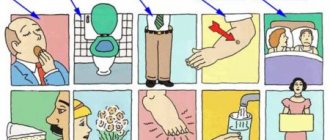
Some diseases are typical for these people. They are often prone to:
- Rh conflict during blood transfusions;
- ulcers in the stomach and duodenum;
- high risk of hypertension;
- hemophilia (especially in men);
- to damage from acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, etc.;
- the appearance of excess weight;
- some allergic reactions.
Can your blood type change?
{banner_banstat8}
In medical practice, there are cases of changes in group affiliation during pregnancy or due to serious illnesses. This is because in such conditions there can be a strong increase in the production of red blood cells. At the same time, the gluing and destruction of red blood cells slows down. In the analysis, such a phenomenon is reflected as a change in markers in the plasma composition. Over time, everything falls into place.
Blood class, like the Rh factor, is determined genetically in a person before birth and cannot change throughout life.
How different types react to vaccination
The researchers also looked at how people with different blood types responded to vaccination. It turned out that representatives of blood type 0 have the highest sensitivity to vaccinations. Their immunity actively responds to the components of the vaccine. As a rule, representatives of the first group in the first three days after vaccination develop weakness, lethargy, irritability, and also an increase in body temperature. In most cases, the reaction is medically acceptable. But to be on the safe side, it is better to immediately seek medical advice. In addition, it is useful for people in the first group to drink a lot of water during the post-vaccination period.
The flu vaccine can be dangerous for pregnant women with blood group 1, especially if the fetus is believed to have blood group 2, 3 or 4. The fact is that after influenza vaccination, the body of the expectant mother activates the production of antibodies that have a detrimental effect on the health of the fetus.
People with type A red blood cells usually tolerate the post-vaccination period well. The exception is the polio vaccine, which is taken orally. Due to the increased sensitivity of the digestive tract, second-graders may have a mild reaction. There are almost no cases of complications after vaccination of persons with blood group 4 (AB). But they, like second-graders, are not advised to receive oral vaccinations.
But vaccination of children of blood group 3 should be approached with extreme caution, since after vaccination they may experience severe neurological reactions. Before vaccination, it is necessary to exclude the presence of possible infectious or other diseases in a child or adult. To avoid complications, if possible, it is better for children with blood group 3 (as well as with the first) to give the vaccine not in the form of injections, but in oral form. The danger of vaccination for people with group 3 lies in the fact that after vaccination a large number of B antigens are produced in the body, which provokes immunological changes. Simply put, the body stops recognizing its own tissues and attacks them.
Character traits by blood type
{banner_banstat10}
Blood type affects not only the physiological characteristics of the body, but also the character of a person.
Zero group
In the world, about 37% are carriers of blood group zero.
The main features of their character are:
- stress resistance;
- leadership skills;
- determination;
- energy;
- courage;
- ambition;
- communication skills.
Holders of the zero group prefer to engage in dangerous sports, love to travel and are not afraid of the unknown (they easily take on any job, learn quickly).
Temperamental shortcomings include hot temper and harshness. Such people often express their opinions unceremoniously and are arrogant.
2nd group
The most common group is considered to be 2 (A). Its bearers are discreet people who are able to find an approach to the most difficult personalities. They try to avoid stressful situations and are always friendly and hardworking. Owners of group 2 are very economical, conscientiously perform their duties and are always ready to help.
Character flaws include stubbornness and the inability to alternate work and leisure. It is difficult to motivate such people to do any rash actions or unexpected events.
3 group
A person whose blood is dominated by group B antigens has a changeable nature. Such people are characterized by increased emotionality, creativity and independence from the opinions of others. They easily travel and take on new things. In friendship they are devoted, in love they are sensual.
Negative qualities often include:
- frequent mood swings;
- inconstancy in actions;
- high demands on others.
Those with blood type 3 often try to hide from the realities of the world in their fantasies, which is not always a positive character trait.
4 group
Speakers of group 4 have good leadership qualities, which is manifested in the ability to negotiate and be collected at a crucial moment. Such people are sociable, easily get along with others, moderately emotional, multifaceted and intelligent.
Despite many advantages in character, representatives of group 4 often cannot come to a common decision, suffer from duality of feelings (internal conflict) and are slow-witted.
The specific composition of the blood and the presence or absence of a dominant factor (antigen D) in it is transmitted to a person with genes. There are 4 blood groups and the Rh factor. Thanks to the classification according to the AB0 and Rh system, specialists have learned to safely transfuse donor blood, determine paternity and avoid Rh conflict during the birth of a child. Each person can check their group affiliation in the laboratory by donating biological material from a finger or vein.
Preferred Diet
People with Rh- blood group 1 often suffer from excess weight. Therefore, in addition to sufficient physical activity, such people are recommended to follow a special diet, the purpose of which is either to lose weight or maintain their weight within the normal range.
Basic rules when creating a diet for people with the first negative:
- minimizing or excluding foods high in vitamin E from the menu: legumes;
- potatoes;
- corn;
- cabbage;
- citrus fruits;
- viburnum;
- rosehip;
- nuts;
- iodized salt;
People with blood type O should eat red meat, preferably lean meat (beef and lamb)
Recommendations for choosing certain products are based on the metabolic abnormalities characteristic of such people.
Table: recommended and not recommended foods for people with the first blood group Rh-
| Recommended Products | Products whose consumption should be limited | Not recommended food |
|
|
|
For those who want to get rid of unnecessary pounds, there are weight loss tips that help normalize metabolism:
- exclude from your menu all foods that interfere with normal insulin production and help slow down metabolism: all types of sweets, including “healthy” ones;
- cereals containing gluten, especially wheat;
- vegetable fats (sunflower, palm, rapeseed oil);
- trans fats;
The diet should not exclude proteins, since since ancient times those with the first blood group were hunters and ate meat
- red meat;
Curious about the data on the diet of people from other groups? Information can be found here:
Video: the secret of the blood type diet
For men and women, having the first blood group with a negative Rh factor is characterized by the presence of its own disadvantages and advantages. Many of these people become honorary donors and save hundreds of lives. To avoid health complications, you should adhere to a certain diet and physical activity.
- Author: Olesya Dunyasheva
Family doctor. For a healthy lifestyle, self-development and sports. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(9 votes, average: 4.1 out of 5)
Share with your friends!