3 September 2021 11:09
Quantity
Alcohol abuse is a pressing problem of modern society, which gives rise to crimes, accidents, injuries and poisoning in all segments of the population. Alcohol addiction is especially difficult to perceive when it concerns the most promising part of society - students. The mortality rate of the working-age population due to the use of alcoholic beverages ranks high. Scientists estimate alcoholism as a collective suicide of the nation. Addiction to alcohol, like cancer, destroys the personality of an individual and society as a whole from within.
How does alcohol affect the human body? Let's look at the effect of alcoholic drinks on all organs and find out how alcohol affects the brain, liver, kidneys, heart and blood vessels, nervous system, as well as men's and women's health.
Effect of alcohol on the brain
All organs suffer from the negative effects of alcoholic beverages. But it’s the neurons—the brain cells—that get the most. People know how alcohol affects the brain from the feeling of euphoria, high spirits and relaxation.
However, at the physiological level, at this time, destruction of cells of the cerebral cortex occurs even after small doses of ethanol.
- Normally, the blood supply to the brain occurs through thin capillaries.
- When alcohol enters the blood, blood vessels narrow and red blood cells stick together, forming blood clots. They clog the lumen of the brain capillaries. In this case, the nerve cells experience oxygen starvation and die. At the same time, a person feels euphoria, without even suspecting the destructive changes in the cerebral cortex.
- Capillaries from congestion swell and burst.
- After drinking 100 g of vodka, a glass of wine or a mug of beer, 8 thousand nerve cells die forever. Unlike liver cells, which can regenerate after alcohol withdrawal, nerve cells in the brain do not.
- Dead neurons are excreted in urine the next day.
Thus, under the influence of alcohol on blood vessels, an obstacle to normal blood circulation in the brain is created. This is the cause of the development of alcoholic encephalopathy and epilepsy.
A postmortem autopsy of the skull of alcohol abusers naturally reveals destructive pathological changes in their brain:
- reducing its size;
- smoothing of convolutions;
- the formation of voids in place of dead areas;
- foci of pinpoint hemorrhages;
- the presence of serous fluid in the cavities of the brain.
With long-term abuse, alcohol affects the structure of the brain. Ulcers and scars form on its surface. Under a magnifying glass, the brain of an alcoholic looks like the lunar surface, pockmarked with craters and craters.
Biochemical indicators
Alcohol has the strongest effect on biochemical blood tests. This analysis is the most complete yet. Using it, you can find out which substances a person urgently needs, and which ones are available in abundance and their concentrations need to be urgently reduced.
The result of a biochemical study under the influence of alcohol changes as follows :
- the amount of urea in the blood decreases,
- data on the absorption of oxygen by the cells of the body are violated,
- quantitative glucose indicators suffer.
The latter factor can pose a threat to the patient’s life, since the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is delayed.
Increased levels of urea are also caused by drinking alcohol. Distorted indicators of its content can hide severe circulatory disease, leading to hemorrhagic shock or acute heart failure. Since urea is involved in the excretion of nitrogen, its increased concentration is a sign of gout and polyarthritis. The accuracy of diagnosis can only be satisfactory if you abstain from alcohol before taking tests.
Drinking alcohol before the procedure can cause increased levels of triacylglycerol in the bloodstream. This neutral fatty substance, when found in the bloodstream, indicates pathological processes such as :
- atherosclerosis,
- ischemia,
- thrombosis of cerebral arteries,
- viral hepatitis.
Most doctors, for reasons of principle, exclude alcohol-containing medications from taking before taking blood from a patient. But there is an opinion that alcohol helps detect the presence of an infectious disease. But even the smallest dose of ethanol distorts test results and makes it unsuitable for a doctor.
According to the stories of nurses and doctors, most people do not admit to drinking alcohol before tests. Another side factor that appears when people who drank alcohol the day before are tested are :
- fainting,
- severe headaches,
- nausea.
The volume of blood that is taken from the body from a vein is insignificant. Its loss is not any problem for a person. But if a patient comes for tests after drinking alcohol, metabolism is usually disrupted and blood circulation in the brain is reduced.
Taking it from a vein can lead to oxygen starvation of the brain. This can lead to severe dizziness and even fainting. After this, the patient may have a headache for a long time.
Alcohol poisoning can upset the gastrointestinal tract. A patient may vomit in a doctor's office or laboratory from the smell of alcohol or chlorine used for disinfection.
The effect of alcohol on the nervous system
The human brain is a kind of control panel for the entire body. Its cortex contains centers for memory, reading, movement of body parts, smell, and vision. Poor circulation and cell death of any center are accompanied by shutdown or weakening of brain functions. This is accompanied by a decrease in a person’s cognitive (cognitive) abilities.
The influence of alcohol on the human psyche is expressed in a decrease in intelligence and personality degradation:
- memory impairment;
- decreased IQ;
- hallucinations;
- loss of critical attitude towards oneself;
- immoral behavior;
- incoherent speech.
Under the influence of alcohol on the nervous system, a person’s behavioral reactions change. He loses his modesty and restraint. He does things that he wouldn't do in his right mind. Stops being critical of your emotions. He experiences unmotivated attacks of rage and anger. A person’s personality degrades in direct proportion to the amount and duration of alcohol consumption.
Gradually a person loses interest in life. His creative and labor potential is declining. All this negatively affects career growth and social status.
Alcoholic polyneuritis of the lower extremities develops after prolonged use of ethyl alcohol. Its cause is inflammation of the nerve endings. It is associated with an acute deficiency of B vitamins in the body. The disease is manifested by a feeling of severe weakness in the lower extremities, numbness, and pain in the calves. Ethanol affects both muscles and nerve endings - it causes atrophy of the entire muscular system, which ends in neuritis and paralysis.
Literature:
- Microcirculation channel and vessels of the brain under the conditions of alcocholic intoxication in experiment / A. A. Kalaev, A. A. Moldavskaya, A. V. Gorbunov; Russian Academician Natural Sciences, Astrakhan State. honey. acad. — Moscow: Acad. Natural Sciences: Astrakhan State. honey. acad., 2007 - 199 p.
- Heart attack, stroke, sudden death. Risk factors, warning signs, prevention. / Lipovetsky, Boris Markovich. - St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2015. - p.
- Risk factors for arterial hypertension / V. R. Weber, B. B. Fishman; Feder. education agency, Novgorod. state University named after Yaroslav the Wise, Novgorod. scientific Center of the Northwestern Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. — St. Petersburg: Novgor. state univ., 2005 (St. Petersburg: Printing house “Science”). — 207 p.
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
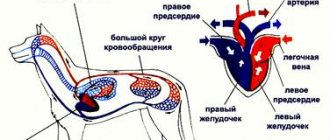
The effect of alcohol on the cardiovascular system
The effect of alcohol on the heart is such that it works under load for 5–7 hours. While drinking strong drinks, your heart rate increases and your blood pressure rises. Full heart function is restored only after 2-3 days, when the body is finally cleansed.
After alcohol enters the blood, a change occurs in the red blood cells - they are deformed due to membrane rupture, stick together, forming blood clots. As a result, blood flow in the coronary vessels is disrupted. The heart, trying to push blood through, increases in size.
The effects of alcohol on the heart when abused include the following diseases.
- Myocardial dystrophy. In place of cells killed as a result of hypoxia, connective tissue develops, which impairs the contractility of the heart muscle.
- Cardiomyopathy is a typical consequence that develops over 10 years of alcohol abuse. It most often affects men.
- Heart arythmy.
- Coronary heart disease - angina pectoris. After drinking alcohol, the release of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood increases, which increases oxygen consumption by the heart muscle. Therefore, any dose can cause coronary insufficiency.
- The risk of developing myocardial infarction in heavy drinkers is higher than in healthy individuals, regardless of the condition of the coronary vessels of the heart. Alcohol increases blood pressure, which causes heart attack and premature death.
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy is characterized by hypertrophy (enlargement) of the ventricles of the heart.
The symptoms of alcoholic cardiomyopathy are as follows:
- dyspnea;
- a cough, often at night, that people associate with a cold;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in the heart area.
Progression of cardiomyopathy leads to heart failure. Shortness of breath is accompanied by swelling of the legs, enlarged liver, and cardiac arrhythmia. When people have heart pain, subendocardial myocardial ischemia is often detected. Drinking alcohol also causes hypoxia - oxygen starvation of the heart muscle. Since alcohol leaves the body over several days, myocardial ischemia persists throughout this time.
Important! If your heart hurts the next day after drinking alcohol, you need to get a cardiogram and consult a cardiologist.
Alcoholic drinks affect heart rate. After heavy drinking of alcohol, various types of arrhythmias often develop:
- paroxysmal atrial tachycardia;
- frequent atrial or ventricular extrasystole;
- atrial flutter;
- ventricular fibrillation, which requires anti-shock treatment measures (often fatal).
The presence of this kind of arrhythmias after taking large doses of alcohol is called “holiday” heart. Heart rhythm disturbances, especially ventricular arrhythmias, are often fatal. Arrhythmias can be regarded as signs of cardiomyopathy.
The effect of alcohol on the human cardiovascular system is a fact that has been scientifically established and substantiated. The risk of these diseases is directly proportional to the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol and its breakdown product, acetaldehyde, have a direct cardiotoxic effect. In addition, it causes a deficiency of vitamins and proteins and increases blood lipids. During acute alcohol intoxication, the contractility of the myocardium sharply decreases, which leads to a lack of blood in the heart muscle. Trying to compensate for oxygen deficiency, the heart increases contractions. In addition, during intoxication, the concentration of potassium in the blood decreases, which causes rhythm disturbances, the most dangerous of which is ventricular fibrillation.
What happens to the heart and blood vessels with constant drinking of alcohol?
With regular consumption of alcohol-containing drinks, the heart accumulates a lot of fat, the tissues become more flabby, premature aging of the organ is observed, and a deterioration in its normal functioning is observed. There are high risks of developing hypertension . Characteristic symptoms:
- persistent and prolonged increase in blood pressure (140/90 or more);
- numbness of fingers and toes;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased performance, fatigue;
- dysregulation of vascular tone;
- swelling of the face, arms and legs;
- frequent migraines, dizziness.
The person will become more irritable and often feel sleepy during the day. At night, on the contrary, attacks of insomnia may occur. With high blood pressure, there is a high risk of developing atherosclerosis. This is a chronic disease caused by a violation of lipid-protein metabolism, excessive formation of cholesterol plaques in the lumen of blood vessels. This can cause them to become completely blocked.
Atherosclerosis often becomes a prerequisite for the development of coronary artery disease. The pathology is characterized by impaired blood supply to the myocardium (the muscular middle layer of the heart, which makes up its main part). The patient needs a large amount of oxygen, which can only be provided by a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and frequent exposure to fresh air. Exacerbation of the disease leads to a heart attack, its chronic manifestations are characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the chest.
The effect of alcohol on blood vessels
Does alcohol lower or increase blood pressure? - even 1-2 glasses of wine increases blood pressure, especially in people with hypertension. After drinking alcoholic beverages, the concentration of catecholamines - adrenaline and norepinephrine - increases in the blood plasma, which increase blood pressure. There is a concept called “dose-dependent effect”, which shows how alcohol affects blood pressure depending on its amount - systolic and diastolic pressure increases by 1 mmHg when ethanol increases by 8-10 grams per day. People who abuse alcohol have a 3-fold increased risk of hypertension compared to abstainers.
How does alcohol affect blood vessels? Let's figure out what happens to our blood vessels when drinking alcohol. The initial effect of alcoholic drinks on the vascular wall is dilating. But after this a spasm occurs. This leads to ischemia of the blood vessels of the brain and heart, leading to heart attack and stroke. Alcohol also has a toxic effect on the veins in such a way that the flow of blood through them is disrupted. This leads to varicose veins of the esophagus and lower extremities. People who abuse libations often experience bleeding from the veins of the esophagus, which ends in death. Does alcohol dilate or constrict blood vessels? - these are just stages of its sequential impact, both of which are destructive.
The main damaging effect of alcohol on blood vessels is related to how alcohol affects the blood. Under the influence of ethanol, red blood cells stick together. The resulting blood clots spread throughout the body, clogging narrow vessels. Moving through the capillaries, blood flow becomes significantly more difficult. This leads to disruption of blood supply to all organs, but the greatest danger is to the brain and heart. The body initiates a compensatory reaction - it increases blood pressure in order to push blood through. This leads to heart attack, hypertensive crisis, and stroke.
General analysis
Exposure to alcohol can distort results in the following ways :
- destroy red blood cells,
- increase cholesterol levels sometimes by 80%,
- reduce hemoglobin levels, as the concentration of red blood cells also decreases.
If you drink alcohol immediately before this test, then the greatest likelihood is that the number of red blood cells (red blood cells that transport oxygen to all organs or tissues and the return transport of carbon dioxide) will be reduced.
Alcohol dissolves the membranes of red blood cells, which prevents their natural random movement and repulsion is reduced. Red blood cells begin to stick together. Their concentration in plasma falls, which leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels. The clumping of red blood cells leads to the formation of blood clots and a decrease in blood microcirculation in the vessel.
The blood becomes thicker after the alcohol gets inside. Its ability to penetrate through the lumens of the capillaries is reduced due to the appearance of clots. This situation is dangerous to the health and life of people and prevents a complete study of the composition of the blood.
In the liver, under the influence of alcohol, lipid production decreases. This reduces the characteristics of the plasma. Such indicators play a major role during the period when the patient is being prepared for surgery. Accurate analysis is necessary to monitor the patient’s health when he has suffered from a serious infectious disease or during the healing of large wound surfaces.
Blood tests taken less than 12 hours after drinking alcohol can only accurately show general intoxication. A decrease in hemoglobin shows only megaloblastic anemia. But the doctor may refuse to make a diagnosis, citing his patient’s recent drinking.
Effect on the liver
It's no secret how harmful alcohol affects the liver. The stage of ethyl alcohol release is much longer than absorption. Up to 10% of ethanol is released in pure form with saliva, sweat, urine, feces and during breathing. That is why after drinking alcohol a person has a specific smell of urine and “fumes” from the mouth. The remaining 90% of ethanol has to be broken down by the liver. Complex biochemical processes occur in it, one of which is the conversion of ethyl alcohol into acetaldehyde. But the liver can only break down about 1 glass of alcohol in 10 hours. Unsplit ethanol damages liver cells.
Alcohol affects the development of the following liver diseases.
- Fatty liver. At this stage, fat in the form of globules accumulates in hepatocytes (liver cells). Over time, it sticks together, forming blisters and cysts in the area of the portal vein, which interfere with the movement of blood from it.
- At the next stage, alcoholic hepatitis develops - inflammation of its cells. At the same time, the liver increases in size. Fatigue, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea appear. At this stage, after stopping ethanol consumption, liver cells are still able to regenerate (recover). Continued use leads to a transition to the next stage.
- Liver cirrhosis is a typical disease associated with alcohol abuse. At this stage, liver cells are replaced by connective tissue. The liver becomes covered with scars; when palpated, it is dense with an uneven surface. This stage is irreversible - dead cells cannot recover. But stopping alcohol consumption stops liver scarring. The remaining healthy cells perform limited functions.
If alcohol consumption does not stop at the stage of cirrhosis, the process progresses to the stage of cancer. A healthy liver can be maintained with moderate consumption.
Important! According to WHO recommendations, the safe dose is 10 grams of alcohol per day for women and 20 grams for men.
The equivalent is a glass of beer or a glass of wine per day. And even with such dosages, you should not drink alcohol every day. It is necessary to allow alcohol to completely leave the body, and this takes 2-3 days.
Glucose test
A blood glucose test is required for people suffering from endocrine disorders. Blood is taken from a finger. If the patient drank alcohol-containing liquids before taking blood, his blood becomes thicker and his blood pressure drops. This makes it difficult to obtain blood and increases the risk of thrombosis.
Exposure to alcohol is a negative factor for liver cells. It also has a negative effect on laboratory equipment and reagents. This makes the result inaccurate. Sugar levels may be increased or decreased relative to the actual state of things.
One gram of alcohol can increase the number of kcal by 7, which is explained by the rapid penetration of ethanol into the tissues and fluids of the body. Sugar levels in this case are increased.
Alcohol causes low blood sugar levels. For about 2.5 hours, stable blood glucose data are provided by carbohydrates from food. The rest of the period, glucose is produced by the liver, attracting the body's energy resource. Alcohol disrupts the normal metabolic process and causes hypoglycemia.
Blood sugar levels return to normal after 1 or 2 days .
If the patient is at risk of diabetes, then it is important for him to give the doctor a normal picture. In another case, the doctor will attribute high sugar levels to drinking alcohol. The period when health can be improved will be missed.
Effect of alcohol on the kidneys
The function of the kidneys is not only the formation and excretion of urine. They take part in balancing the acid-base balance and water-electrolyte balance, and produce hormones.
How does alcohol affect the kidneys? — when consuming ethanol, they go into intensive operation mode. The renal pelvis is forced to pump a large volume of fluid, trying to remove substances harmful to the body. Constant overload weakens the functional ability of the kidneys - over time, they can no longer work constantly in an enhanced mode. The effect of alcohol on the kidneys can be seen after a festive feast by a swollen face and high blood pressure. Fluid accumulates in the body, which the kidneys are unable to remove.
In addition, toxins accumulate in the kidneys, then stones form. Over time, nephritis develops. Moreover, after drinking alcohol, it happens that the kidneys hurt, the temperature rises, and protein appears in the urine. The progression of the disease is accompanied by the accumulation of toxins in the blood, which the liver is no longer able to neutralize and the kidneys to remove.
Lack of treatment leads to the development of renal failure. In this case, the kidneys cannot form and excrete urine. Poisoning of the body with toxins begins - general intoxication with a fatal outcome.
Contraindications
Express contraindications include:
- allergy to the active substance and components of the drug,
- Gastrointestinal diseases, including erosions, ulcers in the acute stage,
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system
- hemorrhagic diathesis,
- pregnancy and lactation (the 1st and 3rd trimesters are considered especially dangerous)
- aortic aneurysm
- renal or liver failure
- and children under 15 years of age.
How does alcohol affect the pancreas?
The function of the pancreas is to secrete enzymes into the small intestine to digest food. How does alcohol affect the pancreas? - under its influence, its ducts are clogged, as a result of which enzymes do not enter the intestines, but inside it. Moreover, these substances destroy gland cells. In addition, they affect metabolic processes involving insulin. Therefore, if you abuse alcohol, diabetes can develop.
When subjected to decomposition, enzymes and breakdown products cause inflammation of the gland - pancreatitis. It manifests itself in the fact that after drinking alcohol the pancreas hurts, vomiting appears and the temperature rises. Pain in the lumbar region is girdling in nature. Alcohol abuse affects the development of chronic inflammation, which is a risk factor for breast cancer.
What factors increase the risk of CVD?
Cardiologists divide all risk factors into 2 groups: controlled and uncontrolled. The first include those that a person is not able to influence. These are gender, age, hereditary predisposition, ethnic characteristics, the presence of diabetes mellitus or immune diseases. The second group includes controllable risk factors for cardiovascular diseases:
- smoking;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
- violation of the ratio of blood lipid fractions;
- arterial hypertension;
- eating a lot of salt;
- obesity;
- alcohol consumption;
- stress;
- low physical activity.
If you arrange them according to the degree of impact on health, then smoking will be in 1st place. It increases the likelihood of CVD by 50%.
But is there any connection between bad habits? Drinking alcohol and smoking are classified as so-called addictive behaviors. It is characterized by the fact that a person strives to escape from a traumatic or unpleasant reality using various means that change the mental state. Did you drink? Smoke...
There is an interesting pattern: among those who drink alcohol, there are much more smokers than the population average. And vice versa: people who smoke are more likely to allow themselves a drink or two.
This feature is associated with the biochemistry of the brain: substances act on nicotinic and other receptors. Their effect is mutually enhanced and reinforced by a feeling of immediate reward and social stereotypes. Studies have shown that vascular damage and the development of atherosclerosis are a common occurrence when smoking and drinking “in moderation” - that is, in people who believe that they “drink like everyone else” and do not harm their health with their behavior.
The effect of alcohol on the female and male body
Alcohol affects a woman's body to a greater extent than a man's. In women, the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, which breaks down alcohol, is found in lower concentrations than in men, so they get drunk faster. The same factor influences the formation of alcohol dependence in women faster than in men.
Even after consuming small doses, women's organs undergo great changes. Under the influence of alcohol on a woman’s body, reproductive function is primarily affected. Ethanol disrupts the monthly cycle and negatively affects reproductive cells and conception. Drinking alcohol accelerates the onset of menopause. In addition, alcohol increases the risk of cancer of the breast and other organs. With age, the negative effect of alcohol on the female body increases because its elimination from the body slows down.
Alcohol negatively affects important brain structures - the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The consequence of this is its negative impact on the male body - the production of sex hormones decreases, which is why potency decreases. As a result, family relationships collapse.
Alcohol negatively affects all organs. It has the fastest and most dangerous effect on the brain and heart. Ethanol increases blood pressure, thickens the blood, and disrupts blood circulation in the brain and coronary vessels. Thus, it provokes a heart attack, stroke, and hypertensive crisis. With long-term use, irreversible diseases of the heart and brain develop - alcoholic cardiomyopathy, encephalopathy. The most important organs designed to remove toxins from the body - the liver and kidneys - suffer. The pancreas is damaged and digestion is disrupted. But stopping alcohol intake early in illness can restore cells and stop organ destruction.
High blood pressure after heavy drinking and even after regular drinking, what is the reason and how to deal with it?
High blood pressure observed after alcohol has a complex mechanism. The hormones adrenaline, norepinephrine, cortisol, aldosterone, hypertensin and renin, calcium and magnesium ions are involved in its implementation. Much depends on the dose of alcohol. A small amount of it - a glass of red wine, a glass of vodka will cause vasodilation and a slight decrease in pressure. The next portion, starting with 60 g of pure ethanol, will lead to vasoconstriction, increased frequency and volume of cardiac output, increased load on the walls of the vascular bed and, accordingly, an increase in pressure. The effect of high blood pressure after binge drinking or drinking large single doses of alcohol is due not so much to the action of alcohol itself, but to the products of its peroxidation in the form of toxic acetaldehyde.
If the blood pressure is already elevated, then a dose calculated from 1.5 g of pure alcohol per 1 kg of weight will be safe for a hypertensive patient. For example, vodka is 3.75 ml/kg, and wine is 2 times more.
Many patients are interested in how to reduce blood pressure after a binge, during which it is almost impossible to control the amount of alcohol consumed. If acute alcoholic hypertension is observed, then 2 mg of dexamethasone will help relieve it, but this drug can only be used on the recommendation of a doctor. Self-medication with hormonal drugs is unacceptable. You can use Captopress or Captopril, but they should not be abused due to the pronounced diuretic effect with the removal of potassium and magnesium ions. ATP inhibitors and blockers of angiotensin receptors and calcium channels are effective against high blood pressure after binge drinking.