The third blood group is considered rare - it is found in only 15% of people inhabiting the Earth. According to some reports, we owe its appearance to the nomadic Mongoloids. The age of the group is more than 17 thousand years. The third negative is, accordingly, even less common. It is more common among people living in Asian countries, the Middle East, and Africa. Interestingly, some researchers say that it determines a person’s character. So let's get to know the third negative category in detail!
General information
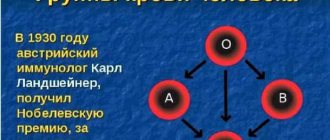
Blood is a biological fluid that circulates throughout the body of every person in a volume of 5-6 liters (approximately 7% of body weight). Researcher K. Landsteiner discovered four of its categories:
- The first one is O.
- The second is A.
- Third - V.
- The fourth is AB.
The most common option is the first, the rarest is the fourth. The third negative will be in honorable second place in terms of non-prevalence.
The third group is compatibility during donation
A person with group 3 will not be a universal recipient. In other words, his blood for transfusion is not suitable for everyone. Blood of the first group is universal. But for those with the 4th category, blood of all groups is suitable - 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Here's what concerns the third blood category in this vein:
- A person with group 3 can become a donor for people with blood categories 3 and 4.
- It is permissible for a person with blood group 3 to receive blood transfusions of the first and third categories.
- The 3rd positive and the 3rd negative are incompatible! Rejection can even be fatal for the patient.
If it is not possible to transfuse suitable blood to a person in need, then specialists use serum or blood substitutes (“artificial blood”) - special sterile liquids that can replace it itself, as well as plasma. Such compositions are not a complete alternative, but are capable of supporting human life.
AB0 blood group system
Determination of blood group according to the AB0 system is based on the detection of group-specific antigens 0, A, B and isoimmune antibodies anti-A (α) and anti-B (β) in the serum on the surface of human red blood cells. A unique feature of the AB0 system is the presence in human plasma of natural α and β antibodies to the missing antigen. There are six possible allelic antigen options: 00, A0, AA, B0, BB, AB. Phenotypically, four groups are distinguished: 0(I), A(II), B(III), AB(IV) - hetero- and homozygous variants are combined (in Russia they use alphanumeric designations).
Group affiliation according to the AB0 system
| Agglutinogens | Agglutinins |
| 0 | α and β |
| A | β |
| B | α |
| AB | No |
- 0(I): antigens A and B are absent, antibodies α and β are detected (35 - 40% of the world's population);
- A(II): A antigen and β antibodies present (35%);
- B(III): agglutinogen B and agglutinin α were detected (15 – 20%);
- AB(IV): presence of agglutinogens A and B, absence of agglutinins α and β (5 – 10%).
As you move from west to east of Eurasia, the frequency of detection of antigen A decreases, and antigen B increases. Antigen 0 is rare in Asia, but is widespread in the indigenous peoples of South America, Polynesia and Australia. The reason is epidemics of infectious diseases.
The result of blood typing is recorded in the medical history or in the donor’s card. The transfusiologist indicates the date and signs.
In some cases, mild agglutination of red blood cells is observed during typing. The insufficiently pronounced reaction is explained by the presence of weak variants of antigens A and B. Subgroups A1 and A2 are of greatest clinical importance. Weak variants were first discovered in 1911 by scientists Dungern and Hirszeld. Later in 1930, Landsteiner and Levine proposed the subgroup names A1 and A2. A2 occurs in up to 20% in group A and up to 35% in group AB. Serum from individuals from A2 blood samples may contain anti-A1 antibodies: 2% of cases in group A2 and 30% of cases in A2B. Anti-A1 antibodies are dangerous due to agglutination of group A red blood cells.
Method for determining blood groups A2 and A2B
The detection rate of A2 red blood cells varies significantly depending on the reagents used. We present a comparison of study results using various methods for typing blood groups A2 and A2B.
- Anti-A1 (lectin, phytohemagglutinin). Diagnosticum clearly (+++/++++) agglutinates A1 erythrocytes immediately after mixing with the sample. Does not agglutinate A2 or causes minor agglutination at the fifth minute and later.
- Standard isohemagglutinating serums.
- Anti-A and anti-AB zoliclones.
- Anti-A zolicone is weak.
| Number of samples analyzed | Blood type A (II) | Blood type AB (IV) | ||
| Number of samples analyzed | Group A2 (II) in % | Number of samples analyzed | Group A2B (IV) in % | |
| Anti-A1 (lectin, phytohemagglutinin) | 1592 | 14,7 | 357 | 23,5 |
| Coliclones: anti-A, anti-AB | 3599 | 2,1* | 357 | 7,03* |
| Tsoliclone anti-A - weak | 3587 | 4,5* | 357 | 11,2* |
| Standard isohemagglutinating serums | 1592 | 17,4 | 344 | 34,2 |
Note: * - agglutination is weakly expressed, there are small agglutinates on a pink background.
Anti-A1 (lectin, phytohemagglutinin) provides the greatest accuracy of the study. The test is recommended for identifying A antigen subgroups in children under two years of age. The reason is the physiological immaturity of newborn erythrocytes, which leads to erroneous test results with standard isohemagglutinating sera.
In 1930, Landsteiner and Levine discovered the Aint subtype: an intermediate variant between A1 and A2. This antigen is characteristic of Negroids and reaches 8.5% in people with blood group A. In Caucasians, Aint was observed in only 1% of people with the second blood group. In extremely rare cases, a person lacks all antigens of the ABO system. The Bombay phenotype is caused by the hh genotype. In the absence of antigen H, individuals in this category exhibit anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Method for determining blood groups
Typing according to the AB0 system is carried out in a direct agglutination reaction using standard hemagglutinating sera or typing reagents with monoclonal antibodies. The use of coliclones is preferable due to their absolute specificity: each reagent does not contain admixtures of other antibodies, ballast proteins and infectious factors.
Algorithm for identifying blood group using hemagglutinating sera
To determine the AB0 blood group by the direct method, two series of standard isohemagglutinating sera are used. Prepare two series of sera from three groups with a titer of 1:32 or higher. Use a separate labeled pipette to collect each serum. Prepare AB(IV) serum for control.
- Provide good lighting and an air temperature of 18 – 25 °C.
- Label the tablet: 0(I) – on the left, A(II) – in the center, B(III) – on the right. At the top center, indicate the donor's last name or the number of the blood being analyzed.
- Apply 1 – 2 drops (approximately 0.1 ml) of serum into the wells in two rows according to the plate labeling.
- Using a pipette or glass rod, place one small drop of the red blood cells being tested next to the drops of serum. The volume of serum should be approximately 10 times the volume of red blood cell fluid.
- Mix the drops in the wells with a stick.
- To speed up the reaction, gently rock the tablet.
- After three minutes, add one drop of NaCl to the wells of the plate in which agglutination has begun. Wait two more minutes.
- After five minutes, evaluate the results of the reaction in the running set. In case of unexpressed agglutination, add one more drop of NaCl.
Reaction results:
- A negative reaction in three wells indicates the absence of antigens on the red blood cells of the test sample. Blood belongs to group 0(I).
- Agglutination in wells with sera 0(I) and B(III) indicates the presence of agglutinogen A and belonging to group A(II).
- The onset of a reaction with sera 0(I) and A(II) indicates the presence of antigen B and group membership B(III).
- The reaction results in all wells indicate the presence of agglutinogens A and B and correspond to the fourth group AB(IV).
In the latter case, you should make sure that there is no nonspecific reaction: apply 2–3 drops of serum corresponding to group AB(IV) to the tablet and add one drop of the analyzed red blood cells. Stir the liquids and evaluate the result after five minutes. The absence of agglutination indicates belonging to group AB(IV), the presence is a sign of a nonspecific reaction. In this case, as well as in case of mild agglutination, repeat the study with other series of sera.
Technique for determining blood group using zoliclones
Monoclonal antibodies to erythrocyte antigens have replaced isohemagglutinating sera. For each typing, one series of anti-A, anti-B, anti-AB reagents is sufficient. The introduction of monoclonal reagents made it possible to significantly simplify and standardize the AB0 typing technique. Here is a brief step-by-step guide to conducting research on a tablet.
- Provide good lighting. Work at room temperature.
- The object of study is erythrocyte-containing media.
- Label the wells of the plate: anti-A, anti-B, anti-AB, or use a plate with a labeled sticker.
- Apply approximately 0.1 ml of the appropriate monoclonal reagent to each of the three labeled wells.
- Add approximately 0.03 ml of red blood cells to be analyzed next to each drop of diagnostic solution.
- Mix the reagent with the red blood cells in the wells using separate individual glass rods.
- Rock the tablet for about three minutes.
- Check for agglutination in the wells.
Usually the reaction is detected within the first seconds after mixing. In this case, weak variants of antigens A and B may cause later agglutination.
blood sample collection
introducing the sample into the well
tablet with added samples
adding zoliclones
tablet with erythrocytes and zoliclones
mixing test samples with reagents
Indirect typing method: algorithm of actions
The determination method is based on the interaction of erythrocytes from pre-typed individuals of groups 0, A, B or a mixture of erythrocytes from several same-group donors with isohemagglutinins α and β in the test serum.
Use dry, clean pipettes when handling each typing reagent. Rinse stir sticks and pipettes in 0.9% NaCl solution.
- Prepare a plate or tablet. Provide good lighting in the room.
- Draw 3–5 ml of blood without stabilizer into a test tube. Let the serum sit for 1.5 - 2 hours at room temperature.
- Wash test red blood cells in 0.9% saline solution. Prepare a 5% suspension.
- Label the sections on the tablet: 0(I), A(II), B(III).
- Place 2 drops (approximately 0.1 ml) of plasma to be analyzed into each of the three wells.
- Add approximately 0.03 ml of test red blood cells to the wells.
- Using separate sticks, mix the typed red blood cells with the serum.
- Rock the tablet gently for 5 minutes.
- Conduct a visual assessment of the results of the agglutination reaction in transmitted light.
Conclusion about group affiliation
| Results of plasma analysis with standard red blood cells | Group affiliation | ||
| 0(I) | A(II) | B(III) | |
| — | + | + | 0(I) |
| — | — | + | A(II) |
| — | + | — | B(III) |
| — | — | — | AB(IV) |
+ — presence of agglutination, — — negative result of the reaction.
- 0(I): reaction in wells A(II), B(III) (antibodies α and β detected).
- A(II): agglutination with erythrocytes B(III) (β agglutinins detected).
- B(III): agglutination in well A(II) (α agglutinins determined).
- AB(IV): no reaction results in all wells (no antibodies detected in plasma).
Rh factor value
So why is the third negative incompatible with the third positive? It's all about the Rh factor (+/-). It was discovered by scientists A. Wiener and K. Landsteiner in 1940.
The Rh factor is a special antigen that is found on the surface of erythrocytes - red blood cells. Interestingly, it does not change throughout a person’s life, and is also transmitted from parent to child.
According to statistics, 85% of the population of our planet have a positive Rh factor and only the remaining 15% are negative (that’s why there are so few people with the third negative group). The meaning of the difference is as follows:
- Blood of the same group, but different Rhesus is incompatible! Transfusion can have consequences for the patient, including death.
- It is important to note that different rhesus diseases with the mother threaten the child with death in the womb. For example, if a woman has third negative blood, and the baby has third positive blood, then the embryo is in danger.
Why is that? A woman’s body perceives a child with a different Rh factor as a foreign body, virus or infection. The mother's immune cells begin a fight against the fetus, which ends with placental abruption or spontaneous abortion. This likelihood is most common for women with strong immunity.
Future parents need to remember that the danger is observed only during a problematic pregnancy! During normal gestation, the blood of the mother and child does not mix, which is why there is no threat.
Planning pregnancy and 3 negative blood group
In women, the Rh characteristic affects the course of pregnancy and its outcome in the case when the girl is negative, and the guy who will become the father is positive. In this case, you need to see a doctor for advice.
Usually, the first pregnancy with such indicators passes without disturbances and risks for the expectant mother and child. Future pregnancies will require close monitoring by a gynecologist.
Rh conflict tends to occur in the last period of pregnancy. To avoid the development of such a scenario, doctors refer the young couple to undergo an Rh test. Based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions.
If a woman who is Rh negative carries a child who is Rh positive, doctors will offer an anti-Rh globulin vaccine. A timely visit to the clinic for specialized help will give confidence in the successful development of pregnancy without subsequent complications.
Compatibility of father and mother
We now know that the discrepancy between the blood characteristics of a pregnant woman and the embryo has serious consequences. They are especially severe in the case when the child has a third negative blood group, and the mother has the first or second. But let us note once again that the danger is real only for problematic pregnancy.
But now let’s move on to the Rh harmony of father and mother. Let's look at the compatibility of parents who have blood group 3:
- The third is negative in a woman. A suitable father is with blood types 1 and 3.
- The third is negative in a man. A suitable mother is with the 3rd and 4th blood groups.
What threatens the incompatibility of mother and father by Rhesus?
Nutrition
People with a third negative blood group are, as a rule, omnivorous and unpretentious, and have a good appetite. But when there is a large choice, they give preference to meat products, smoked meats, overly spicy and salty dishes, which leads to intestinal problems.
Dietary recommendations to maintain their health include moderate consumption of meat - lamb, poultry, preference for protein foods from fish and seafood. Any cereals, low-fat dairy products and cheeses, nuts, legumes, and almost all vegetables and fruits are recommended. Black tea and coffee are recommended to be consumed in moderation.
The following products are not recommended for consumption:
- fatty meat of pork, chicken, duck;
- smoked meat and fish products;
- crustacean dishes, shrimp;
- baked goods, ice cream, cakes;
- tomatoes and ketchup;
- alcohol;
- from herbs and infusions - aloe, hops, linden.
Herbal teas and drinks made from rosehip, mint and lemon balm, ginger, sage will be very useful, that is, they have a calming effect on the nervous system and improve digestion.
The danger of Rh-conflict between parents
Everything is simple here - a mismatch in the Rhesus of the parents causes a mismatch in the Rhesus of the mother and the embryo. After all, as you remember, it is inherited.
Rhesus conflict is dangerous for mother and baby in the following ways:
- Stillbirth of a child.
- Miscarriage is a spontaneous abortion.
- Fading pregnancy is stopping the development of the embryo in the mother's womb.
- The appearance of pathologies in the fetus that are incompatible with life.
It is important to note that open Rh conflict will manifest itself only in the last months of pregnancy. Before this, it can affect the abnormal formation of the internal organs of the embryo - mutational changes are possible.
Doctors also note the fact that when parents have a Rh conflict, the first child is born without problems in most cases. And the second baby will be in danger. Therefore, if the first pregnancy went perfectly, a woman should still carefully prepare herself for the second.
However, Rh mismatch is not a 100% predictor of dire consequences. Today, future parents can undergo a course of special treatment, which significantly increases the chances of having a healthy and healthy baby.
Even if there is Rh harmony between the father and mother, planning a child still needs to be approached with all responsibility - use tests to determine ovulation, regularly visit a specialist and follow his recommendations, follow a diet, a healthy lifestyle, etc.
How do your chances of conceiving depend on your blood type?
Quite a lot is already known about the influence of blood groups, for example, on the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's disease, cancer, blood clots, etc. However, virtually nothing was known about the effect on fertility. And finally, thanks to the efforts of Turkish doctors, research has appeared in this area.
A study published last week found that men with type O are four times less likely to develop impotence compared to guys with other blood types. Experts from Ordu University in Turkey noted that blood type is as important a risk factor as smoking, excess weight, and high blood pressure. The reason is not clear, but scientists have said that in people with type A blood, the penis has a large number of veins, the lining of which can become damaged, leading to erectile dysfunction.
Blood type also affects female fertility. Girls with the second group are more likely to bear a healthy child for a long time than with the first. Studies have shown that women in the first group quickly deplete their egg reserves early in life. But at the same time, women with type 0 have a lower risk of developing preeclampsia - high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can be dangerous for mother and baby.
Naturally, representatives of the rest of humanity (which, by the way, are a little more than half, because people of the 1st group account for a little more than 40%) should not panic either - a higher probability does not mean a 100% chance. Likewise, representatives of the “happy” group should not relax ahead of time - reduced risk does not mean zero.
Rh factor, blood group, blood protein, antibody production, anemia, immune reaction, Rh compatibility, anemia, hydrops, fetal edema, immunoglobulin
Physical characteristics of the group
It is noted that people with the third blood category for the most part have strong immunity. However, for this group there are a number of diseases to which, according to statistics, they are most susceptible:
- Inflammation of the lungs - pneumonia.
- Apathy, depression.
- Sclerosis.
- A number of joint diseases.
- Osteochonrosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- In women, complications develop after childbirth.
You should not assume that every person with blood type 3 must necessarily get sick from this entire list. This is just a reason to remember your exposure - lead a healthy lifestyle, monitor your emotional state, eat healthy foods
Psychological characteristics of the group
Surprisingly, the ratio of antigens (A and B) affects not only the physical characteristics of a person, but also his psychological portrait! In this vein, the third negative blood group in women and men is manifested by the following personal characteristics:
- High level of creativity.
- Cunning and wisdom.
- Manifestation of some selfishness in behavior.
- Excellent oratorical qualities - emotional speech, a penchant for diplomacy. In other words, these are people who are capable of leading.
- Frequent and rapid mood swings, some nervousness.
- Sometimes there is excessive emotionality.
- Carriers of the 3rd blood group are most often surgeons, lawyers, accountants, and representatives of other serious professions.
Pregnancy
If necessary, completely reliable prevention of Rh conflict is prescribed by administering anti-Rhesus globulin. For women with an Rh-conflict pregnancy who wish to have children in the future, it is recommended that after childbirth or abortion, administration of globulin is also recommended to eliminate the formed antibodies.
Due to the tendency to diseases of the genitourinary tract, which can then cause complications after childbirth, it is necessary to undergo an examination in advance by a urologist.
It is impossible not to touch upon this topic. There are two types of antigen proteins - A and B. There are also agglutinin antibodies - alpha (α) and beta (β).
So, if a person with a third negative blood is transfused with blood of the same group, but with a positive Rh, then an irreversible process will begin. β-agglutinin found in plasma will destroy red blood cells with β-antigen. Therefore, only identical blood is suitable for people with B (III) Rh-. And the first one is negative.
People with the third positive were a little more lucky. She has not two, but four donors. For people with this blood, the third and the first with any Rh factor are suitable. But others will cause a reaction of rejection. The fourth, second and third blood groups do not combine at all.
If blood transfusion is necessary, only blood of the same group, that is, the same blood, can be transfused to a person with the third group. In emergency cases, it is possible to introduce the first one, but with constant monitoring of the analysis for individual compatibility.
It is imperative to take into account not only group affiliation, but also the Rh factor.
- If the fetus chooses a positive paternal Rh, then the mother will develop antibodies against her own child. In this case, a rejection reaction will begin, which is very dangerous for the health of the mother and fetus. Interruption and miscarriage are possible in the early stages.
- If the fetus is more prone to maternal genes and chooses Rh negative, then the pregnancy will proceed normally, without conflict.
In order to prevent possible complications, obstetricians refer the mother and father for tests, including checking the group and Rh factor.
The first pregnancy of a negative woman may be the least dangerous. What matters here is the rate of accumulation of antibodies in the mother, and they gain sufficient strength only towards the end of pregnancy. In subsequent pregnancies, even those ending in abortion, the mother’s body already has a fairly high concentration of antibodies.
This is how the mother and father group are determined
A solution has been found: in such cases, it is necessary to administer anti-Rhesus globulin to the woman within the first three days after childbirth or abortion. Its effectiveness in reducing unwanted antibodies has been established. This allows the family to safely have a second and subsequent child.
How to determine the third negative?
The determination method is universal for all groups - this is giving a blood sample for analysis. The collection is carried out from a vein. The study can be carried out by almost any clinic. This procedure is worth going through not only out of curiosity. You will receive vital information for donation and family planning. The event always precedes blood transfusion, tissue and organ transplantation.
Preparing for the analysis is simple:
- It is better to donate blood in the morning and on an empty stomach (at least 4 hours after the last snack).
- After completing the course of drug treatment, at least 2 weeks should pass.
- If it is not possible to stop taking your medication, be sure to tell your specialist what you are taking.
- The day before the procedure, avoid alcohol, salty, fatty, and spicy foods.
- Before taking blood, protect yourself from physical and emotional stress.
The third negative blood category is one of the rarest. However, for its carriers the fact will not be a problem. On the contrary, this is a feature of the psychological portrait of the individual, which, according to scientists, is also influenced by antigens. It is important to know this blood group for planning pregnancy, donating blood, tissues, and organs.
What else is prescribed with this study?
Antigens of the KELL system
5.4. Venous blood 3 days
680 som Add to cart
AT to Rh factor (titer)
5.2. Venous blood 1 day
350 som Add to cart
Clinical blood test with leukocyte count and ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear to detect pathological changes) (venous blood)
3.9.1. Venous blood 1 day
550 som Add to cart
Determination of immune antibodies using the ABO system
50.3.2193. Venous blood 10 days
1,100 som Add to cart
Phenotyping of erythrocytes by antigens C, c, E, e, Cw, K, k
5.5. Venous blood 6 days
1,360 som Add to cart