Medicinal and herbal diuretics.
Thursday, September 23
5182
4.7
1
Content
- How to choose a diuretic
- What are the types of diuretics?
- Classes of diuretics and indications for their use
- The best diuretics
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Furosemide
- Indapamide
- Veroshpiron
- Torasemide
- Triampur compositum
- Diuver
- Dog-rose fruit
- Diuretic collection
- Juniper fruits
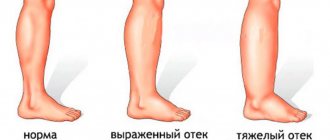
The doctor prescribes diuretics for various edema, hypertension, for the prevention of kidney stones, etc. It is no secret that some women even try to lose weight with the help of diuretics, but this is dangerous to health. The fact is that diuretics, together with liquid, remove potassium from the body - muscle contraction (including the heart muscle) is disrupted. That is why such drugs should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the underlying disease, possible contraindications and side effects.
Read also How to treat dehydration: 5 solutions for rehydration What drugs for dehydration are most often prescribed by doctors?
Precautions and contraindications
Contraindications depend on the type of herb. The list will be different for each plant. Experts recommend either collecting herbs yourself or buying them at a pharmacy. The first option is preferable, since the points of sale most often end up with cake from which most of the beneficial substances have already been removed.
However, it is better to collect plants either in the field or in the garden.
Do not pick herbs in environmentally unfavorable areas or near roads.
Rules for collecting medicinal herbs.
When choosing a diuretic, preference should be given to a plant that is already familiar to the body or at least grows in your region. This will reduce the risk of allergies. Undesirable reactions can worsen the patient’s condition, especially with infectious and cardiac pathologies.
When brewing medicines, you must follow all the rules regarding the proportions of ingredients, preparation technology, etc. You cannot independently change the dosage of ready-made products or extend the course. This can only be done by a doctor after assessing the patient’s condition. Herbal diuretics can be taken longer than synthetic ones, but this cannot be done on an ongoing basis. Otherwise, the metabolism will be disrupted and a deficiency of microelements will occur.
How to choose a diuretic
There are specific factors to consider if you choose a diuretic.
- Speed of action.
There are diuretics for emergency use: if you need to quickly lower high blood pressure (used in combination with other drugs), remove morning puffiness under the eyes. You should not take such medications often because they are addictive. Long-acting diuretics are prescribed to treat hypertension and edema associated with poor heart and liver function. - Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Any diuretic medications are prohibited for pregnant and lactating women. And only in cases where a pregnant or lactating woman has a threat to her health and life, is it possible to use them. Usually this phrase sounds like “the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the fetus.” The exception is practically harmless herbal diuretics, but a woman should talk to her doctor before using them. - Tendency to allergies.
People with allergies may experience an undesirable reaction to both the active ingredient of the diuretic drug and its minor components. If you are allergic, consult your doctor before treatment.
In addition to diuretic medications, mild herbal remedies are often used. They are usually prescribed in the complex treatment of cystitis, urethritis, etc. Herbal diuretics not only remove excess water, but also relieve inflammation.
Drinking diuretics for weight loss is dangerous - the heart muscle suffers
Photos from open sources
Mechanism of action of diuretics[edit | edit code]
The main thing in the mechanism of action of diuretics is their effect on the kidneys, the structural and functional unit - the nephron, on the processes that occur in it (glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, secretion).
To understand the mechanism of action of diuretics, let us briefly consider the process of urine formation. Each kidney contains about 1 million non-communicating nephron formations, consisting of a vascular glomerulus (glomerulus), glomerular capsule and tubules. In the renal glomerulus, plasma is filtered from the capillaries into the capsule cavity. The endothelium of the capillaries does not allow blood cells and proteins to pass through. The filtrate is called primary urine, which enters the kidney tubules from the glomerulus through the capsule. Filtration in the kidneys requires that the blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries exceed the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma. With a decrease in blood pressure, filtration in the glomeruli decreases; with an increase, on the contrary, it increases. The glomerular filtration rate depends not only on the blood supply to the kidneys, but also on the number of functioning nephrons.
Glomerular filtration in an adult averages 100 ml/min. During the day, 150-200 liters of fluid are filtered in the kidneys, and only 1.5-2 liters of urine are excreted, i.e. 99% of the primary urine is again absorbed (reabsorbed) in the tubules. The tubules are divided into proximal, which passes into the loop of the nephron (Henle) (V-shaped convoluted tube), and distal, through which urine passes from each nephron into the collecting ducts, and from them into the renal pelvis and through the ureters into the bladder.
The reabsorption process occurs throughout the nephron. In order to increase diuresis by 2 times, it is necessary to increase glomerular filtration by 2 times, which is practically impossible to do, or to reduce reabsorption by only 1%. Thus, urine formation can be significantly increased by reducing tubular reabsorption (Fig. 3.11). In addition to water, sodium, chlorine and potassium ions are reabsorbed in the tubules. It should be taken into account that in the tubules it is necessary to reduce the reabsorption of sodium ions, and water passively follows this osmotically active ion.
The effect of increasing filtration and decreasing reabsorption by 10% on the amount of diuresis
Sodium reabsorption in the kidney tubules occurs as follows. From the lumen of the tubule, Na+ enters the cell through the apical membrane. It is believed that sodium transport within the cell is carried out using a special carrier protein, the synthesis of which is regulated by aldosterone. Aldosterone binds to receptors in cells, is transferred to the nucleus and, influencing DNA, stimulates the synthesis of messenger RNA, which promotes the activation of the synthesis of the carrier protein in the ribosomes. Sodium, which entered the tubule cell, creates a fund (pool) of sodium, which is subsequently actively reabsorbed. Reabsorption is carried out using special pumps that are located on the basement membrane of the tubule wall cells. Several types of such pumps are known, one of them transports Na+ in exchange for K+. Others reabsorb Na+ together with SG or HCO~. This active transport of sodium is carried out due to the energy produced by mitochondria located near the basement membranes.
Reabsorption of sodium by epithelial cells of the renal tubular wall
About 70-80% of the total filtered Na+ is reabsorbed in the proximal tubules, followed by passive reabsorbment of water and SG. Carbonic anhydrase reabsorbs hydrogen carbonate (HCO3). The point of application of diuretics may be the proximal nephron, but their effect is insignificant, since a decrease in reabsorption in the proximal tubule entails a compensatory increase in it in the nephron loop and the distal tubule.
Active transport of Na+ and SG occurs in the nephron loop; its wall is impermeable to water. The action of diuretics primarily occurs in this part of the nephron; they are called loop diuretics. Blockade of sodium reabsorption in this department causes the greatest natriuresis.
Diagram of the nephron and localization of the action of diuretics (Farmakolopya, 2001): 1 - xanthines; 2 - diacarb; 3— mannitol; 4— furosemide, ethacrynic acid; 5 - dichlothiazide; 6— spirolactone, triamtren
Urine formation is completed in the distal nephron and collecting ducts. Transport processes here are controlled by hormonal influences. The sodium-retaining effect of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and the water-retaining effect of the antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) are manifested. Passive secretion of K+ from nephron cells occurs through the apical membrane along an electrochemical gradient. The distal tubule and collecting ducts can also be the point of application of diuretics (aldosterone antagonists, triamterene and others), but they are ineffective. Blocking Na+ reabsorption in this compartment, when about 90% of the filtered Na+ has already been reabsorbed, can increase its excretion by only 2-3% - the filtration charge. Sodium transport in the kidneys is also regulated by other factors. This is an atrial natriuretic hormone that is released from the atria when they are stretched, which causes an increase in glomerular filtration rate and inhibition of sodium reabsorption in the collecting ducts. In addition, there is natriuretic hormone - a low-molecular compound that enters the blood when volumoreceptors are stimulated and, like ouabain, blocks Na*, K+-ATPase in the kidneys, which reduces Na+ reabsorption. Substances that act as potential regulators of sodium excretion include estrogens, somatotropin, insulin (increase Na+ reabsorption), progesterone, parathyroidin, glucagon (reduce Na+ reabsorption). Factors that are formed in the kidneys (kinins, prostaglandins, dopamine, etc.) also act locally.
Considering the principles of functioning of the urinary system, it becomes clear that drugs that stimulate urination can directly affect the urinary function of the kidneys or change their hormonal regulation.
The use of diuretics, primarily as a means of symptomatic therapy aimed at reducing edema, also has an important pathogenetic effect on the complex chain of reactions in diseases that are accompanied by the retention of salts and water in the body.
There are more than 20 drugs in the arsenal of diuretics. Which of them should be preferred in a given situation should be helped by knowledge of pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, possible side effects, and more.
What are the types of diuretics?
All diuretic drugs are divided into several categories: according to their spectrum of use and mechanism of action.
- Loop diuretics.
These drugs have the strongest effect (they begin to act literally a few minutes after administration), but the effect ends just as quickly. Such drugs are well suited for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. But loop diuretics have a significant disadvantage - along with water, they remove potassium from the body, which is fraught with the development of arrhythmia. - Thiazide diuretics.
Another effective diuretic drug. They not only get rid of excess fluid, but also dilate peripheral vessels. Thiazide diuretics also reduce the response of blood vessels to adrenaline, so they spasm less. Such diuretics are also prescribed for the treatment of urolithiasis. Among the “side effects” are the excretion of potassium and an increase in uric acid, which can then accumulate in the joints and cause gout. - Potassium-sparing diuretics.
Such diuretics do not remove potassium from the body, protecting the patient from various heart complications. But these drugs are not as potent as the previous ones. - Osmotic diuretics.
This group of drugs reduces blood plasma pressure - excess water is quickly removed from the tissues, swelling goes away. The pressure in the tissues and in the plasma becomes the same. Typically, osmotic diuretics are prescribed to relieve swelling of the brain, lungs, and high intraocular or intracranial pressure.
List of other diuretic herbs
For convenience, diuretic herbs are divided into categories depending on their effect.
Medicinal fees
Among the medicinal fees, the following can be distinguished:
- Diuretic collection No. 1. Contains bearberry, cornflower and licorice in a 3:1:1 ratio. Removes moisture, destroys germs and suppresses infections.
- Diuretic collection No. 2. Contains licorice, bearberry and cornflower. The drug helps relieve pain in kidney pathologies and reduces foci of inflammation.
- Diuretic collection No. 3. Contains horsetail, juniper and wheatgrass root. The product is potent, so it is used with caution. Most often, the collection is prescribed to patients suffering from an allergy to licorice root.
- Collection of herbs No. 6. Contains lemongrass, corn silk, horsetail and chamomile. Helps restore water-salt balance.
Diuretic herbal mixtures are presented in various combinations.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Relieving inflammation helps reduce pain due to pathologies of the urinary system.
This is useful for cystitis and pyelonephritis. Internal swelling disappears due to the elimination of stagnation and excessive blood flow to the damaged area. The most powerful anti-inflammatory diuretics are the following herbs:
- burdock root;
- pink radiola;
- stinging nettle;
- lingonberry leaves;
- parsley;
- corn silk;
- marshmallow
For hypertension and heart failure
For hypertension, it is advisable to take herbs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels. This promotes proper blood circulation and helps the cardiovascular system withstand high stress without side effects.
Herbal tea for hypertension strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
For heart failure and hypertension, the following herbs and berries are brewed:
- shepherd's purse;
- red rowan;
- swampy dried grass;
- barberry roots;
- motherwort;
- mint;
- lemon balm.
For facial swelling
If you experience frequent swelling of the face, it is recommended to pay attention to the symptom. Its location indirectly indicates the source of the problem. For example, swelling in the upper lip or brow ridges indicates cardiac pathology.
Swelling of the eyelids is a sign of kidney disease.
The following remedies help with facial swelling:
- half fell;
- flax seeds;
- beet leaves;
- corn silk.
A decoction of corn silk will eliminate swelling on the face.
For the kidneys
For infectious pathologies of the urinary system, horsetail and knotweed are used. Herbs increase fluid circulation, prevent congestion, destroy bacteria, and relieve inflammation from damaged tissues.
For swelling of the legs
Swelling of the legs is most often observed due to impaired lymph outflow, pathology of the liver, heart, thyroid gland, and renal failure.
To improve the condition, use chamomile, horsetail, bearberry, nettle or lemon balm.
For weight loss
Diuretic herbs are used as an adjuvant. On their own, they will not provide sustainable weight loss, but they can improve the results of diet and exercise. For weight loss, horsetail, bear ears, and lingonberry leaves are used. The latter are the mildest and safest remedy.
Classes of diuretics and indications for their use
Main indications for the use of diuretics of various classes
| Diuretic class | Indications |
| Osmotic | Edema of the brain, lungs, acute attack of glaucoma, barbiturate poisoning |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors | Edema due to pulmonary heart failure, glaucoma, epilepsy |
| Loop | Hypertensive crisis, cerebral edema, chronic renal failure, poisoning with water-soluble poisons |
| Thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics | Hypertension, cardiovascular failure, liver cirrhosis, nephrosis, pregnancy nephropathy, glaucoma |
| Potassium-sparing | Hypertension, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypokalemia during treatment with diuretics of other groups |
| Vegetable | Renal edema, whistitis, chronic renal failure |
| Xanthine derivatives | Hypertension, heart failure (in complex therapy) |
Hydrochlorothiazide
One of the most effective means for removing excess fluid and sodium salts from the body. Hydrochlorothiazide is prescribed for diseases of the kidneys, heart, lungs, to reduce blood pressure and reduce swelling. The drug does not form metabolites and is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The maximum effect of the diuretic is achieved 4 hours after administration, and it lasts for 12 hours. Patients about it has a pronounced diuretic effect, any swelling quickly goes away, it is inexpensive. Among the disadvantages is a large list of “side effects” and the removal of important microelements from the body (including potassium and magnesium).
Hydrochlorothiazide
OZON, Russia; Pranapharm LLC, Russia; PJSC "Biokhimik", Russia; OJSC Borisov Plant of Medical Preparations (Borimed), Belarus; PJSC Valenta Pharm, Russia
A diuretic drug that is used for: Arterial hypertension, edema syndrome of various origins (chronic heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, fluid retention in obesity), diabetes insipidus, glaucoma (subcompensated forms).
from 34
5.0 1 review
546
- Like
- Write a review
Use of diuretics[edit | edit code]
Triamterene
(pterophen); chemical structure 2,4,7,-triamino-6-phenylpteridine is a derivative of pteridine, similar to folic acid.
Pharmacokinetics
. Well absorbed in the intestines. The effect occurs after 15-20 minutes and lasts 6-8 hours. The maximum concentration in the blood is determined after 1.5-2 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys. Intensively secreted in the proximal nephron. The half-life is 45-70 minutes.
Pharmacodynamics
. Due to the similarity of the triamterene molecule with the hydrated sodium ion, the drug interacts by the principle of competition with the carrier protein, which reduces the flow of sodium from the lumen of the tubule into the cell. A decrease in the intracellular sodium pool negatively affects its active transport through the basement membrane. Chlorine ions and uric acid are also removed.
A special feature of the drug is that it does not affect the excretion of potassium ions in the urine. At the same time, the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma does not decrease, which allows, if necessary, the use of triamterene together with cardiac glycosides. The drug reduces the excretion of magnesium and calcium. Triamterene does not affect acid-base balance. Its action does not depend on the content of aldosterone in the blood plasma.
The drug somewhat enhances the secretion of uric acid, certain disturbances in folic acid metabolism occur, which must be taken into account when prescribing the drug to pregnant women and young children.
Indications for use
: To prevent hyperkalemia, used with loop and thiazide diuretics. They produce the drugs triampur compositum and diuretidin, which contain triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide.
Side effects
: hyperkalemia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, azotemia, cramps in the lower extremities.
Klopamide
(britaldix); chemical structure of 4-chloro-N-(cis-2,6-dimethylpiperidino)-3-sulfamoylbenzamide. Refers to thiazide-like diuretics.
Pharmacokinetics
. Absorbed well. After absorption in the digestive canal, the effect occurs within 1-2-4 hours and lasts up to one day (18-20 hours). Excreted by the kidneys and intestines.
Pharmacodynamics
. Reduces the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions in the distal tubules, partially in the proximal ones, increases the excretion of potassium and magnesium.
Indications for use
: arterial hypertension as part of complex drugs (normatens, cristepin, normatisk), etc.
Side effects
: as with similar thiazide diuretics.
Indapamkd
(ariphon, indapres, lorvas) occupies a special place; chemical structure of 4-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-indolinyl)-3-sulfamoylbenzamide.
Pharmacokinetics
. It is quickly and completely absorbed in the digestive canal, the maximum concentration is reached in the blood after 1-2 hours. About 70% of indapamide binds to blood plasma proteins. The drug is metabolized by the liver, excreted slowly, mainly by the kidneys, in the form of metabolites (about 70%), approximately 8% unchanged. Indapamide is also excreted in breast milk. The half-life is approximately 18 hours.
Pharmacodynamics
. The drug reduces sodium reabsorption in the cortical segment of the nephron, increases the elimination of sodium and chlorine, and has a lesser effect on the excretion of potassium and magnesium ions. The effect on the vascular wall is associated with the high lipophilicity of the drug. The antihypertensive effect is also explained by a decrease in the tone of smooth muscles of blood vessels due to changes in the transmembrane flow of calcium ions and a decrease in the sensitivity of the vascular wall. Stimulates the synthesis of substances with vasodilatory activity (prostaglandin E and prostacyclin 1a). A decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure was noted. Indapamide reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and does not affect the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates.
Indications for use
: arterial hypertension.
Side effects
: hypokalemia, hyponatremia, orthostatic hypotension, rarely - leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, nausea, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, asthenia, paresthesia, headache, possible hypersensitivity reactions (maculopapular rash, purpura, etc.).
Amiloride
(hypertas); chemical structure of N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide hydrochloride.
Pharmacokinetics
. When used internally, 50% of the drug is absorbed. The effect occurs after 2 hours and lasts 24 hours. The drug is not biotransformed and is excreted by the kidneys.
Pharmacodynamics
. In terms of diuretic action and clinical use, it is close to triamterene, but has an antihypertensive effect.
Indications for use
: as a potassium-sparing drug, it is used alone and in combination with other drugs. The drug moduletic contains amiloride and hydrochlorothiazide.
Side effects
: hyperkalemia, nausea, vomiting, headache.
Spironolactone
(veroshpiron, aldactone); chemical structure of y-lactone-3-(3-oxo-7a-thio-acetyl-17-hydroxy-4-androsten-17a-yl)propionic acid. As the name suggests, spironolactone is structurally similar to the mineralocorticoid aldosterone.
Pharmacokinetics
. Well absorbed in the intestines. The effect occurs after 2-3 days and lasts 2-4 days. It is rapidly metabolized in the liver, resulting in the formation of the active metabolite canrenone. It can accumulate with insufficient liver function, as well as in elderly people.
Pharmacodynamics
. Spironolactone, like triamterene, interferes with the reabsorption of sodium into the cell wall of the renal tubules. However, its mechanism of action is somewhat different. It prevents the interaction of aldosterone with nuclear chromatin, as a result of which the DNA-dependent synthesis of messenger RNA is blocked, which, having entered the ribosomes, would ensure the synthesis of the sodium transporter protein (permease). A decrease in sodium reabsorption contributes to its increased excretion from the body; also removes chlorine. In this regard, spironolactone is often called a competitive antagonist of aldosterone, since its action is due to the blockade of the action of this hormone. Taking into account this mechanism, the effect occurs only on the 2-5th day from the start of taking the drug. Like triamterene, spironolactone has virtually no effect on the excretion of potassium and magnesium from the body, and is effective against acidosis and alkalosis.
Indications for use
: arterial hypertension, chronic heart failure, liver cirrhosis with edematous-ascitic syndrome. The drug is most effective in cases of hyperaldosteronism (kidney tumors, chronic heart failure, etc.).
Side effects
: dizziness, drowsiness, skin rashes, hyperkalemia, gynecomastia.
Eplerenone
(inspra) has a specific effect, indications, and side effects similar to spironolactone. At the same time, eplerenone has a greater diuretic activity.
Source:
Furosemide
This diuretic is one of the most popular and frequently prescribed, and is a strong diuretic. Furosemide removes excess water and sodium salts from the body well and quickly, and relieves swelling. The drug is indicated for hypertension, poor functioning of the heart, kidneys and liver. Diuretic tablets begin to act 20-30 minutes after administration. Furosemide is usually used in emergency cases. You cannot take the drug without medical supervision, because self-medication can lead to dehydration. Furosemide is inexpensive, acts quickly, but has many side effects, including the removal of potassium and magnesium.
Furosemide
Sopharma, Bulgaria; PJSC "Biosintez", Russia; Binnopharm, Russia; JSC Avexima, Russia; Update, Russia; JSC Pharmstandard-TomskKhimPharm, Russia; "Moskhimfarmpreparaty" named after. N. A. Semashko, Russia; Ozon LLC, Russia; OJSC Borisov Plant of Medical Preparations (Borimed), Belarus; JSC Dalkhimfarm, Russia
Edema syndrome of various origins (with chronic heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver (portal hypertension syndrome); edematous syndrome of renal origin (with nephrotic syndrome, treatment of the underlying disease is in the foreground), acute heart failure, especially with pulmonary edema (used in combination with other therapeutic agents) measures); cerebral edema; severe forms of arterial hypertension; hypertensive crisis; forced diuresis in case of poisoning with chemical compounds excreted unchanged by the kidneys.
from 17
2.0 1 review
924
- Like
- Write a review
Indapamide
This is a moderate-acting drug that is usually prescribed for edema associated with heart failure. "Indapamide" is quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. Diuretic tablets reduce the load on the heart and peripheral vessels and stabilize blood pressure. The effect occurs an hour after taking the drug and lasts 12-18 hours. You can buy Indapamide with a prescription, it is inexpensive, but it is a generic (not the original drug). Be sure to check the possible side effects.
Indapamide
OZON, Russia
Arterial hypertension;
sodium and water retention in chronic heart failure. from 8
771
- Like
- Write a review
Herbal diuretic tablets
The most popular herbal diuretics are:
- Cyston;
- Urolesan;
- Phytolysin;
- Canephron.
Popular herbal diuretic tablets.
Diuretics in tablet form are preferable because manufacturers include a balanced complex of herbs. The ingredients enhance each other's effects. It is more convenient for patients to take medicine in tablet form rather than brew dried plants.
Veroshpiron
This is a potassium-sparing diuretic, which is prescribed for edema due to chronic heart failure and hormonal problems. And although Veroshpiron has a weak diuretic effect, the drug does not remove potassium and does not upset the acid-base balance in the body. The maximum effect of the diuretic occurs after 2-3 days and lasts a long time. You can buy Veroshpiron with a prescription; it is important to take into account the impressive list of contraindications.
Veroshpiron
Gedeon Richter, Hungary
The drug Veroshpiron is a potassium-sparing diuretic.
from 72
762
- Like
- Write a review
Read also Diet pills: effective drugs for weight loss List of the most effective weight loss pills.
Classification of diuretics[edit | edit code]
Today there is no perfect classification that would take into account all aspects of the action of diuretics. Diuretics, having different chemical structures, differ in localization, mechanism, strength of action, speed of onset of effect, its duration, and side effects. For a long time, the classification of diuretics was based on their chemical structure. Attempts have been made to classify diuretics according to the nature of their effect on the kidneys. However, many diuretics also have extrarenal effects. Attempts to classify diuretics according to their ability to influence one or another part of the nephron are also associated with difficulties. The diagram (Fig. 3.14) shows that some of these drugs (xanthines, furosemide, ethacrynic acid, osmotic diuretics, etc.) act throughout the nephron. Therefore, it is rational to classify diuretics based on their mechanism of action.
Points of action of diuretics at different levels of the nephron
Depending on pharmacodynamics, modern diuretics are divided into three groups: saluretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, osmotic diuretics.
Saluretics include thiazide derivatives (hydrochlorothiazide, cyclomethiazide), thiazide-like (clopamide, chlorthalidone), loop diuretics (furosemide, torasemide, ethacrynic acid, bumetanide), carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (diacarb).
Potassium-sparing diuretics include triamterene, amiloride and spironolactone, eplerenone, which increase sodium excretion and have a slight effect on potassium excretion.
Osmotic diuretics (mannitol, urea), increasing osmotic pressure in the tubules, prevent water reabsorption. However, it should be noted that this systematization does not include diuretics that affect blood circulation in the kidneys; it is not very focused on the mechanism of action of the drugs.
To better understand the action of modern diuretics, a classification of diuretics is recommended, which takes into account not only the mechanism, but also the localization of their action.
I. By localization and mechanism of action.
1. Agents acting at the level of renal tubular cells.
1.1. Agents acting at the level of the apical membrane.
1.1.1. Competing for the sodium transporter, or non-competitive aldosterone antagonists—triamterene, amiloride.
1.1.2. Competing aldosterone antagonists are spironolactone, eplerenone.
1.2. Agents acting at the level of the basement membrane.
1.2.1. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - diacarb.
1.2.2. Thiazide diuretics - hydrochlorothiazide, cyclomethiazide.
1.2.3. Thiazide-like diuretics - chlorthalidone, clopamide, indapamide.
1.2.4. Loop diuretics - furosemide, ethacrynic acid, bumetonide, torsemide.
2. Osmotically active diuretics - mannitol, urea.
3. Drugs that increase blood circulation in the kidneys - xanthines, aminophylline, aminophylline, etc.
4. Preparations of medicinal plants - horsetail, bearberry leaves, birch buds, orthosiphon leaves, lingonberry leaves, leaves and stems of Lespedesa capitata, torment leaves, strawberries, etc.
From a clinical point of view, strength, speed of onset and duration of action are of practical importance when choosing a drug. Therefore, diuretics are classified as follows.
II. By force of action.
1. Strong diuretics - furosemide (Lasix), torasemide (Trifas), ethacrynic acid (Uregit), clopamide (Brinaldix), osmodiuretics (mannitol, urea), etc.
2. Medium diuretics - thiazides: hydrochlorothiazide (hypothiazide, dichlothiazide), cyclomethiazide and thiazide-like - chlorthalidone (oxodoline, hygroton), etc.
3. Weak diuretics - spironolactone (veroshpiron, aldactone), diacarb (acetazolamide), triamterene (pterophen), amiloride, xanthines aminophylline (euphylline), medicinal plant preparations (bearberry leaves, orthosiphon leaves, birch buds, etc.).
III. According to the speed of onset of the diuretic effect.
1. Fast (emergency) action (30-40 min) - furosemide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid, mannitol, urea, triamterene.
2. Medium-acting (2-4 hours) - diacarb, aminophylline, amiloride, cyclomethiazide, clopamide, chlorthalidone, etc.
3. Slow action (2-4 days) - spironolactone, eplerenone.
IV. According to the duration of the diuretic effect.
1. Short-acting (4-8 hours) - furosemide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid, mannitol, urea, etc.
2. Medium duration (8-14 hours) - diacarb, triamterene, hydrochlorothiazide, clopamide, aminophylline, etc.
3. Long-term action (several days) - chlorthalidone, spironolacgon, eplerenone.
Diuretics acting at the level of renal tubular cells Drugs that disrupt sodium transport across the apical membrane of renal tubular cells include triamterene, amiloride, spironolactone, and eplerenone. They act at the level of the distal nephron. These are drugs that reduce the processes of physiological reabsorption of sodium and water.
Torasemide
This diuretic drug is one of the most effective today. "Torasemide" is prescribed for acute and chronic heart failure, as well as renal failure. The product can also be taken to prevent edema. The drug effectively reduces high blood pressure by quickly removing excess fluid and sodium salts. The effect occurs an hour after administration and lasts 12-18 hours. Patients note that the diuretic effect does not occur immediately, so in the first hour after taking the drug you do not have to limit your activity. "Torasemide" is inexpensive and works well to relieve swelling of the face. You can buy diuretic tablets with a prescription; there are some side effects.
Torasemide
Berezovsky Pharmaceutical Plant, Russia
Edema syndrome of various origins, incl.
for chronic heart failure, diseases of the liver, kidneys and lungs; - arterial hypertension. from 81
436
- Like
- Write a review
Triampur compositum
This diuretic does not have a very pronounced effect and does not remove potassium from the body, only water, salts and toxins. That is why Triampur compositum is considered the safest diuretic drug, which is prescribed for edema due to chronic heart failure and liver problems. Triampur begins to act 15 minutes after administration, and the effect lasts about 12 hours. Doctors say that this diuretic is safe for relieving facial swelling, is quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, and has a gentle effect.
Triampur compositum
AVD.pharma, Croatia
-arterial hypertension;
—edematous syndrome of various origins (with chronic heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, liver cirrhosis). from 256
306
- Like
- Write a review
How to quickly relieve facial swelling in adults
If this is physiological swelling of the face, not associated with serious pathologies that require medical supervision and the use of selected medications, excess fluid can be eliminated through certain simple measures and actions.
Taking a contrast shower or washing with cold/hot water. This method refreshes, increases tissue tone, enhances the outflow of fluid from the skin and reduces swelling.
Using ice – a couple of pieces of ice will help deal with swelling on the face quickly and effectively. In addition, you can prepare herbal decoctions with a tonic effect in advance and freeze them, using them for washing.
Facial massage is an effective remedy that helps improve microcirculation and swelling. Manual massage, the use of rollers, ice cubes, and cold spoons help. Sometimes you can first wipe your face with green tea and apply compresses with it to your face and eye area.
Diuver
Modern diuretic tablets from the group of loop diuretics. The active ingredient of the drug, turasemide, copes well with edema of various natures. “Diuver” has the mildest, prolonged action; the effect after administration occurs within 3-4 hours. Although it is not a potassium-sparing diuretic, it removes much less potassium than other diuretics. Diuver is prescribed for diseases of the kidneys, liver, lungs and heart failure. You can buy Diuver with a prescription (by the way, it is not cheap), be sure to familiarize yourself with the contraindications and side effects.
Diuver
JSC "Biolek", Ukraine
- edematous syndrome of various origins, incl.
for chronic heart failure, diseases of the liver, kidneys and lungs; - arterial hypertension. from 236
613
- Like
- Write a review
Natural Diuretics
Photos from open sources
Dog-rose fruit
In addition to medicinal diuretics, herbal drugs have a mild diuretic effect. Firstly, it is rosehip. In addition to being a diuretic, it is famous for its general strengthening effect, helping the body resist various infections (also for urinary tract diseases). Rosehip improves the functioning of the digestive and cardiovascular systems. The value of rosehip is that it contains a lot of useful vitamins. Rose hips relieve swelling, reduce cholesterol levels, normalize blood clotting, and help cells recover faster.
Rosehip fruits
OJSC Krasnogorskleksredstva, Russia
For the prevention of hypovitaminosis C and R. In the complex therapy of acute and chronic infectious diseases, asthenic conditions, during the period of recovery after serious illnesses, surgical operations
from 28
379
- Like
- Write a review
Diuretic collection
Herbal infusions are very popular for the treatment of many diseases, including as a diuretic for edema. Diuretic collection in complex treatment helps cure urinary tract infections. Medicinal herbs in the diuretic collection act very gently, relieve spasms and inflammation. A diuretic preparation is often prescribed for cystitis; it is suitable for preventing relapses of this disease and is available in almost every pharmacy. Disadvantages include an unpleasant taste and green coloration of urine.
Diuretic collection
ST-Medipharm, Russia
Combined product of plant origin.
It has diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antispasmodic effects. from 76
5.0 1 review
262
- Like
- Write a review
List of the best diuretic herbs
The list of the best diuretic herbs includes milk thistle, thyme, calendula, horsetail, bearberry, etc. They differ in their effects and dosages.
Milk thistle
Milk thistle not only has a diuretic effect, but also cleanses the liver of toxins, accelerating cell regeneration. In the pharmacy the product can be found in the form of seeds, powder or meal. The first option is preferable, but you will have to grind the grains yourself to release the active substances. 2 tsp. raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, cover and leave for 15 minutes. Then the liquid is drained and drunk up to 3 times a day, regardless of meals.
Thyme
Thyme stimulates urination, relieves pain and inflammation, and destroys bacteria. It stimulates the digestion of food and, in case of pulmonary diseases, facilitates the removal of fluid from the bronchi. To prepare the medicine 1 tbsp. l. dried herbs, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and filter. The product is drunk half an hour before meals, up to 4-5 times a day.
Thyme removes water and toxic substances from the body.
Calendula
Calendula relieves swelling and inflammation, destroys bacteria and viruses, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and also activates regeneration processes. To brew tea, 2 tbsp. l. inflorescences are poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and place in a dark place for 15 minutes. At the end, the liquid is filtered. Drink 100 ml of tea up to 3 times a day.
Horsetail
Horsetail enhances fluid removal, stops bleeding, enhances tissue regeneration and relieves inflammation. The plant has an antimicrobial effect, improves the condition of the renal ducts and vascular walls, which is most useful for cystitis and pyelonephritis. The medicine is prepared from 4 tbsp. l. dry horsetail. It is poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. The product is drunk warm. Dosage - 2 tbsp. l. infusion up to 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Bearberry
Bearberry helps remove excess moisture from the body by irritating the kidney tissue. The product has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. To prepare the decoction 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves are ground to a powder. 250 ml of hot water is poured into the mass. The mixture is placed in a water bath for 20 minutes, then allowed to brew for 40 minutes and filtered. After this, the volume is adjusted to the original volume by adding water. The drug is taken 50 ml half an hour after meals up to 3 times a day.
Bearberry normalizes metabolism and eliminates swelling.
Rose hip
Rosehip not only removes moisture from tissues, but also has an anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effect. It protects the kidneys and liver, prevents the development of cancer, and heals wounds. 1 tbsp. l. The berries are passed through a meat grinder, placed in a saucepan and poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and steam for 30 minutes. Then filter the liquid, pour in another 2 cups of boiling water and leave again for half an hour. Ready-made tea is drunk up to 3-4 times a day, 250 ml.
Nettle
Nettle has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. It stops bleeding, normalizes the activity of the immune system, blood sugar and cholesterol levels. The product reduces pain in the back, neck and lower back, cleanses the body of toxins. The decoction is prepared from 1 tbsp. l. leaves and 1 tbsp. water. The mixture is brought to a boil. Leave the container under a towel in a warm place for 1 hour. The finished broth is filtered. Take up to 1-2 glasses daily; for internal bleeding, the portion is increased to 1 liter.
Chamomile
Chamomile is not only a diuretic, but also an antispasmodic. This helps ease urination during cystitis. The product relieves inflammation, calms a person, dilates blood vessels, improves blood circulation. The infusion is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. inflorescences and 250 ml of boiling water. The mixture is left covered until completely cooled. The finished product is taken 1 tbsp. before meals up to 3 times a day.
Chamomile decoction is used in the treatment of many diseases, including cystitis.
Birch
Birch leaves are a natural diuretic, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. They are often used for inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system. A decoction is prepared from 2 tsp. crushed leaves and 200 ml of hot water. The product is infused for 20 minutes, then filtered. Take 100 ml before meals twice a day.
Linden
Linden normalizes digestion, removes moisture through the bladder and skin pores, and reduces body temperature. A compress of flowers relieves headaches and treats burns. 1 tbsp. l. dried raw materials are poured with 200 ml of boiling water. The product is drunk warm before meals. This is done 2-3 times a day.
Valerian
Valerian is a weak diuretic. It copes better with edema than with cystitis or pyelonephritis. However, the plant has a beneficial effect on the heart. It is recommended to be used together with other herbs. You can add mint in a 1:1 ratio. 1 tbsp. l. collection pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, drink 200 ml once a day.
Motherwort
Motherwort has general strengthening properties. It improves the condition of the immune and nervous system, relieves swelling, relieves cramps, cough and inflammation. The product reduces pain. 1 tbsp. l. motherwort is poured with 300 ml of boiling water. The finished infusion is drunk 150 ml twice a day.
Motherwort decoction is used to treat diseases of the nervous system.
Mint
Mint not only helps remove moisture, but also disinfects tissues. It helps with flu and colds, relieves pain, and improves digestion. Tea is prepared from mint: 2 tsp. crushed raw materials, pour 200 ml of boiling water for 20 minutes. After filtering, drink the product up to 2-3 times a day.
Oregano
Oregano is often used in gynecology. It normalizes hormonal levels, protects the genitourinary system from tumors, and relieves inflammation. Men treat urethritis, prostatitis and infections with oregano. Tea is prepared from 2 tsp. dry herbs and 250 ml of hot water. The mixture is infused for half an hour. It is drunk before meals or between meals, 50-100 ml three times a day.
The course of treatment should not exceed 1 week.
Juniper fruits
Juniper helps with urinary tract infections by reducing inflammation and destroying germs. And thanks to the diuretic effect, pathogenic microflora is quickly eliminated from the body. Juniper fruits are also used as an appetite stimulant and to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, this herbal preparation stabilizes blood pressure and has a mild laxative effect. Contraindications include pregnancy, breastfeeding and childhood.
Juniper fruits
OJSC Krasnogorskleksredstva, Russia
In the complex treatment of edematous syndrome (with heart failure, insufficiency of kidney and/or liver function), cystitis
from 41
212
- Like
- Write a review