The vessels of the brain form a complex circulatory system, which must ensure constant delivery of nutrients and oxygen to nerve cells.
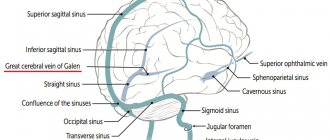
The circle of Willis is a closed complex of arteries that provides blood supply to the structures of the central nervous system due to the redistribution of blood.
Pathologies in its structure and function lead to various neurological disorders. We will talk further about what the Circle of Willis is and what it means if it is open.
About the Circle of Willis of the brain
The circle of Willis protects the brain from hypoxia when blood flow through the arteries is impaired. Redistribution of blood helps prevent the death of neurons due to thrombosis, compression or rupture of blood vessels.
A closed circle system with anastomoses ensures normal blood flow due to the blood that flows through the vessels of the opposite side. An anastomosis is a small artery that connects two areas of the nervous system with separate blood supplies.
Anatomical structure
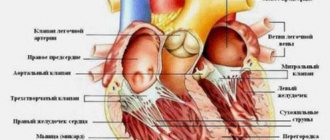
The vessels of the circle are located under the arachnoid membrane in the area of the optic chiasm at the base of the brain. In most people, several vessels are involved in the formation of the arterial circle:
- anterior communicating artery;
- posterior communicating arteries;
- left and right anterior cerebral arteries;
- left and right posterior cerebral arteries;
- supracuneiform part of the internal carotid artery.
All arteries connect with each other, forming a vascular heptagon. Due to this, anastomoses are formed between the carotid and basilar arteries. This makes it possible to prevent ischemic brain damage due to unilateral disturbances of blood flow through the vessels.
Functions
The main function of the arterial circle is to ensure normal blood supply to the brain in case of pathology of individual vessels. This is achieved due to its closed structure and constant blood flow through several arteries.
Variant anatomy of the arteries of the base of the brain
There are many types of structure of the Circle of Willis. They depend on how the process of vessel formation occurred in the prenatal period, and it is impossible to predict this process.
Among the most common anomalies of the cerebral arteries are: aplasia, hypoplasia of individual branches, trifurcation, fusion of two arteries into one trunk and some other varieties. Some people have a combination of different vascular anomalies.
The most common variant of the development of the circle of Willis is considered to be posterior trifurcation of the ICA, which accounts for almost a fifth of all anomalies of the arterial ring. With this type of structure, three cerebral arteries immediately begin from the ICA - anterior, middle and posterior, and the PCA will be a continuation of the posterior communicating branch.
A similar structure is typical for the circulatory system of the fetal brain at 16 weeks of pregnancy, but later the sizes of the vessels change, the posterior connective branch decreases, and the remaining branches increase significantly. If such a transformation of the vessels does not occur, then the child is subsequently born with posterior trifurcation.
Another common variant of the structure of the circle of Willis is considered to be aplasia of the PCA, which occurs under various unfavorable external conditions and genetic abnormalities during embryogenesis. In the absence of this artery, the circle of Willis does not close on the side where it is not present, that is, there is no relationship between the internal carotid artery system and the basilar area.
The absence of PSA is also diagnosed, but much less frequently than the posterior one. With this type of structure of the arterial ring, there is no relationship between the branches of the carotid arteries, so it is impossible, if necessary, to “transfer” blood from the vessels of the left half to the right.
Aplasia of the anterior communicating artery does not provide a chance for blood flow to the affected part of the brain by delivering blood from the opposite vasculature, since the carotid arteries are disconnected. When the PCA is not formed, there is no relationship between the anterior and posterior parts of the circle of Willis, and the anastomoses do not function. This type of branching of the arterial system seems unfavorable in terms of possible decompensation of blood flow disorders.
Rare forms of the circle of Willis structure include:
- Median artery of the corpus callosum;
- The union of the anterior cerebral arteries into one common trunk or their parietal course, when they are in close contact with each other;
- Anterior trifurcation of the internal carotid artery (two anterior cerebral arteries arise from one carotid artery);
- Split, double anterior communicating artery;
- Bilateral absence of PCA;
- Trifurcation of the carotid arteries on both sides.
Non-classical types of the circle of Willis are more typical for its anterior part, but since defects of the posterior part are of greater clinical significance due to a worse prognosis, they are diagnosed more often. The conclusions of experts indicate that the vast majority of patients with impaired blood flow in the brain have certain anomalies of the circle of Willis, and this indicates its enormous importance in supplying the brain with blood in pathology.
Anomalies in the branching of blood vessels and the openness of the circle of Willis make it unable to perform the role of an anastomosis in critical situations - during a hypertensive crisis, thrombus formation, spasm, atherosclerosis. In addition, some types of branching involve large areas of necrosis of nervous tissue due to circulatory failure. For example, anterior trifurcation means that most parts of the hemisphere receive blood from the branches of just one artery, so if it is damaged, the scale of necrosis or hemorrhage will be significant.
When the arteries of the base of the brain are classically developed, all the necessary connecting branches are present between them and the caliber of each vessel is within normal values, they say that the Circle of Willis is closed. This is the norm, indicating that the anastomosis is stable, and in case of pathology, the blood flow will be compensated to the maximum.
fully open VC
An open circle of Willis is considered a serious anomaly that predisposes to various types of cerebrovascular accidents. There is an openness of the anterior part of the arterial ring, which occurs with aplasia of the PSA or anterior trifurcation of the carotid artery, and an openness of the circle of Willis due to anomalies of the posterior part of the vascular bed - aplasia of the posterior communicating, basilar artery, posterior trifurcation of the ICA.
If the connecting branches are completely absent, they speak of a complete openness of the circle of Willis, and when the arteries are preserved, but stenotic, hypoplastic, then the openness is considered incomplete.
What pathologies are possible
The circle of Willis has a complex structure and consists of 10-12 arteries. Therefore, some people may have diseases associated with vascular damage. They are divided into two groups: congenital, which arose during intrauterine development of the fetus, and acquired, developing after birth. The most common pathologies are:
- Aneurysm is a local protrusion of the arterial wall outward. A person can go for a long time without any symptoms, which makes timely diagnosis difficult. If blood pressure increases, the aneurysm may rupture. In this case, an intracranial hematoma develops. The patient complains of headache, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. He experiences neurological disorders, including severe paralysis or death. Aneurysms can be located on any vessel;
- hypoplasia is characterized by underdevelopment of the artery with a decrease in its diameter and lumen. This leads to insufficient blood flow. If the circle is closed, then the disease is asymptomatic, since blood flows to the brain through other vessels;
- aplasia is complete underdevelopment of the artery. Can be observed in any vessel. Aplasia of the anterior or posterior communicating artery leads to the fact that the circle of Willis becomes open. This is fraught with the development of cerebral ischemia against the background of concomitant pathologies: atherosclerosis, aneurysms, thrombosis, etc.;
- trifurcation of the carotid artery with its splitting into three vessels. The condition is not manifested by any diseases, however, if the patency of the artery is impaired, cerebral ischemia is possible.
What are the dangers of improper development?
Congenital abnormalities can gradually create obstruction of the blood supply or signs of decompensation when excessive stress is placed on the arteries.
The consequences can be completely catastrophic - the development of an aneurysm, hemorrhagic or ischemic strokes.
Even young people can experience periodic migraine attacks.
In the older age category, aneurysms caused by acquired pathologies (atherosclerosis, vasculitis infections, syphilis) more often occur.
An aneurysm is a protrusion on the wall of an artery; the development of pathology occurs without visible symptoms. Most often localized inside the circle of Willis (in the ACA or PCA, at the bifurcation of the ICA and BA) against the background of the asymmetric structure of the arterial ring.
When an aneurysm forms, there is a danger of rupture of the vessel and, as a result, hemorrhage in the brain.
Clinical syndromes caused by arterial ring aneurysms:
- pseudotumor - nerve tissue and brain matter are compressed;
- hemorrhagic extracerebral basal - after rupture of a vessel with subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- discirculatory - with slow growth or with the development of a dissecting form of aneurysm.
Anomalies in branching options and deformation of the shape (broken circle) weaken or lead to loss of compensation in complex cases (hypertensive crisis, thrombophlebitis, spasm, etc.).
Is an open circle of Willis good or bad?
The structure of the arterial circle has many variations. Normally, it is closed, which helps protect nervous tissue from ischemia and damage.
In some people, the circle of Willis is not closed on the side of the anterior or posterior communicating artery. This condition is not always regarded by doctors as a pathology.
An open arterial circle is bad. In the absence of all anastomoses, a person has an increased risk of developing ischemia of nervous tissue against the background of atherosclerosis, thrombosis and arterial embolism.
However, the condition itself does not require treatment, since pathologies arise only against the background of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Symptoms of disease
The open circle of Willis, unlike other arteries of the brain, is not balanced by the pressure of the brain tissue.
This may cause the following symptoms:
- often feel dizzy;
- when the body turns sharply, unpleasant sensations arise;
- severe headache that does not respond to painkillers;
- migraine attacks accompanied by nausea, sometimes vomiting, photos and phonophobia.
The symptoms of aneurysms of an open arterial ring depend on the location, size and nature of the pathology, which in most cases affects the nervous system.
When the surrounding nerve tissue is compressed by an aneurysm, the clinical picture consists of the following signs:
- seeing double;
- pupils dilated;
- pain in the inner orbit of the eyeballs;
- headache.
With aneurysms of the ACA (anterior communicating artery), visual and olfactory impairment is added.
If the arterial circle is not closed, then spontaneous sensations appear when the aneurysm ruptures:
- heaviness in the head;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- stiffness in the cervical spine;
- temporary loss of vision or unconsciousness.
Anomalies of the patent arterial circle increase the risk of ischemic stroke, which is accompanied by sudden manifestations:
- weakness or numbness of the muscles on one side of the body;
- confusion;
- speech and vision impairment;
- unsteady gait;
- dizziness;
- lack of coordination of movements;
- cephalgia.
Clinical manifestations
Violations of the structure of the circle and its openness lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. Depending on where ischemia develops, a person may develop different symptoms. The first symptoms are often:
- dizziness that occurs during severe physical or emotional stress;
- severe headache that does not disappear when taking painkillers;
- migraine attacks with nausea, vomiting, and fear of loud sounds and lights.
As anemia progresses, neurological disorders occur. The patient may complain of impaired sensitivity on the skin, decreased muscle strength or complete absence of movements in the arm or leg, frequent dizziness, etc. Cognitive functions are also impaired: the ability to remember information decreases, the patient takes a long time to make decisions, forgets the way home, etc. With ischemia frontal cortex, speech is impaired. The patient cannot speak clearly or does not perceive the speech of other people.
Methods of treating pathologies
Treatment of anomalies in the development of the circle of Willis is not required. The vast majority of people have no idea they exist.
It is necessary to treat the diseases to which they can lead. Pathologies of the arterial circle belong to the field of neurology. Therefore, a course of therapy with drugs to normalize blood circulation is prescribed by a neurologist.
The therapeutic course for pathologies of the circle of Willis includes:
- Ingestion or intravenous injections of drugs to improve blood circulation (Cavinton, Pentoxifylline).
- Prescribing nootropics to improve brain metabolism (Phesam, Vinpotropil, Nootropil).
- A course of antioxidants (Mexidol, Cytoflavin).
- A course of metabolic drugs (Actovegin).
- Vitamin therapy, B vitamins are especially useful.
Author of the article: Yulia Dmitrieva (Sych) - In 2014, she graduated with honors from Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky. Currently working as a cardiologist at the 8th City Clinical Hospital in the 1st clinic.
Diagnostic measures
Detection of an open arterial circle requires instrumental studies: angiography, Dopplerography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
These methods allow you to visually assess the condition of the arterial vessels and identify their pathological changes. Only the attending physician should interpret the examination results.
Angiography
“Gold standard” for examination of cerebral vessels. Angiography allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels, detect aneurysms, narrowings and complete blockage of the lumen. The principle of the method is similar to radiographic studies. Radiocontrast agents are used only to identify blood vessels on images.
They are inserted through a small catheter into the artery. Contrast agents circulate along with the blood and are clearly visible on the resulting images. They are excreted from the body in the urine, without having a negative effect on internal organs. Modern angiography allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the arteries of the circle of Willis.
Dopplerography
The method is carried out simultaneously with ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels. Dopplerography allows you to evaluate the structure of the vessels of the circle of Willis and identify their anomalies. In this case, the doctor can examine the speed of blood flow.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a vascular surgery specialist. It is possible to involve a neurologist.
The measures are mostly standard; it is necessary to carefully evaluate the anatomical structure of the circle of Willis.
- Angiography. Essentially an x-ray with contrast. A special drug is introduced, which, accumulating in the blood, enhances the pattern. Then doctors take a series of photographs and, based on the results, evaluate the nature of the structure of the ring-shaped structure. It is considered an accessible and relatively simple diagnostic method with a minimum of contraindications.
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels. Required to assess the speed and quality of blood flow in cerebral structures, used as part of a functional examination. Prescribed in all cases.
- MRI. To identify complex forms of anomaly. This is perhaps the most informative technique among others. Maximum safe, does not create a load on the body, and is not accompanied by pain. But the research costs on average more than its analogues. That’s why they resort to this method when others have failed.
- It is possible to prescribe invasive, selective angiography.
Activities can be adjusted during the examination and supplemented with other techniques. The issue is resolved at the discretion of the specialist.
Treatment approaches
If the arterial circle is not closed, special treatment is not required. Without accompanying changes in the blood vessels, people do not experience any symptoms of disease. Therapy should be aimed at preventing arterial pathologies and eliminating them.
For this, patients are prescribed a number of medications, and are also advised to adhere to a diet and change their lifestyle.
Non-drug approaches
All patients should adhere to medical recommendations regarding lifestyle:
- exercise regularly. To prevent vascular diseases, aerobic exercise is recommended: walking, jogging, cycling and swimming. Classes should be ongoing and suitable for the person’s level of physical fitness;
- eliminate bad habits: smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Avoid fatty, salty, fried and spicy foods in your diet. They contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension. Both conditions are often complicated by thrombosis, aneurysms and their rupture;
- It is recommended to eat more vegetables, fruits, berries, nuts and lean meats. They are rich in beneficial amino acids, vitamins, microelements and biologically active substances that have a positive effect on the condition of the cardiovascular system;
- Limiting salt intake to 5 g per day. If the patient has severe arterial hypertension, then the volume of consumption is reduced to 1 g;
- avoid stressful situations at work and in your personal life.
These recommendations reduce the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases by preventing pathological changes in the arterial circle of the brain.
Medicines
Medications are recommended for people with vascular pathology of the circle of Willis and accompanying changes in the arteries. Medicines of the following pharmacological groups can be used:
- drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Cerebrolysin, Cavinton, etc.). They normalize vascular tone and increase the intensity of blood flow in the arteries of the brain. This avoids ischemia and neurological disorders;
- nootropics – Phenotropil, Glycine, Nootropil, etc. They enhance metabolic processes in neurons and reduce their sensitivity to damaging factors. Requires long-term use over several months to obtain a therapeutic effect;
- antioxidants (Dihydroquercetin, Mexidol) protect nerve cells from damage, including toxic substances. The effect is achieved by blocking free forms of oxygen, which negatively affect the structures of neurons;
- antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine and their analogues) are prescribed for spastic changes in blood vessels. Allows you to dilate arteries and restore normal blood supply to the brain. They have only a symptomatic effect and do not affect the underlying disease;
- B vitamins, which stimulate the restoration of nerve tissue and neuron membranes. Used in courses in the form of intramuscular injections;
- To eliminate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nise, etc.) are prescribed. They are highly effective for any form of headache, except migraine.
All medications are prescribed only by a doctor. Medicines have contraindications, failure to comply with which may cause progression of the underlying disease or lead to the development of side effects.
Surgical treatment
In case of multiple blood flow disorders, the patient is prescribed surgical interventions. They may be associated with the creation of a shunt or mechanical expansion of the lumen of the arteries. A shunt is a bypass for blood flow, which is placed around a narrowed area, an area of hypo- or aplasia. Mechanical expansion of the vessel is carried out using a stent or ballooning.
Signs and diagnosis of anomalies of the circle of Willis
Clinical signs of abnormalities in the branching of vessels in the circle of Willis occur when blood flow through collaterals becomes insufficient for various reasons. For example, fatty plaques have formed in the arteries, a blood clot has appeared or an embolus has migrated from the left side of the heart, or an aneurysm has ruptured. A healthy person does not feel non-classical branching of blood vessels, since his brain does not experience the need for bypass blood flow paths.
development of stroke/disorders associated with insufficient blood supply to the brain area
Symptoms of obstructed blood flow can vary widely. If we are not talking about a stroke, then patients complain of dizziness, headaches, decreased intellectual abilities, memory, and attention. Psychological problems are also common - often abnormal branching of blood vessels is accompanied by neuroses, panic attacks, and emotional lability of its owners.
Migraine is considered a characteristic manifestation of the non-classical development of the circle of Willis. Many observations have been devoted to the issue of the relationship between the structure of the cerebral arteries and migraine, which indicate that the majority of patients with migraine have certain anomalies. Especially often with migraine, deviations in the structure of the posterior part of the arterial system are diagnosed. When the circle of Willis is open, hypoplasia or aplasia of the posterior communicating arteries, the posterior trifurcation, those parts of the brain that are responsible for vision do not receive enough blood, therefore an intense headache is preceded by a visual aura in the form of flashes, zigzags, etc.
A decrease in blood flow through the vessels of the arterial ring of the brain can provoke periodic headaches and disorders similar to dyscirculatory encephalopathy - apathy or irritability, decreased performance, fatigue, etc. Typically, such a conclusion can be found in the results of MR angiography and it indicates hypoplasia of those or other vessels.
In case of aplasia of the arterial trunks, when some vessels are absent at all, the absence of blood flow is recorded during the study. For example, aplasia of the posterior communicating arteries will be accompanied by a lack of blood flow through them, respectively. Such aplasia can also be asymptomatic, but only when a sufficient amount of blood passes through the main arteries. With atherosclerosis or spasm of the arteries, signs of insufficient blood supply to the brain will not be long in coming.
% distribution of aneurysm cases among cerebral arteries
If, against the background of an abnormal structure of the arteries at the base of the brain, an acute circulatory disorder occurs, then the clinic will have obvious symptoms of a stroke - paresis and paralysis, speech disorders, pathological reflexes, impaired consciousness up to coma.
Separately, it is worth mentioning aneurysms - dilations of blood vessels in the brain. According to statistics, it is in the arteries of the Circle of Willis that the greatest number of them are found. An aneurysm of the arteries in this area is fraught with rupture and massive subarachnoid hemorrhage with clinical stroke, coma and severe neurological manifestations.
Aneurysm is an independent pathology, and not a variant of individual branching of vessels, but it much more often accompanies non-classical types of the circle of Willis.
The diagnosis of a particular anomaly in the development of the circle of Willis can only be established with the use of modern instrumental examination methods. Opportunities in diagnostics have given specialists a chance to analyze the nature of the prevalence of variants in the structure of brain vessels and their varieties, but until relatively recently, conclusions could be drawn mainly from the results of autopsies of deceased patients.
The development of ultrasound Dopplerography and magnetic resonance imaging techniques has made it possible to make the study of the nature of the structure of the Circle of Willis a publicly accessible and safe event. The main methods for diagnosing variants of the vascular system of the brain include:
- X-ray contrast angiography is one of the most informative methods, but has contraindications associated with the need for contrast (liver, kidney pathology, allergies to contrast, etc.);
- Transcranial Doppler ultrasound - the procedure is safe, affordable, and requires devices with a Doppler sensor, which are available in many medical institutions;
- MR angiography - performed on a magnetic tomograph, has contraindications, a significant drawback is its high cost.
Circle of Willis on a diagnostic image
Selective angiography of the cerebral vessels is an invasive procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and advanced to the area of interest in the cerebral arteries. When the desired area is reached, a contrast agent is applied. The method is most often used during surgical treatment (stenting, angioplasty).
, CT angiography can be used when a contrast agent is injected intravenously, and then pictures of the head are taken in different projections and sections. Subsequently, a three-dimensional image of the vascular structures of the brain can be recreated.
Transcranial Dopplerography makes it possible to determine the nature of blood flow in the vessels of the brain (reduced, absent), but it does not provide enough data regarding the anatomical structure of the arteries. Its important advantage is considered to be the almost complete absence of contraindications and low cost.
MR angiography is one of the most expensive, but at the same time quite informative methods for diagnosing the structure of the circle of Willis. It is performed in a magnetic tomograph and the contraindications for it are the same as for conventional MRI (high degree of obesity, claustrophobia, the presence in the body of metal implants that conduct a magnetic field).
The MRI picture shows the structure of the vessels of the circle of Willis, the presence or absence of connections between them, aplasia or hypoplasia of the arteries. When assessing the result, a specialist can determine the diameter of each artery and the characteristics of its branching.
Video: example of MR angiography of the brain
(The circle of Willis is closed; a convoluted S-shaped course of the intracranial section of the left vertebral artery is determined; a C-shaped course of the basilar artery; otherwise, in the segments of the ICA and paired arteries of the ring of the base of the brain, no data were obtained for the presence of hemodynamically significant stenoses or pathological tortuosities).
As you can see, each method has both advantages and disadvantages, so they are combined to obtain accurate conclusions regarding the arteries of the brain. An integrated approach makes it possible to determine the anatomy of the vessels and the nature and direction of blood flow through them, which is very important in assessing the degree of risk of vascular accidents and possible prognosis.
Many people who have discovered any variant of the structure of the Circle of Willis are immediately interested in treatment methods. Since deviations in the branching of blood vessels are not considered an independent disease, treatment as such is not required. Moreover, in the absence of a clinic for blood flow insufficiency, it does not make sense.
In cases where there are specific complaints (migraines, decreased mental capacity, etc.), you need to seek help from a neurologist who will prescribe vascular drugs (nootropil, fezam, actovegin), drugs to improve metabolism in the brain (mildronate, vitamins B), if necessary - sedatives, tranquilizers, antidepressants, in case of migraine - analgesics, anti-inflammatory, specific anti-migraine drugs (ketorol, ibuprofen, paracetamol, askofen, triptans).
Surgical treatment is indicated for severe circulatory disorders with progression of vascular encephalopathy, diagnosed aneurysm, and sometimes after a stroke. It consists of stenting, clipping or exclusion of the aneurysm from the bloodstream, and balloon angioplasty for narrowing of the arteries.
Diagnosis of pathologies
Angiography of elements of the circulatory system of the brain is a priority method for detecting pathologies. Other instrumental methods:
- Doppler ultrasound.
- Interventional angiography of selective type.
- CT angiography, MR angiography.
The conclusion after an MRI study of the circulatory system in the area of the brain and the circle of Willis confirms or refutes the presence of non-classical development options. Instrumental examination makes it possible to determine the degree of patency and features of the morphological structure of blood vessels.
Signs of abnormal structure
Detection of signs of an open circle of Willis and other pathologies of the circulatory system of the brain at an early stage allows for timely treatment of disorders. Symptoms of vertebrobasilar insufficiency in patients with anomalies in the development of the circulatory system appear at the slightest disturbance of blood flow in the vertebral artery. Signs of chronic ischemic processes in the brain provoked by circulatory disorders:
- Pain in the head area.
- Dizziness, transient confusion.
- Noise, buzzing in the ears.
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities - memory, mental activity.
- Violation of sleep and wakefulness (insomnia at night, drowsiness during the day).
If a lack of blood flow is observed in the carotid system, the patient may additionally experience symptoms such as numbness, weakness in the limbs, and speech dysfunction. If blood flow deteriorates in the vertebral arteries, symptoms appear: ataxia, impaired motor coordination, difficulty maintaining the body in balance. If such symptoms are present, it is recommended to undergo an instrumental examination to identify the causes of the disorders.