Many of us, at least once in our lives, have been involved in a situation where it was necessary to provide assistance to a person who has fainted, and some have even found themselves in the role of a victim. The most common symptoms that precede the onset of fainting are most often darkening of the eyes, which may be accompanied by tinnitus, general weakness, nausea and dizziness.
Darkening in the eyes occurs quite often in people and can be not only simply a consequence of a person’s overwork, but also a harbinger of serious health-related complications.
Causes
Darkening of the eyes can be a consequence of two main fundamental reasons, the first of which is the lack of oxygen and various nutrients that should have reached the brain. The second may be pathology or disorders of the visual system.
Darkening of the eyes is often the first symptom, followed by dizziness or fainting.
More often than not, most fainting and darkening of the eyes that are common in everyday life are low-risk and do not indicate vital health problems or damage. But sometimes such phenomena indicate the development of quite serious processes in the human body and require urgent contact with doctors, where, after a thorough examination and possible confirmation of negative changes in the body, a serious course of treatment can be prescribed. However, it is worth emphasizing that the treatment will not be the consequence, which is darkening in the eyes, but the root causes that caused this failure.
Content:
- Causes
- Safe causes of darkening of the eyes
- Darkening of the eyes from disease
- Characteristics of diseases
- Local visual problems
- First aid
- Diagnosing the problem
- Preventing dark eyes
Treatment
Sometimes, in order to get rid of attacks, it is enough to simply change your eating habits, as well as follow a routine and devote a sufficient amount of time to sleep. Although in some cases dizziness is caused by dangerous conditions that require serious treatment.
Drugs that can be prescribed to the patient:
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. They are prescribed to treat otitis media, as well as infections that affect the brain.
- Antidepressants, sedatives and drugs that normalize blood flow. This treatment is indicated for patients with VSD, with surges in blood pressure, as well as for people who have suffered severe stress or are suffering from depression.
- B vitamins, calcium antagonists and drugs that improve brain nutrition. Such drugs are indicated for use by patients with hypoxia and people engaged in heavy mental work.
- Massage, physiotherapy, as well as taking medications that normalize vascular tone are indicated for patients suffering from osteochondrosis or other diseases of the cervical spine.
- Hormones should be taken by patients with disorders of the endocrine system.
- Iron supplements are prescribed to patients with anemia.
The dosage of medications, as well as the duration of the course of treatment, is determined by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease.
Safe causes of darkening of the eyes
Overwork and excessive stress, which accompany the lives of most students, athletes, and some workers overloaded with responsibilities, can often lead to darkening of the eyes. With all this, there is also tinnitus, a general deterioration in hearing, loss of orientation in space, but, as a rule, there is no pain. Even with such symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor and conduct examinations for a qualified conclusion to find the cause and source of the problems, as well as draw up a plan for getting rid of the negative consequences and not repeating this in the future. Based on this, relatively negative reasons include overwork and its subtypes, as well as a reduced level of hemoglobin.
Quite often, darkening of the eyes and malaise occurs due to a drop in blood glucose levels in the case of diet, from overwork and exhausting physical activity, or in the case of strong emotions that a person experiences.
After confirmation of precisely such reasons, a person will need significant time for rest, good nutrition and a transition to a healthy lifestyle. You will also have to give up stress for a while.
Dizziness: the most common causes and forms
According to modern research, most often this disease is a symptom of diseases such as:
- BPPV (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo);
- basilar migraine;
- psychogenic dizziness;
- Meniere's disease;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- vestibular neuritis;
- brain tumors.
Note that BPPV accounts for more than 80% of cases of true dizziness. Below we will consider the main diseases that are accompanied by dizziness, and also describe the characteristics of dizziness in each case.
1. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is one of the most common forms of true vertigo. The name itself is deciphered as follows: “benign” means a favorable, harmless course of the disease, “paroxysmal” means the sudden onset of dizziness; “positional” - the appearance of dizziness when turning the head in a certain direction.
The reason for the development of BPPV is irritation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus by otolith stones, which are located in the semicircular canals of the inner ear. This disease can also occur spontaneously in a person of any age, but in most cases it appears in people over 50-60 years old, after an injury or infection.
The main symptoms of benign positional vertigo are:
- the occurrence of severe dizziness when tilting or turning the head, when turning in bed, when throwing the head back;
- severe dizziness lasts from several seconds to several minutes, and it may be accompanied by weakness, severe nausea or vomiting;
- attacks of dizziness can appear in series, after which they disappear without a trace for some time.
Treatment of BPPV is carried out with a special exercise, and always under the supervision of a neurologist. Its duration is only 1-2 minutes, and its effectiveness reaches 90%.
2. Dizziness with migraine. Migraine is one of the most common types of headaches. In some cases, during a migraine attack, blood circulation is disrupted in the areas of the brain that control the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, which causes severe dizziness, after which a severe headache in the back of the head may immediately develop, imbalance may occur, vomiting, noise and light intolerance may occur. . Some people with migraines may only have severe dizziness and nausea, but no headache. In children, one of the precursors of migraines in adulthood are attacks of severe dizziness, imbalance, nausea, vomiting, which over time turn into typical migraine attacks.
3. Psychogenic dizziness ranks second in prevalence after BPPV. But unlike it, psychogenic dizziness is not true dizziness, since it is not associated with disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
The main characteristics of this disease:
- description of dizziness as a feeling of fog in the head, confusion, fear of falling and losing consciousness, but not as one’s own spinning or other objects;
- attacks of dizziness occur spontaneously, often under stress, in a confined space (transport, elevator), as well as in crowded places;
- in addition to dizziness, patients have other complaints that resemble some diseases of the internal organs: a lump in the throat, soreness, pain in the chest, abdomen or in the heart area, pain and tension in the muscles, a feeling of lack of air, a feeling of tension and internal fear, anxiety, irritability, anxious sleep, strong and unreasonable concern about one’s own health, as well as the health of loved ones, etc.
Psychogenic dizziness can also be considered one of the most common manifestations of VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia). Particularly often, attacks of false dizziness can be observed in patients with anxiety disorders and panic attacks.
Determining the psychogenic nature of dizziness plays a big role in determining the correct treatment, so if you have an idea that dizziness in your case may be psychogenic, we recommend that you study information about vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as its treatment.
In particular, with psychogenic dizziness, treatment that is intended for VSD (sedatives, psychotherapy) will be much more effective than specific drugs for dizziness, prescribed for all cases of true dizziness.
4. Dizziness with Meniere's disease. This disease is characterized by periodic attacks of severe dizziness and deafness (usually in one ear), gradually leading to hearing loss.
At the moment, the exact cause of Meniere's disease is still unknown. But there are suggestions that in some cases it may be caused by injury, viral infections or allergies.
A typical manifestation of Meniere's disease is an acute attack of severe dizziness, which lasts several hours or days and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, hearing loss (in one ear) and a feeling of pressure inside the ear.
Typically, attacks of this disease appear one after another over several weeks, after which they disappear for some time, but then begin again.
5. Dizziness due to osteochondrosis, as well as vertebrobasilar insufficiency, neck and head injuries. As we have already said, the work of the human balance control system involves sensitive receptors of the muscles, bones, joints, ligaments of the whole body and mainly the muscles, bones and ligaments of the neck.
Degenerative diseases of the cervical spine, including osteochondrosis, are one of the most common causes of dizziness, which patients often describe as unsteady gait and rarely as a feeling of spinning.
Osteochondrosis of the spine disrupts the functioning of the sensory receptors in the neck, and can also cause disruption of blood circulation in the vertebral arteries, which supply blood to the parts of the brain responsible for balance and maintaining the body, located in the brain stem.
Chronic circulatory disorder in the lower parts of the brain (vertebrobasilar system) is called vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Atherosclerosis of the neck vessels and long-term hypertension (increased blood pressure) also play a certain role in its development. Most often, vertebrobasilar insufficiency occurs in older people. In addition to dizziness, it is accompanied by symptoms such as memory loss, headaches (mainly in the back of the head) and tinnitus.
Attacks of acute circulatory disorders in the vertebrobasilar region can manifest as severe dizziness, loss of consciousness, vomiting, weakness and double vision.
Injuries to the head and cervical spine (especially after car accidents) can also cause dizziness. In such cases, it is usually more pronounced in the first days after the injury and gradually decreases as the patient rehabilitates.
6. Dizziness with vestibular neuritis. This disease is an inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which carries impulses from the receptors of the inner ear to the brain. When the vestibular nerve becomes inflamed, it temporarily loses its ability to conduct impulses. This, in turn, is manifested by severe dizziness, unsteady gait, nausea and vomiting.
The main cause of vestibular neuritis is viral infections, so attacks of associated dizziness may be accompanied by weakness, fever, cough or runny nose.
7. Dizziness due to brain tumors. Some brain tumors that are located near the inner ear can cause severe and progressive dizziness.
Symptoms of a tumor, in addition to dizziness, may include the following phenomena:
- hearing loss (usually one ear);
- nausea;
- tinnitus, hearing loss;
- headache;
- the appearance of strabismus, paralysis of the facial muscles.
Dizziness as a symptom of a brain tumor is most often observed in young people and children.
Darkening of the eyes from disease
Darkening in the eyes can occur in the morning when a person gets out of bed, with sudden movements of the body and turns of the head and torso, and also occur with strong physical stress on the person’s body. Such cases are often accompanied by headaches, nausea and vomiting. The latter signs are more serious and may be a confirmation of the following diseases:
- hypotension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- all kinds of diseases caused by infections;
- diseases of the nervous system.
Main symptoms
In this regard, we can say with a high degree of probability that if your eyes get dark when you try to stand up, then we are talking about hypotension. This disease, in addition to the above, also has the following symptoms:
- Dizziness;
- Weakness, lethargy;
- A feeling of constant exhaustion, as if at night, instead of sleep, the carriages were unloaded;
- Absent-mindedness;
- Problems concentrating;
- A veil appears before the eyes;
- Shortness of breath even with minimal physical activity;
- Memory impairment.
During hypotensive crises, which are exacerbations of the disease and usually occur in spring and autumn, fainting can also occur.
Characteristics of diseases
The consequence of hypotension is a negative effect on brain cells due to oxygen starvation. With this syndrome, blood pressure drops significantly, because of this the brain does not receive enough oxygen and its cells begin to die, which is precisely manifested by darkening of the eyes, as well as headaches and nausea. Like any other serious health problem, this requires a certain course of treatment and a review of the patient’s lifestyle.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia has similar symptoms. The causes here are extensive and require long-term rehabilitation treatment.
If the problem with darkening of the eyes is caused by an infection in the body, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs, which, along with eliminating the infection, will lead to the disappearance of symptoms associated with vision, headache, weakness and lethargy.
Also, darkening in the eyes is included in the primary list of factors that may indicate diseases such as osteochondrosis, various aneurysms, compression of arteries and nerve endings. In such situations, darkening and pain occur only with certain movements and positions of the body or its parts and will most often be the first symptoms of the emerging disease.
The main types of diseases that lead to darkening of the eyes include diseases of the thyroid gland, malfunctions of the heart valves and disruption of metabolic processes in the body. In the case of such problems, the phenomenon will be only one of a whole complex of symptoms.
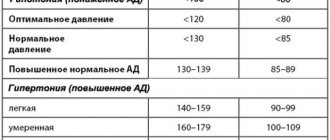
It's about the pressure
However, an ophthalmologist is not the specialist who will help solve this problem. Doctors who hear about such a symptom confidently state that there is a problem with blood pressure. Hypotension, which is the culprit of this condition, is low blood pressure, the levels of which do not exceed 100 per 60 mmHg. Art. However, depending on the gender of the person, these indicators may vary slightly. So, for women, hypotension is diagnosed if the systolic pressure figures fluctuate at around 95 mmHg. Art., and for men - up to 100. At the same time, the characteristics of the body of a particular person are also added here.
Local visual problems
Do not forget that sometimes the cause of darkening in the eyes can be problems that are associated only with the visual analyzer itself. Among them are the following:
- visual field defects;
- violations of the integrity of the optic tract;
- optic nerve diseases.
Darkening is caused by pathological loss of visual fields. A sudden movement in this case, or a sharp turn of the head can cause such a reaction in the eye.
Patients with glaucoma and people with farsightedness and myopia also complain of similar problems after prolonged visual strain.
Problems can arise when the signal from the eyes to the brain is disrupted, which occurs when the optic nerve or optic tract becomes spasmed or paralyzed.
To determine an accurate diagnosis that will reliably show the source of the problem and possible ways to eliminate it, a comprehensive ophthalmological examination will be required, including ophthalmoscopy, refractometry and several other manipulations that the doctor deems necessary in a particular individual case.
What not to do?
If a person does not know the cause of the attack, it is prohibited to take any medications. Otherwise, you may harm your health. You should not make sudden movements, you should not quickly turn your head or tilt it down, as this can lead to a fall. You definitely need to visit a doctor or call a medical team to your home.
Squatting and bending are prohibited. You need to take the most comfortable position possible. You should not start smoking or drinking alcohol after the attack is over.
First aid
Symptoms of darkening of the eyes appear very quickly, so their manifestation can be noticed and the negative consequences of this type of incident can be minimized, including strong falls, bumping into surrounding objects, and loss of balance. If such symptoms occur, the best solution is to sit or lie down, provide fresh air, drink cold, clean water or sweet tea.
If darkening of the eyes is accompanied by fainting, then it is recommended to lay the person on his side, in order to avoid swallowing the tongue when relaxing, it is better not to raise the head, so as not to interfere with the flow of blood to the brain. It is also permissible to use ammonia or splashes of cold water to try to revive the person.
general information
The sense of balance and position in space is formed through the joint work of several systems:
- visual;
- vestibular (perceives position in space);
- proprioceptive (responsible for the perception of the relative position of individual parts of the body and their movements).
Incoming signals are processed by the central nervous system. If there is a malfunction in any of the departments, you may feel dizzy. Often, based on the characteristics of sensations and accompanying symptoms, the doctor can guess the cause of this condition.
Many people consider dizziness to be a state of lightheadedness, lightness in the head, as well as severe imbalances: instability, staggering when walking. By themselves, they do not belong to vertigo, but often the mechanisms and causes of their development coincide.
Diagnosing the problem
If you suspect such a problem, you should immediately consult a therapist and ophthalmologist. If this symptom is not a consequence of overwork, then a series of studies are prescribed.
These examination methods include the following four main types:
- MRI of the brain.
- MRI of the orbits.
- Computerized perimeter visual field testing, which can detect scotomas.
- MRI of the vessels of the neck and head, which diagnoses disorders in the circulatory system.
It is worth remembering that after visiting a doctor with a similar problem, a patient complaining of darkening in the eyes must be prepared for the fact that he will have to clearly answer many questions of interest to the doctor. It is necessary to describe in as much detail as possible what exactly the nature and signs of the symptoms are, how often the most serious of them or maximum darkening occur, whether the person has previously experienced injuries associated with damage to the skull and brain, and whether there have been certain diseases recently. Only after listening to a detailed answer from the patient, the doctor can prescribe the necessary examination with research from one or another specialist, and subsequently save the person from this serious problem.
Diagnosis of hypotension
If, when you try to stand up suddenly, your vision becomes dark, you must undergo a full medical examination. In this case, it is worth contacting a neurologist, who, after observing the blood pressure, will draw conclusions about the condition of the blood vessels and the causes of the disease.
You may also need a visit to a cardiologist, whose examination is necessary for a final conclusion and to receive recommendations for treatment and further lifestyle.
Correct diagnosis of the disease is the key to adequate subsequent treatment. It is after an examination by the above-mentioned specialists that it will become clear whether medical intervention is necessary at all and which drugs should be used. Or, perhaps, the situation will improve by changing the usual rhythm of life, diet, and normal physical activity.
Treatment of hypotension using traditional methods
Medications used for hypotension should only be selected by the attending physician. However, very often drug therapy in such cases is unnecessary and the specialist recommends taking regular pharmacy tinctures of medicinal herbs. Particularly effective in the case of hypotension is taking lemongrass tincture. It is recommended to drink 20-30 drops twice a day, half an hour before meals in the morning and evening.
Ginseng tincture also has an excellent effect. The course of its use is 20 days. The tincture is taken twice a day, 5-20 drops before meals in the morning and in the middle of the day.
Prevention
With many chronic diseases, dizziness becomes common. The frequency, severity and duration of attacks can be reduced not only by taking medications, but also by following preventive measures. Necessary:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- minimize caffeine and table salt;
- sleep on an orthopedic pillow and mattress;
- regularly engage in amateur, recreational sports, visit the pool;
- eat well, consume enough vitamins and microelements;
- normalize the work and rest schedule, ensure continuous night sleep for at least 8 hours;
- avoid excessive physical activity and heavy lifting;
- undergo examinations in a timely manner and follow doctor’s orders.
Symptoms of cloudy lens of the eye
As already mentioned, clouding of the pupil does not occur immediately, and the stage of the disease at which a diagnosis can be made without additional research methods is terminal and requires immediate treatment if a person wants to preserve vision. As a rule, in this situation, the diagnosis of cataract is not subject to doubt and the patient no longer needs additional symptoms, the presence of which can suspect this disease. Below are symptoms, the presence of which may tell a person that his health is beginning to steadily decline towards eye diseases.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Blurry, unclear image. Some patients talk about this “everything is in a fog.” A “veil” or “waterfall” appears before your eyes.
- Excessive sensitivity to light sources appears, but this phenomenon is not accompanied by pain.
- For reading, there is a need for an additional source of lighting, since without it it is not possible to read.
- At night, the patient is visited by sensations of bright flashes in the eyes, glare of light.
- When looking at light sources, halos of blinding, blurry light appear around them.
- Color perception changes, color perception decreases.
- Contrast suffers: transitions become blurry and foggy.
- Temporarily, the patient may experience refractive error towards myopia. Such patients note that they can read without glasses, which were previously necessary for reading. This phenomenon is short-lived and does not actually represent a change in the visual apparatus for the better.
- More often, visual impairments progress and cannot be corrected with glasses or lenses, and if it is possible to select a means of correction, due to the rapid change in visual acuity, it becomes irrelevant.
Finally, the most obvious sign of cataracts is the clouding of the lens itself. The final clouding, visible to the eye, occurs in the last stages of the disease, of which there are only four.
- Initial. At this stage, there is no visible clouding of the natural lens of the eye. Microscopic areas of impaired transparency on the periphery of the lens lead to consequences in the form of minor symptoms, which, however, may be absent altogether. During this period, the patient often encounters a violation of the refractive power of the eye, and this is where the notorious difficulty in selecting or quickly changing means of correcting visual acuity manifests itself.
- Immature. This stage of cataract is manifested by the beginning of clouding of the lens, which can be seen with the naked eye. The patient's vision sharply decreases due to the gradual movement of opacities from the periphery to the center. The altered lens of the eye swells, which leads to an increase in intraocular pressure, which means the addition of glaucoma as a secondary process developing in the pathologically altered eye.
- Mature cataract. The lens is completely restructured, and the clouding of the lens of the eye gives its symptoms. Visual acuity decreases so much that the patient sees “no further than his nose,” not in a figurative, but in a literal sense. Everything that happens beyond the level of the patient’s face is beyond the reach of his vision.
- Overripe, where the lens shrinks/liquefies. The symptoms remain the same, and may even improve somewhat due to the “softening” of the substrate of the disease. However, these improvements are insignificant, and the patient will still be able to see only at the level of his face and light perception.
Types of fainting
In medicine, there are three main types of fainting.
With neurogenic, there is a temporary disorder of cardiovascular reflexes that control the dynamics of blood in the body. This type is varied:
- vasodepressor – consequences of excessively strong emotions, stress, fear, they occur most often;
- orthostatic are caused by a sharp transfer of the body from a lying position to an upright one;
- fainting due to tight collars is explained by too high sensitivity of the carotid sinus;
- loss of consciousness in older men when urinating at night, coughing, defecating - a consequence of a sharp increase in intrathoracic pressure.
If a patient has disturbances in heart rhythm, problems with the conduction of cardiac tissue are observed, and myocardial infarction is diagnosed, then they speak of cardiogenic loss of consciousness.
If, due to sudden fear, panic, or anxiety, a person’s breathing unconsciously quickens and deepens, causing loss of consciousness, such fainting is classified as hyperventilation .
In addition, there are classifications that distinguish:
- maladaptive form - when fainting is caused by adaptation to external conditions (a person overheats, etc.);
- anemic – when the volume of hemoglobin and red blood cells drops sharply, and what remains is not enough to fully supply the brain with oxygen;
- hypoglycemic – when glucose levels in the body drop;
- extreme forms – when the body is exposed to extreme conditions: high mountain air, burns, intoxication with harmful substances, medications.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the rescue with attacks of dizziness. We offer:
- a full range of diagnostic measures to identify the cause of vertigo;
- treatment of diseases of the ENT organs;
- modern drug regimens to improve the functioning of the central and autonomic nervous systems;
- physiotherapeutic procedures if indicated;
- massage and exercise therapy;
- services of an osteopath and chiropractor;
- acupuncture;
- supervision of specialists throughout the course of treatment;
- advice on normalizing your daily routine, nutrition, etc.
We always use an integrated approach in the treatment of pathological conditions. This allows us to achieve high efficiency of therapeutic measures.