The text is for informational purposes only. We strongly urge you not to use diets, resort to any therapeutic menus or fasting without medical supervision. We recommend reading: “Why you can’t go on a diet on your own.”
Nutrition for hypertension is the most important component of antihypertensive treatment aimed at lowering blood pressure. If you do not control your diet, the disease will only progress. The most common causes of death among hypertensive patients are: pathologies of the heart and blood vessels (stroke, myocardial infarction), renal failure, complications of the nervous system.
The goals of diet therapy: correction of metabolic disorders (especially cholesterol), improvement of the functional state of the heart muscle, normalization of the parameters of the blood coagulation system, increasing the elasticity of blood vessels, increasing the synthesis of neuroregulatory hormones (serotonin and dopamine, which prevent mood swings).
Clinical picture
Hypertension is a pathology of the cardiovascular system, characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure. Today, every third person on the planet suffers from the disease (mostly people in the older age group).
Content:
- Clinical picture
- Basic principles of nutrition
- Products that lower blood pressure
- Sample menu
- Bee products against hypertension
- Conclusion
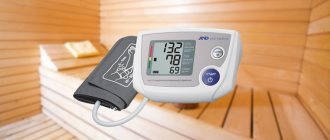
The unit of measurement for blood pressure is considered to be millimeters of mercury. The value of arterial indicators is expressed by two numbers: the larger (systolic) and the smaller (diastolic). Moreover, the first value is recorded during maximum contraction of the heart muscle, and the second - at the moment of complete relaxation of the myocardium.
Normally, systolic pressure varies between 100 - 125 millimeters of mercury, diastolic in the range of 70 - 85. If these indicators exceed 140 (upper) and 90 (lower) units, arterial hypertension occurs.
In the pharmaceutical industry, it is customary to distinguish between 3 degrees of severity of pathology.
Mild (preclinical)
This stage of the disease is characterized by frequent abrupt pressure drops (short-term). At the same time, the systolic indicator varies in the range of 140 - 159 units, and the diastolic in the range of 90 - 99 units.
To correct preclinical hypertension, it is advisable to use folk remedies (since medications are not required).
Moderate (borderline)
The second degree of pathology is accompanied by an increase in upper pressure to 179 millimeters of mercury, and lower pressure to 109 units.
To reduce arterial values, pharmaceuticals (hypotonic drugs) are used. In the absence of proper therapy, a hypertensive crisis is possible, since the indicators remain at the borderline (upper) level for a long time.
Severe (chronic)
At the 3rd stage of the disease, systolic pressure exceeds 180 units, and diastolic pressure exceeds 110. Arterial parameters can only be stabilized with the help of medications.
If the disease is not stopped for a long time, irreversible changes develop in the “target organs” (kidneys, heart, brain, fundus vessels). At the same time, uncontrolled hypertension entails severe complications (strokes, encephalopathy, heart attacks, cognitive disorders, dementia, renal failure, etc.).
Symptoms characteristic of the first two stages of the pathology:
- dizziness;
- tinnitus (fullness);
- headache;
- fatigue;
- irritability;
- puffiness of the face;
- insomnia;
- “double vision”;
- swelling of the eyelids.
At the third stage of pathology, the following disorders occur:
- pain in the heart area;
- nausea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- tachycardia;
- redness of the skin;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- cognitive disorders (decreased memory, attention);
- blurred vision;
- "weakness" in the limbs.
Remember, timely diagnosis of the disease will help avoid serious complications: stroke, heart attack, heart failure.
Fruit juices
Pineapple juice, which contains a lot of potassium, is considered very beneficial for blood vessels and blood circulation. But it is better to be careful with it, since pineapples are contraindicated for people with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. And even if there are no such diseases, gastroendocrinologists recommend diluting it and drinking it in small portions throughout the day, but not more than 1 glass.
Pomegranate juice is used to fight arterial plaques, watermelon juice fights dehydration and improves kidney function, apple juice tones veins and blood vessels, grape juice improves metabolic processes in the body.
Important! Note that drinks have a positive effect over time. That is, to achieve visible improvements, you need to drink tea with hawthorn for at least a couple of months.
There are contraindications. Be sure to consult your doctor.
Basic principles of nutrition
To maintain good health, hypertensive patients should pay special attention to their diet. Remember, the patient’s health depends 80% on compliance with the doctor’s instructions and diet therapy.
Nutrition rules for hypertension:
- Limit your daily salt intake. Considering that NaCl increases fluid retention in the body, consumption of large doses of salt is fraught with swelling of the tissues surrounding the capillaries. At the same time, due to increased pressure on the arteries, blood release from the heart cavities increases (the beginning of the development of hypertension). However, the product cannot be completely excluded from the daily menu of hypertensive patients (due to the possible accumulation of nitrogenous compounds in the blood plasma). The optimal portion of salt is 4–5 grams per day. To improve the taste of food, you can use spices (basil, dill, garlic, parsley, onion), cranberry and lemon juice.
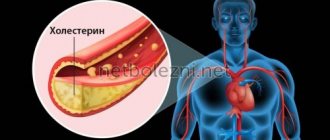
- Sharply limit animal fats (saturated) in the menu. The most common cause of high blood pressure is blockage of blood vessels with “bad” cholesterol. To improve capillary permeability, it is extremely important to avoid foods that worsen lipid metabolism. Namely: offal, sausages, fried or smoked lard, processed cheese, fatty meats.
- Enrich your diet with foods containing potassium and magnesium. Arterial hypertension, in 70% of cases, is accompanied by massive edema, circulatory failure, and cholesterol metabolism disorders. To minimize these problems, potassium and magnesium are included in the patient’s daily diet. These microelements improve myocardial function (including increasing its endurance), accelerate the removal of excess fluid from tissues, have a relaxing effect on the arteries, reducing spasm of smooth muscles, and prevent the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of capillaries.
Natural sources of potassium are dried apricots, bananas, prunes, potatoes (baked), melon, watermelon, raisins, pumpkin, rose hips (fruits), avocado.
Magnesium is present in large quantities in bran, cereals (oatmeal, barley, buckwheat, wheat), leafy greens (parsley, lettuce), vegetables (carrots, beets), nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts).
- Eliminate alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine-containing drinks from your diet. When taking stimulants, most hypertensive patients experience increased heart rate and some parts of the brain are overexcited. Due to the increased load on the cardiovascular system, blood pressure readings “grow” upward.
- Replace simple carbohydrates with complex ones. Saccharides are the main suppliers of energy to the human body. When consuming simple carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery, jam), a sharp increase in blood glucose levels occurs, which leads to the release of large doses of insulin. As a result, its excess is transformed into adipose tissue (since the monosaccharides in the modern human diet are 4 times higher than normal). In addition, excessive intake of monostructures is fraught with the development of metabolic syndrome, which, in 90% of cases, is accompanied by arterial hypertension.
Complex saccharides (as opposed to simple ones) are absorbed more slowly, without causing metabolic disorders and sudden increases in blood glucose. The best sources of high molecular weight carbohydrates are whole grain bread, cereals, berries, herbs, vegetables, and fruits.
- Use gentle cooking methods. The best options for heat treatment of food are baking, stewing, steaming, and boiling. Avoid frying food, as heating fat releases large amounts of carcinogens and “bad” fats.
- Follow a fractional diet. The optimal frequency of meals is 5 – 6 times a day.
- Maintain the ratio of the main components of food. The daily diet of a hypertensive patient should include: 15% proteins (90–100 grams), 30% fats (80–85 grams), 55–60% complex carbohydrates (350–400 grams).
- Maintain drinking regime. Among hypertensive people, there is an opinion that you need to consume less water, since it increases blood pressure. This is a dangerous misconception. In fact, with a lack of fluid in the body, blood viscosity increases, vascular turgor decreases, and the concentration of low-density lipoproteins increases.
The daily portion of water (in addition to drinks) is calculated based on the ratio of 35 - 50 milliliters per kilogram of body weight.
Interestingly, each cup of coffee drunk (volume 150 milliliters) removes 4 equal portions of liquid (600 milliliters) from the body. The body, trying to retain such a valuable resource, creates edema, as a result of which blood pressure rises.
In case of hypertension accompanied by obesity, the energy value of the daily menu is reduced to 1000–1500 kilocalories (by reducing the daily dose of carbohydrates and increasing the daily portion of proteins and healthy fats).
Strict low-calorie diets and fasting with high blood pressure are contraindicated. Overweight hypertensive patients are allowed to have vegetarian fasting days 2 times a week.
What to exclude or limit?
Products that increase blood pressure
Patients with high blood pressure are prohibited or limited:
- eggs - fried or boiled until the yolk is firm;
- partially fish menu - fatty fish varieties (Caspian sprat, herring, mackerel, eel, halibut), caviar, as well as those prepared by smoking and canning;
- first courses - broths cooked from fish and meat, as well as mushrooms;
- vegetable preparations - salted and pickled;
- some vegetables and herbs - onions, spinach, rare, radishes, garlic;
- fatty meat - duck, goose, as well as liver, kidneys, other offal, smoked meats, canned goods;
- grape juice;
- flour - fresh, flaky, rich pastries;
- dairy products - fatty (above 40%) and salty types of cheese;
- animal and cooking fats;
- dishes with legumes and mushrooms.
Products that lower blood pressure
The basis of a hypertensive person’s diet should be products that improve lipid metabolism, reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, increase the strength of blood vessels, accelerate the removal of excess fluid from tissues, eliminate capillary spasms, and improve the functioning of the heart muscle. When drawing up a daily nutrition plan, it is better to give preference to foods that include vitamins B4, , , , , , macroelements (potassium, magnesium, iodine, selenium), and polyunsaturated fats (omega-3).
List of products that lower blood pressure:
- Unsalted seafood (fish, oysters, scallops, seaweed). They contain a large amount of polyunsaturated fats (omega-3, omega-6), amino acids (arginine, tryptophan, lysine, threonine, tyrosine), micro- and macroelements (selenium, iodine, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium). Thanks to its rich ingredient composition, seafood reduces the level of harmful cholesterol, regulates the tone of blood vessels, improves the functioning of the heart muscle, and normalizes blood viscosity.
- Low-fat fermented milk products (whey, cottage cheese, cheese, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk). Supplies easily digestible calcium to the body. This nutrient is extremely important for the cardiovascular system, as it reduces the permeability of the capillary wall, participates in blood clotting mechanisms, and stimulates the regenerative potential of the myocardium.
- Vegetables (jerusalem artichoke, beets, potatoes, zucchini, pumpkin, cabbage, avocado, eggplant). These are natural sources of dietary fiber that have an anti-sclerotic and detoxifying effect on the human body.
- Leafy greens (parsley, celery, basil, cilantro,
- Fruits, berries, dried fruits (lemon, cranberries, rose hips, viburnum, black currants, grapes, apples, oranges, grapefruit, dried apricots, prunes). These products contain natural “strengtheners” of cell membranes (rutin, vitamin C, quercetin), which prevent capillary permeability when pressure increases. In addition, fruits and berries are rich in powerful antioxidants (polyphenols), which prevent the deposition of cholesterol on the arterial wall, and also enhance the production of nitric oxide, which “creates” a vasodilating effect.
- Unrefined vegetable oils (olive, cedar, flaxseed, camelina). These are natural sources of omega-3 fats that reduce the concentration of exogenous deposits in blood vessels, reduce the fragility of the capillary wall, and prevent the development of inflammation in the heart muscle.
- Whole grain products (rye bread, bran, green buckwheat, brown rice, unpolished millet, flattened oats, coarse wheat pasta). An essential food for overweight hypertensive patients, as it contains “slow” carbohydrates that prevent the rapid transformation of glucose into fat.
Along with this, cereals are a source of dietary fiber and protein structures that accelerate the elimination of cholesterol metabolism products and stimulate intestinal motility. With regular consumption of whole grain foods, the rheological parameters of the blood improve, the load on the kidneys and liver decreases, and the permeability of the capillary bed increases.
- Legumes (lentils, soybeans, beans). Champions among plants in terms of easily digestible protein content. With regular consumption of legume products, the distensibility of the arterial wall increases, the risk of developing myocardial hypertrophy decreases, and the concentration of low-density lipoproteins decreases.
- Herbal teas. A rise in blood pressure, in 70% of cases, is accompanied by neurological disorders (insomnia, palpitations, headaches, anxiety). To reduce psycho-emotional excitability in the diet of a hypertensive patient, it is important to include decoctions of sedative herbs: valerian, lemon balm, mint, chamomile, motherwort, hops, hawthorn, calendula, peony, oregano.
Remember, for moderate to severe hypertension, along with healthy food, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions and take medications regularly.
Spices and seasonings
Ginger has blood pressure-normalizing properties. Although formally it cannot be attributed to this group. This is a full-fledged independent product.
- The substances based on it thin the blood, acting as a natural antiplatelet agent.
- In addition, they help relax the vascular muscles, preventing further spasm and an increase in tonometer readings.
Turmeric is called a good help in prevention and even therapy. The substance of the same name in its composition helps to quickly reduce blood pressure, but gently, and therefore does not create health risks.
Hot cayenne pepper. He's chili. The product is used to rapidly reduce blood pressure. This is a reflex response to the use of capsaicin, which the product is so rich in.
But this can be dangerous, since a sharp jump in blood pressure does not affect the condition of the blood vessels (their elasticity). Pepper is allowed for hypertensive patients, but it should be eaten with caution.
Sample menu
This menu can be prescribed by a doctor and adjusted at his discretion for a more effective fight against hypertension.
Monday
Breakfast: 200 g of steamed oatmeal, 100 g of assorted dried fruits (figs, dates, dried apricots, prunes).
Lunch: 150 g of fruit mousse (banana, apple, persimmon).
Lunch: 150 g whole grain pasta, 80 g goulash, 70 g broccoli salad.
Afternoon snack: 200 g of berry-curd dessert (fresh).
Dinner: 200 g fish meatballs, 30 ml sour cream,
2 hours before bedtime: 250 ml of 1% kefir.
Tuesday
Breakfast: 200 g of rice and fruit porridge (raisins, banana, dates), 70 g of rye bread (dried), 20 ml of honey.
Lunch: 150 g of berry-nut mixture (grapes, cranberries, blackberries, almonds, hazelnuts).
Lunch: 200 ml fish soup, 150 g beetroot-prune salad, 10 g garlic.
Afternoon snack: 150 g potatoes (baked or boiled), 100 g tomatoes, 20 ml camelina oil.
Dinner: 200 g buckwheat, 100 g sauerkraut, 70 g boiled turkey.
2 hours before bedtime: 250 ml of green cocktail (kefir, herbs, honey, banana).
Wednesday
Breakfast: 200 ml of chicory drink, 100 g of cranberry jam (ground with sugar), 70 g of whole grain bread (dried), 50 g of walnuts.
Lunch: 200 g curd soufflé, 50 g raisins.
Lunch: 250 g lentil soup, 100 g chopped vegetables, 15 ml flax seed oil.
Afternoon snack: 150 ml yogurt, 100 g fresh fruit (strawberries, banana, apples).
Dinner: 200 g chicken breast with vegetables (stewed), 100 g beet-garlic salad, 40 g celery leaves.
2 hours before bedtime: 200 ml of homemade serum.
Thursday
Breakfast: 150 g apple pudding with raisins, 150 ml rosehip broth, 30 ml flower honey.
Lunch: 150 g berry compote, 100 g cottage cheese casserole.
Lunch: 200 g borscht with beans, 100 g rice meatballs, 50 g vegetable mixture (tomato, cucumber, celery).
Afternoon snack: 150 g seaweed salad, 20 ml cedar oil
Dinner: 150 g mashed potatoes, 100 g zucchini-eggplant caviar, 70 g chicken cutlets (steamed).
2 hours before bedtime: 150 ml of yogurt.
Friday
Breakfast: 150 g egg omelet, 100 g sauerkraut, 70 g bacon.
Lunch: 200 ml hibiscus tea, 100 g oatmeal cookies.
Lunch: 200 g pilaf, 100 g beetroot-garlic salad, 20 ml flax seed oil.
Afternoon snack: 200 g of fruit and berry jelly.
Dinner: 250 g vegetable stew, 50 g boiled veal.
2 hours before bedtime: 250 ml of yogurt.
Saturday
Breakfast: 200 g of oatmeal, 100 g of fermented baked milk, 70 g of dried fruits (unabi, dates, raisins, prunes), 50 g of biscuits.
Lunch: 200 ml cinnamon milkshake.
Lunch: 200 g squash-eggplant caviar, 100 g bean puree, 50 g leafy greens.
Afternoon snack: 200 ml yogurt, 50 g walnuts.
Dinner: 250 g of green buckwheat, 150 g of boiled vegetables (eggplant, beets, zucchini, carrots), 70 g of chicken steak (baked).
2 hours before bedtime: 200 ml of serum.
Sunday
Breakfast: 200 ml cocoa, 70 g bran bread, 50 g cheese, 30 g butter.
Lunch: 200 g seasonal berries, 50 g almonds.
Lunch: 150 g jacket potatoes, 100 g cauliflower in batter, 100 g baked turkey, 15 ml camelina oil.
Afternoon snack: 200 ml mint tea, 150 g oatmeal-curd casserole.
Dinner: 150 g fish steak (stewed), 100 g vegetable mixture (tomatoes, celery, peppers, cucumbers, garlic).
2 hours before bedtime: 200 ml of kefir.
Drinks to lower blood pressure
For hypertension, it is recommended to increase the consumption of drinking water and healthy drinks:
- fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt,
- fresh fruit and vegetable juices prepared at home without heat treatment,
- hot cocoa,
- hibiscus tea drink,
- valerian decoction,
- coconut water.
Many people know about the benefits of fermented milk drinks and fresh juices, but cocoa is unfairly considered a harmful product. In fact, cocoa prevents the formation of blood clots and this drink is recommended for people suffering from hypertension.
Coconut water is one of the natural diuretics and perfectly removes sodium salts.
Bee products against hypertension
To increase the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy, in conjunction with traditional methods of treatment, bee waste products (apiproducts) are used.
Beneficial features
Propolis (“black wax”)
It has antiseptic, regenerating, antioxidant, hypocholesterolemic, diuretic (light) and anticoagulant (blood thinning) effects on the body. With regular use of propolis, lipid metabolism improves, myocardial endurance increases, vascular wall rigidity decreases, platelet aggregation decreases, and pain in the heart region decreases.
For people suffering from the first stage of hypertension, it is advisable to use pure propolis (under the tongue) or a phytocomposition with lingonberry juice (20 drops of 30% “black wax” tincture per 50 milliliters of nectar). For moderate and severe hypertension, the product is taken in the form of an aqueous solution as an addition to the main treatment (35 drops of 30% alcohol extract per 200 milliliters of liquid).
In addition, propolis-based ointment has an excellent hypotensive effect. To create a healing mixture you will need: 5 grams of “black wax” (crushed), 15 milliliters of honey, 15 grams of butter. These ingredients are mixed and then heated to 40 degrees in a “water bath”. The cooled mixture is applied to the feet, after which cotton socks are put on.
Royal jelly
A powerful metabolic agent containing high concentrations of potassium and magnesium. Royal jelly improves myocardial nutrition, stabilizes heart rate, reduces psycho-emotional excitability, eliminates vascular spasm, strengthens capillary walls, stimulates hemoglobin synthesis, and removes excess fluid from the body.
At the first stage of the disease, bee milk is used mainly fresh (20 - 30 milligrams under the tongue). Before using the product, the oral cavity is thoroughly cleansed with vegetable oil.
At higher blood pressure levels (grade 2 and 3), royal jelly is used in combination with antihypertensive herbs (valerian, mint, horsetail, cucumber, motherwort, hop cones, sweet clover). To prepare the composition, the dry ingredients are mixed in equal volumes. After this, 30 grams of the mixture is poured with 500 milliliters of hot water. Herbal tea is consumed three times a day, 100 milliliters (40 minutes before meals). After taking the decoction, dissolve 3 milliliters of a mixture of honey and royal jelly (proportion 1:100).
Wax moth extract
Bee parasite larvae (moths) contain a unique digestive enzyme (cerase) that dissolves low-density lipoproteins. As a result, the concentration of endogenous deposits on the walls of the arteries decreases, the vascular lumen increases, and blood lipid parameters are normalized.
Bee venom
An effective remedy for “hypertension”, used in the form of “bee stings”. Under their influence, arterial spasms are eliminated, the frequency of nerve impulses is normalized, the work of the heart muscle is stabilized, and the peripheral vessels of the kidneys are relaxed.
Bee venom is an excellent remedy for relieving hypertensive crises (in the first stages of the disease).
Remember, this method of reducing pressure can only be used under the supervision of a doctor (to avoid an allergic reaction). To increase the effectiveness of therapy, the “healing” poison is combined with other apiproducts: propolis, honey, beebread, royal jelly.
Perga (pollen)
Includes a huge amount of nutrients (vitamins, salts, organic acids, proteins, fats, enzymes) necessary for hypertensive patients to replenish wasted resources (especially after diuretic therapy). In addition, beebread normalizes the tone of the vascular bed, strengthens the capillary wall, promotes blood thinning, inhibits the oxidation of “good” lipoproteins, and reduces the permeability of veins and arteries (due to the high content of rutin).
To prevent hypertensive crises, take 5–15 grams of bee pollen per day (start with 1 gram).
Honey
A natural source of easily digestible carbohydrates (glucose, fructose, oligoses), enzymes (amylases, lipases, proteases, invertases), amino acids (lysine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, arginine, tyrosine), micro- and macroelements (potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur, calcium ), vitamins (, , B6).
Honey, thanks to its rich ingredient composition, strengthens the heart muscle, “calms” the nervous system, increases the elasticity of the vascular wall, improves cholesterol metabolism, eliminates anxiety, stabilizes heart rate, and relieves headaches. This product is used to treat the “mild” stage of hypertension.
For preventive purposes, to strengthen the heart muscle, it is advisable to use a honey-rosehip mixture. To do this, 15 grams of crushed berries are poured with 400 milliliters of hot water (80 degrees) and left in a thermos for 7 - 8 hours. Then the resulting extract is filtered and combined with 15 milliliters of flower honey. The composition is taken 100 milliliters three times a day. Interestingly, chestnut and buckwheat honey have the most pronounced hypotensive effect.
In addition, apiproducts are used for the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease, myocardial dystrophy, vascular atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, non-rheumatic myocarditis,
Vegetables
Several names can be included here.
- Beet. Like the previous group, it contains a lot of ascorbic acid, which acts as an antioxidant. Prevents changes in the vascular wall and its destruction and degeneration.
In addition, this healthy vegetable contains potassium. An important element for maintaining electrolytic balance and regulating vascular tone.
There is no need to abuse it, since the vegetable has a pronounced laxative effect and provokes intestinal disorders if used excessively.
- Garlic. Contains allicin, an important ester compound. It is this that gives the vegetable its sharp taste and creates a burning sensation. Promotes reflex relaxation of the walls of blood vessels (thereby lowering pressure), then, when absorbed, helps consolidate the result.
In addition, the product has a diuretic effect, although not strong. Eliminates excess water from the body. At the same time, with excess consumption it provokes the opposite effect. 1-2 cloves per day is enough.
- This also includes spinach. It contains many vitamins, as well as magnesium and potassium. Important electrolytes that help equalize blood pressure and restore vascular elasticity.
Kalina
Viburnum is considered the most powerful natural remedy that can fight hypertension and more. The composition of the red berry is simply unique; each berry contains:
- multivitamins,
- essential oils,
- antioxidants,
- flavonoids,
- saturated fatty acids.
A small bunch of viburnum can quickly lower blood pressure, relieve inflammation, normalize the functioning of the head and vascular system, and improve immunity.
It should be collected after the first frost and can be stored frozen or dried.
Recipe for a delicious “medicine”:
Wash the viburnum, dry it, and pass through a meat grinder. Add natural honey to the resulting mass at a ratio of one to one, mix thoroughly. Store in the refrigerator, eat one tablespoon daily.
Cranberry
Cranberry is one of the most powerful remedies that helps cope with colds, inflammation and high blood pressure. The beneficial substances that the berry is rich in can:
- ensure elasticity of blood vessels due to the high content of flavonoids;
- normalize heart function due to a high concentration of vitamin C;
- boost immunity due to a large number of antioxidants.
WE RECOMMEND: Dark chocolate and blood pressure The berry is good not only for relieving blood pressure and eliminating cold symptoms, cranberry perfectly relieves swelling during pregnancy.
The sour berry is also recommended for children to boost their immunity. Storage recipe:
Fresh berries should not be frozen for long-term storage. Just rinse them, put them in glass jars and fill them with cold water. This way cranberries can be stored until spring without losing their beneficial properties.