The concentration of cholesterol (in chemistry - cholesterol) in the blood is one of the key markers of the state of lipid (fat) metabolism in the body. In clinical hematology, analysis of HDL and LDL cholesterol is performed using a colorimetric, photometric or electrophoretic method.
The study is called a lipidogram, otherwise the lipid profile (status) of the patient. If prescribed by a doctor, indicators of cholesterol metabolism can be included in a detailed biochemical analysis of venous blood.
What are HDL and LDL in cholesterol metabolism?
Cholesterol refers to fat-containing alcohols. The substance is concentrated in cell membranes and serves to protect cells. The body needs cholesterol as a participant in the most important processes that support life:
- hormonal synthesis (steroid and sex hormones);
- production of bile acids;
- absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D);
- maintaining pregnancy;
- interaction between the spinal cord and brain.
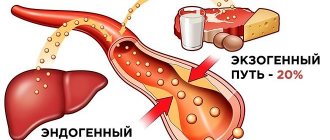
Cholesterol is divided into two types: exogenous, entering the body with animal fats (butter, meat, milk, etc.); endogenous, produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) inside the body.
Reference: The share of exogenous cholesterol is 20% of the total amount.
Cholesterol, like fat, cannot move through the bloodstream on its own. Once in the blood, its molecules combine with apoprotein proteins and other lipids (triglycerides, phospholipids), forming courier lipoproteins of different densities. The less protein there is in lipoproteins, the lower their density.
20% of cholesterol enters the body with food, and 80% is produced by liver cells
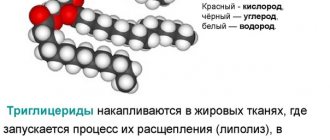
Triglycerides (TG or TG) are formed from fatty foods and are stored in fatty tissues. Essentially, this is the body's lipid reserves, used to replenish energy. Phospholipids are a special type of fat that is not synthesized by the body; they consist of fatty acids, polyhydric alcohols and phosphoric acid and are necessary for the construction of cell membranes.
Types of lipoproteins
Five main types of lipoproteins are involved in cholesterol metabolism.
Accepted classification of lipoproteins and main functions
| Full title | Function | Abbreviation | The average size | |
| Latin | Russian | |||
| low density lipoproteins | transport endogenous cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues and cells of the body | LDL | LDL | 18-26 nm |
| very low density lipoproteins | VLDL | VLDL | 30-80 nm | |
| lipoproteins of average (otherwise, intermediate) density | BOB | 25-35 nm | ||
| high density lipoproteins | collects excess LDL and VLDL and delivers them to the liver for excretion | HDL | HDL | 8-11 nm |
| chylomicrons | transport exogenous cholesterol from the intestines to the liver and body tissues | HM | 75-1200 nm | |
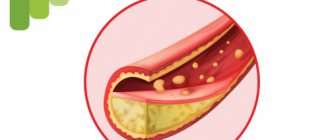
LDL and VLDL are positioned as “bad” cholesterol. When moving through arteries and capillaries, they “cling” to microdamages in the intima (the inner layer of the vascular wall) and settle.
A cholesterol stain forms inside the vessel, on the basis of which a cholesterol plaque is subsequently formed, which becomes the cause of atherosclerosis. HDL is called “good” cholesterol because it escorts low-density and very low-density lipoproteins out of blood vessels, preventing them from sticking to the intima.
Components of lipoproteins in percentage
The table shows that chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins contain the most fat (triglycerides).
Treatment for Low Cholesterol
What to do if low-density cholesterol is low. After hypocholesterolemia has been confirmed by a biochemical blood test, you should immediately make an appointment with a specialist in the field of endocrinology. He will help you accurately determine the cause of low cholesterol and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Important! If your readings are low, self-medication is unacceptable!
How to increase cholesterol in the blood? First of all, you will have to make adjustments to your diet and follow the recommended dietary intake. The daily menu should consist of foods that help increase cholesterol levels, namely:
- Dutch hard cheese;
- caviar and beef brains;
- sea fish;
- flax and pumpkin seeds;
- eggs;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- beef kidneys and liver;
- butter.
The doctor's recommendations regarding nutrition must be strictly followed by the patient, otherwise the effectiveness of therapy will be minimal. In no case should you saturate your diet with too fatty foods. As a rule, this leads to a sharp increase in bad cholesterol, which increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
Greens must be present on the dining table in unlimited quantities. Dill and parsley are considered especially useful. It is better to start the morning with a nutritious salad consisting of bell peppers, fresh carrots, white cabbage, celery, dill, and olive oil. If you want a heartier breakfast, you can serve boiled beef or turkey with the salad.
Quite often, to normalize the functioning of the liver, experts advise cleaning the liver using various recipes. In cases where the patient does not suffer from serious pathologies, normalization of cholesterol occurs by changing the diet. In addition, you will have to completely give up alcohol-containing products and smoking. Instead of harmful addictions, experts advise starting sports.
If you have hypocholesterolemia, you will need to review your diet
Lipid profile parameters
The laboratory measurement value for total cholesterol and its fractions is mmol/l. Indicators included in the lipid profile:
Normal blood cholesterol levels
- OX (Cho);
- HDL;
- LDL;
- VLDL;
- HM;
- TG;
- KA (IA).
TC – total cholesterol level. KA – coefficient (otherwise, index) of atherogenicity. When assessed by electrophoretic method, fractions are divided:
- alpha lipoproteins or HDL;
- beta lipoproteins – LDL;
- prebeta lipoproteins – VLDL.
The CA value is a laboratory marker that reflects the degree of danger of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. It is calculated using the formulas: KA = (LDL + VLDL) / HDL or IA = (Cho – HDL) / HDL.
Symptoms
It is impossible to determine hypocholesterolemia by external manifestations. To determine cholesterol levels, the patient must take a biochemical blood test performed on an empty stomach. In cases where you cannot visit the hospital for some reason, you should pay attention to your own well-being.
Symptoms such as lack of appetite for a long time, decreased sensitivity, systematic weakness, fatigue, and the presence of fatty loose stools can signal low cholesterol.
Enlarged lymph nodes, rapid mood swings, and decreased sexual activity appear. The listed symptoms may indicate hypocholesterolemia, so it is important to urgently consult a doctor and get tested!
Preparing to donate blood for a lipid profile
Preliminary preparation for analysis is necessary to obtain accurate results. 2-3 days before the prescribed procedure, it is recommended to refuse foods rich in animal fats and alcoholic beverages (including weak alcohol), and stop taking any medications other than those necessary for medical reasons.
The day before the procedure:
- reduce physical activity;
- limit sugar intake.
Blood sampling is performed strictly on an empty stomach. The fasting regime should be at least 8 hours.
Consequences if left untreated
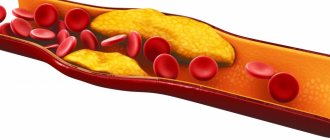
The fact that HDL cholesterol is elevated indicates an excess intake of fats in the blood. The condition is dangerous due to a subsequent increase in the amount of LDL and VLDL. They are formed after the molecules delivered to the liver are processed. Excess “bad” cholesterol settles exclusively on the walls of damaged blood vessels. Platelets cover microdamages and form a blood clot to stop intravascular bleeding. Their cells have the same charge as LDL, so they are attracted to each other.
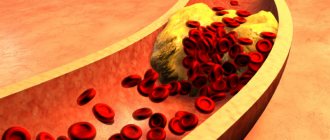
A clot of platelets and “bad” cholesterol forms an atherosclerotic plaque. Over time, it hardens, the walls of the vessel lose their elasticity, and blood flow is disrupted. In order for blood to leak through a narrow passage closed by a blood clot, the pressure reflexively increases. The patient develops hypertension. The heart begins to work at an increased pace, the myocardium increases in size due to excessive contractions, and the flow of nutrients in the myocytes (myocardial cells) is disrupted. At advanced stages, foci of local cell death form. They are deprived of food and oxygen. It's a heart attack.
Formation of atherosclerotic (cholesterol) plaques.
Another complication of high cholesterol is the detachment of a blood clot or part of it from the vessel wall. The clot travels further along the bloodstream. It gets stuck in the first narrow vessel or capillary it comes across. If this process occurs in the heart, there will be a heart attack, in the brain - a stroke.
Atherosclerosis in 82% of cases ends in premature and sudden death. It is simply necessary to treat it.
Normal lipid status
The norms for total cholesterol do not depend on gender. For men and women from 20 to 45 years old, the indicators should fall within the range of 3.2-5.2 mmol/l. If the result is equal to or greater than 6.7 mmol/l, then the patient is diagnosed with hypercholesterolemia.
At values below the norm of 3.2 mmol/l – hypocholesterolemia. Both disorders are considered pathologies. Reference values for high-density and low-density lipoproteins differ by gender and age category.
Normal indicators
The values of triglycerides and very low density lipoproteins for men and women are identical:
- TG – 0.41-1.8 mmol/l;
- VLDL – 0.26-1.04 mmol/l.
For the atherogenicity coefficient, only inflated values are of diagnostic value. The higher the KA, the higher the risk of atherosclerosis.
CA norm table
HDL (HDL) is the norm in women (table by age)
Norms of HDL / HDL cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) in the blood of girls, young women and adult women by age (table)
| Age (girls/girls/women): | Norm HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) | LDL-C norm (mg/dL) |
| children from 5 to 10 years old | 0.93 – 1.89 | 36.0 – 73.1 |
| 10 – 15 | 0.96 – 1.81 | 37.1 – 70.0 |
| 15 – 20 | 0.91 – 1.91 | 35.2 – 73.9 |
| 20 – 25 | 0.85 – 2.04 | 32.9 – 78.9 |
| 25 – 30 | 0.96 – 2.15 | 37.1 – 83.1 |
| 30 – 35 | 0.93 – 1.99 | 36.0 – 77.0 |
| 35 – 40 | 0.88 – 2.12 | 34.0 – 82.0 |
| 40 – 45 | 0.88 – 2.28 | 34.0 – 88.1 |
| 45 – 50 | 0.88 – 2.25 | 34.0 – 87.0 |
| 50 – 55 | 0.96 – 2.38 | 37.1 – 92.0 |
| 55 – 60 | 0.96 – 2.35 | 37.1 – 90.9 |
| 60 – 65 | 0.98 – 2.38 | 37.9 – 92.0 |
| 65 – 70 | 0.91 – 2.48 | 35.2 – 95.9 |
| over 70 years old | 0.85 – 2.38 | 32.9 – 92.0 |
Also read (link): about AGE CHANGES IN CHOLESTEROL NORMAL IN WOMEN
Deviation from normal levels of LDL and HDL
Non-standardized lipoprotein values should be considered only in conjunction with triglyceride values and the level of total cholesterol in the blood. When HDL cholesterol is elevated with normal levels of TC and other fractions, this indicates good lipid metabolism. An unfavorable combination is when the level of LDL and TC is increased, and the level of HDL is decreased.
The following indicators accompany chronic diseases:
- hepatobiliary system (hepatosis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, etc.);
- renal apparatus (pyelonephritis, nephritis, etc.);
- endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- cardiovascular system (hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis, etc.).
As well as some autoimmune and oncological pathologies. If there are no such diagnoses, then the cause may be an unhealthy lifestyle:
- unhealthy diet (predominance of animal fats in the diet, deficiency of vegetables and fruits);
- alcohol and nicotine addiction;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- long-term stress.
In this case, the results of the lipid profile should be regarded as a high risk of developing atherosclerosis and heart disease. With a decrease in HDL, “bad” cholesterol settles on the inner wall of blood vessels, forming cholesterol spots, from which atherosclerotic plaques eventually form. Such growths inside the vessel block blood flow, which causes heart attack, stroke, and dry gangrene of the lower extremities.
Hypocholesterolemia is also harmful to the body. Lack of cholesterol threatens hemorrhagic stroke, destruction of cell membranes, anemia (anemia), osteoporosis, neuropsychological disorders and depression.
With cholesterol deficiency, the synthesis of sex hormones is disrupted. As a result, libido decreases, men experience problems with potency, women's menstrual cycles become disrupted, and there is a risk of infertility.
Possible complications
Cholesterol can be both bad and good. Is low blood cholesterol good or bad? What does the pathology threaten and is it dangerous? Hypocholesterolemia poses a danger to human health. In addition to the fact that cancerous tumors may begin to develop, low cholesterol can cause:
Cholesterol test interpretation
- development of vascular fragility and circulatory disorders in the brain, which often leads to internal hemorrhages;
- disruption of the functioning of serotonin receptors, which provokes the occurrence of depression or attacks of aggression, in which the patient is unable to control his behavior;
- development of a syndrome of increased intestinal permeability, as a result of which accumulations of toxins are not eliminated from the body, but penetrate into the bloodstream and have a negative impact on the functioning of internal organs and systems;
- vitamin D deficiency in the body, which increases the risk of osteoporosis;
- low production of sex hormones, increasing the risk of infertility;
- impaired digestion of fats, which entails a risk of developing obesity.
Hypocholesterolemia is a dangerous disease that can provoke the development of various ailments. That is why it is important to take a blood test at the first symptoms and seek help from a doctor who will create an individual method of therapy that will allow you to overcome the unpleasant disease.
Results
HDL and LDL are the most important participants in cholesterol metabolism, the amount of which in the blood must meet certain standards. Low-density lipoproteins supply the body's cells with cholesterol, which is produced by the liver. High-density lipoproteins cleanse blood vessels of excess fat, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
Dyslipidemia, otherwise an imbalance of LDL and HDL, accompanies a number of chronic diseases or is a consequence of unhealthy eating behavior, bad habits, and physical inactivity. You can check your fat metabolism levels by donating blood for a special test - a lipid profile.
HDL (HDL) is the norm in men (table by age)
Norms of HDL / HDL cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) in the blood of boys, young men, adolescents and adult men by age (table)
| Age (boy/youth/men): | Norm HDL cholesterol (mmol/l) | HDL-C norm (mg/dL) |
| children from 5 to 10 years old | 0.98 – 1.94 | 38.0 – 75.0 |
| 10 – 15 | 0.96 – 1.91 | 37.1 – 73.9 |
| 15 – 20 | 0.78 – 1.63 | 30.2 – 63.0 |
| 20 – 25 | 0.78 – 1.63 | 30.2 – 63.0 |
| 25 – 30 | 0.80 – 1.63 | 31.0 – 63.0 |
| 30 – 35 | 0.72 – 1.63 | 27.8 – 63.0 |
| 35 – 40 | 0.88 – 2.12 | 34.0 – 82.0 |
| 40 – 45 | 0.70 – 1.73 | 27.0 – 67.0 |
| 45 – 50 | 0.78 – 1.66 | 30.2 – 64.2 |
| 50 – 55 | 0.72 – 1.63 | 27.8 – 63.0 |
| 55 – 60 | 0.72 – 1.84 | 27.8 – 71.1 |
| 60 – 65 | 0.78 – 1.91 | 30.2 – 73.8 |
| 65 – 70 | 0.78 – 1.94 | 30.2 – 75.0 |
| over 70 years old | 0.85 – 1.94 | 32.9 – 75.0 |
(Follow the link) in more detail about CHANGES IN CHOLESTEROL NORMAL IN MEN BY AGE
How to increase the content of high density lipoproteins?
To increase HDL, you need to balance your diet. If the situation is advanced and the HDL level is too low, the doctor will prescribe medications. Moderate physical activity is also necessary. Good blood supply to all parts of the body promotes the resorption of atherosclerotic plaques and prevents the formation of new ones.
Non-drug treatment
If there is a slight deviation from the norm, the diet will correct the situation; if carefully followed, it will quickly raise the HDL level to the desired numbers. Its main principle is the exclusion of animal fats and replacing them with vegetable ones.
Healthy and unhealthy fats.
It is prohibited to use:
- fat meat;
- lard, sausage (smoked and raw smoked);
- meat broths;
- red and black caviar;
- fried foods;
- “fries” - dishes (fast food);
- margarine, butter;
- high fat dairy products.
Vegetable fats are found in:
- oils: olive, flaxseed, nut, sesame, hemp, corn;
- nuts;
- avocado.
Replace mayonnaise and other sauces with vegetable oils. They are not inferior in taste and have a positive effect on the body.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are of great importance in the treatment of atherosclerosis: omega - 3, omega - 6, omega - 9. They resolve cholesterol plaques and are found in vegetable oils and fish fat: trout, salmon, mackerel, herring, capelin. Use fish broths, they are well absorbed, and essential fatty acids are instantly absorbed by the body.
Ways to Increase HDL Cholesterol
Olive oil in nutrition
Saturated fats, found in dairy products and fatty meats, increase LDL and HDL levels in the blood. Replacing these saturated fats with “healthy fats” (polyunsaturated or monounsaturated fats from nuts, seeds, avocados, vegetable oils) has been shown in studies to help lower LDL levels. []
Numerous studies have also shown that supplementing your diet with olive oil can help lower total cholesterol and increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Olive oil contains antioxidants called polyphenols, which are responsible for its protective properties for the cardiovascular system. []
Olive oil also improves cholesterol profiles by improving the ability of HDL to properly interact with cholesterol. A study of 26 healthy volunteers suggests that olive oil ( 25 ml/day or 2 tablespoons ) improves cholesterol levels by increasing the production of ABCA1 and ABCG1 proteins, which are essential for the transport of fats across cell membranes. []
Olive oil also helps enhance the anti-inflammatory properties of HDL. Another study of 20 healthy adults found that drinking 25 ml of extra virgin olive oil per day for 12 weeks increased the amount of protein associated with HDL (paraoxonase 1), which helps HDL exert its anti-inflammatory properties. []
Eggs in the diet
A small study of 28 obese people found that a low-carbohydrate diet supplemented with 3 eggs per day increased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels by 25%. Including eggs in the diet helped reduce the risk of developing metabolic syndrome. And this effect was more pronounced in obese people. []
In another study of 15 obese people, 3 chicken eggs a day also increased HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels by 52%. However, this second study was sponsored by the American Chicken Egg Association. []
Another study involving 42 elderly men and women demonstrated that 3 chicken eggs per day increased HDL cholesterol by 23%. []
And a study of older adults taking statins and eating 4 eggs a day concluded that these people experienced a 5% increase in HDL levels over 5 weeks without an increase in LDL (“bad” cholesterol). []
Low Carb Diet
Reducing carbohydrates in the diet
Numerous studies demonstrate that reducing carbohydrates and increasing healthy fats in your diet can provide many health benefits, including lower blood sugar , weight loss , and improved insulin sensitivity . Another big benefit of this diet is the increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL). []
In a randomized controlled trial of 115 obese adults with type 2 diabetes consuming less than 50 g. carbohydrates per day, as a result of weight loss, there was an increase in HDL cholesterol levels almost 2 times higher than in those people who did not switch to such a diet. []
Overweight people with diabetes (a total of 194 people) followed Mediterranean diet for 12 months in a randomized trial. At the end of these 12 months, these people had an increase in HDL in their blood, which did not occur in those subjects who simply followed a Mediterranean diet without reducing the amount of carbohydrates. []
In a prospective study, 22 obese adults with metabolic syndrome followed a “Spanish Mediterranean ketogenic diet” for 12 weeks. The long-term result of this diet was an increase in HDL levels in their blood, as well as the fact that their metabolic syndrome was completely cured . []
Another cohort study followed 64 obese adults for 56 weeks while on a ketogenic diet . The result of this experiment was an increase in HDL levels and a decrease in total cholesterol levels along with a decrease in HDL (“bad” cholesterol). []
Fruits and vegetables containing anthocyanins
Fruits and vegetables with anthocyanins
Blueberries , blackberries, pomegranate, eggplant, red cabbage and other purple fruits and vegetables that are high in anthocyanins, which are powerful antioxidants, may help increase HDL cholesterol. []
In one experiment, 58 adults with diabetes were given 160 mg of anthocyanin concentrate twice daily for 24 weeks, which resulted in a 20% increase in HDL cholesterol. []
Another study of 120 patients with high cholesterol showed a nearly 14% increase in HDL cholesterol after 12 weeks of anthocyanin supplementation (160 mg, twice daily). []
Exercise stress
Exercise increases HDL in the blood through multiple pathways, and recent research suggests that any amount of physical activity can be beneficial, and its effects accumulate over time . []
A study involving 18 obese men and women for 12 weeks examined the effects of regular endurance training on HDL levels. As a result of the experiment, an increase in HDL in men and a favorable shift in HDL fractions in women was recorded. The important thing is that no diets were followed. []
The result of regular physical activity for 12 months: an increase in HDL and a decrease in LDL along with total cholesterol.
Another study (prospective observation) of 200 men found that an increase in HDL occurred with regular endurance training. However, the most significant positive changes occurred in patients who had high levels of harmful triglycerides in the blood and had a large amount of fat in the abdominal cavity (abdominal obesity). []
Weight loss
Many studies have shown that weight loss (losing weight), regardless of the diet used, necessarily increases the level of HDL (“good” cholesterol). A study of 3,480 Japanese adults showed that losing 3 kg of weight resulted in an average increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels of 4 mg/dL. []
Reducing alcohol consumption
The association between alcohol consumption (1 drink per day for women and 1-2 drinks per day for men) and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease has been observed in many studies. However, increasing the amount of alcohol consumed above these designated values not only leads to a sharp increase in the risk of heart disease, but also stimulates the risk of developing many other diseases, such as diabetes or stroke. []
A study of 2,473 men and 1,530 women found that moderate (no more than 1-2 drinks per day, where the drink is 200 ml of wine or beer, but not spirits) alcohol consumption showed higher levels of HDL cholesterol. []
Adding coconut oil
Several studies have found that consuming edible coconut oil (usually about 2 tablespoons per day) can raise HDL levels more than other types of fat. Coconut oil also helps lower the LDL to HDL ratio, which can reduce the risk of heart disease. []
Oily fish in the diet
There are conflicting reports about the effect of consuming oily fish or fish oil supplements on HDL cholesterol levels. Some studies have noted an increase in HDL when participants consumed large amounts of fish, but the effects were minimal, and other studies have found an increase in HDL in response to increasing the amount of fish in the diet or taking supplements. []
Medicines
Note : When writing this section, we do not recommend these medications for use. We are simply providing information that is available in the scientific literature. Please discuss your medications with your doctor.
Statins
Statins can lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol. However, whether this actually has a significant impact on the risk of developing cardiovascular disease is still unclear. A meta-analysis of 12 large studies, including more than 26,000 patients, found that changing blood cholesterol levels with drugs has no beneficial effects, as people do not reduce their risk and remain at high risk of heart disease. []
Statins increase the risks of diabetes and insulin resistance (https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/63/11/3569)
Fibrates (alpha-agonists) or thiazolidinions
Fibrates and thiazolidinediones are two classes of compounds that activate the PPARα protein, which helps increase fat breakdown in the liver and other parts of the body. These drugs are sometimes used by patients who cannot tolerate statins and require an increase in HDL and a decrease in LDL.
Paradoxically, in some people and in rare cases, these drugs can cause a sharp decrease in HDL (“good” cholesterol). Therefore, it is very important to take fibrates and thiazolidinediones under the guidance of a doctor. []
Functions
Lipoproteins play an important role in the human body. Thanks to transport proteins, cholesterol dissolves in the blood plasma and begins to move throughout the body. Cholesterol enters the body not only from food. Almost 80% of the fat metabolism component is produced in the liver.
Cholesterol takes an active part in the synthesis of sex hormones and has a strengthening and protective effect on cell membranes. In addition, the fat metabolism component contributes to the restoration of cell membranes and the production of vitamin D.