The Chart of Accounts includes account 97 “Deferred expenses” and account 98 “Deferred income”. What are these bills? What are they used for? What should you consider about them? In this article we will talk about the features of accounting for income and expenses related to future periods in these accounts, and we will analyze the postings.
Each enterprise has expenses that are associated with the development of new workshops, enterprises, and equipment that arise before the release of products. These are costs associated with the development of estimate documentation for commissioning work, wages for employees who participate in this type of work, etc.
These expenses should be included in expenses for future periods and in the cost of goods, services, and work in proportion to their output.
These are expenses that were incurred in the reporting period, but which relate to future reporting periods.
Norm and deviation
Blood pressure 90/60 – what does this mean? The doctor receives information about blood pressure based on the indicators determined by the tonometer. The first number is systolic (upper) - indicates the time of contraction of the heart muscle. The second - diastolic (lower) - shows the pressure of the blood during the period of its pushing into the arteries.
Important! Doctors take 120/80 mm as the physiological norm. rt. Art.
Blood pressure levels can fluctuate and largely depend on a person’s current emotional and physical state. If blood pressure drops only periodically, then there is no cause for concern. But if low pressure is a constant condition, then it is necessary to find the reasons for such a deviation.
In some cases, the blood pressure level is 90(99)/60(66) mm. rt. Art. is considered by doctors as the norm. This statement applies to people with an asthenic body type, teenagers. In addition, many women feel great with this level of pressure.
Another group of people whose “working” blood pressure is 110(120)/70(80), if it decreases to the level of 90/60, begin to experience unpleasant symptoms. In this case, it is necessary to consult a therapist.
Possible complications of low blood pressure during pregnancy
In pregnant women with hypotension, as with other vascular disorders, gestosis often (in 25% of cases) develops (the appearance of edema, protein in the urine, increased blood pressure). In this condition, in patients with hypotension, blood pressure may not exceed normal values (120/80 mmHg), but it will be 30% higher than the initial one, and this is considered to be a pathology. As already mentioned, such patients are more likely than healthy women to develop early toxicosis of pregnancy with arterial hypotension.
The main complications of pregnancy with arterial hypotension include its spontaneous termination. With this disease, it is observed at various stages of pregnancy 3-5 times more often than in healthy women. The opposite effect is also noted: in women who remain in bed for a long time due to the threat of miscarriage, blood pressure steadily decreases, apparently due to muscle inactivity.
Arterial hypotension contributes to intrauterine growth retardation due to reduced uteroplacental blood flow.
In patients with arterial hypotension, complications of labor are often observed; they are mainly associated with impaired contractility of the uterus. This creates difficulties in the management of childbirth and promotes the expanded use of surgical methods of delivery (caesarean section) in order to provide assistance to the suffering fetus. Childbirth is often accompanied by bleeding.
Causes
There are two types of hypotension. It is customary to highlight:
- Primary (physiological). It forms independently and does not cause serious changes in a person’s well-being.
- Secondary. Hypotension develops as a complication of an existing disease and is accompanied by severe symptoms.
Primary
Low blood pressure can be inherited. Women and girls with an asthenic body type are especially often hypotensive. The condition is not accompanied by severe symptoms. A natural decrease in blood pressure occurs during periods of hormonal changes:
- period of bearing a child;
- menstruation;
- menopause
Adolescent hypertension is an acceptable norm. The condition is caused by hormonal changes occurring in the body, lack of stability in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and too rapid growth of the child. Blood pressure stabilizes on its own after puberty and does not require any medical adjustment.
The development of primary hypotension can also be provoked by:
- overwork – nervous and physical;
- dependence on weather conditions;
- climate change;
- sedentary lifestyle.
In adults, primary hypotension occurs due to lack of physical activity. The result of physical inactivity is a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. But if an elderly person leads a fairly active lifestyle, then the primary form of hypotension does not threaten him.
No ads 1
Secondary
Secondary hypotension occurs as a complication of another serious disease. The reasons can be:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- disruption of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands;
- anemic conditions;
- heart disease;
- brain injuries;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- infections;
- severe burns;
- allergy;
- intoxication of various origins.
The effectiveness of treatment for secondary hypotension depends on the results of therapy for the disease that provoked it.
Secondary hypotension sometimes occurs during long-term use of the following medications:
- diuretics;
- antispasmodics;
- ACE inhibitors;
- calcium antagonists.
[node:field_similarlink]
Pregnancy in women with low blood pressure
The effect of pregnancy on blood pressure is observed very often. It can be expressed to varying degrees. More often it is limited to a decrease in systolic and diastolic pressure to values close to the minimum limit of normal fluctuations, but it can fall lower. Therefore, women with arterial hypotension often experience an exacerbation of the disease during this period.
For most women, deterioration occurs in early pregnancy. In 8 out of 10 women, pregnancy occurs with symptoms of early toxicosis, the addition of which aggravates hypotension, because Frequent vomiting, causing a lack of fluid in the body, helps lower blood pressure.
A condition called inferior vena cava syndrome should not be considered a manifestation of hypotension in pregnancy. It develops in the second half of pregnancy. When a woman is positioned on her back, as a result of the pregnant uterus squeezing the inferior vena cava, the blood flow to the heart is disrupted and a fainting state develops with a drop in blood pressure, a weakening of the pulse, and often with loss of consciousness. The condition quickly returns to normal when the woman turns on her side or sits down.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Physiological (primary) or secondary hypotension should be considered as a pathology if the condition is accompanied by the development of characteristic symptoms. These are:
- morning weakness for no apparent reason;
- migraine attacks;
- pain in the heart area;
- attacks of suffocation (lack of air);
- sleep disorders (insomnia);
- lethargy, depressed state;
- periodic causeless disturbance of health;
- poor appetite;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate above 100/120 beats per minute).
The symptoms discussed may occur periodically, but can be observed constantly. This significantly worsens the patient's quality of life. For this reason, if a person feels unwell due to low blood pressure, it is necessary to consult a doctor and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.
At normal heart rate
At the initial appointment with the doctor, the patient will have their blood pressure measured. In addition to the obtained indicators, heart rate is of diagnostic interest for a physician. Normally, a person’s pulse should fall within the range of 60–80 beats per minute.
What does blood pressure 90/60 mean against the background of the permissible myocardial contraction frequency? In this case, the doctor will advise the patient to reconsider his usual lifestyle: rest more, get better sleep, eat well and give the body feasible physical activity.
Important! Low blood pressure is dangerous if it is accompanied by a deviation in the number of heartbeats up or down.
High heart rate
The combination of low pressure and increased frequency of myocardial contractions is quite rare. An accelerated heartbeat is called tachycardia and is one of the types of arrhythmia. Blood pressure of 90/60 with a pulse of 90 beats per minute or higher may be accompanied by the following conditions:
- soreness in the temple area;
- sensation of heart contractions;
- chest pain;
- unreasonable anxiety;
- increased sweating;
- attacks of nausea.
Tachycardia in combination with hypotension often indicates diseases of the heart and blood vessels, but can also be a sign of other serious pathologies. In particular:
- infectious diseases;
- blood loss;
- low hemoglobin level;
- dehydration;
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- varicose veins;
- atherosclerotic disease, etc.
If the tonometer shows blood pressure 90 over 60 and pulse 110 and such measurements are repeated frequently, then you need to consult a doctor.
No ads 2
Low heart rate
A weak pulse is typical for hypotensive patients. But if the number of heart contractions drops below 60 beats per minute, then we are talking about the development of bradycardia. The condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- attacks of morning sickness and vomiting;
- headache;
- fainting;
- increased fatigue even after a good night's rest;
- apathy, weakness;
- cold extremities.
Bradycardia due to low blood pressure is a serious danger
In young people
In healthy young people, a decrease in blood pressure can be considered an acceptable norm and does not require treatment. But if the condition is accompanied by weakness, dizziness, fatigue, then you need to consult a doctor.
In old age
People over 60 years of age should monitor their blood pressure more carefully. Reducing its level to 90/60 mm. rt. Art. should be considered a serious deviation from the age norm. As a rule, it indicates the presence of a serious illness.
During pregnancy
If a pressure of 90 to 60 is detected during pregnancy, a woman is prescribed an ultrasound examination. If the condition does not affect the development of the fetus in any way, then it does not need correction. If during the procedure symptoms of fetal developmental delay or signs of hypoxia are diagnosed, then the pregnant woman is prescribed adequate treatment for the condition.
No ads 3
Hypotension: symptoms of the disease
Arterial hypotension as an independent disease (it is also called neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type) is a typical vascular neurosis. The onset of the disease can often be associated with neuropsychic trauma, emotional stress, and fatigue.
In cases where arterial hypotension is manifested only by a decrease in blood pressure, and there are no complaints or discomfort, it is classified as stable
(
compensated
) stage of the disease.
Unstable
(
subcompensated
) stage of the disease, in addition to a decrease in blood pressure, is manifested by other symptoms. Patients usually complain of headache, dizziness, general weakness, palpitations, discomfort in the heart area, sweating, memory loss, decreased ability to work, chilliness of the hands and feet, and meteosensitivity (deterioration when the weather changes). Some women experience so-called orthostatic phenomena: when getting out of bed, they experience dizziness, darkening of the eyes, even fainting. Fainting of a non-orthostatic nature can develop during an exacerbation of the disease or occur against the background of good health. Patients often develop irritability, emotional instability, and a tendency toward low mood.
Decompensated
arterial hypotension is characterized by hypotensive crises, easily occurring fainting, sleep disturbances, the appearance of acrocyanosis (bluish coloration of the fingertips, nose, lips, earlobes), loss of ability to work.
Hypotonic crises can last several minutes. During a crisis, blood pressure drops to 80/50 mmHg and below, headache and dizziness intensify, and vomiting may occur; patients feel severe weakness, a feeling of stuffy ears; A short-term loss of consciousness may occur, the skin and mucous membranes turn pale, and cold sweat appears. Fainting often develops in a stuffy room, in transport, after excitement, or during prolonged standing. Fainting is a fairly common occurrence in pregnant women.
In patients with arterial hypotension, blood pressure does not always remain persistently low: periodically it can reach normal and even elevated numbers - for example, when excited, upon admission to the hospital. However, it is rapidly declining.
Women with hypotension more often have an asthenic build (tall, thin) with pale skin. Almost half of them have varicose veins in their legs. The arms and legs feel cold to the touch, the pulse is somewhat lower than usual (about 60 beats per minute). No changes were detected during cardiac examination, including electrocardiography.
Treatment
What to do if you have low blood pressure? To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the condition, it is necessary to raise blood pressure. If the pressure has dropped, then to normalize the condition, it is recommended to drink a cup of hot coffee or strong brewed tea. But doctors do not advise using stimulants too often, since the development of addiction is possible.
There are a number of recommendations that will help increase blood pressure. The tips are as follows:
Causes of low blood pressure with high heart rate
- You need to get out of bed slowly in the morning. First, you need to lie down for a while, wake up completely, and only then get up. This will prevent the development of dizziness, nausea and fainting.
- You should always drink at least two liters of fluid during the day.
- Meals should be fractional. Food should be taken at least 4 times a day. At the same time, the diet must fully satisfy all the body’s needs for nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) and essential vitamins and microelements.
- It is advisable to exclude fried, fatty foods, smoked foods, and spices from the menu.
- Water procedures give good results. Hydromassage and contrast showers are beneficial (but you should avoid sudden temperature changes).
- Age-appropriate physical activity. Static loads are not suitable for hypotensive patients. You should give preference to swimming, tennis, volleyball.
When treating mild forms of hypotension—pressure readings of 90/60 indicate this—specific medications are used in rare cases. Medicines containing caffeine may be prescribed: Pentalgin, Citramon and others.
As a rule, doctors advise using alcoholic herbal tinctures. Most often prescribed:
- Aralia Manchurian. Take 30 drops three times a day.
- Ginseng, Eleutherococcus. The drugs have a tonic effect and improve myocardial function. Course duration – 2 weeks. Dosage regimen: 20 drops three times a day.
Emergency help
If the pressure drops too sharply, it can be stabilized using the following methods:
- Strongly brewed sweet hot tea. The drink helps eliminate headaches, warms and speeds up blood flow. This combination increases blood pressure.
- Strong coffee. A rapid increase in blood pressure occurs due to the presence of a large amount of caffeine in the drink. But the drink provides a short-term, short-lived effect.
- Bitter chocolate. A few pieces of sweet tea help improve vascular tone and normalize your overall well-being.
Consequences and prognosis
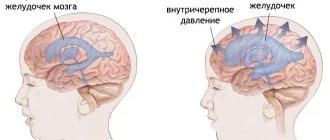
Against the background of a constant decrease in blood pressure, the organs and tissues of the body do not receive the oxygen they need in full. In this case, the brain cells suffer the most. Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) causes the development of cognitive disorders: a person’s memory decreases, concentration and coordination are impaired. In old age, senile dementia develops.
Complications of hypotension may include:
- injuries sustained after fainting;
- visual impairment;
- heart, kidney failure;
- ischemic stroke;
- neurological pathologies;
- depressive states.
Predicting the outcome of the disease is quite difficult. It all depends on the effectiveness of blood pressure level correction.
Primary hypotension is difficult to treat. Blood pressure can be normalized in approximately 70% of all diagnosed cases. But this condition does not pose a particular threat to human life. A decrease in pressure to the level of 90/60 can occur for various reasons. And if the condition is accompanied by poor health, then the person needs to consult a doctor.