Over the past few years, everyone has been talking about how important it is to monitor your heart rate while playing sports, running at a low heart rate has become fashionable, and heart rate monitors are being released in the form of very cute designer gadgets and are built into smart watches. We'll tell you why monitoring your heart rate is really a good idea.
Short answer : Heart rate measurements tell us how the heart is working at any given moment, the main goal here is to avoid too much stress and overwork, which can lead to health problems. In addition, taking into account your heart rate zones, you can make your workout more effective.
What are pulse zones?
So, the pulse tells us the heart rate. In order to measure it, it is not necessary to use special gadgets - in ordinary life it will be enough to count the number of heart beats per minute, armed with a stopwatch.
At times of stress, which includes physical activity, the heart rate increases. This occurs due to the fact that the body has an additional need for oxygen, which the blood delivers to all organs and tissues.
Depending on the speed of heart contraction, several so-called pulse zones are distinguished. There are many classifications, but they usually include 4 to 8 zones ranging from resting heart rate to maximum heart rate.
The maximum frequency varies depending on age; quite roughly it can be determined by the formula “220 minus your age”: for example, for twenty-year-olds, the maximum heart rate is 200 beats per minute, and for people 50 years old - 170. Further classification of zones is based on this indicator. A pulse at 50-60 percent of the maximum heart rate is called very light, light - 60-70 percent, medium - from 70 to 80, and, finally, heavy - 80-90.
You need to understand that in any case, such a formula is only theoretical. In each individual case, you can establish the maximum heart rate more accurately using special tests, however, if you have just started your training, at first this conditional classification will be enough.
Why should you monitor your heart rate during exercise?
The main reason is that such control allows you to avoid health problems. First of all, there is too much stress on the heart during high-intensity training. Achieving high heart rate values - more than 80 percent of the maximum - is acceptable during strength training, but only for a short period of time (from 20-30 seconds for beginners and up to 5 minutes for experienced athletes).
When you see that the pulse is approaching a heavy one, you can pause in time and avoid unpleasant consequences such as dizziness and nausea, and in addition, prevent more serious dangers. In particular, recent research suggests that training at a heavy heart rate (more than 85 percent of maximum) increases the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, atrial fibrillation and heart attack.
It’s clear with the maximum values, but how else can you use the information from the heart rate monitor?
Beyond basic safety, measuring your heart rate can help make your workouts more effective. For example, if your goal is to lose excess weight, know that this process occurs most effectively in the light heart rate zone (60-70 percent of the maximum). If your goal is to develop endurance, stick to average heart rates. This zone is suitable for basic anaerobic exercise - training on machines and exercises with weights. And finally, a high heart rate signals that you have reached your maximum load and it’s time to stop and rest.
Dynamic loads
The most beneficial thing for the body is dynamic load - that is, movement. This type of physical activity includes running, swimming, walking, as well as such popular exercises as lunges, squats, and crunches.
What do regular dynamic loads give?
- A well-developed exercise program helps build the body;
- Exercise promotes muscle growth;
- Energy consumption increases - not only during load, but also at rest;
- Lung volume and depth of breathing increases;
- All tissues of the body are more intensively supplied with oxygen;
- Metabolism improves;
- The risk of developing diseases of the musculoskeletal system is reduced.
Possible violations
If the pulse is too rapid or, conversely, slower than it should be according to standards, then perhaps we are talking about a deviation.
If, after all the calculations, the pulse falls outside the acceptable range, then you need to find a way to normalize the indicators. First of all, you need to take a second measurement approximately half an hour after the first one. During this time, you should rest well and avoid physical activity. Breathing exercises help some people cope with the problem.
If, after repeated measurements, the pulse is again very different from the norm, then you need to understand why this is happening.
Low performance
This condition is called bradycardia, that is, the heart rate is below normal. If at the same time a person does not experience weakness and continues his usual sports training, without noting any deviations for the worse, then such a condition does not apply to disorders or malfunctions in the body.
If a person has never played sports, then such a manifestation is usually accompanied by:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- rapid fatigue.
If at least one of these symptoms appears, it is recommended to consult a doctor to understand the cause of the low pulse and malaise.
High performance
If your heart rate increases, you need to make sure that the change in heart rate is not associated with:
- overwork after intense physical exertion;
- severe emotional stress;
- anemia, which is characterized by low hemoglobin levels;
- increased body temperature as a consequence of the initial stage of a viral disease;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular or respiratory system.
An increase in heart rate is not considered normal if it exceeds the standard values by 20%.
If your heart rate increases, you should immediately consult a doctor if, at the same time as your heart rate increases, you experience confusion, dizziness, attacks of vomiting and nausea. Also, with an increased heart rate, a person may feel faint, sweating increases, and vision becomes worse.
Static loads
Load is not necessarily movement. Staying in one position for a long time can also be a strain on the muscles. If your health does not allow you to practice dynamic loads, you can resort to static ones. They do not require active movement; on the contrary, during the process you must maintain a certain position or change it very slowly (as, for example, in yoga or Pilates). Such loads are indicated even for diseases of the cardiovascular system or musculoskeletal system, which do not allow dynamic activity.
What should your heart rate be during exercise?
In many ways, heart rate depends on the specific load. When walking and training, heart rate indicators differ and have their own characteristics.
When walking
During normal walking, the norm is considered to be from 100 to 150 beats per minute. If these indicators increase, then the person experiences shortness of breath, dizziness, tingling in the side and heart area. If this happens, then this indicates that the person needs better physical preparation.
Walking belongs to the category of loads that is estimated at 35% of the load. That is, this is an acceptable standard of gravity for a person who does not play sports. This is why walking is most often recommended for older people.
During cardio training
Fitness training falls into this category. That is, the pulse should be within 135-150 beats/min . However, you must first undergo a specialized computer examination, which will help determine the lower and upper threshold of your heart rate.
Heart rate zones depending on physical activity
If we talk about cardio training, the recommended duration of such exercises is 40-50 minutes.
Male indicators
The pulse during physical activity (the norm for the stronger half of humanity differs from the standard indicators for women) changes throughout the day. The values are influenced by the degree of training of men. For example, an athlete’s heart rate is approximately 20-30% lower than that of those who do not train.
If we talk about men, their heart rate can change depending on the conditions. For example:
- During active walking, heart rate is about 90-100 beats/min. If, when walking, the pulse rises to 120 beats/min, then this is not considered critical if the man does not experience shortness of breath or dizziness.
- In a calm state, heart rate indicators are in the range of 60-80 beats/min.
- If a man is overweight and leads a sedentary lifestyle, then the heart rate can be up to 120 beats/min.
After training, a man’s pulse returns in approximately 30 minutes.
For girls
For representatives of the fairer sex, the pulse may vary depending on a greater number of factors. For example, heart rate changes during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, weight gain, and overeating.
During physical activity, the pulse intensity of a woman aged 20 years should be 110-150 beats/min. At 30-40 years old, this figure decreases to 105-140 beats/min. After exercise, heart rate should recover in approximately 20 minutes. If training is aimed at endurance, then full recovery occurs after 40 minutes.
When walking, heart rate should be within 100-120 beats/min. A lower value indicates that the woman is in good physical shape. With a pulse of 120 beats/min. It is worth reducing the load and increasing the time for walks and quieter activities.
Also, the pulse of men and women is greatly influenced by lifestyle. If a person drinks coffee very often, drinks alcohol and smokes, then the heart rate will not be stable and may increase without physical activity.
In childhood
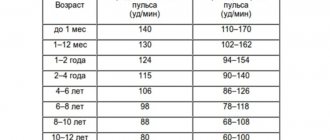
Normal heart rate indicators in this case can be divided into several periods:
- In a newborn . During this period, the child’s pulse is 120-140 beats/min. However, how long the child was in the womb is also taken into account. Premature babies have a faster heart rate.
- In a baby . By the first month of life, the baby's heart rate begins to gradually decrease. By 1 year, it is usually about 132 beats/min.
- In young years . The average heart rate at 2 years is considered to be 124 beats/min. However, at this age the child is very active, he is constantly on the move, and his emotional state can change frequently. Therefore, a heart rate in the range of 94-154 beats/min is considered normal. With such parameters, there is no reason to assume the presence of pathology.
- At a preschooler . At the age of 5-6 years, the pulse is considered normal at about 106 beats/min. Gradually, the heart rate stabilizes, as does the moral state of the child.
- At a schoolboy's. At 10 years old, the normal heart rate is 68-108 beats/min. However, at 7 years old the heart rate will be higher despite the fact that this is the same age category. It is recommended to consult a doctor to more accurately clarify the norm at this age.
A teenager's heart rate is the same as an adult's. On average, heart rate is 75 beats/min.
How to calculate heart rate for sports
The abbreviation HR stands for “heart rate,” in other words, it is the pulse. The easiest way to measure it is to place your finger on your wrist about 3-5 cm below the bend of the hand and count your heart rate for 15 seconds. Multiply the result by 4 to get the number of heartbeats per minute.
The same work can easily be done by modern fitness bracelets and smart watches. If you just started playing sports, these devices will help you track your daily activity and heart rate.
Measuring your pulse during exercise is very important: this allows you to understand how your heart reacts to physical activity and prevent overload.
In an adult, the resting pulse should vary from 60 to 80 beats. When under load, the norm is considered to be up to 200 beats - and the figure of 100-130 beats per minute belongs to the zone of moderate loads, during which fat is intensively burned. 130-170 beats per minute are already intense loads that are suitable for training the heart. Above are high-intensity workouts, which are stressful for the body. You can only exercise with such a pulse under the guidance of an experienced trainer.
Please note that your heart rate may be higher if you exercise in a stuffy room, get sick, or drink coffee shortly before your workout. In this case, monitor your well-being - the higher the pulse, the harder the load is tolerated.
Why does the heart need help when playing sports?
When determining the permissible load based on heart rate, only the gender and age of a person are usually taken into account, without taking into account the individual characteristics of the body. If, for example, you have never trained seriously, then loads, even at an acceptable heart rate, can cause oxygen starvation in the myocardium.
It will not be difficult to increase your heart rate to the maximum, but staying at this figure for 40 minutes (the recommended duration of cardio training) will not be possible immediately. The heart will beat faster, but the circulatory efficiency will be low. Fatigue and shortness of breath are signals of ineffective blood circulation. In this case, training through force is dangerous, since you can cause irreparable damage to the heart muscle.
But even if you are sufficiently trained and not tired, you cannot be completely sure that the heart is receiving enough oxygen. For example, with a heart rate above 160, you can feel quite normal, but your heart will suffer and be damaged.
With regular training, cardiologists recommend taking medications that improve metabolic processes in the myocardium, thus preventing heart failure. The optimal drug for this is Eltacin® , which consists of structural components natural to the body and is safe for long-term use.
The basis of Eltacin® is amino acids. They improve the absorption of oxygen by the myocardium and protect the heart even under high loads.
Blood pressure and sports
Normally, a person’s blood pressure should be approximately 120/80. But people who lead a healthy lifestyle may have lower blood pressure - for example, within the normal range, blood pressure is 100/60.
Sports are not contraindicated for people with hypertension - but they need to carefully monitor the level of stress and start exercising in a gentle manner. You can start with walking - first accustom yourself to walking more, then increase the pace. Later you can switch to running or swimming.
It is better to start training after consulting with your doctor.
IMPORTANT! If your blood pressure exceeds 190\110 at least periodically, if during physical activity you experience a burning sensation or pressure in the chest, intensive training, unfortunately, is contraindicated for you. But you can do static exercises, such as yoga.
Normal heart rate, permissible maximum heart rate
In a healthy middle-aged person, the heart rate at rest is about 65-75 beats/min. If we are talking about an indicator above 90 beats/min, then such a condition is usually called tachycardia (the heart beats faster). If the average heart rate drops below 60 beats/min, then this is a sign of bradycardia (the heartbeat slows down).
However, if we are talking about athletes, then for them at rest a heart rate of about 40 beats per minute is normal. Also, heart rate decreases during sleep, which is also considered normal.
However, if you wish, you can independently calculate the average maximum value of the pulse zone . To do this, you need to subtract your age from the number 220. For example, if a person is 35 years old, then it turns out 220 – 35 = 185.
That is, at this age, the pulse should not exceed 185 beats/min if a person plays sports. However, you need to understand that this is an average value that differs depending on numerous parameters.
It is worth considering that these calculations are only suitable for those who have been involved in sports for a long time. In addition, this is not the only method for determining the maximum permissible heart rate level.
There is another calculation scheme:
- For men . To obtain data on the maximum permissible heart rate, you need to subtract the man’s age from 214, and then multiply the resulting figure by 0.8. For example, 214 – 35 = 179, then 179 * 0.8 = 143 beats/min. That is, according to this scheme, at the age of 35 a man should not have a pulse above 143 beats/min.
- For women . Age must be subtracted from 209 and the resulting number multiplied by 0.7. For example, 209 – 35 = 174. Next you need to multiply 174 by 0.7, you get 121.8 beats/min. This is the maximum limit recommended for women aged 35 years.
You can also calculate the maximum permissible value even more accurately if you take into account not only the age, but also the weight of the person:
- For men . Must be subtracted from 210 ½ age. For example, 210 – 17.5 = 192.5. Next, you need to subtract 5% of the man’s body weight from the resulting number. That is, if he is 35 years old and weighs 100 kg, then it turns out 192.5 - 5 = 187.5. It remains to add 4, that is, 191.5 beats/min.
- For women . The calculation is the same, but you don’t need to add 4. That is, if a woman is 35 years old and her weight is 60 kg, then it turns out 210 - 17.5 = 192.5. Next 192.5 – 3 = 189.5 beats/min.
In this case, we are also talking about those people who play sports.
For a person who does not work out in the gym, the maximum heart rate usually does not exceed 100 beats/min. If your heart rate increases while doing housework or after climbing stairs, this is normal, but only if your heart rate returns quickly. The pulse during physical activity (the norm is calculated individually) and under other conditions may increase due to the following reasons:
- During sports training that is aimed at cardio loads.
- Because of fear or, conversely, intense joy. Also, the pulse increases in a stressful situation, if a person is very worried.
- If the body temperature has risen to 37 °C or higher or if the environment is very hot.
- Due to hormonal changes in the body.
It is noteworthy that in the morning the heart rate is calmer, and in the evening it increases.
It is also worth noting the so-called zones of activity severity:
| Zone of activity severity (how many beats/min) | Name | Under what conditions is it considered normal? |
| 50-60% (95-115) | Initial (warm-up area) | During an easy run. The training is aimed at strengthening the cardiovascular system. Breathing should be calm, the person can speak. This type of load is suitable for a beginner. |
| 60-70% (115-135) | Initial (activity zone) | More intense light running, during which fat is actively burned. This type of workout is also suitable for beginners and those who want to lose weight. |
| 70-80% (135-150) | Fitness (aerobic zone) | Exercises aimed at developing endurance. Breathing becomes more rapid, it is difficult to talk. |
| 80-90% (150-170) | Anaerobic (endurance zone) | Power training. This level of heart rate is allowed only for a prepared body. Otherwise, the condition is considered dangerous. There is redness of the face. It's almost impossible to talk. |
| 90-100% (170-180) | Red line (danger zone) | Endurance and speed training. Suitable for experienced professionals only. This type of training can only be done over a fairly long period of time. |
Charging at the workplace
Everyone knows that a sedentary lifestyle has a negative impact on health. It is not without reason that most office workers, who sit for up to 10 hours a day, have musculoskeletal diseases.
To prevent the development of illnesses, experts recommend doing a short warm-up at the workplace every two hours. It looks like this:
- First, pay attention to your neck. Slowly rotate your head back and forth, up and down. Repeat this at least 10 times.
- Then stretch your arms. Lift them up, clasp your palms together and stretch as high as possible. Next, make circular movements with your shoulders, 10 times.
- Pay attention to your wrists. Make 15 circular movements with your brushes.
- Stand on the floor and try to reach your palms to your feet without bending your knees. If it doesn't work, stretch as far as you can. Hold the position for 15 seconds.
- Sit on the edge of a chair with your legs extended in front of you without bending your knees. Keeping your back straight, pull your feet towards you and then back.
This complex must be carried out every 2-3 hours at work.
Who is prohibited from training?
If a person experiences severe discomfort after training, and it takes too long for the heart rate to recover, then it is worth reviewing the exercise regimen and switching to a simpler level of physical activity.
You should not engage in sports activities if you have cardiovascular diseases, cancer, or poisoning . Doctors also prohibit training for those diagnosed with hormonal disorders and disruptions in the central nervous system. If the pulse does not level out within 40 minutes. after completing the workout, this is a reason to visit a therapist and cardiologist.
For those who play sports, heart rate is an extremely important parameter.
Before starting training, during future physical activity, it is necessary to determine the maximum and minimum permissible heart rate values and only after that begin training.
Gradually, the body will become stronger and during training the pulse will be lower, closer to those indicators that are normal for a person in a calm state.
Calorie counting
If you want to not only become healthier, but also lose weight, it is important to pay attention to nutrition. Diet determines 70% of weight loss success. The most effective way to lose weight is to count calories. In order to accurately calculate them, you need to purchase a kitchen scale. It is convenient to use various applications for counting - they automatically calculate calorie content depending on the weight of the product. To maintain healthy and comfortable digestion, an adult should consume about 1700 kcal for women and about 2200 kcal for men. To lose weight, it is enough to reduce this number by 20%.
For active people
The most stable heart rate indicators are observed in people aged 15 to 50 years. If we talk about heart rate in athletes, there is no clear optimal value, since everything depends on the specific load.
During aerobic exercise, the heart rate is usually slower, and when running it can reach its maximum value. Heart rate also differs when swimming and cycling. To calculate the approximate parameter of an athlete’s maximum heart rate when running, it is necessary to multiply the person’s age by 1.03 and subtract the resulting number from 220.
For example, if the athlete is 30 years old, then it turns out 1.03 * 30 = 30.9. After this, you need to subtract this number from 220, you get 189.1 beats/min. However, during a normal workout that does not involve running, the maximum value is usually considered to be 180 bpm.
Thus, when running, an increased heart rate is allowed, but only in the case of a short exercise or if a person has been involved in sports for a long time and does not experience breathing problems while running.