The heart is one of the vital organs, so without it it would be impossible for a single person to exist. The structure, like the appearance of the heart, is quite diverse, but quite amenable to logical explanations. A correct understanding of what the human heart looks like allows you to sensibly assess the capabilities of the body as a whole.
The human heart is a hollow organ primarily composed of muscle fibers. Large vessels in the form of veins approach it, through which blood enters the cardiac cavities. After a regularly performed contraction, blood is released into the circulatory system through the aorta. A similar closed cycle is observed throughout the entire period of human existence.
Normally, in an adult, the heart contracts from 60 to 90 beats/min. During physical training or excitement, the heart rate increases, and during sleep or rest, the heart rate decreases.
The study of the appearance of the heart is directly related to the anatomy of the organ. Over the course of three centuries, various studies have been conducted that have made it possible to study many of the features of this amazing organ. Both outside and inside, the human heart looks very interesting and thoughtful, so it’s worth taking the time to learn unusual details about this organ.
Video Human Anatomy – Heart
Appearance of the fetal heart
The appearance of the heart depends a lot on the period of human development. For example, at the very beginning of fetal development, the heart looks like a tube, which in principle resembles a blood vessel. During the development of the embryo, the walls of such a formation thicken, as muscle fibers begin to actively form, which later become part of the structure of the myocardium. At the same time, the fetal heart has the opportunity to contract.
The first contractile activity of the heart tube is observed on the 22nd day after conception. At first it is weak, but gradually the strength of the contractions increases and after a couple of days blood begins to circulate through the blood vessels of the embryo. Thus, on the 28th day from the beginning of development, the fetus has a primitive blood supply system.
Correct formation of the heart during fetal development allows one to avoid many congenital diseases of this organ. That is why it is extremely important in the first months of pregnancy to avoid various nervous shocks, physical stress, the harmful effects of alcohol, smoking, medications, and infections, which often lead to various heart pathologies.
Interpretation of photo MRI images of the heart
The scans are black and white images of the anatomical area. The device takes pictures at intervals from 1 to 10 mm (depending on the equipment). Detailed and clear images are obtained using high-field tomographs with a power of 1.5 Tesla or more.
Image interpretation requires knowledge of anatomy and MR semiotics of pathologies. Heart functions are described in the form of indices and indicators that should be studied by a cardiologist. Depending on what the MRI of the heart shows, a conclusion is drawn up. The scanning protocol describes the main parameters of the organ and notes signs of pathological changes. Finally, the information is summarized. When presenting the results to the patient, the radiologist can briefly explain the situation. For more detailed information, please contact your doctor.
Scanning the cardiovascular system requires special equipment capabilities, so it is not performed in all diagnostic centers. Whether MRI of the heart and blood vessels is performed in a particular institution, you need to find out in advance. At the Magnit DC, scanning of this organ is not carried out. Any questions you may have can be clarified by phone.
What does an adult's heart look like?
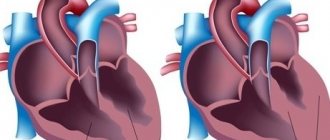
When externally examining a formed and fully developed human heart, one immediately notices an expanded part, or base, and a narrowed part, or apex. The edges of the heart also differ from each other: the left one is more blunt, and the right one, on the contrary, is pointed. The grooves located on the surface of the heart indicate the boundaries within the cavities. The grooves themselves are often covered with fatty tissue, which in pathological cases (with obesity or fatness) is determined throughout the entire musculature of the organ, which does not allow it to function fully.
In a normal state, the weight of the heart averages from 250 to 350 g. In this case, the length of the organ is equivalent to an average of 12-13 cm, width - 9-10 cm, and transverse size - 6-7 cm.
The heart resides and contracts throughout its life in the pericardium, the pericardium. Its role is to protect the heart from other organs. Also in the pericardial sac there is a certain volume of fluid, which in normal condition acts as a “lubricant”, which allows the heart to work smoothly.
In the chest, the heart is located asymmetrically, so outwardly it looks like this: 2/3 of the organ from the center line is to the left, and 1/3 to the right. Also, relative to the longitudinal projection, the heart can have different positions: horizontal, vertical and oblique.
Video How the human heart works
The anterior part of the heart mainly refers to the right ventricle, compared to which the left ventricle is directed posteriorly. Also in front is the right atrium and the adnexal cavity, called the appendage, covering the ascending part of the aorta, is especially noticeable. From the front, the left atrium is almost invisible, while the smaller appendage is in greater contact with the pulmonary trunk.
Preparing for cardiac MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging does not require special organizational measures on the eve of scanning. Before a cardiac MRI, there is no need to follow a diet, stop or take any medications.
Women of reproductive age should make sure that there is no pregnancy (the procedure is contraindicated in the early stages). The best option is to take a blood test for hCG or undergo a urine test. After week 13, native (without contrast enhancement) cardiac tomography can be performed.
Persons with metal implants (endoprosthesis, vascular clips, pins, etc.) will need to obtain a document on the compatibility of the product with a magnetic field. A passport or an extract from the medical institution where the structure was installed will do. After vascular stenting, MRI can be performed no earlier than six months later. The time of the operation must be confirmed with the appropriate certificate. The presence of a pacemaker, defibrillator or other electronic device is an absolute contraindication to MR scanning of any anatomical area. Devices may stop working under the influence of the magnetic field of the tomograph.
It’s worth organizing a light snack 40-45 minutes before leaving the house. Yogurt, a small sandwich or fruit, or an egg will do. This measure will allow you to avoid the manifestation of vegetative reactions (nausea, vomiting, dizziness, etc.) to the drug.
Women supporting lactation can undergo MRI. But you need to purchase formula for the baby in advance or stock up on expressed breast milk for 2-3 times. Natural feeding can be resumed 6-12 hours after contrast administration.
Children undergo MRI if they remain motionless during the scan. If the child is not able to lie for 20-30 minutes in one position, tomography is performed under anesthesia in a hospital setting or an alternative method is found.
Heart from the inside
A longitudinal section of an organ provides an opportunity to see its structure from the inside. The main components of the heart are chambers or cavities, which are separated by partitions. Each portion of blood enters or exits from certain vessels:
- blood from the vena cava is sent to the right atrium;
- the pulmonary veins approach the left atrium;
- arterial blood flows from the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk (pulmonary circulation);
- from the left ventricle the blood passes into the aorta (the systemic circulation begins).
Thus, it turns out that the pulmonary circulation originates from the right ventricle and ends at the left atrium. The systemic circulation of blood accordingly begins with the left ventricle and ends with the right atrium.
In addition to the chambers of the heart, the longitudinal section shows valves, which are necessary to ensure normal blood flow. These structures of the heart open only in one direction and, as a rule, blood should not pass between the valves either. For precise differentiation, each valve is given its own name:
- mitral - has two valves and is located between the atrium and the ventricle on the left side;
- tricuspid - is tricuspid and is located on the border between the atrium and the ventricle on the right side;
- pulmonary valve - controls the flow of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk;
- aortic valve - regulates blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta.
The coronary arteries pass around the heart and provide coronary blood supply. They look like a crown, which is why they got the name “coronary arteries”.
Diagnosis and treatment of coronavirus in children
Taking into account the fact that coronavirus in the average child occurs as an acute respiratory viral infection or without symptoms at all, we note that the disease can only be detected using laboratory blood tests: a PCR test or an immunoglobulin test (considered more accurate).
If a child is bothered by symptoms of an acute respiratory illness (cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing), it is necessary to do a computed tomography scan of the chest to check the lungs for inflammatory foci and exclude pneumonia. An auxiliary method of analysis will be pulse oximetry, which shows the percentage of saturation - oxygen saturation of the blood. If the rate drops to 95%, then the child may need hospitalization with oxygen support. The higher the pulse oximetry reading, that is, the closer to 100%, the better.
In Russia and abroad, the main points of pediatric therapy for coronavirus are: drug treatment (antibiotics if a bacterial infection has been added to a viral infection and in the absence of contraindications), inhalations, nutritional correction, maintaining the balance of fluids, electrolytes, oxygen (if necessary). The treatment plan is determined by a pediatrician.
Unusual Facts About the Heart
- The heart rate in a fetus is several times higher than in an adult, and is approximately 140 beats/min, while after 10 weeks the volume of circulating blood is equal to 60 l/day.
- In an adult, the heart rate is approximately 72 times/day, so over the course of approximately 65 years, more than 2 million heartbeats are detected.
- The total length of all blood vessels is more than 120 million meters, which allows you to circle the Earth three times along the equator.
- Blood vessels also pass through adipose tissue, and with obesity, the heart has to pump blood through vessels more than 8 thousand kilometers long.
- One cycle of blood supply lasts approximately 23 seconds and is approximately the same time it takes a person to run 200 meters.
- In one cubic milliliter of blood, there are about 5.5 million red blood cells, which are also called red blood cells. It takes 120 days to fully update them.
- Heart disease is the most common cause of human death. It has been proven that cardiovascular diseases have claimed more lives than all the wars in the entire history of mankind.
Video 10 unknown facts about the human heart. I Vam Science
4.80 avg. rating ( 94 % score) – 5 votes – ratings
Heart diseases
The heart is exposed to many negative factors throughout its life, which makes it susceptible to various diseases. For many years, cardiovascular disease was the leading cause of death, much more dangerous than cancer.
Cardiac ischemia
Coronary heart disease - otherwise coronary heart disease - is a chronic disease caused by hypoxia of heart muscle cells, leading to its failure. This is mainly caused by:
- atherosclerosis (an insidious disease in which excess cholesterol and other lipids are deposited on the walls of the arteries),
- less commonly, blockage, narrowing or underdevelopment of the coronary arteries,
- some injuries
- or after carbon monoxide poisoning.
Coronary artery disease is also called angina because its symptoms include severe pain and shortness of breath in the chest during exercise. The pain can spread (most often on the left) to the arms, hands and even jaws.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction, also known as heart attack, is necrosis of the heart muscle caused by ischemia. This is caused by the closure of the coronary vessel that carries blood to the heart.
Previous coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis are the cause of myocardial infarction in more than 90% of cases.
Myocardial infarction is usually sudden, severe, and manifests itself with severe pain in the chest area. Patients also complain about:
- feeling of shortness of breath,
- breast expansion,
- nausea
- and vomiting.
A heart attack is a very serious disease with a high mortality rate, often leading to many complications and can permanently damage the heart as a pump.
Heart attacks are being diagnosed in increasingly younger people, mostly men under 45, burdened by stress and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Cardiac arrhythmia
Heart rhythm disturbances - so-called cardiac arrhythmias - are a large group of disorders that can be divided into 2 types:
- Supraventricular arrhythmias (such as atrial fibrillation, nodal or atrioventricular tachycardia)
- and ventricular arrhythmias.
Supraventricular disorders are usually found in people without additional heart disease and may be a risk factor for future cardiovascular disease (such as stroke).
Ventricular arrhythmias (including additional ventricular contractions, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia) are, in turn, very serious diseases, usually associated with the need to call an ambulance and treatment in a hospital.
There can be many causes of arrhythmias: from complications of coronary heart disease to acquired and congenital heart defects, genetically determined diseases of the conduction system or arterial hypertension.
Arrhythmias can manifest themselves, for example:
- palpitations and tachycardia (i.e. heartbeat too fast)
- feeling short of breath
- dizziness
- fainting.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis - unlike the previously mentioned diseases - this disease occurs as a complication of past infections:
- viral (such as influenza, chickenpox, or rubella)
- or bacterial (staphylococcal, salmonella or pneumococcal infections).
- In young people, this inflammation may also have an autoimmune basis.
Symptoms accompanying this disease:
- rapid fatigue during any physical activity,
- dyspnea,
- heartbeat,
- heat.
Untreated heart inflammation can cause fibrosis to replace normal cells, leading to a significant reduction in heart muscle performance.
Valve defects
Valve defects are a congenital or acquired disease (for example, after severe infections). The most common types of valve defects include:
- valve stenosis - when a narrowed blood outlet makes it difficult for blood to pump properly,
- and valvular regurgitation, which leads to “leakage” of blood and its outflow.
Due to valve defects, the heart works harder and harder, and the disease worsens. Symptoms may include:
- dyspnea,
- chest pain,
- dizziness
- or swelling around the ankles and feet.
Accessory chord: symptoms
A person can comfortably live their entire life with additional chordae, unaware of their existence. Most often they do not cause any sensation. But sometimes patients may notice the following symptoms:
- fast fatiguability;
- periodic manifestation of fatigue;
- pain in the heart area;
- headache;
- rapid heartbeat (the heart “jumps out”), especially during excitement or conflict.
The described symptoms do not necessarily indicate the presence of a chord, since they may be associated with other causes. Therefore, to accurately determine the cause, it is necessary to undergo professional diagnostics.
MEDICAL CENTER
- home
- Information
- Articles
- THE HEART IS MORE THAN JUST AN ORGAN
>
>
>
THE HEART IS MORE THAN JUST AN ORGAN
Nowadays it is hardly possible to find a person who perceives the heart simply as an organ that pumps blood. Many people know, and if they don’t know, then they guess that the heart is an emotional organ directly connected to the “emotional brain.” Can the heart also be an “intellectual” organ? Is the heart directly connected to our brain?
According to a study published in 2001 in the Journal of Medicine by Mark Newman, memory, attention, and concentration are slightly reduced immediately after bypass surgery. A similar decline was observed five years later. This means that the shunt can affect blood flow to the brain. It turns out that there is a direct connection between the heart and the brain through blood circulation. Researchers at the Institute of Heart Mathematics also argue that the heart plays an important role in the functioning of human intelligence, emotions and personality.
According to existing ideas, it is the heart that is associated with intuition, love, creativity, wisdom, gratitude, faith and other similar human feelings. The best human qualities are associated with the heart, and not with the mind. How do we know all this? We know this because we feel all these emotions in our hearts. Are there any scientific explanations for all this?
The heart physically “communicates” with the brain and the rest of the body, and these communication pathways are through the part of our brain responsible for emotions, and also pass through the parts of the brain responsible for thinking and reasoning processes. The heart has a complex nervous system capable of remembering and storing information.
The impulse produced by the heart is transmitted with a wave of blood pressure. This impulse reaches and energizes every cell of our body and brain.
The heart also emits powerful electromagnetic energy.
It penetrates every cell of our body, including every cell of the brain. The strength of the electromagnetic signal coming from the heart is so strong that it passes through the skin, extends around 360 degrees, and approximately 3 meters in the space around us. No other organ has such great electromagnetic force.
The heart is also a “hormonal organ.”
Along with some other hormones, the heart also produces the so-called “balance hormone”, which ensures the balance between hormones. The heart also produces oxytocin, the famous “love hormone” that appears when a person is in love.
"Love Hormone"
The “love hormone” plays an important role in our emotional and social development. For example, oxytocin is released when a mother feeds and nurtures her baby. Kindness, caring, love, appreciation, gratitude, forgiveness and other behaviors that are products of family and society can have a lot to do with how well the heart functions on the physical, emotional, mental and spiritual levels.
So why do you need all these scientific facts about the heart?
In order for you to appreciate even more what you have, and for you to become even more motivated to monitor and care for this amazing “mechanism” called the heart, which was gifted by nature.
Intelligence without heart is a dangerous thing. Making decisions without involving the heart is risky. There are a lot of really smart but heartless people in the world. But their short or long lives are of little use. The brain is capable of creating a nuclear bomb, but creating ways to utilize energy or process waste for the benefit of people still requires the intervention of the heart.
Expressions such as “Open your heart” or “My heart is with you” can be more than symbolic. Some people who began to visualize their heart opening to others began to feel much calmer and more confident.
Monitor your heart health in one of the best cardiodiagnostic centers www.cardianmed.by. We take care of your health and value your time. Contact us by phone: 8 (029) 670-33-45.