Every woman’s body is individual, especially when it comes to hormonal levels. Therefore, the menstrual cycle, period and amount of bleeding are different. On average, the maximum duration is 5 days. If sudden changes occur, the presence of abnormalities or diseases is assumed. Diseases of the genitourinary organs may occur, leading to bleeding similar to menstruation. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo examination by a gynecologist or urologist to determine the cause of the symptoms.
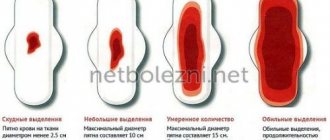
The nature of discharge during menstruation
The normal duration of the menstrual cycle is 22-35 days. With the advent of menstrual periods, many women complain of malaise, headache, abdominal cramps, weakness, and drowsiness. This is completely normal and does not pose a health risk. However, sometimes heavy discharge with the onset of menstruation should be a reason to find out the true reasons. Especially if they have changed in character, color, or come off completely differently than before.
You should take a closer look and be wary if the following symptoms appear:
- blood flows out continuously, without clots;
- a specific smell and particles of pus appeared;
- The discharge acquired a more liquid consistency and increased sharply in volume.
So how can you distinguish uterine bleeding from menstruation? The fact that bleeding occurs long before the next menstruation or lasts for a more usual number of days cannot be ignored.
Many women do not know how to distinguish normal from pathology. How can you tell if it’s sudden implantation bleeding or heavy periods? Implantation usually occurs mid-cycle. As the egg is fertilized, it begins to penetrate into the uterine cavity, slightly damaging the mucous membrane. However, this occurs infrequently, in only 30% of women. You can determine the differences between menstruation and uterine bleeding yourself. So how can you tell the difference? According to the following characteristics:
- Color. In case of implantation, the color of the discharge is initially pink, gradually changing to brown.
- Duration 3-4 hours. Basal temperature is below 37 degrees, then there is a sharp increase to 37.5°. These are normal indicators during pregnancy in women.
- Signs. You can tell by the painful sign. Implantation does not lead to much pain, while during menstruation the lower abdomen often hurts greatly. It is worth noting that there should be no other discharge during fertilization. Otherwise, the reasons: placental abruption, rupture of the fallopian tube, ectopic pregnancy, placenta previa, and this is a mortal threat to the fetus.
The danger comes from prolonged but scanty discharge with small portions of blood. This is fraught with the development of anemia, especially if additionally observed:
- dizziness;
- thinning, brittle nails;
- constant lethargy, drowsiness;
- fast fatiguability;
- discharge of unusual light discharge;
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood.
If negative signs appear, you need to sound the alarm, contact doctors for advice, and conduct a full examination.
Poor blood flow during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is extremely important to continuously monitor the state of the maternal body of the mother and the baby, it is important that they perform all vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as cerebral vessels and the fetal aorta. The main causes of perinatal morbidity and mortality include disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow of 1A, 1B, second and third degrees.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies the embryo with nutrients, as well as oxygen from the mother’s blood; it also removes waste products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two rather complex vascular systems - the female, which connects the vessels of the uterus and placenta, and the fetal, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the child.
The circulatory systems mentioned above are separated by a membrane, which does not allow maternal and child blood to mix. The placenta is a kind of barrier that is resistant to numerous harmful substances, as well as viruses.
Often, for completely different reasons, placental insufficiency may appear, which inevitably affects the performance of transport, metabolic, trophic, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the maternal and child organisms deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with various consequences.
What are the causes of impaired placental blood flow?
Poor circulation in the uterine cavity can be caused by pneumonia, increased blood pressure, various intrauterine infections, as well as insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body (hypoxia).
To diagnose the blood flow system in modern obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound (so-called Doppler ultrasound) is used, with which the vessels are visible in a 3D (three-dimensional) image. With the help of this diagnostic technique, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. This technique is irreplaceable, since with its help it is possible to examine defects even in the most microscopic vessels that form the microvasculature, to observe the peculiarities of the formation and development of intraplacental hemodynamics, and in addition to control the amount of nutrients, as well as oxygen, that should enter the fetal body . New prospects have opened up for the early detection of obstetric complications, and if treatment or correction is started without wasting time, then circulatory disorders and subsequent pathologies associated with it can be almost completely avoided.
Hemodynamic disorders during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disorders are divided into 3 degrees of severity:
1. 1st degree includes two subtypes:
- disturbance of patello-placental blood flow 1Is the mildest. Fetal-placental blood circulation is preserved with it. Intrauterine infections often lead to this problem;
- in degree 1B, uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, but fetal-placental pathologies appear.
2. Grade 2 is characterized by the presence of disturbances in both blood flow systems, however, these disturbances do not carry any fundamental changes. 3. In grade 3, uterine circulation disturbance causes defects in normal blood circulation at the level of the fetus.
In the case of the first degree of violations, timely detection and adequate treatment can avoid fetal death. In the case of the second degree, perinatal mortality is about 13.3 percent, in the case of the third - 46.7 percent. During Doppler diagnostics, it was revealed that treatment aimed at correcting placental insufficiency in women with third-degree uterine blood flow disorders was ineffective. In this situation, with conservative childbirth, perinatal mortality was 50 percent, then, thanks to a cesarean section, losses can be avoided. 35.5 percent of newborns are admitted to the intensive care unit with grade 1 blood flow disorders, 45.5 percent with grade 2, and 88.2 percent with grade 3.
The difference between menstruation and pathological bleeding
Many young girls or women in labor for the first time ask how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding that appears after childbirth. When lochia begins to recede during the postpartum period, lasting up to 4-5 weeks, this is a normal phenomenon. Further, in the case of breastfeeding, the discharge should gradually acquire a brownish tint, begin to decline, or stop altogether. Normal signs:
- discharge of red-scarlet discharge of a slightly rusty brown hue without foreign impurities or odor;
- absence of blood clots or their insignificant content in the lochia.
If, however, unpleasant signs appear after observing the nature of the discharge, then you should see a gynecologist. It is important for women to distinguish implantation bleeding from pathological bleeding in time. During examination, it is recommended to pay attention to the amount of blood lost and the duration of discharge. During pregnancy they should not be long and abundant. It is normal to stop after 2-3 hours.
IMPORTANT! The following signs will indicate serious blood loss during uterine bleeding:
- frequent replacement of gaskets every 1-2 hours;
- duration of discharge for more than 7 days in a row;
- the appearance of abundant blood clots;
- a sharp deterioration in health;
- temperature increase;
- the presence of weakness, fatigue, vomiting, nausea, pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of blood particles after sexual intercourse;
- signs of anemia;
- paleness of the skin;
- hair thinning.
Blood loss is an alarming harbinger of anemia, so to avoid complications you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. For example, infection of the uterine cavity can lead to infertility.
Other types of bleeding that can be confused with periods
There are several types of pathological bleeding:
- Profuse, accompanied by copious bleeding, which is dangerous for infection with microbes and the development of anemia. The phenomenon is often observed in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
- Juvenile bleeding, which occurs in adult women or girls during puberty with the appearance of signs of vitamin deficiency.
- Breakthrough bleeding before menstruation if an intrauterine device is installed or a number of contraceptives are taken.
- Dysfunctional, characterized by severe blood loss, can appear in women at any age. There is a failure of the functions of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and ovaries. Provoking factors: sudden climate change, endocrine system disorders, overwork, constant stress.
On a note! The symptoms should not be ignored: the appearance of heavy bleeding between periods, fatigue, fatigue, pale skin, thinning hair, pain during sex. Most likely, women need to undergo a complete examination of their reproductive organs. It is worth understanding that there should be no side signs during menstruation, and heavy bleeding leads to anemia, including loss of consciousness.
Profuse bleeding is especially dangerous, and it happens with oncology, the development of a tumor in the body. In this case, the woman may be hospitalized for the purpose of curettage of the uterine cavity.
Diagnostics
At the international clinic Medica24, a full range of diagnostic tests is carried out to determine the cause of bleeding and provide the necessary treatment.
Examination, history taking
The gynecologist questions the patient in detail about the nature of the symptoms, the circumstances of their occurrence, the regularity and duration of menstruation, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the use of medications.
After this, he conducts an examination in a gynecological chair.
Laboratory research
General and biochemical blood tests show the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, estrogens, progesterone, prolactin, cortisol, estradiol, LH, FSH, thyroid hormones (T3, T4, TSH), thyroxine.
A coagulogram shows blood clotting.
If polycystic ovary syndrome is suspected, the levels of glucose, insulin, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate are examined.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound examination of the pelvis shows the structures of the uterus, ovaries, and helps to detect neoplasms (polyps, fibroids, carcinomas, etc.).
Hysteroscopy
A visual examination of the uterus is carried out using a miniature video camera - a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the vagina. Hysteroscopy makes it possible to study the uterine walls in detail, detect neoplasms, and also take samples of tissue from the mucous surface and tumors for histological examination.
Histological examination is the examination of a tissue sample under a microscope. With its help, you can confidently determine the type of tumor, distinguish benign tumors from malignant ones, and diagnose cancer.
MRI
If additional information is needed, magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvis is performed.
Additional Research
The cause of blood discharge may be hormonal imbalance, disruption of the endocrine system, in which the hypothalamic-pituitary system plays a key role. This may require additional examinations, such as:
- CT scan of the brain.
- Echoencephalography.
- Electroencephalography (EEG).
- MRI of the brain.
An ultrasound of these organs can be performed to assess the condition of the thyroid and adrenal glands.
Reasons for education
Women need to learn in time to distinguish between implantation bleeding and menstruation. Various factors that lead to disorders in sexual life, the appearance of unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse, and the main causes of this condition can provoke heavy discharge that is not associated with planned menstruation:
- the arrival of menopause;
- development of a benign (malignant) neoplasm in the uterine cavity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- ovarian diseases;
- pregnancy;
- birth process;
- endometriosis;
- blood clotting disorder;
- abuse of hormonal drugs;
- blood diseases that favor increased bleeding.
The main difference between heavy bleeding and menstruation is heavy blood loss of a light red or deep pink hue, associated with malfunctions of the reproductive organs, leading to the development of iron deficiency anemia and other unpleasant consequences. To understand how to distinguish pathological bleeding from menstruation and what the consequences may be, you must definitely visit a doctor if the following signs appear:
- discharge of heavy discharge lasting more than 10 days in a row;
- the appearance of particles of pus and mucus in the composition of lochia;
- temperature increase;
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- the presence of a feeling of thirst, dry mouth.
Attention! There is an urgent need to find out the causes of profuse bleeding that appears accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen or the onset of protracted menstruation.
Bleeding due to uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial and cervical canal polyps
Uterine fibroids, endometriosis and polyps and endometrial hyperplasia are diseases associated with benign growth of uterine tissue. They appear most often during reproductive age.
All this pathology is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. As a rule, no additional examination methods are required. You can read about possible treatment options for uterine fibroids in the corresponding section of the website www. ya-zdorova.ru. In the presence of pathology of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy with the appropriate amount of surgical intervention is indicated to eliminate the cause of bleeding.
Doctors' opinion
Doctors advise women to learn how to distinguish periods from implantation bleeding at home without undergoing tests. So, uterine bleeding with the onset of pregnancy carries a threat of miscarriage and you need to urgently contact a gynecologist. It is important to identify in time the bleeding that has begun, to monitor how and in what portions it leaves, or whether it began during menstruation. It is also important to be able to correctly provide first aid before the ambulance arrives in the event of heavy, profuse blood loss. So, you need to do the following:
- place the patient in a comfortable position;
- slightly raise the pelvic area by placing a pillow;
- apply a cold compress to the lower abdomen to narrow the vessels of the uterus;
- open the window and ventilate the room.
Treatment of bleeding directly depends on the provoking factors that lead to decreased blood clotting and signs of anemia. It is important for women to take care of their health:
- do not lift heavy objects;
- dose physical activity;
- review your diet and include foods high in iron;
- relax more, walk in the fresh air;
- refuse to visit the steam room, sauna, hot bath;
- do not drink alcoholic drinks or strong coffee;
- apply ice to the lower abdomen when there is blood discharge, but for 15 minutes, no more, in order to avoid colds;
- respond in time to the appearance of pathological discharge, especially when accompanied by pain, pain, ichor, pus, and an unpleasant odor.
First aid methods
As soon as spotting occurs, the following rules must be used:
Advertising:
- ban on any physical activity;
- exclusion from the diet of meat-type foods and iron-rich foods (beets, pomegranate, beef liver);
- lying down with the pelvis slightly elevated to eliminate the abundant blood flow to the reproductive organs (to do this, you can place a pillow under the pelvis, put your feet on a wall or sofa);
- applying a towel or heating pad to the stomach that has been supplied with cold water (this will help narrow the blood vessels and reduce blood flow).
The symptoms that appear cannot be ignored. It may be the first sign of a serious illness that needs to be treated promptly. If bleeding occurs in a pregnant woman, urgently contact a clinical facility so that she does not die or lose the child. It is important to know the difference between menstrual blood and bleeding, this will help identify abnormalities at an early stage.
Results
Blood loss is dangerous due to the development of anemia. To understand how to determine the permissible volume of blood released, it should not exceed 80-90 ml per day. Uterine bleeding can be caused by difficult childbirth, hormonal imbalance, or menopause in women. The main and distinguishing symptom from menstruation is the continuous discharge of bright scarlet blood for more than 7 days in a row with a protracted course. What is this? How to determine menstruation or bleeding? Of course, postpartum lochia can take quite a long time to go away. But they also have a certain color, should be quite moderate and not cause any particular discomfort. Women need to pay attention to the frequency of replacing pads and the duration of bleeding. If bleeding continues continuously for more than 7 days, it becomes protracted, which is already dangerous and it is probably best to seek advice from experienced doctors.
What can you do at home to ease heavy periods?
- If you are in pain, take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. You can also apply a heating pad to your stomach—the heat eases cramps.
- Iron-rich foods and iron-containing supplements can help ease heavy menstruation and cope with iron deficiency in mild forms of anemia.
- Foods rich in iron include beef, liver and other offal, turkey, spinach, fish, pumpkin seeds, dried apricots, white beans, cocoa beans, and champignons. It also makes sense to increase your vitamin C intake because it helps with iron absorption. A lot of vitamin C is found in kiwi, bell peppers, strawberries, citrus fruits, broccoli, tomatoes, kohlrabi, pineapple.
- Drink enough water.
If you have heavy bleeding for several days, your blood volume may decrease significantly. Drink 4-6 extra glasses of water to maintain your blood volume.