There is probably no person in the world who has never experienced external bleeding in their life - for example, from careless handling of a knife when cutting food or from an unfortunate fall from a bicycle that ends in broken knees. The rules of first aid in such situations are simple and well known to everyone. You need to disinfect the wound and stop the bleeding with a bandage or plaster. And if a large vessel (artery) is hit and blood spurts out, then it is necessary to clamp the vessel above the wound site to avoid large blood loss.
Obviously, any bleeding occurs due to the fact that the integrity of the blood vessels is disrupted. Blood stops circulating in the closed space of the vessels and flows out of them. If the integrity of the uterine vessels is compromised, blood flows out through the vagina. It is this external sign that is the reason to suspect something is “off” and consult a doctor.
Uterine bleeding is a symptom of many diseases. These may be gynecological or oncological diseases, as well as complications of pregnancy and childbirth.
In case of uterine bleeding, it is very important not so much to stop the blood loss - this, by the way, is not always the first priority measure - but to identify the cause of the bleeding and, if possible, eliminate it. If this is not done, then there is a high probability of relapse and other manifestations of the disease, as well as its complications. Manipulations aimed at stopping bleeding are carried out in cases where the process of blood loss occurs at a high rate - in this case there is a direct threat to life. After the bleeding has been eliminated, in addition to treatment, restorative procedures must be prescribed: regimen, nutrition, maintaining water balance in the body, vitamin therapy.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is bleeding associated with dysfunction of organs, in the absence of any organic pathology (uterine fibroids, internal endometriosis, pathology of the cervix, tumors of the uterus and ovaries).
Ovarian dysfunction is caused by a violation of their hormonal function and occurs quite often. Many women take this disease lightly and do not see it as a direct threat to health. In addition, there is a very common opinion that dysfunction is just a minor malfunction of the body, with which you can live safely, but it is useless to treat it. This approach is fundamentally wrong. Firstly, ovarian dysfunction may be a manifestation of some deep hormonal imbalances that require certain correction. Not to mention that it is unlikely that you will be able to “live well,” because dysfunction is almost always accompanied by physical and moral discomfort and pain. A woman is forced to constantly use analgesics, the body gradually gets used to them, the pain intensifies again... It turns out to be a vicious circle.
The main symptom of dysfunctional bleeding is irregular menstrual cycle. The reason to consult a doctor is when the interval between menstruation is less than 21 days and more than 35 days. It is also not considered normal if:
- menstruation lasts more than 7 days;
- menstrual bleeding is very heavy, a woman is forced to change pads or tampons every hour, including at night;
- Menstruation is accompanied by severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
If such symptoms recur over three or more menstrual cycles, then you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Endocrine causes are not always the cause of dysfunction. The functioning of the ovaries can also be affected by factors such as:
- overweight or underweight;
- diabetes;
- frequent stress and depression;
- infectious diseases (flu, pneumonia, sore throat);
- strict diet and fasting;
- genital infection;
- sudden climate change.
Therefore, when going to see a doctor, be prepared that he will ask you questions about your diet, nervous stress, previous diseases and changes in the climatic environment.
Diagnosis of ovarian dysfunction includes a gynecological examination, smear analysis, blood test for hormones, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pelvic organs. The doctor may also prescribe magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and separate diagnostic curettage of the uterus.
Treatment is selected individually in each case. First of all, it is aimed at normalizing hormonal levels and correcting lifestyle. In any case, the doctor tries to choose the most gentle therapy. In cases where adolescents or premenopausal women suffer from dysfunction, it is often enough to reduce the level of tension, review the diet and allocate time for active rest and good sleep. The body reacts sensitively to changes that are favorable to it and successfully self-regulates without drug treatment.
We care about your health
The reasons why a woman may experience bleeding from the uterus, vagina or other part of the reproductive tract, which prevail in different age groups, are different. Regardless of age, their danger lies in the occurrence of anemia (anemia), if blood loss is large enough and bleeding occurs regularly. If a woman is not pregnant and is not in labor, then the following types of bleeding can be distinguished, the source of which is the uterus:
- Dysfunctional bleeding in girls - occurs at a young age, a little after menarche, due to hormonal disruption of the ovaries
- Dysfunctional bleeding in women of reproductive age requires increased attention from a doctor, as it can serve as a harbinger of infertility.
- Menopausal bleeding occurs as a result of hormonal changes in the female body and may indicate a proliferative process, both benign and malignant. Most often it is benign: the appearance of polyps, myomatous nodes due to hyperestrogenemia (excess of the female sex hormone estrogen)
- Bleeding that occurs in postmenopause occurs some time after the onset of menopause, during which there was no bleeding from the genital tract. They may be a symptom indicating the process of tumor formation in the female reproductive organs.
- Postcoital bleeding is a special type of uterine bleeding that occurs after intercourse. It can be based on different reasons, both formidable and not posing a danger to a woman’s health.
Based on the moment at which bleeding from the genitals was detected, they can be classified into menorrhagia: this is the name for bleeding that coincides with menstruation, but the volume of blood lost clearly exceeds normal; as well as metrorrhagia: such bleeding does not coincide with the beginning of the menstrual cycle, but is noted by a woman before or after her menstrual period.
It is also worth noting three conditions that require immediate, urgent, prompt seeking of medical help
- A) Bleeding from the genital tract that occurs during pregnancy. It is important to note that such bleeding can rapidly increase in speed and lead to serious complications for both the fetus and the expectant mother.
- B) Bleeding that does not stop for a long time, which is accompanied by symptoms of anemia. The latter include pallor of the skin, decreased blood pressure, dizziness when trying to stand up or even sit down, constant headaches, a rare and weakened pulse in the radial arteries (on the wrist), and fainting.
- B) Internal bleeding. You should think about it if the bright symptoms of anemia are combined with the absence of visually recognizable blood discharge from the genital tract, especially if the patient also has a feeling of severe pain in the abdomen, and its anterior wall is very dense to the touch, board-shaped.
Uterine bleeding in women during the reproductive period
Many women suddenly notice bloody vaginal discharge that occurs between periods, or an excessive increase in the latter. If spotting, a small amount of discharge occurs at the time of ovulation (the release of an egg from a ruptured ovarian follicle), usually on the 14-18th day of the cycle, depending on its duration for a particular woman (28-32 days), then this should be considered normal . However, severe sudden bleeding should alert a woman, as it may indicate a gynecological pathology. If metrorrhagia that suddenly arises intensifies or simply does not end for a long time, then you need to consult a doctor who will stop the bleeding and also prescribe the necessary examinations to understand the reasons for its occurrence.
In addition to ovulation, the cause of uterine bleeding that occurs between two adjacent menstruation can be sudden changes in the amount of the female sex hormone estrogen in the blood, which is produced by the ovaries, any pathological process in which can cause the above-described manifestation. In addition, the basis of such metrorrhagia may be the end or beginning of the use of hormonal contraceptives, a significant decrease in the level of thyroid hormones, the use of emergency contraceptives, as well as other medications that somehow contain estrogen. In addition, bleeding between menstruation may be due to an infectious, tumor process of the genital organs or trauma, miscarriage, or the consequences of recent gynecological manipulations.
Treatment of the bleeding described above is prescribed according to the main reason due to which they occurred. If metrorrhagia is caused by a gynecological disease, then properly selected treatment for this disease will also stop bleeding.
Uterine bleeding in young girls
Bleeding from the genital tract that occurs in girls aged 12-18 years is called pubertal or juvenile. If such bleeding is severe, then there may be a threat to the health and life of a teenage girl, and therefore it is necessary to quickly consult a doctor who can prescribe adequate treatment so that this bleeding does not progress into the reproductive period, in which, in this case, it will increase danger of infertility for this patient. Quite often, juvenile metrorrhagia occurs in the winter-spring period due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the girl’s body. Often the main cause can be stress, infectious processes or unhealthy diet. Most often, in the puberty period, bleeding in girls occurs after menstruation has been delayed (several weeks), and lasts more than seven days, sometimes increasing in intensity, sometimes decreasing, which can ultimately lead to large blood loss and anemia. This process needs to be stopped, and therefore it is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist immediately.
At the same time, both sudden and severe bleeding and prolonged and sluggish bleeding can lead to anemia. The symptoms of anemia are similar regardless of the cause that caused it: pale skin, weakness, dizziness when trying to sit or stand, drop in blood pressure, short-term loss of consciousness.
If a girl stops metrorrhagia on her own, she still needs to see a doctor, since the goal of treatment, in this case, will be to prevent anemia and a terrible complication - hemorrhagic shock.
Menopausal uterine bleeding
It is impossible to ignore the discharge of blood from the genital tract during menopause, as it can be a symptom of a pathological process, even uterine cancer. For many women, menopause is quite difficult. Along with uterine bleeding, surges in blood pressure, mental disorders, and metabolic disorders can occur.
Typically, the cause of menopausal bleeding from the genital tract is massive hormonal changes in a woman’s body, but they can also indicate tumor growth. Menopausal bleeding can be classified into:
- Metrorrhagia in premenopause
- Metrorrhagia in postmenopause
During the premenopausal period, bleeding from the reproductive tract most often occurs due to improper production of sex hormones due to disorders associated with the ovulation process, which, in turn, leads to changes in the change in the functional layer of the endometrium (epithelial lining of the uterus). Such bleeding may recur over several years with varying strength and frequency. Anemia in this case occurs infrequently, compared to teenage girls, however, if it occurs, it can be combined with uterine fibroids or with more complex and dangerous pathological processes in the female body.
Bleeding occurring in the postmenopausal period is the most dangerous, as it requires an immediate diagnostic search to exclude malignant neoplasms. Such metrorrhagia is an indication for diagnostic hysteroscopy (curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal).
Postcoital bleeding
If bleeding occurs in a woman immediately after intercourse, then it is called post-coital (coitus. Sin.: penetration, copulation, copulation, sexual intercourse). Such bleeding from the genital tract can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Mechanical trauma to the genital tract
- Sexually transmitted diseases (often chlamydia)
- Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive tract (vaginitis - in the vagina, cervicitis - in the cervix, etc.)
- Erosions and polyposis (require surgical treatment)
- Due to the use of certain medications, including hormonal
- Dysplastic changes (replacement of the epithelium with the wrong one for a given part of the reproductive tract) up to the tumor process
If bleeding is accompanied by severe pain and occurs suddenly during or after copulation, then it is necessary to call an ambulance, because the situation can be life-threatening. In this case, you need to pay attention to the symptoms in case the woman has internal bleeding, which may be accompanied by acute pain in the abdomen, groin, lower back, weakness, dizziness, fainting, profuse sweating (“cold sweat”).
Timely consultation with a doctor usually contributes to a quick cure.
Metrorrhagia after medical abortion
Typically, bleeding that occurs after a medical abortion stops in most women during therapy. And the cycle is completely normalized within 1-2 months. However, if, due to metrorrhagia after an abortion, two sanitary pads are completely soaked within one hour, then the bleeding should already be considered severe and requiring immediate intervention by a gynecologist.
Treatment of bleeding from the reproductive tract
The goals of treating metrorrhagia usually come down to stopping the bleeding itself and replenishing the lost blood volume, finding and eliminating the already found cause of metrorrhagia, preventing recurrence of bleeding and treating its consequences (anemia, hemorrhagic shock).
Uterine bleeding should be treated taking into account its causes. Often the bleeding itself stops when its cause is eliminated surgically or conservatively. Therapy should be comprehensive: hormonal, symptomatic, restorative (promotes the restoration of the female body). Treatment is usually based on hormonal therapy and symptomatic therapy - drugs that increase blood clotting and uterine contraction. In addition to the conservative approach, a surgical approach is often used: this occurs if the bleeding is quite severe and/or prolonged. Such treatment usually begins with diagnostic hysteroscopy.
It should be remembered that contacting a gynecologist should be an indisputable and indispensable component of the treatment of uterine bleeding. There should be no talk of self-medication, because if the cause of the bleeding is serious enough, the latter can cost the woman her health, and often her life itself.
To prevent uterine bleeding, every woman should visit a gynecologist twice a year for examination. In this case, early diagnosis of diseases associated with the reproductive tract will become possible, which will allow for quick and gentle treatment without waiting for dangerous bleeding.
Bleeding due to uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial and cervical canal polyps
Uterine fibroids, endometriosis and polyps and endometrial hyperplasia are diseases associated with benign growth of uterine tissue. They appear most often during reproductive age.
All this pathology is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. As a rule, no additional examination methods are required. You can read about possible treatment options for uterine fibroids in the corresponding section of the website www. ya-zdorova.ru. In the presence of pathology of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy with the appropriate amount of surgical intervention is indicated to eliminate the cause of bleeding.
What is fibroid and why does it bleed?
The tumor, which is called fibroid, consists of connective tissue cells and smooth muscle. It originates deep in the tissues and, up to a certain point, represents a small node that does not stand out in any way on the internal or external surface of the affected organ. As soon as the size begins to increase, the tumor formation can appear both in the uterine cavity and outside it - on the outside. Its location determines the likelihood of developing uterine bleeding. Discharge appears, as a rule, if the fibroid has “gone” into the uterus. In addition to the location of the tumor, the appearance of bleeding is influenced by:
- size of leiomyoma - with small sizes up to 2.5 cm, the appearance of blood is unlikely unless we are talking about submucosal formations on the stalk;
- a variety of pathologies in the anamnesis, for example, the development of endometriosis, the presence of polyps or hyperplastic processes of the endometrium;
- the patient’s health and well-being, blood diseases.
Uterine bleeding requiring emergency hospitalization and intervention is defined as blood loss of more than 80 ml.
Determining the volume is simple: use a regular sanitary pad. If it is completely soaked in less than an hour, it’s time to call an ambulance.
Emergency medical care for bleeding
Bleeding in cancer
One of the first manifestations of uterine and cervical cancer is uterine bleeding, although, as a rule, the process may not be at such early stages. It may not cause the woman any painful sensations, be scanty and short-lived. If such bleeding occurs during a regular menstrual cycle, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A timely visit to a gynecologist allows you to detect a tumor at an early stage and significantly increases the chances of a successful cure. The diagnosis can be made based on a gynecological examination, ultrasound and a number of tests.
Hygiene as a prerequisite for successful recovery
It is no secret that compliance with hygiene standards, especially in the intimate area, is the key to the health of not only the woman herself, but also her partner and offspring. The rules of personal hygiene are learned in early childhood and subsequently must be strictly observed throughout life.
Expert opinion
Today, modern methods of maintaining natural cleanliness may differ significantly from those used by our mothers and grandmothers. Refusal of soaps with a high alkali content, the use of hypoallergenic sanitary pads, special compositions for treating the intimate area based on mild ingredients - all this ensures comfort and health for many years.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
The Ginocomfort series of intimate hygiene products is not just detergent and soothing compositions - it is the result of long-term research, careful selection of components, strict compliance with the recipe and quality control. Using Gynocomfort intimate hygiene gels, you will forget about irritation, provide powerful antibacterial protection to the body and comfort for a long time. This is especially important for uterine bleeding caused by myomatous formations. The secreted blood is a breeding ground for a large number of bacteria. It quickly coagulates, an unpleasant odor appears, hyperemia appears on the skin and mucous membranes, a burning sensation occurs, and pustular lesions appear.
To eliminate discomfort from uterine bleeding and prevent bacterial infection, you should use the following products from the popular Gynocomfort series:
- Revitalizing intimate gel - suitable for eliminating vaginal discomfort. Restores the natural balance of the skin in the intimate area and the microflora of the mucous membrane after suffering from inflammatory diseases.
- Washing gel for intimate hygiene “Basic care” - provides comfort and safety, is suitable for daily use and does an excellent job of protecting against the development of pathogenic microflora on the vaginal mucosa.
All Gynocomfort products are great for women of any age and with any health condition, can be combined with any therapy and are indispensable during the recovery period.
Intimate gel for women's health
Obstetric hemorrhage
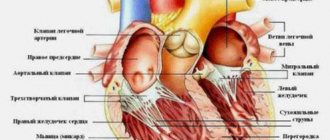
This term refers to intense bleeding that occurs immediately after childbirth. Their cause is a violation of the contractility of the uterus (atony or hypotension of the uterus), or a pathology associated with the blood coagulation system. Hypotony is a decrease in the tone of the uterus, which leads to its inability to actively contract. Atony is a complete loss of the ability to contract and respond adequately to medications and other types of stimulation. Obstetric hemorrhage is very dangerous because it leads to a large loss of blood in a short time. Very often the question is literally about saving a woman’s life - and then doctors decide on a hysterectomy, that is, removal of the uterus.
Let's sum it up
As we have already found out, there can be quite a few reasons for the occurrence of uterine bleeding due to fibroids. Obvious symptoms and a wide range of treatment options make it possible to effectively combat the painful condition, but only if you seek medical help from specialists in a timely manner. No self-medication should be allowed in this condition! Neither self-administration of drugs to improve blood clotting, nor herbal medicine, nor hormone therapy carried out without careful medical supervision will give positive results.
Any delay in diagnosing and treating uterine bleeding can lead to loss of health and even become life-threatening.
Do not hesitate to regularly contact the antenatal clinic for a routine examination. Timely detection of myomatous nodes and monitoring the condition will help to avoid problems and prevent heavy blood loss. Sources:
- Ailamazyan E.K. Emergency care for extreme conditions in obstetric practice. – St. Petersburg, 2003.
- Bodyazhina V.I., Zhmakin K.N., Kiryushchenkov A.P. Obstetrics. - M.: Medicine, 1986. – 496 p.
- Gynecology: Textbook / Ed. G.M. Savelyeva, V.G. Breusenko. - M.: GEOTAR-MED, 2004. - 480 p..
- Bokhman Y.V. Guide to gynecological oncology, L.: Foliant, 2002.
- Malevich K.I., Rusakevich P. Treatment and rehabilitation for gynecological diseases. – Minsk, 1994. – 367 p.
Bleeding during menopause
Menopause is a natural physiological process. You shouldn’t be overly emotional or wary about him. But at the same time, a woman during menopause needs to listen to her condition so as not to miss truly significant and alarming symptoms. One of them is bleeding.
Uterine bleeding during menopause may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the hormonal system, the occurrence of tumors in the body of the uterus or in the ovaries. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease using ultrasound and tests.
I would like to say a few words about bleeding during sexual intercourse. If this symptom appears, you should definitely consult a doctor. They may indicate cervical disease, be a manifestation of endometriosis, as well as vaginal pathology. In some cases, spotting during sexual intercourse may be associated with dryness of the vaginal mucosa, for example, during the postmenopausal period. In any case, to clarify the diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
General recommendations
To avoid such problems, we strongly recommend that you follow the simplest rules of the rehabilitation period:
- Eating can be done no earlier than 3 hours after tooth extraction.
- Don't eat hot or cold foods.
- Give preference to liquid porridges and broths. Supam. Solid foods should be avoided until the hole is completely healed.
- Avoid taking hot baths and saunas.
- Avoid heavy lifting and exercise for a week.
- After tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth; this will significantly increase the healing time of damaged tissue.
- Limit brushing your teeth for the first 24 hours.
- You should not drink alcohol for a week after the operation.
- Never apply warm or hot compresses to your cheek.
How to feel about “grandmothers’ recipes”?
In preparing this article, we conducted a survey and found out that, without exaggeration, a huge number of women are trying to cope with the situation of uterine bleeding on their own - using traditional medicine recipes. Naturally, in this case we are talking about moderate or scanty bleeding. The reasons for this state of affairs most likely lie in the absence of a certain culture of treatment and constant monitoring of one’s health. On the other hand, many books and brochures with various folk recipes can now be bought at any bookstore. It is also not difficult to find such information on the Internet. Recipes based on nettle, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum are presented there as safe, effective, affordable, and, moreover, tested by several generations of women.
Without criticizing traditional medicine and recognizing its merits, we would like to focus your attention, first of all, on the inadmissibility of self-medication in case of uterine bleeding. As noted above, the causes of bleeding can be different. Bleeding is only a consequence, a symptom of the disease. You need to treat what caused it: tumor, dysfunction, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, etc. Therefore, it is extremely important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and correctly diagnose the causes of bleeding. And only then, in the treatment regimen, in some cases folk remedies can be used.
How to stop nosebleeds on your own
First of all, you need to ensure complete peace - sit down, calm down, don’t talk, don’t make sudden movements. Then proceed like this:
- Unfasten the collar, loosen the belt and other compressive elements.
- Tilt your head forward (you can’t throw it back or lie down).
- Place any cold object on the bridge of your nose, for example, ice in a rag or a bottle from the refrigerator.
- Open the windows, create a draft. If the patient is outdoors, an urgent need to move into the shade.
- If it is hot indoors or outdoors, additionally apply cold compresses to the head and chest.
- If bleeding continues profusely, it is necessary to press both nostrils to the septum. Breathe deeply and calmly only through your mouth. You need to stay in this state for 5 to 10 minutes. In this case, the blood will enter the oral cavity - you just need to spit it out.
- Make 2 cotton balls, dip them in hydrogen peroxide and place them in your nostrils. If there is no peroxide, you need to moisten it at least in water - you should not insert dry balls.
- Drink cool water or compote (but not tea or coffee).
Medicines to help with vomiting
For frequent vomiting, when there is a risk of dehydration, doctors use effective antiemetic drugs (antiemetics). They allow you to stop painful attacks and prevent health-hazardous consequences. They work by blocking various pathogenetic components of the gag reflex.
Antiemetics include serotonergic and dopaminergic drugs, some antihistamines, anticholinergic drugs, and NK1 receptor antagonists. It is not recommended to take them without a doctor's prescription, as negative side effects may occur.
Other ways to combat the gag reflex during alcohol poisoning
The following simple techniques help some people with alcohol intoxication:
- taking five grams of vitamin C;
- drinking small sips of a weak solution of baking soda (take 5 teaspoons of the composition per liter of water);
- using freshly squeezed lemon and orange juice (but you should not drink them if you have stomach diseases);
- Take three tablespoons of glucose solution every hour.
It is clear that these recommendations will not help with severe vomiting after binge drinking. You can resort to them only in case of nausea or periodic vomiting. If an alcohol addict feels very bad and there is blood in the vomit, it is unacceptable to refuse medical help.
Drug therapy
Treatment of diseases that cause bleeding from the uterus is carried out in a hospital setting. Additionally, the doctor prescribes medications to the patient to help stop the bleeding.
Hemostatic medications are taken only on the recommendation of a medical specialist; taking medications at your own discretion is strictly prohibited.
Below is a list of medications most commonly used to stop bleeding.
- Etamzilat . This drug stimulates the synthesis of thromboplastin and changes the permeability of blood vessels. Blood clotting increases, resulting in decreased bleeding. The medication is intended for intramuscular injection.
- Oxytocin . A hormonal drug often used during childbirth to improve uterine contractility. As a result of contraction of the uterine muscles, bleeding stops. The drug oxytocin is prescribed for intravenous administration with the addition of glucose and has a large list of contraindications.
- Aminocaproic acid . This medicinal substance prevents blood clots from dissolving under the influence of certain factors, thereby reducing bleeding. The medicine is either taken orally or administered intravenously. Treatment of uterine bleeding with aminocaproic acid is carried out under close medical supervision.
- Vikasol . The drug is based on vitamin K. With a deficiency of this vitamin in the body, blood clotting worsens. The medication is prescribed to patients who have a tendency to uterine bleeding. However, vitamin K begins to act only 10–12 hours after entering the body, so it is not advisable to use the drug to stop bleeding in emergency cases.
- Calcium gluconate . The drug is prescribed for calcium deficiency in the body. Deficiency increases the permeability of vascular walls and impairs blood clotting. This medicine is also not suitable for use in emergency cases, but is used to strengthen blood vessels in patients prone to bleeding.
Danger
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is not a harmless disease. During the juvenile period it can lead to:
- anemia;
- hormonal disorders;
- infertility;
- endometriosis.
In women of reproductive age, the disease can be caused by:
- infertility;
- anemia;
- endometrial cancer, breast cancer;
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- uterine fibroids.
In premenopausal and menopausal patients, dysfunctional uterine bleeding can cause anemia, cancer, and also cause the growth of existing tumors into neighboring organs. from a gynecology clinic at the first symptoms of the disease.
.
Popular questions
I am 47 years old, I have multiple uterine fibroids, two fibroids, a large and a medium one (76 mm and 40 mm) had blood flow along the periphery, yesterday I had an ultrasound on the same machine and by the same doctor, it turned out that the large fibroid has not changed in size, but there is no blood flow, can this be the case, until yesterday I had an ultrasound scan there 2 times, once every six months, and the blood flow was IR 0.5 and IR 0.55 in the periphery, what is the risk of this, could there be necrosis due to malnutrition?
and can it shrink in size without blood flow? A decrease in blood circulation in the nodes of uterine fibroids indicates the process of completing the growth of the formation. This requires ultrasound control after 3 months. In the absence of pain, fever, or ultrasound changes in the node described as necrosis, it is not possible to assume this process.
I am 31 years old and have fibroids. Buserelin spray was prescribed for 2 months. If side effects occur, tell me if there are any medications. I’m very afraid because according to reviews it’s a very scary drug. And approximately how long does it take for side effects to appear?
You should follow the recommendations of your doctor. When using this drug, drug-induced menopause occurs. This may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations - fever, hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbance and genitourinary syndrome - dryness in the genital tract. The use of Climafemin Ginocomfort will help improve your well-being, and the Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract will cope with dryness.
Good day. We discovered a 45mm fibroid (submucous), and there is bleeding after menstruation. It's been 2 weeks already. The doctor talks about the operation. I'm waiting for the commission. What operation is done in this case? They scared me that it was possible to remove the uterus. I'm 38 and still want to give birth.
Hello! You should tell your doctor about your reproductive plans. This will resolve the issue in favor of organ-sparing surgery - conservative myomectomy. Method - hysteroscopic or strip surgery is decided collectively, taking into account technical capabilities, medical practice, type of submucosal node, its location, etc.
Good afternoon, I am 31 years old, I have fibroids. Buserelin spray was prescribed for 2 months. If side effects occur, tell me if there are any medications. I'm very afraid, because... According to reviews, it is a very terrible drug. And approximately how long does it take for side effects to appear?
Hello!
You should follow the recommendations of your doctor. When using this drug, drug-induced menopause occurs. This may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations - fever, hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbance and genitourinary syndrome - dryness in the genital tract. The use of climafemin Ginocomfort will help improve your well-being, and the Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract will cope with dryness. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Traditional ways to stop nosebleeds
The standard recommendations were listed above, but it is possible to turn to effective traditional medicine.
Try putting freshly squeezed lemon juice on your nose, a few drops in each nostril. You can dip a cotton swab in lemon juice and insert it into your nose for a few minutes. Change it if necessary.
If you have nettle on hand (let's say you are in nature), squeeze the juice out of it and insert a cotton wool soaked in this juice into your nose.
Some people successfully stop nosebleeds using the su-jok system. To do this, you need to bandage your thumb approximately at the level of the middle of the nail (use a rubber band or twine for this) and hold it there for 10 minutes. According to the su-jok technique, in this place there is a reflex zone corresponding to the area of the nose.