Heart arythmy
These conditions are not dangerous; they arise under the influence of physiological processes and pass quickly.
But cardiac arrhythmias that occur for no apparent reason require consulting a doctor. The cause of heart rhythm disturbances is a violation of the sequence of excitation and contraction of the heart muscle. These failures occur under the influence of various factors: first of all, heart disease and endocrinological diseases; brain damage, including traumatic ones. Arrhythmia is provoked by taking certain medications, deficiency or excess of certain microelements, amino acids, and vitamins.
Chronic intoxication is of great importance (which, unfortunately, many people are simply not aware of). This includes smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs, living near highways and large enterprises. Anemia, consumption of certain foods and drinks (for example, coffee, cheese) play a certain role; arrhythmias are common in infectious diseases and febrile conditions.
“The heart freezes,” “the heart does not beat for several seconds,” “the heart beats very hard, as if it wants to jump out, then it freezes, and then beats like a hammer - slowly and loudly,” “the heart hangs like a stone in the chest” - these are typical complaints with cardiac arrhythmias. These symptoms are often accompanied by a feeling of difficulty breathing, a desire to cough, cold sweat, weakness, dizziness and fainting.
Medicines for effective treatment of tachycardia
Tachycardia is a common disease in which there is an increase in heart rate. The heart always beats faster during strong excitement and physical work. But in these cases, this is the norm, that is, this is how the body naturally reacts to stress. For example, your heart rate increases when you walk or run quickly. Normally, it should recover within 5 to 10 minutes.
If the heart rhythm is not restored for a long time, or the rapid heartbeat has no apparent reason, then we are most likely talking about a disease. This is tachycardia, in which there is an increase in heart rate. This condition requires contacting a cardiologist. Even if the disease does not affect your well-being in any way, you should know that with this mode of operation, the main organ wears out faster. If you miss time, complications may develop, such as impaired blood supply to the brain, pulmonary edema, or cardiac arrest. A person with tachycardia of healthier people is at risk by drinking strong coffee or alcohol. In addition, some medications may cause an unexpected attack of tachycardia. Therefore, the disease must be treated, including taking medications.
Read also: How much alcohol should you not drink after Botox?
What drugs are there for tachycardia?
Many medications have been developed to treat tachycardia, but only a doctor can decide which drugs to take in each individual case. Therapy depends on the causes of tachycardia, which is most often a symptom of other diseases. In this case, treatment is aimed at the primary disease. Drug treatment of tachycardia gives a good effect, but in search of a better result you have to try different remedies.
There are medications intended for symptomatic treatment. This is a large group of medications with different mechanisms of action to normalize heart rhythm. The dosage and duration of therapy is strictly individual and can only be discussed with a doctor.
The course of drug treatment is chosen only by the doctor, taking into account many factors. There are several types of medications that are used for tachycardia. They can be divided into two groups: sedative (with a calming effect) and antiarrhythmic.
Sedatives can be natural or synthetic. They normalize the functioning of the heart and nervous system, reduce the number of attacks.
Natural medicines
- Valerian. Available in the form of tinctures and coated tablets. The drug dilates the blood vessels of the heart, promotes rapid sleep, and slows the heartbeat. Valerian is a weak choleretic and antispasmodic agent. It has a moderate, slow-onset, but stable sedative effect due to alkaloids and essential oils. The effect occurs only with long-term and constant use (at least 1.5 months). Medicines may have contraindications, so you should not self-medicate. An overdose of the drug can lead to the opposite effect - overexcitation.
- Hawthorn tincture. Indications: atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal tachycardia. Reduces heartbeat and excitability, normalizes blood pressure, and has a calming effect.
- Persen is a moderate sedative. Available in capsules and coated tablets. It contains valerian, peppermint, lemon balm. Preparations based on these medicinal herbs reduce fatigue, irritability, nervousness, anxiety, excitability, help you fall asleep faster, and improve appetite.
- Motherwort. Medicinal plants have long been used to normalize the functioning of the nervous system. In pharmacies you can purchase drugs in tablets or in the form of alcohol tincture. Motherwort has a sedative and mild antispasmodic effect, normalizes heart rate, improves heart function, relieves insomnia and has virtually no side effects.
- Peony. Alcohol tincture relieves nervous tension, improves mood, and has a mild hypnotic effect.
Diagnosis and treatment
Any malfunction of the heart requires qualified diagnosis. There are often cases when a person complaining of bradycardia received advice... to lie down and relax, to lie down and rest. The result was an even greater decrease in heart rate, which required the professional intervention of resuscitators. The examination begins with the simplest methods: counting the number of heartbeats with determination of rhythm, measuring blood pressure, and examining the skin. The main method for diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias is ECG.
Sometimes, to clarify the group arrhythmia, 24-hour monitoring of cardiac activity and an esophageal ECG are performed. Depending on the type of arrhythmia, treatment is prescribed, which can be aimed at the cause of the arrhythmia (as in the case, for example, arrhythmia due to medication), and at reducing the frequency of attacks, if the underlying cause cannot be cured. Treatment can be conservative - with the use of appropriate medications, or surgical - the introduction of a pacemaker or other pacemakers.
According to statistics, about 25% of the population suffers from one or another arrhythmia. The main types of arrhythmias with adequate treatment do not pose a direct threat to life, but for this it is necessary to know exactly the cause and type of arrhythmia. Treatment of arrhythmias is quite effective, subject to compliance with the medication schedule, exercise regimen, nutrition, and lifestyle.
DO YOU WANT TO QUIT SMOKING?
Then come to us for a marathon on quitting cigarettes. With its help it will be much easier to quit.
Why does the heart stop between two beats?
Heartbeat disturbances also occur in completely healthy people. Photo Interpress/PhotoXPress.ru
Extrasystole is one of the most common types of heart rhythm disturbances. According to world statistics, about 70% of people of different ages are susceptible to it. What is this disease? Why does it occur and how dangerous is it? What is the treatment? These questions concern many people.
Let's start with the term “extrasystole”. It refers to a contraction of the heart or its parts that occurs earlier than the next contraction should normally occur. Failures are caused by the appearance of premature excitation in the heart muscle (myocardium). Let me explain in this regard that in a healthy person, electrical impulses are generated in a certain part of the heart, which is called the sinus node. The heartbeat remains normal. If the patient has extrasystole, then excitation signals arrive to the myocardium from areas located outside the sinus node. As a result, the heart contracts prematurely, then there is a pause, which can be compared to freezing, and later the next beat occurs.
Thus, extrasystoles, or extraordinary contractions of the myocardium, are the main sign of one of the common types of arrhythmia - extrasystoles. It occurs in various heart diseases, as well as in disorders of the regulation of its function. In other words, extrasystole is observed not only in those who suffer, for example, from ischemic disease or cardiosclerosis (excessive development of connective tissue in the myocardium), but can also occur in completely healthy people. Its appearance is usually promoted by factors such as stress, smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea, and coffee.
Depending on the cause of its occurrence, extrasystole can be functional or organic. The first is observed mainly in young people against the background of depression, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and neuroses. A person often feels its symptoms at rest, say, in the evening, before going to bed or in the morning, after waking up. Changes in heart rhythm can also manifest themselves while reading or working at the computer. Functional extrasystole occurs even in children, for example, as a result of overwork. As for organic extrasystole, the risk group is mainly for older people who have serious diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine system.
Usually the patient is worried about noticeable interruptions in the functioning of the heart, for example, unnaturally strong shocks into the chest from the inside. They are often accompanied by a short-term increase (tachycardia) or slowdown (bradycardia) of the heart rate. In this case, a person may experience breathing problems, weakness, a feeling of anxiety, a feeling of interruptions and cardiac arrest. However, all these symptoms often go away when the emotional background changes. Sometimes extrasystoles can appear very weak compared to normal beats of the heart muscle and are diagnosed only on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Based on ECG data and the results of the initial examination, the doctor will determine the presence or absence of extrasystole in the patient. It is believed that a healthy person can have up to 100 extrasystoles per day. However, if you periodically feel heart beats and pauses following them, it is better to consult a cardiologist. The fact is that even without myocardial damage, with frequent extrasystoles, the ejection of blood from the heart decreases and the blood supply to many organs deteriorates. And this negatively affects their activities.
If we are talking about the functional form of extrasystole, then sometimes it is enough to quit smoking, “quit” alcohol, give up excessive coffee consumption - the symptoms of the disease will disappear without any medications. With arrhythmia of neurogenic origin, it is important to try to reduce the negative effects of stress, for example, change the environment and go on an exciting trip. In addition, in this case, the doctor may prescribe sedatives. An infusion of such a proven remedy as valerian root helps quite well with functional extrasystole.
The presence of organic extrasystole usually indicates serious diseases of the cardiovascular system. In this case, therapeutic measures should be aimed both at treating the underlying disease and at restoring normal heart rhythm. Extrasystole can also be caused by endocrine diseases, for example hyperthyroidism - increased function of the thyroid gland. In this case, you cannot do without consulting an endocrinologist. In addition, heart rhythm disturbances are sometimes observed with osteochondrosis and scoliosis, especially in children.
Irregular heartbeat
If a person listens to his heart and feels his pulse fading, this does not indicate the presence of health problems. This problem often occurs in healthy people. It can be caused by certain foods, stress and experiences. The main thing is to determine the cause of the uneven pulse, after which we can already talk about the need for treatment.
Causes of intermittent heartbeat?
Normally, the pulse should be uniform and rhythmic.
The heart works intermittently due to the following reasons:
- excessive coffee consumption;
- lack of blood sugar;
- lack of potassium;
- psychological problems;
- heart pathologies.
Return to contents
Drinking coffee
Coffee contains a lot of caffeine, which speeds up the heart rate, raises blood pressure and makes the pulse uneven. If the heart beats quickly, then the patient should forget about this drink. In addition, it is worth limiting drinks containing caffeine: green tea, chocolate, energy drinks. It is not advisable to drink coffee with medications that contain caffeine. You can not remove coffee from your diet, but drink one cup in the morning or during the day before 16:00.
Lack of sugar
Irregular heartbeat is caused by a lack of sugar in the blood. To correct an uneven pulse, you don’t need to see a doctor, you just need to eat 4-5 times a day. Breakfast needs to be hearty and should include complex carbohydrates (oatmeal, buckwheat or lentils are suitable). This will help normalize the heartbeat.
Potassium deficiency
Potassium strengthens the walls of blood vessels and helps the body cope with stress. If your heartbeat is abnormal, it is important to take potassium to normalize your irregular pulse. An intermittent pulse will go away if you include bananas, buckwheat, lean fish, and apricots in your diet. Along with potassium, both magnesium and calcium affect the state of the cardiovascular system. Their imbalance leads to the same problems.
Psychological problems
Psychological problems are a common cause of an uneven heart rate. Against the background of stress and anxiety, the nervous and cardiovascular systems malfunction. This is also reflected in the indicator. The heart beats quickly, sometimes it freezes or suddenly begins to beat slowly. In this case, he prescribes a course of sedatives (valerian, motherwort, Corvalol) and drugs that normalize heart rate.
Heart pathologies
There are pathologies of different types in the heart. If the patient follows the recommendations, but the problem remains, then it makes sense to contact a cardiologist. He will make the correct diagnosis after the patient has done an ECG and cardiogram. After this, the specialist will prescribe treatment and you can forget about the uneven pulse. Sometimes surgery is needed.
Why does the heart beat intermittently and other rhythm disturbances?
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
Interruptions in the functioning of the heart - changes in the strength, frequency and regularity of contractions. Such disorders in medicine are called arrhythmia, which is a symptom of other diseases. Arrhythmia is usually not considered an independent disease; only sometimes a short-term and spontaneous arrhythmia is present in a completely healthy person.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
Often, when there is a malfunction in the heart, a person experiences other symptoms, such as shortness of breath, pain, and others. Much depends on the cause of the arrhythmia, which can be not only problems with the heart itself, but even osteochondrosis, VSD, and sometimes a person feels problems after eating. It is important to understand why the heart rhythm is disrupted, how it manifests itself and what to do about it.
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Causes
First you need to understand what types of arrhythmia there are, since some causes are characterized by one of them.
- Tachycardia. This is the name for beating too quickly, the number of beats in one minute exceeds 90. This condition can be a natural response to stress of an emotional or physical nature, therefore, it can appear even after eating or an increase in body temperature. However, tachycardia may indicate that the heart muscle is under constant stress and is not functioning well. If the heart rate accelerates constantly, for example, every day, it means that the heart does not have time to relax and rest, which increases the risk of a heart attack or coronary artery disease.
- Bradycardia. In this case, the heart, on the contrary, beats too slowly, less than 60 beats per minute. This is a natural state if the heart and vascular system is well trained, for example, in athletes when they are at rest. However, too slow a heart rate always threatens fainting, oxygen starvation of the brain, and even cardiac arrest.
- Atrial fibrillation. It manifests itself in the absence of effective contraction of the entire atrial myocardium. Atrial fibrillation is a sign of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Extrasystole. These are extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle, which in most cases is a response to excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, strong tea, coffee, nicotine, and can also be a dangerous signal of active myocardial damage.
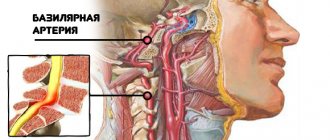
In diseases of the spine, for example, osteochondrosis, the vertebral artery, which runs along the spinal column, is pinched. Spasmed muscles or bone osteophytes compress the vessel, which increases intravascular pressure. The pathological condition leads to the development of tachycardia. In order for blood to be pumped well through a compressed vessel, the body and, of course, the heart have to put in more effort, which leads to an increase in heart contractions, which is how interruptions occur in the heart.
Read also: Is it possible to drink beer for diarrhea?
Tachycardia in osteochondrosis is permanent, that is, it is present even at rest. When a person changes posture, it becomes more pronounced. Of course, if osteochondrosis is treated, tachycardia will decrease. But the effect will be noticeable after effective treatment.
If the heart muscle cannot cope with the increased load, extrasystole begins to develop. With osteochondrosis, it manifests itself in the later stages. At first, the rapid beating of the heart is short-term. If osteochondrosis is localized in the lumbar region, it has a strong impact on organs located in the abdominal cavity, for example, the adrenal cortex. Increased production of catecholamines begins, but they cause vascular spasm, leading to disruptions in heart rhythm and blood pressure.
VSD is another reason why a person may feel disturbances in the functioning of the heart. VSD has various symptoms that can make a person's life difficult, but it is not fatal. Many patients with VSD feel as if their motor stops and starts again. Often it really only seems like it. There were patients who claimed that their heart stopped for 10 minutes or even half an hour, but this was impossible.
There are cases when a person, after measuring his pulse, came to the conclusion that he had about 200 beats per minute, although in fact there were 70-80 of them, that is, within the normal range. There was even a study of patients with VSD, which showed that in almost half of the patients the heart beats normally and even well every day, that is, there are no rhythm disturbances. In fact, many of the phenomena that a patient with VSD complains about, for example, shortness of breath, pain, and the like, are only functional in nature. They are associated with disruption of the autonomic system, after treatment of which everything improves.
Of course, interruptions in the heart, shortness of breath, weakness, abnormal pulse values in patients with VSD can be real symptoms of a serious illness that has nothing to do with the autonomic system, especially if these signs are felt day after day. Therefore, timely diagnosis is very important not only for those who have VSD, but also for everyone who has encountered similar symptoms.
Interestingly, arrhythmia can occur in a person after eating. Moreover, the number of people who encounter this is growing. To understand why some people lose heart rhythm after eating, it is important to remember that the intensity of the beating of the vital motor depends on the state of the body and the conduction system. If normal impulse transmission occurs and the body receives the amount of oxygen it needs, there is no doubt that the number of strokes will be normal.
The digestion process leads to the fact that the activity of the vagus nerve increases, so the function of the sinus node is inhibited, namely, it is where impulses are formed that form heart contractions.
How does the heart react to this? His response is frequent beating, but the contractions are uneven due to the load.
When considering arrhythmia recorded after eating, it is important to remember that attacks can also be triggered by drinking alcohol. Studies have shown that alcohol leads to paroxysms of atrial fibrillation, which in especially severe cases can cause death.
These are common reasons why heart rhythm disturbances occur. Heart failure is also caused by the following factors:
- stress;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, nervous system, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, heart;
- anemia;
- oncology;
- atherosclerosis;
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- viral infections;
- heart defects.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the arrhythmia, in addition to heart rhythm disturbances, other symptoms are observed. The most common are shortness of breath and heart pain.
Dyspnea is rapid, difficult breathing. In a calm state, a person performs approximately 16-18 breathing movements. If breathing quickens, a person begins to feel short of air, he cannot breathe deeply. In this condition, a person may have difficulty breathing.
Shortness of breath is often a sign of a serious illness, especially when combined with arrhythmia. Therefore, if shortness of breath occurs, you should immediately go to the hospital.
Sometimes shortness of breath can cause another symptom, pain in the heart, which can also manifest itself. The pain can be of a different nature and radiate to other parts of the body. Arrhythmia, shortness of breath and pain - these symptoms often occur together. After eating, with VSD and other conditions, weakness, dizziness and other signs that require attention may occur along with arrhythmia.
Treatment
What to do if a person discovers such unpleasant symptoms, whether they occur after eating, during physical activity, or in other situations? Go to the doctor immediately. It is impossible to describe the treatment, since it depends entirely on the results of the examination.
If your heart beats intermittently, you feel weak, it’s hard to breathe, you need to calm down. You can lie down and breathe some fresh air. In especially severe cases, you should call a doctor. Effective treatment will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms, which will improve the quality of life.
– by leaving a comment, you accept the User Agreement
- Arrhythmia
- Atherosclerosis
- Varicose veins
- Varicocele
- Vienna
- Haemorrhoids
- Hypertension
- Hypotension
- Diagnostics
- Dystonia
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Ischemia
- Blood
- Operations
- Heart
- Vessels
- Angina pectoris
- Tachycardia
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis
- Heart tea
- Hypertension
- Pressure bracelet
- Normalife
- Allapinin
- Asparkam
- Detralex
What can you do to prevent intermittent heart rate?
To eliminate heart palpitations, you need to give up bad habits (smoking and alcohol).
All preventive actions are aimed at normalizing the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To do this, you need to get a good night's sleep and plenty of rest. It is important to do cardio training (running, walking outdoors). Nutrition should be balanced. It should contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals. For normal functioning of the body, a person must eat 4-5 times a day (every 3 hours).
Secrets of bradycardia prevention
Prevention of bradycardia is associated with the prevention of cardiovascular disease. People who have already developed heart disease should monitor it and follow the doctor's recommendations.
It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes: physical activity, a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, controlling cholesterol and blood pressure, stopping smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
You should also avoid stress, which has a negative effect on the heart. Untreated bradycardia can be very dangerous to our health and life. Because of this, individuals at risk of bradycardia should remember to get regular checkups, as well as seek medical attention if alarming symptoms occur.
What is the normal heart rate
You don't need a special device to measure your heart rate. Simply place your finger on a point on the inside of your wrist, on your neck or on the top of your foot and count the beats for a minute. To determine your resting heart rate, do it while sitting in a relaxed state, without drinking coffee beforehand, and repeat the measurement several times. Also pay attention to the regularity of the rhythm.
Most people have a resting heart rate of 60-100 beats per minute. And there are several factors that can influence whether you fall into this range. Some of these are completely normal, while others may be cause for concern. For example, physically active people tend to have lower resting heart rates because their heart muscles are stronger and more efficient. Also, the frequency of contractions is affected by certain medications, emotions, body position, weight and even air temperature.
But sometimes heart rate can warn of certain diseases or signal future problems. Therefore, it is important to control him to know what he is trying to say.
Heart rate stimulator
Electrical stimulation of the heart involves initiating its contractions using external electronic devices. The stimulator contains an electrical pulse generator, electrodes that transmit pulses and a microcomputer, which can be freely programmed, selecting individual settings for each specific patient. You can choose the heart rate, the strength and duration of the impulse, sensitivity and other parameters of its operation.
pacemaker implantation procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The electrode is inserted through a vein under the control of an X-ray machine, into the right ventricle, and sometimes into the right atrium.
During the implantation operation, measurements of heart parameters are taken to allow the device to be programmed correctly. The stimulator itself is implanted subcutaneously under the collarbone.
A patient with an implanted pacemaker should undergo routine annual examinations. Unfortunately, having an implanted system carries a certain risk of complications.
The most common are:
- movement of the electrode into the heart, causing disruption of pacing (in such a situation, another procedure is necessary);
- increasing the stimulation threshold (reprogramming the pacemaker is required);
- tachycardia (results from improper programming of the pacemaker);
- local infections: with weakened immunity, it can even lead to sepsis.
Slow heart rate
Several factors can contribute to a slow heart rate. In a healthy person, this is due to excellent physical fitness, sleep and taking certain medications, including blood pressure medications. Athletes may have a resting heart rate of 40 beats per minute, and this is normal.
But sometimes a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) can signal a serious problem. For example, about the malfunction of the sinoatrial node (natural pacemaker), the conduction system of the heart, or damage to the latter. A slow heart rate can also be a sign of hypothyroidism (too much potassium in the blood) or infections (such as Lyme disease).
A slow heart rate can make you feel tired, weak, dizzy, or confused. The patient experiences shortness of breath and cannot tolerate physical exertion. If left untreated, it can lead to blood pressure problems, fainting, chest pain, and even heart failure, so it's important to tell your doctor about any of these symptoms.
Bradycardia
- home
- Articles
- Arrhythmias
- Types of arrhythmias
- Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a heart rate that is too slow.
It is important to distinguish pathology from the norm, because a low pulse does not always indicate problems with your heart. If since childhood you have had a pulse of 50-60 beats per minute and no pathology has been detected, and you feel great, most likely everything is fine with you. This is especially typical for people who are actively involved in sports: a trained heart pushes blood through the vessels much more efficiently - because of this, the heart of athletes beats quite rarely at rest (up to 40 beats per minute). When should you be wary? Firstly, if your heart has always beat at a frequency of 70-90 beats per minute, and then suddenly it began to beat at a frequency of 40-50 or lower. Secondly, if symptoms such as darkening of the eyes, unsteadiness of gait or loss of consciousness appear - i.e. signs that the heart cannot cope with its work and blood flows to the brain with a delay. The most common reason why the heart suddenly begins to beat rarely is a pathology of the sinus node, the place where the electrical impulse is born and where it comes from, exciting the entire heart. This is called sick sinus node syndrome (SSNS) and there are many reasons for it (from atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels to infectious heart disease - myocarditis). This syndrome is diagnosed simply - just do an ECG. Treatment: implantation under the skin of an electrical pacemaker (ECS) - a device that will artificially generate an impulse and work for the sinus node. Its dimensions are more than modest, its weight does not exceed 45 grams, its service life is from 5 to 10 years. Once a year, preventive examination and reprogramming (if required). It should be noted that one of the leading Russian specialists on the problem of SSSU is the scientific consultant of our Center, Professor V.A. Shulman. The second main reason is damage to the conduction pathways of the heart, when the impulse from the atria does not reach the ventricles. This is called AV block. It arises for the same reasons as SSSU. AV block has 3 degrees, which differ in the depth of damage: 1st degree - the impulse passes, but with a delay, 2nd degree - the impulse does not always pass and 3rd - the impulse does not pass at all. The worst thing is the 3rd degree, because the atria and ventricles begin to contract independently of each other (each in its own rhythm), which ultimately leads to ineffective blood circulation and increases the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. In terms of symptoms, diagnosis and treatment, AV block is very similar to SSSS: rare pulse, weakness, loss of consciousness; Taking an ECG is usually sufficient for diagnosis; it is treated by implantation of an pacemaker. And finally, the third main cause of bradycardia is hypothyroidism or decreased functioning of the thyroid gland. The fact is that an excess of thyroid hormones causes the heart to contract at an increased speed, and their deficiency leads to bradycardia. For diagnosis, you just need to donate blood for TSH (usually, when a person is diagnosed with bradycardia, an ECG and a blood test for TSH are prescribed to him immediately) and everything will fall into place. Treatment is replacement therapy. Typically, a lack of thyroid hormones is the result of a disease called autoimmune thyroiditis, which gradually affects the thyroid gland. Fortunately, in the 21st century, thyroid hormones have been synthesized a long time ago and it will be enough for a person to take them in the form of tablets, which is very convenient (unlike insulin, which can only be injected) Total:
— Bradycardia may be normal, especially in athletes. — If your pulse becomes less than 60 (although before that it was 70-80), and/or you have complaints of weakness, lethargy, darkening of the eyes or even loss of consciousness, this may indicate serious problems in the heart (for example, damage to the conduction systems heart) or hormonal dysfunction (thyroid problems). — For diagnosis, you need to do an ECG, take blood tests for TSH and consult a doctor.
For adults, a pulse of less than 60 beats is considered bradycardia. Bradycardia usually results from a whole range of concomitant diseases. With pronounced manifestations of bradycardia, the patient experiences: weakness, pain in the heart area, cold sweat, dizziness, fainting or complete loss of consciousness.
Basically, bradycardia can be caused by two reasons: the inability of the sinus node to generate impulses (the so-called sick sinus syndrome SSS) and poor conduction of these impulses. Bradycardia is often a consequence of coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, myocarditis, taking certain medications, endocrine diseases, increased potassium levels in the blood, increased intracranial pressure, etc.
Methods for diagnosing bradycardia:
— Electrocardiography — Holter monitoring — Electrophysiological study — ECG by phone
IMPORTANT!
Heart rhythm disturbances are perfectly diagnosed and treated by all cardiologists at our Center.
Complex cases of cardiac arrhythmia requiring surgical correction are advised by cardiologists-arrhythmologists at the TERVE Medical Center on Partizana Zheleznyaka, 21A.
Particularly complex clinical cases (referred by cardiologists of our Center) are dealt with by cardiologist-arrhythmologist Professor G.V. Matyushin
Rapid pulse
Just like a slow heart rate, a fast heart rate can sometimes be completely normal. Exercise, of course, increases your heart rate, especially if it is too intense or involves dehydration. Emotions can also make the heart beat faster, as can stimulants such as caffeine. In addition, pregnancy causes increased heart rate in women.
On the other hand, certain diseases and the use of certain medications are associated with increased heart rate. Most infections and fevers are accompanied by increased heart rate. It may also be a sign of low potassium levels, anemia, an overactive thyroid, or asthma. The symptom is characteristic of cardiomyopathy (in which the pumping function of the heart is reduced), atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. This symptom may also warn of future heart problems.
A high resting heart rate is associated with poor fitness and may be a predictor of premature death, according to research. People with a resting heart rate of 81-90 beats per minute are twice as likely to die, and those with an even higher heart rate are three times as likely.
Symptoms of heart palpitations include shortness of breath, chest pain or tightness, dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue. But sometimes people have no symptoms, so it is recommended to monitor their heart rate and lead a healthy lifestyle.
How does tachycardia manifest?
The state of the heart can be quickly determined by the heart rate (HR) - through the pulse, which can be easily felt in large peripheral arteries. Normally, its frequency coincides with the heart rate, since the pulse is the response of the arteries to the ejection of blood from the heart when it contracts. Indicators for a healthy person are 60–80 beats per minute. If your heart begins to beat faster, it may physically feel like it is jumping out of your chest.
However, this does not always happen, and then the presence of tachycardia can be suspected based on a number of other symptoms.
Different pacemakers (sources of impulse generation) are responsible for different types of tachycardia.
Clinical signs of tachycardia
- Pain or discomfort in the chest.
The chambers of the heart contract alternately: while some parts are filled with blood, others are resting. The stronger the tachycardia, the shorter the periods of myocardial relaxation. Working without rest causes pain in the heart.
- Dizziness and general weakness.
In the pulmonary circulation, blood oxygenation (oxygen saturation) occurs. With tachycardia, the time required for complete gas exchange decreases. Rapid contractions of the heart release blood into the vascular bed with a reduced content of O2, which is why the tissues do not have enough of it. To make it easier for organs to receive it, vascular resistance decreases. This results in a compensatory decrease in pressure in the blood vessels, accompanied by dizziness and general weakness. Sometimes it can lead to loss of consciousness.
- Dyspnea.
It occurs both during movement, since during physical activity the body requires more oxygen, and at rest - if tachycardia persists for a long time. The same oxygen starvation leads to the development of shortness of breath: increased breathing is an attempt to restore oxygenation.
- Cyanosis, or blueness of the skin.
With hypooxygenation (decreased oxygen concentration in the body), the blood contains a large amount of reduced hemoglobin, a substance responsible for binding oxygen. Low oxygenation leads to cyanosis of the lips, tips of the ears, or fingers.
Tachycardia can be expressed by less significant symptoms: cough, headache, nausea, sleep disturbances, decreased appetite and performance. These complaints are not typical for an increase in heart rate, but you should mention them when visiting a doctor
Monitor your heart rate during exercise
In addition to alerting you to health problems, your heart rate can also help improve your workout performance. Knowing your target heart rate zone is key.
First, calculate your maximum heart rate. To do this, subtract your age from 220. The resulting number is the maximum number of times your heart should beat in one minute during exercise. Your target zone for moderate to vigorous training should be 50-85% of your highest heart rate.
Doctors recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week or 75 minutes of intense aerobic activity. And your heart rate can be an objective indicator of how hard you're working. Moderate activity should be 50-70% of your maximum heart rate, and vigorous activity should be 70-85%.
Well-being assessment
However, before you start checking your heart rate during exercise, be sure to also evaluate how you're feeling. Research shows that perceived tension correlates well with heart rate. So if you think you're working hard, your heart rate is probably higher than usual.
Moderate activity after about 10 minutes of exertion should make you breathe faster (but not out of breath), sweat slightly, and be able to carry on a conversation. After a few minutes of vigorous exercise, you should be breathing deeply and rapidly, sweating, and losing the ability to speak without inhaling after a few words.
Listen to your body and don't overload yourself. If you find the workout particularly challenging or your heart rate is too high, rest. If your heart rate is too low, you can speed up the pace. Of course, always consult your doctor about changes in your physical activity or problems that arise during exercise. This little extra attention to your heart rate can make a big difference in your health in the long run.
The child's heart beats either quickly or slowly
Continuing the series of publications for parents of children with cardiac arrhythmias, we offer a series of lectures based on materials from the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association
If your child has been diagnosed with a heart rhythm disorder, you are probably worried. And this is understandable. But as you learn more about your child's condition, you will be less afraid. You will also be able to take better care of your baby. We will help you find out:
- How the heart works
- What are the most common heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias) found in children?
- How Your Doctor Can Diagnose and Treat an Irregular Heart Rhythm
Chapter I. About heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heart beats in one minute. In older children or teenagers, the heart beats about 70 times per minute at rest; in newborns about 140 times per minute. Usually the heart rate is regular. This means that the heart beats evenly (at regular intervals). Heart rate depends on the age of the child; its average values are presented in the table:
Arrhythmia: symptoms and treatment
The article was prepared by cardiologist Ksenia Nshanovna Borel
Arrhythmia... Perhaps the interpretation “I am worried about arrhythmia” is one of the most common complaints of cardiac patients of any age.
In fact, there is no diagnosis of arrhythmia. There is a specific disturbance in the rhythm and/or conduction of the heart, which must be recognized in time by the attending physician in order to take measures to eliminate it, if required.
I will not tire of singing the praises of my heart: this is a unique organ not only in terms of the functions it performs, but also in terms of its structural features. Did you know that the heart muscle (myocardium) is very unusual? It does not simply contract mechanically, like any other muscle in the human body.
Deep in the myocardium there are special cells of the conduction system that are capable of generating nerve charges, converting an electrical impulse into a mechanical muscle contraction:
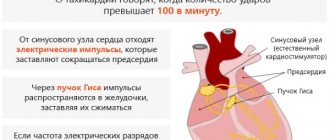
- The main conductor of this complex composition is the sinus node (also known as the first order pacemaker), located in the wall of the right atrium. It is the power plant that reproduces charges at a frequency of 60-90 per minute, which is the normal (in terms of frequency and regularity) heart rhythm. Next, nerve impulses are transmitted to the underlying sections.
- From the sinus node, the nerve impulse runs along three highways to the atrioventricular node. It is a kind of gateway with selective throughput and provides a physiological delay in the conduction of charges formed in the sinus node. The atrioventricular node is capable of generating nerve impulses with a frequency of 40-60 per minute (this is a second order pacemaker).
- This is followed by the His bundle (third order pacemaker) with the right and left legs, which generate nerve impulses with a frequency of 20-40 per minute.
- Well, the most extreme branches of the conduction system of the heart are Purkinje fibers, operating at a frequency of 15-20 impulses per minute.
A peculiarity of the conduction system of the heart is that its normal operation is regulated by the sinus node: nerve impulses “born” in it spread from top to bottom, occupying all conduction tracts, leaving no chance for other pacemakers to generate their own nerve impulses, suppressing their activity . Thus, if a patient develops arrhythmia, it means that either the formation of a nerve impulse in the sinus node is disrupted, or so-called ectopic (not from the conduction system) foci of nerve impulse formation appear, or the conduction of a nerve impulse in various parts of the conduction system is disrupted (aka blockades) .
How does a patient suffering from rhythm disturbances feel?
Very often we hear various metaphors from patients when describing their condition when they feel an arrhythmia. They often say that the heart “gurgles”, “turns over”, “quivers”, “freezes”, “shakes like jellied meat”, “beats like a bird in a cage”, “pounds” and many others. Remember the words from the song of the group “Spleen”? “My heart stopped, my heart froze...” Sasha Vasiliev sang about arrhythmia.
In a conversation with the patient, it is very important to find out several factors that will help to predict the nature of the arrhythmia and determine its potential danger to life. So, if you are worried about arrhythmia, try to characterize it using the following parameters:
- What causes arrhythmia? What is the cause of arrhythmia?
- Does the arrhythmia begin paroxysmally or gradually, with a “warm-up” period?
- What is the heart rate for arrhythmia?
- How long does the arrhythmia last?
- During an arrhythmia, do you feel pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, dizziness, or decreased blood pressure? Or maybe you even develop a fainting state or briefly lose consciousness?
- Does the arrhythmia stop spontaneously? Or does it stop only after using certain medications or when performing specific manipulations?
- How often does arrhythmia bother you? Is there a frequency of its repetition?
As you already understand, arrhythmias can be classified into paroxysmal (non-paroxysmal and paroxysmal) and constant. In addition, arrhythmias can be with an increase (more than 90 per minute) or a decrease (less than 60 per minute) of the heart rate.
We must not forget that changes in heart rhythm can be normal. For example, sinus tachycardia in response to emotional experiences or physical activity. And, conversely, sinus bradycardia during sleep under the influence of the vagus nerve or in professional athletes. In addition, the presence of up to 20 extrasystoles per hour is not considered a pathology when performing daily ECG monitoring.
What are the causes of arrhythmias?
The reasons are varied, but they can be standardized into 2 large groups, which often determine the patient’s management tactics: a distinction is made between organic (associated with anatomical defects in the structure of the heart and blood vessels) and functional (due to changes in the tone of the autonomic nervous system).
Among the organic causes, the main ones are coronary heart disease and previous myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, previous myocarditis, heart failure with low ejection fraction, left ventricular hypertrophy (due to hypertension or valve defects). Functional arrhythmias are more common in young patients and usually manifest as sinus tachycardia or sinus (respiratory) arrhythmia.
In addition, it is important to separately identify the so-called channelopathies, or electrical heart diseases, which, as a rule, are congenital pathologies in which the normal content of ions and electrolytes changes at the biochemical level.
There are a huge number of types of arrhythmias. Despite this, they are quite easy to diagnose. You just need to register an ECG. As a rule, major difficulties may arise here: it is not always possible to record an ECG at the moment when the patient feels an arrhythmia.
It often happens that the ECG outside an attack of arrhythmia is absolutely normal and uninformative for diagnosing the nature of the heart rhythm disturbance. I always recommend to my patients to call an ambulance or go to the nearest medical facility where they could record an ECG while the patient is experiencing arrhythmic sensations.
But it also happens that the arrhythmia persists for a very short time, or the heart rhythm returns to normal before the ambulance arrives. In such situations, it is necessary to recommend that the patient perform Holter (24-hour) ECG monitoring, in which the heart rhythm is recorded throughout the day. But even here there can be a catch: in the absence of daily frequency of arrhythmia, monitoring may be uninformative. Then it is necessary to carry out transesophageal pacing to actively provoke arrhythmia.
Treatment of arrhythmia directly depends on its nature and the reasons that caused it.
- For organic arrhythmias, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. For example, in patients with a history of myocardial infarction, the appearance of ventricular extrasystoles is an unfavorable sign and may be associated with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
- For functional arrhythmias, normalization of the work and rest regime is sufficient.
- For arrhythmias with a low pulse rate, which are accompanied by poor health (weakness, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, dizziness, loss of consciousness), implantation of a pacemaker is indicated.
- For arrhythmias with a high pulse rate, the prescription of tableted antiarrhythmic drugs or, if they are ineffective, radiofrequency ablation (laser cauterization) of the heart rhythm disturbance is indicated.
- If the arrhythmia is life-threatening, then patients are advised to undergo implantation of a cardioverter defibrillator.
- For some arrhythmias, so-called vagal tests are effective: holding your breath with straining at the height of inspiration for 5-10 seconds, reproducing the gag reflex by pressing on the root of the tongue with your fingers, immersing your face in a basin of ice water (“diving reflex”). But these tests are not a way to treat arrhythmias, but more often serve as assistants in their diagnosis.
The topic of arrhythmia is quite extensive. In each specific case, the approach is very individual. The patient’s task is to consult a cardiologist in a timely manner.
Take care of your health, and then the melody of your heart will always be rhythmic.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH A CARDIOLOGIST
The most important muscle
In terms of its durability and stability, the heart is one of the most resilient and reliable organs in the body. During the day, it makes more than 100 thousand contractions, and for each one it pushes blood through vessels, the total length of which is more than 100,000 kilometers. Just 40-80 contractions are enough to pump all the blood in the body, that is, one full circle of blood circulation takes an average of one minute.
The heart is a muscle whose main function is to contract and relax sharply. Contracting, it pushes out blood, acting as a kind of pump for pumping blood in our body. This work never stops - from the moment of birth until death. As long as the heart functions normally and pumps blood through the vessels, a person feels great. But as soon as the heartbeat rhythm begins to go astray, a certain discomfort is felt and thoughts of an inevitable death come.
Causes of rhythm disturbances
Arrhythmia can be congenital, acquired and idiopathic (when the cause is not identified). Acquired atrial fibrillation is most often a consequence of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. However, remember that having abnormalities does not necessarily mean you have heart disease. Arrhythmia can have many causes, which cannot always be determined.
There are factors other than heart disease that can cause or worsen arrhythmias. These terms include the following:
- infections and fever;
- physical or emotional stress;
- anemia or thyroid disease;
- taking stimulants (caffeine, tobacco, alcohol, amphetamines) and certain prescription and over-the-counter medications;
- some arrhythmias can also be inherited.
Dangerous symptoms
Common symptoms of arrhythmia include the following:
- heartbeat;
- a “missed contraction” that resembles a jerk;
- feeling as if “the heart is pounding in the chest.”
In addition, some patients experience symptoms such as feeling tired and weak, shortness of breath, and chest pain or discomfort.
When to see a doctor?
Most people have noticed palpitations, tremors in their chest, or a feeling that their heart has skipped a beat. If this happens once or occurs relatively rarely, without other symptoms, then it usually does not pose a serious danger. However, any questions or concerns should be discussed with your doctor.
More serious symptoms should be assessed directly at the emergency department of the nearest hospital:
- any unexplained shortness of breath;
- darkening of the eyes or fainting;
- a feeling that the heart is beating too slowly or too quickly;
- chest pain combined with any of the above symptoms.
People with such a clinical picture should immediately call an ambulance to call emergency help at home, and not try to get to doctors on their own.
Start with a survey
To find out the causes of heart palpitations, it is not enough to discuss the symptoms with a doctor; a medical examination is required. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is mandatory. If rhythm disturbances are present at the moment, they are recorded by the ECG and the problems can be identified immediately. Otherwise, more in-depth research may be required. Often they resort to recording the heartbeat for 24 hours (24-hour monitoring). However, if the arrhythmia occurs even less frequently, long-term monitoring may be used.
Ultrasound examination of the heart, called echocardiography, is often used to study its structure and function. In more serious cases, diagnostics are used using electrodes implanted inside the heart. This is a so-called invasive electrophysiological study (EPS), which may be recommended to determine further treatment and monitor the condition.
The course is for cure
Treatments for arrhythmia vary depending on the presence or absence of symptoms, the frequency of attacks, and the severity of the underlying heart disease. Treatment can range from medications to more complex surgical procedures such as an implanted cardiac cardioverter defibrillator. Sometimes simple or specialized pacemakers may be needed to eliminate arrhythmia.
The choice of medication depends on the specific type of heart rhythm disorder. A detailed discussion is possible only with the attending physician if the diagnosis has been accurately made.
Follow-up care for a patient with arrhythmia is usually performed by a cardiologist. The effectiveness of treatment, relapses, side effects of medications are monitored, regular examination of general condition and additional procedures are carried out.
Methods for identifying and treating cardiac arrhythmias are constantly being improved. In recent years, there has been significant progress in knowledge about these conditions. Timely detection and treatment of arrhythmia will improve the quality and length of your life.
Interruptions in the heart: what causes the heart to work incorrectly?
Interruptions in the heart (impaired heart rate, arrhythmias) occur due to a disruption in the formation of an excitation wave in the sinus node and its further propagation.
There are several types of heartbeat disorders - tachycardia, bradycardia, extrasystole. Normally, the contraction frequency is 60-90 beats per minute with equal intervals between them.
Types and risk factors
With tachycardia, the heart rate increases to 100 beats per minute.
The following types of tachycardia are distinguished by location:
- sinus;
- atrial;
- ventricular;
- atrioventricular.
With the flow:
- acute form (first appears in the acute period of any disease);
- paroxysmal (characterized by inconsistency, there may be periods of normal heartbeat or a single episode of arrhythmia may be recorded);
- recurrent (repeated heart failure);
- constant.
8
24/7
Depending on the pathogenesis:
- returnable;
- automatic;
- focal.
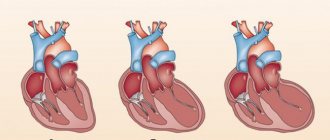
One form of tachycardia is atrial fibrillation. It consists in their frequent and irregular reduction. It is rarely diagnosed at a young age. It can be asymptomatic for a long time, but carries a high risk of death, as it is associated with the development of heart failure and thrombus formation.
Frequent and regular contraction of the atria is called flutter. Characterized by the occurrence of attacks, the chronic form is practically not recorded. Atrial flutter quickly leads to heart failure with the formation of edema.
However, it should be noted that there is also physiological tachycardia - this is a normal reaction of the body to increased physical activity, increased temperature, and excitement. Such cases do not require treatment and are not dangerous.
Tachycardia can also be a reaction to taking a number of medications and goes away upon completion of treatment.
Bradycardia is a slowing of the heart rate to less than 60 beats per minute.
Along the flow they distinguish:
- paroxysmal;
- chronic form.
Type:
- sick sinus syndrome;
- atrioventricular blockade.
With atrioventricular node weakness syndrome, there is a decline or shutdown of the activity of the sinus node, where the excitation impulse necessary for the functioning of the heart occurs.
With atrioventricular blockade, there is a disturbance in the conduction of electrical impulses to the ventricles. Both forms are characterized by a progressive course.
Atrioventricular blockades can be of varying degrees - there are 3 degrees in total. With the second and third, there is a high probability of cardiac arrest.
Extrasystole is the occurrence of additional contraction of the heart muscle.
There are several classifications according to which they are distinguished:
Depending on location:
- sinus;
- atrioventricular;
- atrial;
- ventricular extrasystoles.
By frequency:
- rare (less than 10 per hour);
- medium frequency (10-30 per hour);
- frequent (more than 30 per hour).
Risk factors for heart failure include:
- Hereditary predisposition. Arrhythmias are often the result of congenital anomalies.
- Thyroid diseases. With hyperfunction, increased production of hormones occurs and metabolic processes accelerate. This leads to increased and irregular heartbeat. As a result, atrial fibrillation develops. With hypofunction, bradycardia or extrasystole may develop.
- High blood pressure. Leads to hypertrophy of the wall of the left ventricle, the process of impulse transmission is disrupted.
- Diabetes. In the decompensated stage, the risk of developing arterial hypertension and ischemia increases significantly.
- Electrolyte concentration. Its change leads to disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart muscle.
8
24/7
Causes
The causes of tachycardia can be divided into several groups:
- Caused by damage to the heart muscle. This group includes heart attacks, myopathies, ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, myocarditis, etc.
- Associated with metabolic disorders in the body. Decreased potassium and magnesium levels, toxic effects of alcohol, nicotine, renal failure.
- Impact of medications. Heart rhythm can change under the influence of glycosides, stimulants of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Thyroid diseases, hyperthyroidism, diabetes.
The reasons for the development of extrasystole are similar to the reasons for the occurrence of tachycardia. Bradycardia can occur due to the following reasons:
- factors related to heart function, as with tachycardia;
- increased levels of calcium, magnesium;
- diseases of the esophagus, stomach;
- the use of antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as some analgesics, in drug therapy;
- vagotonia;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland.
Symptoms
The following symptoms are characteristic of tachycardia:
- interruptions in the heart;
- increased heart rate or missed beats;
- rapid and uneven heartbeat;
- increased fatigue under standard loads;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of oxygen during physical activity;
- dizziness, circles before the eyes, fainting;
- drop in blood pressure;
- chest pain.
Extrasystoles, as a rule, are not accompanied by the occurrence of additional symptoms. There may be interruptions in the heart, a feeling of increased shock or cardiac arrest.
Symptoms characteristic of bradycardia:
- slow heartbeat;
- feeling of cardiac arrest, irregular heartbeat;
- severe weakness, inability to perform usual workload;
- changes in blood pressure levels;
- disturbances of consciousness, deep fainting is possible;
- the occurrence of chest pain not associated with physical activity.
Diagnostics
When heart problems begin, what should you do first? It is necessary to undergo diagnostics that will confirm the arrhythmia and help identify concomitant diseases.
Diagnosis of arrhythmias involves a thorough examination of the patient’s complaints, after which standard examinations are carried out:
- ECG;
- Holter monitoring – registration of impulses using a special device during the day;
- Ultrasound of the heart - performed through the chest or esophagus, can detect clots.
Treatment
How to treat heart failure? When treating tachycardia, one of 2 possible treatment tactics can be chosen:
- restoration and maintenance of normal heart rhythm;
- control of heart rate without restoring rhythm.
Treatment of heart failure must begin as early as possible. The general principles of treatment are as follows:
- the need to restore heart rhythm in young patients without cardiac dysfunction;
- maintaining heart rate in elderly patients at a level not exceeding 90 beats at rest and not more than 115 during exercise;
- using anticoagulants to prevent clot formation;
- Identification and elimination of the causes that caused interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
Heart failure can be treated in several ways:
- “Restarting” the heart involves the use of medicinal methods (Propaphenol, Flecainide), an electrical method (discharge) or a hybrid option.
- Drug therapy to normalize the rhythm involves taking beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and glycosides.
- Ablation may be used to restore normal rhythm. During the procedure, those areas where pathological electrical activity is observed are destroyed. Cardiac ablation can be performed by catheter or by open surgery (in cases where intervention is necessary for other reasons).
- Special devices can also be installed to regulate the rhythm frequency. The methods used depend on the patient's condition. In severe forms of heart failure, surgery is indicated, while non-life-threatening conditions can be corrected by taking medications in combination with ablation.
Treatment of extrasystole involves taking beta blockers, as well as ablation of the area where the additional impulse originates.
Treatment of bradycardia involves eliminating the root cause that caused the slow heart rate. Drug treatment consists of taking xanthines and anticholinergics. If there is a risk of cardiac arrest, a pacemaker is installed.
Forecast
Heart failure can be a warning sign of life-threatening conditions. Possible development of stroke and heart failure.
When blood flow is slow, clots can form. When they enter a vessel and block it, a stroke occurs, which can be fatal.
Heart failure may also develop, in which the efficiency of the heart decreases, it runs idle, and wears out faster.
Interruptions in heartbeats caused by non-cardiac pathologies can be corrected when the root cause is eliminated.
Types of arrhythmias, the occurrence of which is caused by damage to the heart muscle, can give a different prognosis - it all depends on the extent to which the blood supply is impaired. You need to know that chronic forms are prone to progression and require constant monitoring by a doctor.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle plays a vital role in heart health. Intoxication with nicotine and alcohol, clogging of blood vessels with cholesterol, physical inactivity and a constant state of stress can significantly harm the functioning of the heart.
Heart failure can have serious consequences. If these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a cardiologist and undergo the necessary examinations.
8
24/7