Pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling is a symptom, the cause of which is determined depending on the nature of the pain, intensity and time of appearance. Discomfort can be caused by spasm of smooth muscles, injuries, gastrointestinal diseases, bronchopulmonary diseases and much more. The severity of pain becomes more pronounced when coughing, sneezing and even inhaling.
The first step is to contact a therapist, who, if necessary, will refer you to a specialist. A qualified doctor first collects anamnesis - all the data about the medical history, conducts an examination and then sends you for tests. All this helps him in making an accurate diagnosis.
Any pain is a signal from the body about an existing disorder and should not be ignored under any circumstances. Early diagnosis allows you to prevent the problem from worsening and the process becoming chronic. Let's take a closer look at the causes of pain in the left hypochondrium in front.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
This disease is very common today.
People who have sedentary jobs are especially susceptible to it. With this pathology, the nerve endings extending from the spine are compressed, which causes pain under the left rib. It often radiates to the back, buttock, and even thigh; it can be encircling in nature, accompanied by numbness and tingling. The fact that the cause of pain is osteochondrosis may also be indicated by a decrease in the mobility of the thoracic region. “Shots” occur not only when inhaling, but also during movements and sudden turns of the body. In most cases, they overtake a person after being in an uncomfortable position for a long time. They often happen during sleep.
Methods for treating pain behind the sternum in the middle
Therapy depends on the disease:
- For tracheitis, pneumonia and pleurisy, antibiotics, immunostimulants, and analgesics are used.
- In case of pulmonary embolism, anticoagulants are used and the blood clot is eliminated surgically.
- Heart diseases require the use of analgesics, anticoagulants, and beta blockers.
- Costochondritis requires physical treatment and NSAIDs.
Chest pain when inhaling can occur with a dangerous pathology. Therefore, when the symptom does not go away, it is better to consult a specialist. Preventive measures will include good nutrition, avoidance of bad habits and exercise.
To determine the cause of the symptom, a comprehensive examination is carried out, including:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- radiography;
- fluorography;
- MRI or computed tomography;
- sputum samples;
- electrocardiography.
Modern laboratory and diagnostic equipment makes it possible to accurately identify pathology in the chest. Treatment depends on the diagnosis.
For lung diseases, the patient is prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- expectorants;
- inhalation;
- physiotherapy.
Detection of a blood clot in the arteries will require the administration of a coagulant. For inflammatory processes, corticosteroids and painkillers are prescribed.
Conservative treatment of pleurisy is carried out:
- antibacterial drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- warming therapy (mustard plasters, thermal physiotherapy).
For intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis, general tonic drugs and vitamins are prescribed. Problems with housing and communal services require, first of all, diet.
The treatment tactics for a patient who complains of difficulty breathing and pain in the middle of the chest depends on the cause of the pain and consists of eliminating the underlying disease.
- Treatment of pulmonary pathologies consists of prescribing antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and immunomodulators. The patient is prescribed bed rest, inhalations, drinking large amounts of hot drinks, quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Treatment of cardiovascular diseases includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating the right foods, doing breathing exercises, walking in the fresh air, and taking medications that dilate coronary vessels and thin the blood.
- Treatment of spinal diseases requires an integrated approach. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, B vitamins are prescribed. Various methods of physiotherapy, osteopathy, massage, and therapeutic exercises are used.
- Treatment of pain due to injuries in the chest, between the shoulder blades in the spine, accompanied by fractured ribs, sprained muscles and ligaments, consists of immobilizing the patient and protecting the damaged area of the body. Ice is applied to the affected area to relieve pain and prevent swelling. Special creams are used to treat damaged muscles. Massage and gentle daily stretches can help speed up recovery from injuries.
Thus, if the chest hurts, it’s hard to breathe - this can be a clinical sign of more than a dozen different diseases.
If such pain occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, as the consequences may be unpredictable.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is another very common factor that causes pain under the ribs on the left. The latter is very similar to the heart, which can cause real panic. The reasons may be:
- osteochondrosis;
- unsuccessful rotation of the body;
- hypothermia;
- draft;
- cold;
- enlarged uterus (during pregnancy).
An attack of intercostal neuralgia is often accompanied by numbness of the upper extremities, muscle twitching, increased sweating, and pallor of the skin. The pain intensifies not only when breathing, but also when coughing, sneezing, yawning, turning the body, and can last from several hours to a couple of days. Often a person is forced to remain immobilized all this time, since every movement brings him pain.
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system
The rib cage is formed:
- sternum;
- ribs;
- collarbones;
- thoracic spine.
The bone apparatus is surrounded by muscle mass and penetrated by nerve fibers. All these formations can become a source of pain. And with a number of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, pain occurs specifically with the deepest breath. The reason for this is the movement of the chest during breathing ( the main form of dissimilation in animals, plants and many microorganisms
).
As you inhale, it rises and expands, which can lead to pain due to certain pathologies.
Osteochondrosis
Degenerative pathology of the spine, from which more than half of the adult population of the planet suffers. With osteochondrosis, atrophic changes in the intervertebral disc occur. The nucleus pulposus of the disc loses its elasticity, due to its pronounced hydrophilic qualities. The moisture leaves, the disc becomes the least flexible and most flattened.
The fibrous ring, which normally maintains the proper size of the nucleus pulposus, also suffers. Due to the displacement and approach of adjacent vertebrae to each other, radial cracks may appear on the ring. The ligaments that support the spinal sector are destroyed. Its instability develops, the vertebrae become displaced, causing radicular syndrome with pain.
Similar configurations occur to varying degrees in all people as they age. They are most pronounced in the presence of excess weight, irrational physical overload, and prolonged immobile life. Chest pain when inhaling occurs with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, when the movement of the chest affects the affected vertebral sectors.
Intercostal neuralgia
A neurovascular bundle runs along the lower edge of all ribs. The nerves passing through it are often the source of neuralgia.
The etiology of this lesion is different:
- hypothermia;
- infringement;
- infection;
- irritation.
More often, episodes of intercostal neuralgia appear against the background of spinal osteochondrosis.
A little less often, the pain is caused by shingles - a herpetic infection. Activation of the herpes virus can be triggered by hypothermia and constantly occurs against the background of a natural decrease in immunity:
- in old age;
- with sweet diabetes;
- with primary and secondary immunodeficiencies.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain is constant, it is localized on the affected side. Its intensification during inspiration is also associated with the movement of the chest, in particular the ribs. The pain is powerful and hot, radiating along the entire length of the nerve fiber, from the sternum to the spine ( the supporting element of the skeleton of vertebrate animals (including the human skeleton)
).
Fractured ribs
Closed chest injury ( Chest - upper body
) in more than half of the situations is complicated by damage to the ribs. More often this occurs in older people, which is explained by increased fragility and fragility of bones. Depending on the number of broken ribs, a person's condition can range from moderate to extremely severe.
Important Tablets for sore throat: inexpensive but effective, for children and adults
Fractures of 1-2 ribs are traditionally not serious, they do not require inpatient treatment. For fractures ( a polysemantic term meaning: Bone fracture General Autofracture Marching fracture Avulsion fracture Pathological fracture Stress fracture Specific Femoral fracture Tibia fracture
) 3 and most ribs (
last name
) the risk of damage to the chest organs increases: heart, lungs, large vessels. Multiple bilateral fractures constantly require emergency medical care.
Chest pain associated with rib fractures is localized at the site of impact or suspected fracture. It intensifies even with shallow breathing and coughing, which can lead to forced hypoventilation and pneumonia.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ovPc971vgyU
Heart diseases
Pain in the left hypochondrium may well be caused by heart diseases, such as ischemia, angina, cardiomyopathy and others. The most serious of them is myocardial infarction. Pain in this case is accompanied by both the development of the pathology and the condition preceding it.
Associated signs indicating a heart attack:
- dyspnea;
- chills;
- cold clammy sweat;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- sharp pallor of the face (even to the point of cyanosis) and puffiness;
- numbness of hands.
Pain on the left side can radiate to the shoulder blade, shoulder, or neck. It is sharp, burning (and not aching, as, for example, with colitis), accompanied by heaviness behind the sternum. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance, as this is a life-threatening condition.
Pain under the left rib behind
Such localization of pain may lead the doctor to think about the presence of kidney disease. To confirm the diagnosis, a general blood test and ultrasound examination are prescribed. Sometimes pain under the ribs at the back indicates the presence of lumbar or thoracic osteochondrosis. X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests may be needed to make a diagnosis.
Pain in the left intestine
Other reasons can cause such pain, namely:
- pericarditis;
- pneumothorax;
- pleurisy;
- renal colic;
- acute pancreatitis;
- myocardial infarction.
Lung cancer
With cancer of the left lung, when the tumor grows into the pleura, pain appears in the chest. They usually appear at a late stage. The pain radiates to the neck, arm and stomach. It can be sharp and stabbing. Often has a girdling character.
This symptom is accompanied by others characteristic of lung cancer:
- This is primarily a cough.
- The patient suffers from lack of appetite and rapidly loses weight.
The signs of this pathology are in many ways similar to dry pleurisy. And pain in the left side when inhaling is one of the common symptoms. Pleurisy is often the first and only manifestation of tuberculosis, occurring at its initial stage. It is diagnosed when there are foci of disease in the lungs or lymph nodes.
Tuberculous pleurisy can be purulent. Accompanied by fever, increased sweating, shortness of breath, chills. A person suddenly loses weight.
Sharp nature of the pain syndrome
The sharp nature of the pain may indicate perforation of the stomach or perforation of the upper parts of the small intestine. This type of pain is a reason to immediately call an ambulance.
Sharp pain also indicates a rupture of the splenic capsule. If the pain becomes girdling, the doctor may suspect an attack of acute pancreatitis. In this case, the discomfort is not associated with changes in body position, sudden movements or coughing.
Sharp pain is a sign of perforation of the stomach walls
Stomach ulcer
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain may also occur under the left rib in front. This symptom is preceded by signs characteristic of colitis (flatulence, bloating). Then the person is overtaken by pain, it is dagger-like and strong. Sometimes tolerable, and sometimes capable of causing loss of consciousness, it can shift slightly to the right.
Often pain occurs after eating. Accompanied by other symptoms: nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, belching with an unpleasant aftertaste. If cutting, stabbing pain occurs and there is a history of a stomach ulcer, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
What can hurt in the chest?
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
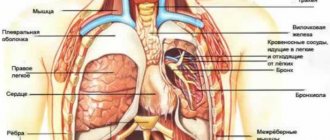
To understand why the chest hurts when you inhale, you will have to remember the anatomical structure and placement of organs in this part of the body. The thoracic region contains:
- the heart located in the heart “bag” - the pericardium;
- thoracic spinal column;
- trachea, branching in the lower part into bronchi;
- the aorta is the largest artery of the human body;
- lungs covered with pleura - a protective film that softens their friction against the costal arches.
In the lungs themselves ( air breathing organs in humans, all mammals, birds, reptiles, most amphibians, as well as in some fish (lungfishes, lobe-finned and multifinned fish)
) there are bronchi and bronchioles, which are supplied with nerve cells, as well as the pleura and all the organs listed above.
In addition, colic from an inflamed gallbladder or from the stomach or duodenum, affected by ulcerative action, can radiate (spread) into it. In the end, for various reasons, the intercostal muscles may ache from excessive overload (for example, pain during intense training or due to prolonged coughing) or the ribs themselves, if they have been injured. As you can see, there is a lot to suffer from in the chest and each option should be dealt with separately.
Gastritis
When there is periodic pain in the upper left side, gastritis can be suspected. Discomfort is also felt in the stomach. The pain is not acute - aching, radiating under the shoulder blade. It usually occurs after eating and then subsides. It often does not bring much discomfort to a person, so many do not attach importance to it for a long time. Meanwhile, the disease progresses.
Painful sensations with gastritis are accompanied by periodic nausea, heartburn, unpleasant belching, vomiting, problems with stool (constipation or diarrhea), weakness, and pale skin. When moving, turning the body, as well as taking a deep breath, the pain in the stomach area and above may intensify. Many manifestations are similar to signs of colitis, so gastritis is differentiated from this disease first of all.
Treatment
Since chest pain during inspiration can be caused by pathologies of different organs and systems, their treatment tactics will vary significantly.
Myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism can be treated with thrombolysis - intravenous administration of drugs that can “dissolve” blood clots. However, such procedures are effective in the first 4-6 hours from the moment pain appears. At a later date, other treatment methods are used.
Other cardiac causes may require normalization of blood pressure, heart rate with the help of appropriate medications, restoration of heart valve function by replacing them, etc.
Infectious lesions of the lungs, accompanied by pain in the heart area, may require the use of antibacterial or antiviral agents. For bronchial asthma, the treatment regimen includes β2-agonists, glucocorticosteroids, etc.
Gastrointestinal pathologies can be brought under control by normalizing nutrition and physical activity; doctors advise fighting obesity and taking medications that affect the pH level of the stomach cavity.
Intercostal neuralgia is treated with analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, B vitamins and muscle relaxants.
In case of psychogenic cardialgia, it is recommended to consult a medical psychologist or psychiatrist to decide on the need to use sedatives.
Pancreatic diseases
The pancreas is located on the left side, and with pathologies of this organ, pain in the hypochondrium often occurs. This is one of the most typical symptoms of pancreatitis. The pain is girdling in nature. It is unsharp, aching, and often quite strong. The intensity increases as you inhale. A person has to “fold” in half to alleviate the condition.
Pain usually occurs after a feast. Especially abundant and with the use of strong drinks. Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by nausea, vomiting with bile, and heartburn. The urine becomes dark, and the stool becomes abnormally light in color. During acute attacks, the temperature may rise significantly.
Diagnostics
It is possible to reliably determine whether the eyelids are affected by mites only through microscopic examination. After this, you need to determine the number of larvae and adults; for this, an acoragram is compiled. With concomitant inflammation of the meibomian glands, a puncture or excisional biopsy should be performed.
The diagnosis is made by a specialist based on examination, patient complaints and tests.
To determine the causative agent of the infection, research is carried out in the laboratory. To do this, three to four eyelashes are taken from the patient from one eyelid and the same number from the other eyelid. They are placed under a microscope and if demodex is detected at any stage of development, blepharitis of the demodectic variety is diagnosed.
Pathologies of the spleen
Another organ located on the left is the spleen. It is closest to the surface of the body, so any abnormal processes occurring in it immediately make themselves felt. Problems with the spleen often occur after or during infectious diseases, since this organ is responsible for filtering blood from dead red blood cells. It greatly increases in size, fighting the virus, which explains the discomfort.
Sometimes the spleen is damaged by the ribs as a result of injury. It breaks. In such cases, pain appears not only when sighing or moving, but also on its own. It can be very strong, difficult to bear, and it radiates to the back.
Pathologies of the spleen are often accompanied by increased body temperature, inflammation of regional lymph nodes, headaches, and enlarged liver. When an organ ruptures, the skin in the navel area turns blue. If such symptoms are present, you should immediately seek medical help.
If you take your breath away
It happens that when a person inhales, he experiences not pain, but a feeling as if his breath is being taken away in the chest. The causes of this condition often lie in pathologies of the respiratory system in all their diversity. But there may also be neurological reasons for the occurrence of such sensations.
To differentiate diagnoses, you should pay attention to some features of the clinical picture:
- when “interception” of breathing occurs (in the morning or before bed, in a calm state or against the background of excitement, etc.);
- how long does the “respiratory spasm” last?
- after which breathing is restored;
- how do you feel after an “attack” of lack of air;
- Are changes recorded on the ECG?
All this is of great importance for diagnosis. The patient needs to keep a health diary and record in it all cases of occurrence of such symptoms, their duration and other details.
Such records will be useful when visiting a neurologist and will help the doctor quickly understand the situation.
The patient needs to keep a health diary and record in it all cases of occurrence of such symptoms, their duration and other details. Such notes will be useful when visiting a neurologist and will help the doctor quickly understand the situation.
What to do if such pain occurs
When a person experiences pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling, it is recommended not to waste time and contact a medical facility to determine its correct cause. The following doctors diagnose this condition:
- endocrinologist;
- cardiologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- gynecologist;
- surgeon.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited, because it will worsen the general condition and provoke the emergence of various complications. You need to know when to go to a medical facility. There are situations when pain cannot be ignored. An ambulance should be called in the following cases:
- aching pain that lasts for an hour;
- dull pain accompanied by coughing and vomiting (often with blood);
- stabbing pain that does not go away for more than half an hour and gets worse;
- sudden sharp pain.
So, we have looked at the most common situations in which pain occurs in the left hypochondrium when taking a deep breath. It can also occur with movement, coughing, sneezing, and even at rest. In most cases, the cause of pain is serious dysfunction of vital organs: heart, stomach, lungs, pancreas, spleen.
And sometimes we are talking about critical conditions when a person needs help urgently. Therefore, if there is pain in the left chest, you cannot endure it and wait for it to go away on its own. You need to contact a doctor as quickly as possible, establish the cause and eliminate it before unwanted complications and consequences appear.
Pathological causes
There is no medicine that would treat pain in the left side. The fight against an unpleasant symptom is, first of all, a search for the root causes. Let's look at diseases that can cause pain on the left side.
Acute appendicitis
The appendix is a vermiform appendix that is an organ of the immune system. The process is not always located on the right side, as is observed in most people. The inflammatory process can be triggered by blockage of the appendix with feces, food fragments, an infectious process, an allergic reaction, bad habits, and stress. Poor nutrition and strict diets can also cause appendicitis.
Almost everyone knows that when the appendix is inflamed, it hurts in the lower right side. But in fact, at the very beginning the pain is localized in the upper abdominal cavity and only then moves to the right side. In addition to pain in the hypochondrium, bloating and colic appear.
After defecation, the pain subsides, and then an attack of acute pain appears again. Deep breathing and physical activity lead to increased discomfort. Lying on the right side reduces discomfort. The pain typically occurs in the evening and at night.
With appendicitis, there is a sharp pain that intensifies with inhalation and physical activity.
Acute appendicitis is a surgical pathology that requires emergency medical care. First aid for appendicitis is extremely important; if it is provided incorrectly, it can blur the clinical picture and cause difficulty in making a diagnosis.
Gastritis
Gastritis can be acute or chronic. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs for a number of reasons: stress, bacterial infection, dietary errors, neuroses, and more. Exacerbation of the disease causes pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium. It has an aching or sharp burning character.
Sometimes patients feel discomfort in the back of the body, radiating under the scapula. The pain is aggravated by diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and belching. The disease disrupts the general condition, causing dizziness, weakness, and irritability.
Stomach ulcer
This is a chronic disease that causes trophic disorders. The process is characterized by frequent alternation of periods of remission and relapse. Exacerbation most often occurs in autumn and spring. The emotional state plays a major role in the occurrence of peptic ulcers. Frequent stress causes muscle and blood vessel spasms.
Peptic ulcer disease causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, belching, and general malaise. Pain in the left hypochondrium occurs against the background of symptoms of general intoxication of the body. The causes of ulcers are similar to the provoking factors of gastritis. Helicobacter pylori infection plays the main role in the occurrence of ulcers. Pain also occurs in the epigastrium, can radiate to the back and intensifies with inspiration.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can be caused by overeating, poisoning, infections, injuries, gallbladder and stomach diseases. The inflammatory process leads to the fact that the organ ceases to function normally and begins to absorb its own cells.
[node:field_field_doprekl]
The acute process causes unbearable pain on the left side under the ribs. The discomfort can be diffuse, occurring over the entire surface of the abdominal cavity and radiating to the back. The person takes a forced position, in which the pain subsides a little - sitting on a chair in a bent position.
An attack may begin after eating and be accompanied by dyspeptic disorders.
The condition is aggravated by the appearance of nausea, hiccups, vomiting, bloating, fever, and weakness. During an attack of pancreatitis, it is forbidden to eat at all. Cold is applied to the upper abdomen. The patient must remain completely at rest.
Splenic rupture
The spleen is the largest organ of the lymphatic system. The organ is located on the left side under the ribs, so if the organ is damaged, painful sensations arise in this area. Essentially, the spleen is a repository of red blood cells, it purifies the blood and is involved in immune processes. The organ is also responsible for neutralizing pathogenic microflora in the blood and accumulating platelet reserves.
Organ rupture causes mechanical damage to the abdominal cavity. The spleen begins to bleed, causing blood to enter the abdominal cavity. Severe shooting pain in the left side under the ribs intensifies not only with physical activity and coughing, but even with inhalation. Over time, discomfort from the left side spreads to the entire abdomen.
Stiffness of breathing is also observed. As the pathological process progresses, the site of the spleen projection becomes bluish, chills, high fever, nausea, vomiting, and arterial hypotension appear.
Rupture of the spleen can also be provoked by acute viral and bacterial infections, excessive motor activity during inflammatory processes in the organ, and a sharp increase in blood volume during pregnancy.
Splenic rupture is a common cause of pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling.
Diaphragmatic hernia
The diaphragm is the main breathing muscle. Conventionally, the diaphragm separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic region. The development of a hernia causes an increase in the lumen of the esophagus and movement of the lower lobe of the stomach upward.
[node:field_field_doprekl2]
The causes of diaphragmatic hernia can be very diverse: heavy lifting, pregnancy, frequent constipation, obesity, diseases of the digestive tract and bronchopulmonary apparatus. The danger of the pathology is due to the fact that the organ that has penetrated into the chest cavity interferes with the normal functioning of the heart and lungs, and even the gastrointestinal tract organs themselves.
This leads to the appearance of aching pain in the left hypochondrium of a constant nature. In addition to pain, there is excessive regurgitation after eating. This is due to the unauthorized reflux of food from the esophagus into the oral cavity. The patient simply cannot take a full breath.
In addition to pain, patients are worried about heartburn, belching of air, bloating, difficulty swallowing, burning behind the sternum, difficulty breathing, persistent cough, tachycardia after eating.
Medications do not eliminate the problem, they only eliminate clinical symptoms and prevent complications. With the help of an operation, the surgeon sets the organ in its place.
Diaphragmatic hernia leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract
Acute pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys is affected. The following reasons can cause inflammation: bacterial infection, chronic foci of infection, neoplasms, stones, hypothermia, overwork, etc.
Inflammation of the left kidney provokes pain in the left hypochondrium and between the ribs with irradiation into the abdominal cavity. The urge to urinate increases, but there is no urine output. Pyelonephritis disrupts the general condition and causes hyperthermia. The clinical picture of acute pyelonephritis is characterized by fever with chills and increased sweating.
Renal colic increases with inhalation and subsides with exhalation. Coughing also worsens colic, and the patient may even experience painful shock. The pain may even cause a person to lose consciousness. Clinical symptoms of an acute process develop at lightning speed. Temperatures rise to critical levels.
Cardiac disorders
The diaphragm is closely connected to the heart, so inhaling can cause severe pain if you have heart disease. Painful sensations in the left hypochondrium can provoke diseases of the muscular lining of the heart - the myocardium.
Cardiomyopathy is fraught with the occurrence of a heart attack, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- inability to inhale;
- acute shooting pain in the area of the heart and shoulder blades;
- discomfort radiates between the ribs and down to the abdominal cavity;
- in an upright position, the pain in the left side of the abdomen intensifies.
With coronary heart disease, adequate nutrition of the organ is disrupted. Periodic shooting pain occurs in the side and left side of the chest, intensifying with inhalation.
Heart diseases can provoke pain in the left hypochondrium
Respiratory system diseases
The main symptom of the bronchopulmonary system is difficulty breathing. Still, some pathologies can cause pain on the left side when inhaling. One of these diseases is pleurisy. Dry left-sided process causes a suffocating cough without sputum production, which causes an attack of acute pain. Along with this, temperature indicators increase.
Pneumonia also causes left-sided pain. The infectious process affects both the lungs themselves and their membranes. The pain is aggravated by hyperthermia, dry painful cough, shortness of breath, hyperhidrosis, rapid breathing, and inability to take a deep breath.
Musculoskeletal disorders
Nagging pain in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies with inspiration, is caused by bruises and injuries to the sternum with damage to soft tissues. This is due to damage to nerve endings. Fractured ribs also cause pain on the left side when inhaling sharply. Due to improperly fused bones, nerve endings are pinched. As a result, the pain becomes permanent.
Intercostal neuralgia also causes acute shooting pain. Inhalation and twisting of the body increase the intensity of pain. Intercostal neuralgia is compression and irritation of the intercostal nerves.
As a rule, the disease is preceded by an acute muscle spasm due to careless sudden movements, physical overexertion, and prolonged exposure to a draft.
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by severe burning pain in the chest
The pain can radiate to the heart, shoulder blade, neck, lower back, arm. The attack is accompanied by redness, sweating and even muscle twitching. Therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving pain, inflammation and muscle spasms.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is one of the most common causes of pain when inhaling. Pressure from the nerve endings causes discomfort on the left side. This part of the spine contains a large number of nerve fibers, which can make it seem like there are problems with the heart, stomach or gall bladder.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, patients complain of numbness in the legs, abdomen and chest, as well as reflex muscle tension. In severe cases, disruption of the pelvic floor organs occurs. Treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis is aimed at stopping the destruction of the vertebral discs, restoring their structure, as well as eliminating disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
What to do at home if your shoulder hurts
If you suddenly experience severe pain, you must first of all calm down and make the right decision: seek medical help.
You should know: any acute diseases, including those accompanied by severe pain, are easier to treat and are often completely cured. Therefore, the sooner you see a doctor, the more favorable the outcome of the disease will be.
But there are situations in life when it is not possible to immediately visit a doctor. What to do if shoulder pain does not improve? The advice is still the same: consult a doctor, he will help even in advanced conditions: he will relieve pain and stop the progression of the disease.
How to help yourself
The pain can be very severe and then the question arises, how to help yourself, how to survive this condition and get to a specialist? You can call an ambulance or help yourself:
- Take painkillers:
- Ibuprofen
- quickly and effectively relieves pain, swelling and fever; if there are no contraindications for use, you can take 1 – 2 tablets of 200 mg, washed down with half a glass of water (this will make the drug work faster); contraindications: erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), increased bleeding; - Paracetamol (Panadon, Efferalgan)
is also an effective drug in sufficient dosage; To eliminate pain, take 1 tablet of 500 mg; There are practically no contraindications; - Ibuklin
is a combination drug; 1 tablet for adults contains 400 mg of ibuprofen and 325 mg of paracetamol; It acts quickly and effectively, but has the same contraindications as Ibuprofen. - Use external agents - gels, ointments. They can relieve pain well, especially in combination with painkillers or injections:
- Diclofenac gel (Voltaren, Diclovit, Ortofen)
– applied in a thin layer to the painful area; very effective ointment; - Ketoprofen gel (Artrum, Bystrumgel)
- after application to the skin, the ointment for shoulder pain is quickly absorbed and has an analgesic effect; - Menovazin
is an alcohol combination solution that contains painkillers and sedatives.
Carrying out pain relief on your own is a necessary measure and it does not in any way cancel a visit to the doctor!
Exercise can help too. Training is carried out after the acute pain has been eliminated. Regular exercise helps improve blood circulation and metabolism in affected tissues, and prevents the development of irreversible changes that block the motor activity of the hand.
Basic training requirements:
- regularity – classes should be held daily;
- lack of heavy physical activity and sudden movements;
- all exercises must be performed smoothly;
- if there is a sharp increase in pain, stop training; exercises are continued after the intensity of the pain syndrome has decreased with lower loads, increasing them very gradually.
Several exercises designed specifically for patients with glenohumeral pain syndrome:
- Starting position (IP) – lying on your back, arms along the body, palms up, legs slightly apart. Inhale: raise your hands and place them behind your head; exhale: smooth return to IP.
- IP - lying on your back, arms outstretched to the sides. Inhale: without lifting your hands from the surface, make a sliding upward movement. Exhale - return to IP. Repeat the exercise moving down and back.
- IP - lying on your stomach, arms extended forward, legs spread. Inhale: raise your right arm and left leg, exhale - move to IP. Repeat the exercise with your left arm and right leg.
Exercises for shoulder pain
What not to do
In case of chronic pain syndrome in the glenohumeral region, the following is contraindicated:
- some hand movements - which ones are determined by the doctor after clinical tests and additional examinations; it all depends on which structures are affected;
- any sudden hand movements and heavy lifting;
- frequent smoking and alcohol abuse - has a negative effect on blood circulation and metabolism, which aggravates the problems;
- self-medication - the result will be impaired hand function and increased pain; treatment must be carried out at a professional level.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
A doctor’s consultation is required if there is pain in the glenohumeral region:
- appeared immediately or some time after the injury; they intensify when the hand moves in a certain direction;
- the shoulder hurt against the background of existing chronic arthritis affecting other joints;
- accompanied by fever, redness, swelling and pain in the shoulder area;
- appeared against the background of cervical osteochondrosis with painful lumbago in the neck, extending to the glenohumeral region;
- discomfort, crunching when moving and occasional minor pain have been bothering me for more than 3 months.
Self-medication for such diseases almost always ends in the development of persistent pain and impaired movement in the hand. You will be provided with qualified assistance at the Moscow Medical Center.
The left side hurts under the ribs when inhaling: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and prescribed treatment
Cases when a person experiences pain when breathing under the ribs on the left side are not uncommon.
If unpleasant sensations are regular, this indicates the development of a pathological process in the body. It is necessary to pay attention to what other symptoms appear, besides pain when breathing on the left.
This will help determine the cause. Most of them require immediate seeking qualified medical help.
Pathologies of the diaphragm
This is the main respiratory muscle, which conditionally separates the chest and abdominal cavity. As a rule, the cause of pain on the left under the ribs in front when inhaling is a diaphragmatic hernia, during the development of which the lower part of the stomach moves upward due to an increase in the lumen of the esophagus.
This pathological condition can occur against the background of:
- regular high-intensity physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- chronic constipation;
- excess body weight;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
Diaphragmatic hernia is a serious illness, the danger of which is that over time the functioning of the digestive system, heart and lungs is increasingly disrupted.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- Aching pain on the left under the ribs when inhaling air. It is permanent.
- Frequent episodes of regurgitation (almost after every meal).
- Heartburn.
- Belching air.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Bloating.
- Cough.
- Tachycardia.
Treatment of pathology involves the use of surgical methods, during which the surgeon returns the stomach to its place and sutures the lumen of the esophagus. Conservative therapy in this case is ineffective. Medications only temporarily reduce the severity of symptoms.
This term refers to a pathological condition, the symptoms of which are similar to those of angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. It is not dangerous in itself, but may be a symptom of diseases characterized by irritation or compression of the nerves located between the ribs.
Reasons for the development of the pathological condition:
- osteochondrosis in advanced form;
- kyphosis;
- spondylitis;
- malignant neoplasms in the spine;
- intoxication of the body;
- aortic aneurysm;
- diabetes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- abnormal development of internal organs;
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- tight underwear for women.
With this form of neuralgia, unpleasant sensations can radiate to the area of the heart, chest, shoulder blades, and often the left side under the ribs hurts when inhaling. The severity of symptoms increases with coughing, sneezing, and playing sports. The pain with intercostal neuralgia is burning. Over time it becomes aching.
Treatment of the disease is carried out using conservative methods. The treatment regimen directly depends on the cause of the pathology. It is important to consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear, since only a specialist can distinguish neuralgia from angina pectoris and myocardial infarction.
Pain on the left side under the ribs in front when inhaling may indicate the development of pleurisy or pneumonia. In the first case, the pathological process affects the lungs, in the second – the serous membrane that surrounds them.
Pneumonia is an acute infectious disease. The clinical picture and severity of symptoms directly depend on the cause, gender and age of the patient.
General symptoms of pathology:
- Increased body temperature. The rise comes sharply.
- General signs of intoxication of the body (weakness, rapid onset of fatigue, headache).
- Dry cough. Appears in 3-5 days. Gradually it turns into a wet form, accompanied by sputum.
- Painful sensations in the chest area, aggravated by inhalation. They can radiate to the area of the left or right hypochondrium, and the pathological process can also be bilateral.
- Dyspnea.
Pleurisy is a disease that, as a rule, is not independent in nature, but accompanies a number of other pathologies of the respiratory system. The disease can have both a dry and exudative form.
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include: pain in the left or right hypochondrium, worsening with inhalation; reflex painful cough; increased body temperature; chills; weakness.
Treatment of pathology consists of eliminating the underlying disease and reducing the severity of symptoms.
Heart pathologies
In the human body, the diaphragm is closely connected with the central circulatory organ. That is why, in the presence of cardiac pathologies, the process of inhaling air can be accompanied by pronounced painful sensations.
As a rule, patients in this case are diagnosed with one of the forms of cardiomyopathy. The most dangerous is considered to be dilation, in which the heart becomes flabby and cannot fully perform its function. The causes of this pathology are unknown.
In addition to pain when breathing on the left under the ribs, patients complain of shortness of breath after performing any physical activity, dizziness, a constant feeling of weakness, swelling of the lower extremities, sleep disturbances, and frequent episodes of fainting.
For cardiomyopathy, symptomatic treatment is carried out. The prognosis for the presence of the disease is usually unfavorable. Until recently, the only option for patients was a donor organ transplant.
But the difficulty is that the queue of patients is extremely impressive. However, finding a donor heart is almost impossible. Currently, the stem cell treatment method is used in practice.
Splenic rupture
This is an organ located in the hypochondrium on the left side. The spleen is a kind of storage of red blood cells. It is involved in immune processes and is involved in cleansing liquid connective tissue from harmful substances.
When the spleen ruptures, a stabbing pain occurs when inhaling on the left side under the ribs. The abdominal cavity is damaged and blood leaks into it. Against this background, the pain when inhaling on the left under the ribs on the side increases significantly. Over time, it covers the entire abdomen. It becomes extremely difficult for a person to swallow air.
In addition to pain when inhaling under the rib on the left, the following symptoms are observed:
- cyanosis of the skin in the area where the spleen is located;
- chills;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- high body temperature;
- arterial hypotension.
If there are signs of organ rupture, you must immediately call an ambulance. But even with timely intervention by doctors, the spleen can be saved only in 1% of cases. Therefore, the main treatment for this condition is complete removal of the organ.
Acute pyelonephritis
If your left side hurts under the ribs when you inhale, this may indicate kidney pathology. The term “acute pyelonephritis” refers to an inflammatory process in which the pyelocaliceal system and intermediate tissue of the organ are involved.
The main reason for the development of the disease is the spread of infection to the kidneys from the lower urinary tract. This occurs in the presence of one or more provoking factors.
These include:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- vaginal dysbiosis, an increase in its acidity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent change of sexual partners (for women);
- increased intrarenal pressure;
- ureteral strictures;
- prostate adenoma or cancer;
- stones in the ducts through which urine is excreted from the body;
- hypothermia;
- diabetes;
- pregnancy;
- overwork;
- viral infections;
- hypovitaminosis.
If the left side of the organ is affected, the disease can be suspected if the following signs are present:
- The urge to urinate becomes more frequent. In this case, urine is not released.
- When inhaling, the left side hurts under the ribs, the unpleasant sensations radiate to the abdominal cavity.
- General health worsens.
- Body temperature rises.
- A feverish state appears.
- Sweating increases.
Gradually, the pain with a deep breath on the left (under the ribs) reaches its maximum peak. Its severity decreases somewhat as you exhale. Coughing, sneezing, any physical activity - all this increases the intensity of painful sensations so much that a person may lose consciousness.
The key to successful treatment is timely provision of medical care. The prognosis is considered favorable if the disease subsides while taking medications. According to statistics, in 30% of patients the disease becomes chronic. At the same time, the risk of developing pathologies that pose a threat to the patient’s life remains.
Osteochondrosis
Currently, this is the most common spinal disease. During its development, degenerative-dystrophic changes in bone and cartilage tissue occur. According to statistics, about 90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- improper formation of the spine during intrauterine development;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the natural aging process of the body;
- disturbance of phosphorus and calcium metabolism;
- unbalanced diet;
- inactive lifestyle or, on the contrary, high-intensity physical activity;
- vibrations that are long-lasting or regular (for example, when driving);
- excess body weight;
- smoking;
- various types of injuries;
- weakness of muscle tissue in the back;
- scoliosis;
- flat feet;
- infectious diseases;
- constantly being in a state of stress;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes, including high-heeled models;
- pregnancy.
If, when you inhale, there is a stabbing sensation in the left side under the ribs, this is considered a symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis. In addition, a person may experience a feeling of numbness in the area of the heart and stomach. Often the pain radiates to the left shoulder blade or shoulder. The patient also experiences rapid onset of fatigue even with minimal mental and physical exertion.
In most cases, the treatment regimen for osteochondrosis includes the following points: medication, physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, traction, kinesiotaping, diet.
Gastritis, stomach ulcer
Often, when inhaling, the left side under the ribs hurts when this organ of the digestive system is damaged.
Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which disrupts the normal functioning of the stomach. The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms Helicobacter pylori;
- unbalanced diet;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- taking certain medications (for example, painkillers, NSAIDs);
- helminthic infestations;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- hereditary predisposition;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hormonal imbalance.
There are several forms of gastritis, each of which has specific symptoms. In order to recognize the disease, it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the pain.
Against the background of exacerbation of gastritis, when inhaling, there is a stabbing sensation in the left side, under the ribs.
The intensity of pain always increases after any meal, drinking alcoholic beverages, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or prolonged fasting.
Treatment of gastritis of any form is carried out using conservative methods.
A stomach ulcer is a chronic pathology, the consequence of which is trophic disorders. Changes in periods of exacerbation and remission occur very often, with relapses usually occurring in spring and autumn.
Pain when inhaling in the left hypochondrium appears due to intoxication of the body. In addition, the following conditions are symptoms of peptic ulcer:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after each meal;
- belching;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- constipation;
- loss of appetite;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- increased formation and accumulation of gases;
- excessive sweating;
- coating on the tongue.
Treatment of the pathology is complex. It includes taking medications, physical therapy, and diet therapy. In very severe cases, surgery is performed, during which part of the stomach is removed.
Pathologies of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is most often diagnosed in patients. Against the background of its development, the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted. The disease can be both acute and chronic.
In the first case, a person is bothered by pain in the left hypochondrium, which intensifies when inhaling; his appetite is impaired; vomiting appears; body temperature rises; diarrhea or, conversely, constipation develops.
In the chronic form, patients complain of constantly feeling unwell, nausea, and flatulence.
Treatment of pancreatitis may include both conservative and surgical methods.
Finally
If you experience pain in the left hypochondrium area that intensifies when you try to inhale, you should consult a therapist. If your health deteriorates significantly, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
This is due to the fact that pain when inhaling in the area of the left side under the ribs, as a rule, indicates the development of serious pathologies, most of which pose a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/385159/bolit-levyiy-bok-pod-rebrami-pri-vdohe-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnoz-i-naznachennanoe-lechenie