Why is it so difficult for many people to quit smoking? The fact is that the addiction caused by smoking cigarettes is akin to a drug addiction, since addiction occurs at the physical level. Nicotine, which is part of tobacco, is included in the metabolism of a smoker. This is why it is so difficult to quit smoking without the help of specialists - for some time after getting rid of a bad habit, the body is rebuilt. And this manifests itself not only in positive, but also in negative aspects.
It is best to know in advance what happens to the body after quitting smoking in order to be prepared for these manifestations. Remember: your decision to quit smoking will help improve your health and improve your overall quality of life.
Negative aspects of quitting smoking
As we have already said, after quitting smoking, the body begins to rebuild its metabolism. As a result, the former smoker begins to experience a number of unpleasant symptoms. Fortunately, this only lasts for the first months, and after the metabolism normalizes, everything returns to normal.
Among the negative manifestations:
- emotional imbalance: tearfulness, irritability, aggressiveness, depressed mood;
- sleep disorders: insomnia, restless sleep, nightmares;
- susceptibility to colds due to a temporary decrease in immunity;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth after quitting smoking, associated with liver recovery;
- headaches, dizziness;
- weight gain, because against the background of emotional discord and the need to do something to drown out the craving for cigarettes, the former smoker begins to eat more.
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system
The composition of tobacco smoke from cigarettes includes about 60 surfactants, including nicotine, tar, acetone, hydrogen sulfide, nitrobenzene, and ammonia.
Nicotine has the most pronounced effect on the blood vessels of the human body. The main mechanisms of vascular damage in smokers:
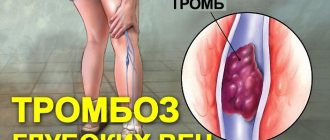
- indirect effect on the endothelium (inner layer) - due to damage to the integrity and smoothness of the vascular wall, blood clots form;
- violation of rheological characteristics - regular tobacco use increases blood viscosity;
- activation of the sympathoadrenal system with an increase in the release of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine), an increase in the frequency and strength of heartbeats;
- peripheral vasospasm (contraction of smooth muscles of arterial vessels) narrows the lumen of the vessel, reducing the volume of blood that is delivered to organs and tissues;
- lipid metabolism disorders - in chronic smokers, the level of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins in the blood increases - risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
The accumulation of other toxins that penetrate through the walls of the alveoli into the blood causes a generalized effect on other organs and tissues. Impaired metabolism increases the concentration of under-oxidized products and inhibits natural antioxidant systems. Because of this, secondary tissue damage develops.
In recent years, there has been more and more talk about the function of the endothelium and its participation in the regulation of the cardiovascular system. It has been proven that it is an endo- and autocrine element that synthesizes and secretes substances to control vascular tone and homeostasis. Nicotine and carbon monoxide act on the surface of endothelial cells, reduce the amount of prostacyclin and slow down parietal blood flow. Because of this, the intima-media complex thickens. In addition, the production of vasodilators (nitric oxide, which is synthesized from L-arginine) decreases, which leads to persistent spasm; The concentration of interleukins increases, promoting the progression of inflammation and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Studies have shown that the amount of pro-inflammatory substances in the blood (C-reactive protein, homocysteine, fibrinogen) directly depends on the number of cigarettes smoked and the concentration of carbon monoxide: the content of carboxyhemoglobin increases, as a result of which the body tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen and an excess of under-oxidized products. Also due to inflammatory factors, an already formed atherosclerotic plaque (the main component in the formation of blood clots) ruptures.
C-reactive protein affects angiotensin receptors, causing spasm and an increase in the number of smooth muscle cells in the vascular wall and their hypertrophy. This is one of the factors in the development of arterial hypertension in a smoker. The biochemical activity of cells also changes - they actively begin to participate in lipid oxidation, pushing the progression of inflammatory processes and the formation of free radicals.
Nicotine and carbon monoxide trigger a cascade of interrelated reactions that have a detrimental effect on the microvasculature, causing atherosclerotic vascular damage, thrombus formation and increased pressure.
You can learn about how smoking affects blood pressure in the video below.
The first 14 days without cigarettes
The body's response to quitting smoking is most intense in the first two weeks after quitting tobacco. All symptoms that appear at this time are a consequence of the so-called nicotine fasting: the body is cleansed of nicotine, but the processes in which nicotine participated have not yet been rebuilt.
We will describe in detail, day by day, below the emotional and physical manifestations that will accompany quitting smoking, and the changes in the body at this time.
Then the symptoms will no longer change daily. A former smoker gets used to the normal state, and the changes will not be as bright and noticeable as in the first days. Therefore, further we will describe the consequences of quitting nicotine on a monthly basis.
First day
At the beginning of the journey, a person who is trying to quit a bad habit feels an emotional uplift, is determined to get rid of the addiction and is confident in future success. Against this background, the craving for nicotine is absent or easily blocked by willpower and distraction by other things.
The carbon monoxide content in the blood gradually decreases and, on the contrary, the oxygen content increases. A person feels that it has become easier to breathe; an excess of oxygen can even cause slight dizziness. For many experienced smokers, this ease of breathing becomes a revelation.
Some experience a decrease in appetite, weakness, and slight anxiety. You may have difficulty falling asleep or have trouble staying asleep.
Quite often it is recommended to keep a diary to record all stages of the addiction recovery process.
Second day
Symptoms of nicotine starvation begin. A severe cough and shortness of breath appear.
The ciliated epithelium of the lungs begins to restore its functions. Sputum production is reduced. The inflamed intestinal mucosa begins to regenerate. Appetite decreases, and mild abdominal pain may occur. There may be an increased urge to urinate.
There is almost no change in the psychological state. The person is still on the rise, but slight irritability appears, which is quite easy to suppress with an effort of will. Self-hypnosis techniques help, constant reminders to yourself why the decision was made to quit (recovery).
Sleep is often restless; nervousness and obsessive thoughts can cause problems falling asleep. You may feel drowsy during the day.
The third day
The tone of blood vessels increases, blood supply to the heart and brain improves. Regeneration of the bronchial mucosa begins, normalization of the pancreas.
The physical craving for cigarettes decreases slightly. While these changes are invisible, they occur at the cellular level.
The skin becomes dry, begins to peel, and small pimples (dry) may form.
Appetite increases, cravings for sweets appear (or intensify). Heartburn may bother you.
Some people experience tinnitus, dizziness, and a feeling that their heart is “squeezing.” Symptoms of psychological dependence intensify. A former smoker becomes more and more nervous, it is difficult for him to concentrate on anything, his thoughts always return to the cigarette.
Fourth
By this time, dizziness usually goes away, and the blood supply to the brain normalizes. But I still have concerns about tinnitus and surges in blood pressure. The face and fingers may swell.
Cough continues; Often a person has the feeling that there is a viscous mucous lump in the throat - the latter means that a restructuring of the system for producing bronchial secretions is taking place in the bronchi.
Emotionally, aggressiveness decreases and depression goes away. Many patients at this stage say that they expected more serious manifestations of nicotine withdrawal.
The sleep is still disturbing and superficial. Increased appetite and cravings for certain foods persist.
Fifth
Regeneration of the respiratory system continues, normalization of the functionality of the bronchi and lungs. But you still feel a lump in your throat, and dark mucus may come out when you cough
By this time, little remains of the emotional high of the first day. There is a risk of breakdown, which is further facilitated by deteriorating health. It is important to remember that all quitters experience this, and many quite successfully.
Small microcracks begin to disappear from the surface of the tongue. The perception of taste is restored.
Sixth
The functioning of the stomach and pancreas continues to normalize. Increased thirst often appears, and with it frequent urination. Some people experience bitterness in the mouth and painful sensations in the liver area. Appetite is reduced.
Many people note sweating, dry mouth, trembling hands, and nausea during this period.
Those who quit smoking become nervous, aggressive, and sometimes whiny. Every little thing causes an emotional reaction, and self-control decreases. You can consult your doctor and start taking anti-anxiety medications.
Seventh
The body is rebuilding to work without nicotine, although mucus continues to be released when coughing, and the feeling of a lump in the throat has not yet gone away. There may be occasional bowel movements. Fatty foods are poorly accepted (heartburn may occur), but overall appetite increases. The skin remains dry and flaky.
“Cigarette syndrome” and other provoking situations.
Tenth
Internal motivation is falling, so now those who quit smoking really need the support and encouragement of loved ones and those around them. A person can hardly tolerate people smoking nearby.
The restoration of the immune system begins. The cough continues. If light yellow or gray clots come out during a cough, you should definitely contact an otolaryngologist. A cough can be softened with a warm drink.
Eleventh
More oxygen enters the body, which can cause dizziness, trembling of fingers, and headaches.
Emotional sensitivity, temper, or vulnerability for any reason persists.
There is a desire to test yourself by smoking “just one cigarette” and remember its taste. At the same time, the smell of tobacco smoke is disgusting.
Appetite is still increased.
Twelfth
The condition of the skin improves, largely due to the normalization of blood circulation. A healthy complexion returns.
The cough softens, and chronic inflammation in the lungs gradually disappears. Intestinal functions are restored.
The neuropsychic state has not yet improved, which means that the person still greatly needs the support of loved ones.
Thirteenth
Malaise of uncertain localization may occur, a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head, and weakness may appear. There are surges in blood pressure.
Usually during this period a person strives to reach the two-week mark, so the risk of relapse is not very high - the desire to take a cigarette is suppressed by this desire.
Fourteenth
The cough begins to subside, the complexion continues to improve, and the yellow coloring of the fingers goes away. Vegetative-vascular disorders may still be present - lethargy, drowsiness, weakness.
Two weeks is the first serious milestone, and it is psychologically important not to break down on this day. A common mistake is to assume that one cigarette after 14 days of abstinence will not harm. In fact, it can derail the entire smoking cessation process.
Changes in the first month after quitting smoking
Let's see how the body recovers after quitting smoking in the second half of the first month.
Feel. Those who quit smoking are still bothered by dizziness, headaches, and blood pressure surges - the brain now receives more oxygen and has not yet adapted to this. The cough with sputum production becomes weaker towards the end of the month. The perception of smells and tastes of food is normalized - for someone quitting smoking, this is felt as a sharpening of the senses of smell and taste, since they were previously dulled. Weight gain is possible due to improved appetite. Since the regeneration of the gastrointestinal mucosa is still ongoing, abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea may still bother you.
Changes in the body. The body is restored at the cellular level, harmful substances, for example, products of the processing of nicotine tar, are intensively removed. Feeling better. Regeneration of the bronchial mucosa occurs.
Blood cells are renewed: leukocytes - faster, red blood cells - slower. Vascular tone increases. This improves immunity and tissue nutrition. The yellowness from the fingers continues to disappear, and the complexion improves.
Psycho-emotional state. Aggression and irritability are less than in the first days. Psychological dependence on smoking still persists, and symptoms of “breathing deep” syndrome are present. Normal functioning of the stomach and intestines was restored. Liver regeneration begins (from 5 months).
Psycho-emotional sphere. The mood is cheerful and stable. Sleep is normalized. The craving for cigarettes is easily suppressed, because at this point it represents only a slight desire to return to a familiar ritual. A person develops other habits with which he replaces the ritual of smoking. But breakdowns are still possible under provoking circumstances.
Possible reasons
When inhaling cigarette smoke, nicotine, tar and other harmful substances regularly enter the human body; they not only “settle” in the lungs, but also affect vascular tone.
Within a few minutes after smoking a cigarette, a spasm of small vessels - capillaries and arterioles - occurred in the body, this caused an increase in blood pressure and caused the development of oxygen starvation of the brain and heart muscle. When you give up cigarettes, after 12-24 hours all traces of nicotine completely disappear from the blood, its effect on the blood vessels disappears and a sharp dilation of blood vessels can provoke a drop in blood pressure and the appearance of pain in the heart associated with an increase in the load on the blood vessels.
Another common reason why the heart hurts after stopping smoking is a decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood and an increase in the amount of oxygen, which also causes an increase in the load on the myocardium. Many smokers note: they quit smoking and now their heart hurts, their heart rate increases, there is a lack of air and a feeling of tightness or pressure in the chest, all these symptoms are similar to those experienced by people who climbed a mountain peak - an excess of oxygen can cause general malaise and pain in the heart.
Unfortunately, pain in the heart can be a symptom of the development of dangerous diseases such as angina pectoris or coronary heart disease, which occur due to disruption of normal blood supply to a certain area of the heart muscle. A sharp change in the level of oxygen and carbon dioxide, dilation of blood vessels and a drop in pressure can cause a reflex spasm of blood vessels and cause cellular necrosis.
Pain in the chest area does not always signal problems in the cardiovascular system; sometimes patients confuse angina with an attack of cholecystitis or exacerbation of pleurisy. If chest pain is accompanied by symptoms of indigestion or increased body temperature, it is necessary to examine neighboring organs to exclude their pathology.
Second six months
In the seventh and eighth months after quitting smoking:
- the restoration of olfactory receptors continues, so the former smoker discovers more and more new shades of smells and tastes;
- cough becomes rare, as the regeneration of cells of the respiratory system is in full swing. Lung capacity increases even more. The hoarseness of the voice goes away as the vocal cords are restored;
- the yellow plaque of a smoker gradually disappears from the teeth;
- liver cell restoration continues;
- the psycho-emotional state is still stable and cheerful.
Ninth month
This is a month of crisis, in which you need to be especially careful not to break down. On the one hand, the habit of smoking has not yet been completely destroyed, on the other hand, the person has already forgotten all the negative aspects of smoking, has become accustomed to feeling good, and he has the illusion that nothing bad happened.
Tenth month
During this period, patients often have realistic dreams that they are smoking again, and this leaves a painful feeling upon awakening.
Eleventh month
Thoughts about smoking come very rarely and are easily dismissed by the mind as something unnecessary. Psychological dependence has almost completely disappeared.
Is it possible to suddenly stop drinking?
Over a certain period of time, the body receives a steady dose of toxic substances that enter the bloodstream with alcohol. If you suddenly stop using it, the usual rhythm of work changes. First of all, the brain reacts to this: the psychoactive components contained in alcoholic beverages stop “feeding” it. Gradually, waste and toxins are eliminated, but the person feels weak, dizzy, there is slowness of thought processes and poor concentration. Abruptly stopping drinking alcohol is a stress for the body, which, however, it really needs. Already in the first day after completely abandoning them, organs and systems will begin accelerated recovery.
One year after quitting smoking
A year without cigarettes is a serious achievement. During this period, the body usually recovers so much that the risk of stroke (by 30%), heart attack (by 50%) and the likelihood of lung and liver cancer (by 80-90%) is reduced. Women who have become pregnant by this point do not have to worry about the risk of miscarriage - its probability is almost the same as for non-smokers.
The risk of relapse is minimal, but it is worth remembering what you went through to get to this point. It is not worth risking such an achievement for the sake of one cigarette.
How to help your body when quitting smoking
Three things will help reduce the intensity of unpleasant symptoms when quitting smoking and recover faster. This:
- Fresh air. Walk in parks and forests more often, ventilate the room more often. Play sports outdoors. This helps clear the lungs faster and restore normal functioning of the respiratory system.
- Special food. Include in your diet foods rich in vitamins C, A, E, and rutin - with their help, nicotine will be removed from the body faster. To normalize the functioning and cleanse the gastrointestinal tract, potato decoction, mucous decoctions of flaxseed, rice or oatmeal are useful.
- Sport. Not immediately (in about six months), but you need to include physical exercise in your schedule. This will strengthen the heart, speed up metabolism, and increase lung capacity. In addition, they have a positive effect on overall well-being due to the release of endorphins.
Benefits of a sober lifestyle
It is impossible to describe all the advantages of a sober lifestyle . When the mind is not intoxicated by alcohol, clarity of thinking, efficiency, ability to make the right decisions, and analyze the situation are preserved. The main advantages of a healthy lifestyle:
- No more hangovers. Every morning begins with plans and the desire to live, and not with hellish headaches and the urge to hangover.
- Nice appearance. It is much more pleasant to observe the reflection of a healthy person in the mirror than to meet the blurred gaze of reddened eyes.
- Vigor and efficiency. The ability to think logically, draw conclusions, solve problems, and integrate into the rhythm of life helps maintain self-esteem and maintain normal brain function.
- Excellent memory. Now the chances of losing your wallet are much less. At least the person remembers where he could have left it.
- Adequate condition. When sober, a person controls his emotions and calculates his strength. Drunk people lack a sense of fear, which leads to domestic tragedies, road accidents and other consequences.
The most important advantage is establishing relationships with loved ones, friends, and colleagues. The person again becomes a full-fledged member of society, loved by his family and respected by his colleagues.
Ethanol methodically destroys the body, destroys family and friendly ties, moral principles, the ability to think and analyze. Giving up it will help you regain your health and position in society, feel the joy of critical thinking and look at the world soberly.
Do you need psychotherapeutic help when quitting smoking?
Of course, willpower, determination and a willingness to overcome difficulties can greatly help a person cope with addiction and restore the body after quitting smoking. However, cravings for cigarettes associated with psychological dependence may still persist.
Some smokers find themselves having to try again to quit the bad habit. This happens when a person returns to it a few weeks or months after quitting smoking. Only a small percentage of people can truly quit smoking permanently without help. Therefore, it is extremely important to seek help from a psychotherapist in a timely manner.
During the consultation, the specialist will explain the consequences of consuming tobacco smoke tar and nicotine and will help to form a strong motivation to quit smoking. With the support of a doctor, it will be easier for a smoker to overcome psychological dependence; he will learn to get out of stressful situations without the help of cigarettes. During sessions, the specialist uses techniques that promote relaxation, overcome psychological discomfort and change well-being, making the process of quitting smoking as painless as possible.
As a result, with the patient’s desire, the support of loved ones and the help of a qualified doctor, the person’s desire to smoke is suppressed, and the effect persists even several years after the end of psychotherapy.
Nicotine withdrawal
Chronic smoking is defined in medicine as tobacco or nicotine addiction.
Nicotine is a psychoactive substance that causes physical dependence at the level of neurotransmitters, causing the production of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine is responsible for joy, pleasure, determination. A drop in dopamine levels stimulates a person to actively search for ways to increase it. Since the smoker’s brain experiences a constant deficiency of this neurotransmitter, only the intake of nicotine in the body raises this level. When dopamine levels drop, a person experiences feelings of anxiety, restlessness, and an automatic urge to smoke.