- Types of neurotic disorders
- Signs of neurotic disorders
- Psychotherapy for neurotic disorders
What is a neurotic disorder
What is a neurotic disorder? It is a heterogeneous group of dysfunctions that arise as a result of acute or chronic psychological trauma. Symptoms are varied, but maladaptation, phobias, asthenia, obsessions and somatovegetative disturbances are always noted. A person's physical and mental abilities are temporarily weakened. Self-awareness and criticism persist. The diagnosis is made based on complaints, medical history and the person’s life history. To eliminate the problem, they resort to psychotherapy and medication.
Neurotic disorder is characterized
Doctors mean by neuroses a group of pathologies that arise due to the influence of mental trauma. A neurotic disorder is characterized by a deterioration in well-being, mood swings are noted, and somato-vegetative symptoms appear. In severe cases, suicidal thoughts are possible.
Treatment of asthenic neurosis at Neopsy
Methods for diagnosing asthenic neurosis at the Center include the clinical-psychopathological method - a conversation with the patient (with his consent - with relatives), studying the medical history at the first consultation during the collection of anamnesis. Usually this is enough for our experienced specialists to identify neurasthenia. But to make a more accurate diagnosis, in the presence or suspicion of the possibility of somatic diseases, additional laboratory and hardware examinations and consultations with related specialists are prescribed. After confirmation of the diagnosis, an individual treatment plan is developed, which includes psychotherapeutic methods of influence, physical and dietary therapy, and drug treatment.
The Center’s specialists are fluent in all modern methods of psychotherapeutic assistance for asthenic neurosis, including hypnotherapy, relaxation, resource trance, autogenic training, etc. Together with the patient, a psychiatrist or psychotherapist develops a way to reduce physical and intellectual stress (up to changing jobs, giving up part-time work). etc.), rest, sleep and nutrition regime. The high professionalism of the specialists at the Neopsi Center for Mental Health allows us to treat asthenic neurosis with high efficiency. Contact us for help through the website services or call the specified phone number.
Call and we will help solve your problems!
Causes of neurotic disorders
Doctors have different opinions regarding the catalyst for neuroses. Some believe that this condition develops due to a genetic predisposition, others – childhood psychological trauma. Children's psyche is weak, their memory is tenacious, any serious stress persists for a long time. Most of the complexes that a person suffers from in adulthood arose in childhood. Women are more susceptible to the disease.
Other causes of neurotic disorders:
- unfavorable environment, poor living conditions;
- prolonged physical overload in combination with stress;
- exhaustion of the nervous system;
- too busy work schedule;
- lack of proper rest;
- alcohol and drug abuse.
Neurotic dysfunctions occur when the body is exhausted.
Diet
Diet for the nervous system
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 months
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1700-1800 rubles per week
A very important point is proper nutrition for neurasthenia. The diet should be enriched with vitamins and minerals, as well as all nutrients important for the body. It is recommended to include the following foods and dishes in your diet:
- whole grain cereals;
- honey, dried fruits;
- fresh vegetables and fruits - bananas, greens, cabbage, asparagus, citrus fruits, sea buckthorn, currants;
- liver;
- Brewer's yeast;
- Fish and seafood;
- cheese, dairy products.
The following should be completely removed from the menu:
- fat meat;
- sugar and confectionery;
- spicy dishes;
- nuts, seeds;
- sauerkraut;
- alcohol.
Classification of neurotic disorders
Disorders are divided into 3 groups:
- hysterical;
- obsessive states;
- asthenic.
This classification of neurotic disorders is not similar to practice. It does not contain approved certain and most common pathologies. The differences lead to different ways of systematizing disorders.
Types of neurotic disorders
When making a diagnosis, doctors take into account the following types of neurotic disorders.
- Anxious-phobic. The main symptom is a sharp increase in anxiety and the appearance of obsessive fears. This group includes panic attacks, simple and complex phobias, and generalized anxiety disorder.
- Obsessive-compulsive. The main symptom is the appearance of obsessive ideas and actions.
- Asthenic disorders are characterized by asthenic syndrome.
- Somatoform. Clinically, they are similar to somatic ones, but do not imply a physical basis.
- Dissociative disorders imply disorders of motor function and sensations. Previously, this disease was classified as hysterical neuroses.
The sooner the patient seeks help, the more favorable the prognosis.
Forms of neurotic disorders
There are such forms of neurotic disorders.
- The most common is neurasthenia; it is divided into 3 stages. The first phase is characterized by irritability. Mental and physical abilities are not affected. The second stage is characterized by a decrease in working capacity, a person understands this. The third phase is manifested by lethargy, reluctance to do anything, and asthenic syndrome.
- Hysterical neurosis is the second form. The disease is caused by inappropriate behavior; the person is unpredictable and extremely irritable. There are signs such as seizures, paresis, vomiting, hypotension. The patient also complains of obsessive thoughts, a “lump” in the throat, and insomnia. During an attack, a person screams, lies on the floor, can get into a fight, or injure himself.
- The third form is depressive neurosis. It is characterized by symptoms such as insomnia, bad mood, loss of the ability to feel joyful emotions, a feeling of burden, and tearfulness. There are also disturbances in heart rhythm, stomach function, slow reaction to events, sexual dysfunction, and hypotension. The patient complains of despondency, sadness appears, and a feeling of uselessness.
- Obsessive states. With it, the patient is unable to control his thoughts and actions.
- Hypochondriacal neurosis - there is a fear of a circumstance from which a person cannot find a way out, or a fear of falling ill with an incurable pathology. The condition is complemented by hysteria and obsessions.
Each form requires an individual approach to therapy.
Neurotic disorders in adults
Neurotic disorders in adults have a reversible, relatively mild course, unlike psychoses. According to statistics, the problem is detected in 20% of the population. The causes include a disorder of brain activity responsible for human adaptation. Somatic and mental disturbances appear. Patients are rarely admitted to the hospital; conservative methods are usually successful.
Neurotic disorders in children
In children, the catalyst for the development of neurosis is delays in personality development. Against the background of separation from parents, stress, loss of a loved one, psychological trauma is possible. A child who experiences these situations becomes infantile or acquires neurosis.
Neurotic disorders in children: features of occurrence and course.
1. The age of 7-11 years is considered the affective stage of personality formation. If at this time the child encounters a traumatic factor, his development as a person may be delayed. In adulthood, such people experience emotional instability; a person cannot adequately assess the situation or think about the consequences. The only and beloved children acquire hysterical traits.
2. At the age of 11-14, a teenager learns to independently assess the situation, analyze, and plan his actions. There is a subsequent development of the affective component of the personality. If at this age a stressful situation arises, neuroses are possible in the future. Such teenagers outwardly look older than their peers and are more reasonable, but subconsciously, the synchronicity of personality development is disrupted.
Attention! The most important role in the successful growth of a child is played by the relationship with parents. Those who felt overprotected in childhood and were not allowed to make their own decisions become timid and unsure of themselves. It is in this category of people that neurotic disorders arise.
Derealization in VSD
VSD and mental disorders can manifest themselves against the background of mental trauma, strong experiences and physical and nervous exhaustion. Some patients with VSD develop signs of mental disorders that do not allow them to lead a full life.
The feeling of unreality of what is happening during VSD or derealization is the brain’s reaction to stress. With this disorder, a person perceives the world around him as distant and unreal.
This disorder is different from panic attacks. The main signs of derealization are:
- perception of reality as unreal;
- changes in the perception of sounds, colors;
- feeling of weakness;
- increased blood pressure;
- fear of madness.
Against the background of these symptoms, the patient maintains adequate behavior and controls his actions. If signs of derealization appear, you must immediately consult your doctor who will prescribe treatment.
When treating derealization, it is necessary to get rid of bad habits and optimize time for rest and work. At the Yusupov Hospital, experienced psychotherapists interact with patients who have a feeling of unreality of what is happening with VSD, who use safe methods to eliminate depression and other manifestations of the disorder.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
Astheno-neurotic syndrome is manifested by chronic fatigue, apathy, increased fatigue and irritability. This disease is complemented by loss of appetite and insomnia. Physical signs are associated with apparent heart disease. It may seem to a person that he has a slow heartbeat, or vice versa – tachycardia. No changes are observed on the cardiogram. However, the patient feels pain in the heart muscle. Stomach problems and migraines are also possible. Diagnostics involves interviewing and examining a person. An examination is being carried out for a viral infection. The prognosis is favorable, especially if the person additionally attends art therapy sessions. Drawing has a relaxing effect on the psyche, negative thoughts dissipate, and the patient feels harmony.
Consequences and complications of the disease
Most often, asthenoneuratic syndrome occurs in a chronic form. But if at least minimal treatment of the pathology is absent, serious complications can arise:
- Stroke;
- Heart attack;
- Stomach ulcer and exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases;
- Hormonal imbalances.
Also, in the absence of adequate therapy, depression may occur, which sometimes even leads to suicide. In the initial stages of the disease, a person is still able to help himself.
Complications of asthenia in children can lead to malfunctions of the thyroid gland, and, consequently, to disorders in the reproductive system. In adults, problems with reproductive function may occur.
Dysthymia – depressive neurotic disorder
The disease is characterized by a depressed state in the patient, which does not go away for more than 2 years. The pathology is characterized by decreased vital energy and increased fatigue. A person feels apathy and is unable to enjoy life. Self-esteem decreases and self-confidence is lost. Such people rarely share their emotions with others. The most severe consequence is suicide. The patient is referred to a psychotherapist. With timely treatment, dysthymia, or depressive neurotic disorder, is treatable.
Who can help with neurosis?
If you can’t cope with a depressed state on your own, it’s better to consult a specialist. Taking sedatives, and especially antidepressants, without medical supervision can only aggravate the condition and cause addiction, and most importantly, the medications do not solve the main problem that caused the disease.
Depressive, asthenic and anxiety-neurotic conditions can be stopped completely after a course of psychotherapy, during which you will work with a doctor on a traumatic situation, change negative attitudes, and competent prescription of medicinal support, relaxation, art therapy and restorative procedures will help consolidate the result.
The doctors of our Center know how to help a person suffering from neurosis with one or another component. An individual approach to psychotherapy and selection of medications, a friendly atmosphere and comprehensive treatment will help break the vicious circle of traumatic events and find a new life - calm, confident, joyful.
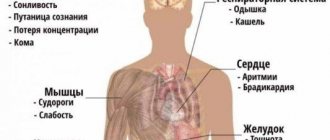
Symptoms of neurotic disorders
Neurotic dysfunctions are characterized by instability of mood and rash actions. Patients suffer from memory impairment, problems with concentration, and a number of other clinical manifestations:
- causeless psychological stress;
- increased fatigue;
- sleep problems;
- isolation;
- fixation on problems in life;
- memory impairment;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- migraine;
- pain in the heart muscle and joints;
- frequent urination;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased potency;
- high or low self-esteem;
- inconsistency, uncertainty;
- tearfulness;
- aggressiveness;
- suspiciousness;
- poor prioritization.
Symptoms of neurotic disorders are often complemented by increased sensitivity to light, sound, and reactions to minor temperature changes.
Signs of neurotic disorders
Signs of neurotic disorders vary by gender. In women, asthenic neurosis more often appears, characterized by aggressiveness, loss of mental and physical ability, and lack of sexual desire. During intimacy, it is impossible to relax. A woman suffering from asthenic neurosis quarrels with relatives and often loses her temper over trifles. Constant tension is fraught with the development of diseases of internal organs.
In men there are the following types:
- depressed – a person is not able to realize himself in the world of work, or adapt to sudden changes in any area of life;
- male neurasthenia - usually appears after physical or moral overstrain; workaholics are susceptible to this type.
Men and women over 45 years of age are prone to these types of diseases. They may still have problems with the functioning of their internal organs.
Neurotic disorder syndrome
The syndrome of neurotic disorders is a reflection of a traumatic circumstance and is often combined with other neurotic manifestations. The patient's mood decreases, but there is no feeling of melancholy. Usually, a bad mood is combined with emotional lability, asthenia, mild anxiety, loss of appetite and insomnia. During the day, no special fluctuations are observed, or they are mild. Mental and motor retardation, self-flagellation, and suicidal thoughts are not typical.
- Neurotic depression is distinguished from reactive depression, which is also caused by traumatic circumstances. In the second type, the symptoms reach the level of reactive psychosis - the patient is depressed, inhibited, consciousness is narrowed, and thoughts of suicide appear.
- In the case of psychotic depression, the patient wishes to die, there is gross disorientation of the personality with separation from life, sudden anosognosia, delusional ideas of self-humiliation, manic episodes. The condition can be controlled with antidepressants and a repeated course of treatment.
- Neurotic depression is characterized by the preservation of the basic personality qualities, the patient is aware of his condition. Obsessive phobias and pronounced hysterical manifestations appear.
Important! Psychotic depression is more dangerous for a person and requires immediate treatment.
Levels of neurotic disorders
Neurotic disorders occur at 3 levels: as a manifestation of individual symptoms, at the level of minor syndromes, and as specific disorders.
Levels of neurotic disorders.
- Individual symptoms. They are also present in those who do not suffer from mental disorders.
- A minor emotional disorder can be complemented by several neurotic syndromes, of which the leading one is not identified.
The patient population consists of 2 types:
- some suffer from an acute, short-term stress reaction;
- others experience long-term, chronic impairment.
Most patients recover within six months, while others recover in no less than 3 years.
VSD with agoraphobia
Fears and panic attacks during VSD occur suddenly in patients. Agoraphobia is one of the defense mechanisms that manifests itself unconsciously. This condition is characterized by a person’s avoidance of open spaces. Experiences arise as a result of traumatic situations that are associated with surrounding people.
The development of agoraphobia is influenced by bad habits, mental illness, trauma received in childhood, and bad habits. The main symptoms of agoraphobia are:
- shallow breathing;
- cardiopalmus;
- tinnitus;
- skin redness;
- intense sweating;
- fear that people around will notice the attack;
- feeling of embarrassment;
- fear of going crazy;
- fear of death.
Patients come to the Yusupov Hospital who say that they seem to be going crazy from VSD; they have read reviews about this disorder online and thereby independently aggravate their condition. Agoraphobia also causes behavioral symptoms. The patient begins to avoid environments or circumstances that cause fear. He becomes more confident when surrounded by close people, for example, when going to the store with a relative.
Agoraphobia with VSD is treated at the Yusupov Hospital through regular sessions with a psychotherapist and taking medications. For drug treatment, tranquilizers and antidepressants are prescribed. These drugs have side effects, psychotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital select the safest drugs for patients.
Diagnosis and treatment of neurotic disorders
A person should contact a psychologist or psychotherapist. Diagnostics requires an integrated approach.
The color technique is widely used.
- All shades take part in it. Neurosis-like syndrome is noted when a person selects or repeats gray, purple, brown or black.
- With hysterical neurosis, the patient chooses 2 colors - purple and red. This also indicates low self-esteem.
To determine the symptoms, a test is carried out - it makes it possible to identify the presence of chronic fatigue, anxiety, and self-doubt. Diagnosis and treatment of neurotic disorders are closely interrelated.
Drug therapy is used in the first stages to relieve internal tension and eliminate insomnia. Antidepressants and tranquilizers are widely prescribed. Depending on the severity and duration of the clinical picture, the doctor prescribes drugs from different groups to the patient:
- non-selective – Amitriptyline, Imipramine;
- selective influence - Maprotiline, Fluoxetine;
- sedative antidepressants – Doxelin, Azafen;
- balanced – Sertalin, Tryptophan;
- stimulants - Heptral, Bupropion.
Obsessive states are well relieved by drugs from the SIDS group - Prozac, Paroxetine, Escitalopram. Frequently prescribed tranquilizers include Phenazepam, Tofisopam, Meprobamate. All medications are prescribed in a short course of 5-7 days, sometimes extended to 10.
Important! If a person self-prescribes medications, the disease may transform and the condition may worsen.
Psychotherapy for neurotic disorders
To achieve maximum effect, doctors recommend supplementing drug treatment with rational, cognitive psychotherapy. The main objective of this technique is to eliminate the consequences of a stressful situation so that the general condition of a person improves and the symptoms of neurosis are eliminated. The doctor discusses the cause of the problem and works through the traumatic circumstances. The patient learns relaxation techniques, the ability to level out negative emotions and complexes. The most difficult thing to eliminate is negative attitudes given by parents. A person must show his will, diligence, and do his homework. Typically, psychotherapy for neurotic disorders consists of 7-15 sessions, depending on the degree of complexity of the problem. In severe cases, the patient is admitted to the department of borderline mental disorders.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease, first of all, involves an oral interview with the patient. The doctor must find out everything that worries the patient. Usually the clinical picture of the disease becomes clear in its first stages. That is why it is not difficult to start treating asthenic syndrome as early as possible. The main thing is to determine the real cause of the disease, since it is its elimination that guarantees successful treatment and complete recovery of the patient.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent the development of neurotic disorders by leading a healthy lifestyle. It is important to sleep 7-8 hours a day, go to bed before 1.00, resolve internal conflicts in a timely manner, and avoid stress. If a person’s work involves difficult situations or psychological overload, it is worth thinking about changing the sphere of work.
Prevention of neuroses: effective tips.
- Do not abuse alcohol or smoking. Intoxication provokes a deterioration in adaptive capabilities, and various diseases appear. When drinking alcohol regularly, the psyche suffers and a severe hangover occurs.
- The food menu should always include a lot of vegetables, fruits, lean meats and fish. It is advisable to rely on dairy products and take a course of vitamins in the off-season. Overeating is also dangerous; you need to consume food in moderation.
- Music. This is an effective prevention method that involves listening to calm melodies. This could be the sound of rain or sea, falling snow and other natural phenomena. You should listen to soothing music before bed, or after a stressful situation. It can be found on YouTube, social networks, it is advisable to record it on a smartphone so that you can always relax.
- It is important to exercise in moderation. Physical activity is the key to mental health. It is advisable to do exercises every morning or evening, you can join a gym, go to the pool 2-3 times a week.
- Plan your actions, act according to the plan. Then there will be fewer stressful situations if a person does not let everything take its course.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner. Regular pain causes emotional stress.
- It should be remembered that family conflicts, especially constant ones, cause serious stress. Family is the rear, not the battlefield. If there are problems in your personal life and they are not resolved, it is better to change your partner.
If it was not possible to prevent neurosis, you need to seek help in a timely manner. Then the chances of leveling out the negative psychological state are maximum.
Hypersthenic form
The first phase of asthenic neurosis is characterized by the dominance of excitability, irritability, and emotional instability. A neurasthenic person is not restrained in emotions, raises his voice in normal conversation, shouts during an argument or quarrel, and allows insults. The absent-minded attention of the sick person leads to a decrease in the productivity of any type of activity, since he is constantly distracted by irritants and has difficulty returning to the work process. The patient is haunted by dreams related to daytime events and problems. Having difficulty falling asleep, he often wakes up, and in the morning he feels exhausted and unrested.
What happens if a neurotic disorder is not treated?
Neuroses can cause complications if left untreated. Many people ignore therapy and do not go to doctors. Post-Soviet stereotypes that going to a psychotherapist is shameful still live in people’s heads. Such negligence entails irreversible changes in the psyche.
What happens if a neurotic disorder is not treated:
- increased symptoms;
- the patient becomes hysterical and hypersusceptible;
- self-esteem suffers;
- other chronic diseases appear;
- the risk of catching a cold increases;
- the formation of an explosive personality that does not tolerate returns, is aggressive, and concentrates only on the negative.
A person becomes a hypochondriac, his personality is destroyed. The last stage is caused by complete apathy, the person does not get out of bed, and may refuse food. The patient is no longer able to do without medications or control his emotions. High risk of suicide. It is extremely difficult to treat this condition; it can lead to more serious mental pathologies. You cannot do without long-term psychotherapy, taking medications and staying in a neurosis clinic.
Pathogenesis
The basis of neurasthenia is a psychological conflict, the essence of which is the contradiction between desires and capabilities.
In the pathogenesis of neurasthenia, both somatic and mental factors are important. The main role is played by the individual’s reaction to psychotrauma. In this case, not only objective life circumstances are important, but also how the patient relates to them. With neurasthenia, there is a contradiction between the individual’s capabilities and his demands on himself. This discrepancy is covered by internal resources and mobilization of efforts, which ultimately leads to disorganization of the body.