Taking blood for analysis
Venous blood collection in children
Venous blood is considered the best material for clinical blood testing.
Taking blood for laboratory tests is regulated by regulatory and technical documentation, namely:
GOST R 53079.4-2008 National standard of the Russian Federation “Clinical laboratory technologies. Ensuring the quality of clinical laboratory research." Part 4, Rules for conducting the preanalytical stage; "Guidelines. Hematology analyzers. Interpretation of a blood test" (approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation on March 21, 2007 N 2050-РХ).
Blood collection rules:
It is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach, avoid physical activity the day before, and sit quietly for 10-20 minutes immediately before blood collection.
- KBC, ESR, leukocyte formula, electrolytes - on an empty stomach or 2 hours after a meal.
- Immune status - fasting on Mon, Tue from 7.00 to 12.00
- Glycosylated hemoglobin - without restrictions.
- Biochemical blood test, glucose - strictly on an empty stomach (if possible 12 hours)
- Total immunoglobulin E - on an empty stomach or 2 hours after a meal.
- Diagnosis of helminth infections - without restrictions.
- Infectious markers - on an empty stomach or 2 hours after a meal, EXCEPTION: - diagnosis of syphilis, hepatitis B, C, HIV-1, 2 - 4 hours after a meal.
- Autoimmune bodies - no limits.
- Genetic research - no restrictions.
- PCR - no restrictions.
- Hormones - on an empty stomach or 2 hours after eating.
Remember that the best time to take a blood test is in the morning; the standards for all tests were developed specifically for the time interval of 8-11 am.
- Donating blood for testing should be strictly on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and the blood draw. It is quite difficult to adhere to this rule with children, but it is quite possible. Drinking juices, tea, or eating cookies in the morning is prohibited, as this can significantly distort the results. You can only drink water. Before going to the laboratory, take something tasty with you so that you can eat immediately after leaving the treatment room.
- The child's diet 1-2 days before the blood test should exclude fatty and fried foods and sweets.
- For better blood filling of the vessels, it is advisable to give the child 100-200 ml of water to drink 30 minutes before blood sampling (for children from 1 year).
- After the analysis, think about how you can please your child for good behavior. A small surprise gift will help smooth out the unpleasant impressions of the hospital.
- It is not recommended to donate blood after undergoing any medical procedures.
- There should be no physical or emotional stress before donating blood. Stress, anxiety and physical activity have a significant impact on the results of tests for hormones and biochemical parameters.
- If a child is constantly taking medications, the doctor who prescribes the tests should be told about this.
- To adequately assess the dynamics of blood tests, it is optimal to take them at the same time of day in the same laboratory.
Features of preparing for blood donation for children from 1 day to 12 months:
- Try to take blood samples from infants between feedings, closer to the second feeding.
- 30 minutes before the procedure, the child should drink 50 ml of water.
- At the time of drawing blood, the child’s hands must be warm. . This is a mandatory and very important condition, because the amount of blood that will be received by the health worker depends on its fulfillment.
- Immediately before blood is drawn, the child should be positioned so that he is as comfortable as possible. A couple of minutes should pass before the nurse begins drawing blood. This time will be enough for the baby to calm down and get used to the environment a little.
When should you take a Reticulocyte (capillary blood) test?
- Assessment of erythropoiesis after bleeding or hemolysis;
- Assessing the ability of bone marrow to regenerate after taking cytotoxic drugs and/or bone marrow transplantation;
- Assessing the resumption of erythropoietin production after kidney transplantation;
- Doping control (for athletes when using erythropoietin);
- Diagnosis of various anemias;
- Assessment of bone marrow function in case of insufficient amounts of vitamin B12, iron, folate, copper and quality control of treatment.
Blood grouping and determination of Rh factor
Blood grouping and determination of the Rh factor is one of the important studies that can save the life of a patient as a result of an accident. This laboratory analysis is also carried out:
Biomaterial is collected from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, the patient should follow simple recommendations - do not consume food or alcoholic beverages for 4 hours, avoid smoking, and reduce the intensity of physical activity 12 hours before the test.
Detailed description of the study
Reticulocytes are young red blood cells (erythrocytes). Reticulocytes are formed in the bone marrow from normoblasts that have lost their nucleus. It takes several days to ripen, usually 4-5. The maturation process begins in the bone marrow and then continues in the peripheral blood. The formation of red blood cells and their forms depends on the hormone erythropoietin, which is produced in the kidneys.
Reticulocytes are larger in size than red blood cells. The internal environment of the cell contains a basophilic network (reticulum), which is located in the form of threads and small grains. An important difference between reticulocytes and mature erythrocytes is their inability to fully transport oxygen and carbon dioxide, since the cells still do not have enough hemoglobin.
There are 5 different stages of maturity of young red blood cells:
- They have a core, the grain is located around the core in the shape of a corolla;
- Granular-mesh mass, which is represented by a ball;
- The grain size is represented by a dense network;
- Mass, which is represented by threads;
- There are individual grains.
It is important to note that about 80% of young forms belong to group 4-5.
In a healthy person, 0.2-1% of reticulocytes are determined in the blood. The percentage is calculated from the total number of red blood cells. With increased destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis) or bleeding, the number of immature forms will increase, so it is important to use the “reticular index” to assess the severity of anemia. Such a small concentration shows that young forms are able to exit into the peripheral blood and can then mature and turn into mature erythrocytes.
In infants in the first days after birth, the concentration of reticulocytes is higher than in an adult; they can be 10%. Gradually their number will decrease. Also, an increased number of young forms is observed due to the destruction of red blood cells with negative Rh factors of the mother and child. In case of blood loss or insufficient intake of iron from food, the concentration is also higher than normal, as the body independently tries to restore the level of red blood cells. There are conditions and/or diseases in which a decrease in the concentration of reticulocytes is observed. This can be due to damage to the bone marrow (after ionizing radiation, chemotherapy treatment or tumor damage), which leads to a decrease in the formation of reticulocytes and, as a consequence, a decrease in their number in the peripheral blood.
There are true and false reticulocytosis - an increase in the concentration of young forms. True is characterized by an increase in the number of immature red blood cells both in the peripheral blood and in the bone marrow. And if false, there will be an increased concentration of reticulocytes in the circulating blood and no increase in the bone marrow. This fact indicates the “washing out” of immature red blood cells from the bone marrow into the blood.
The concentration increases with accelerated erythropoiesis, and decreases with its slowdown. Erythropoiesis is the process of hematopoiesis during which red blood cells are formed. Determination of reticulocytes in capillary blood shows that the bone marrow is capable of regeneration and evaluates the hematopoietic system.
Selected studies
General rules apply to all tests, but some tests require special preparation and additional restrictions. It is very important to strictly follow the recommendations below, since only in this case will reliable research results be obtained.
- General blood analysis
- Urea
- Cholesterol, lipoproteins
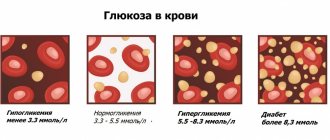
- Glucose
- Glucose tolerance test
- Haptoglobin
- Alpha-2-macroglobulin
- FibroTest, FibroMax, SteatoScreen
- Hormonal studies
- Thyroid hormones
- Sex hormones
- Prolactin, Macroprolactin
- Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH/MIS), Inhibin B
- Adrenaline and norepinephrine
- Renin, angiotensin
- Aldosterone
- ACTH, cortisol
- Insulin, C-peptide
- Gatrin 17, Gastrin-17 stimulated, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, H. Pylori IgG
- Protein C, Protein S, von Willebrand factor
- PSA (total, free)
- CA-125 ovaries
- Tests for infections
General blood analysis
Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach (or in the afternoon/evening hours, 4-5 hours after the last meal). 1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from your diet.
Urea
1-2 days before the study, you must follow a diet: stop eating foods rich in purines - liver, kidneys, and also limit meat, fish, coffee, tea in your diet as much as possible. Intense physical activity is contraindicated.
Cholesterol, lipoproteins
Two weeks before the study, it is necessary to discontinue drugs that lower blood lipid levels, unless the goal is to determine the lipid-lowering effect of therapy with these drugs.
Glucose
When donating blood for glucose (in addition to the basic requirements for preparing for tests), you should not brush your teeth, chew gum, or drink tea/coffee (even unsweetened). A morning cup of coffee will dramatically change your performance. Contraceptives, diuretics and other medications also have an effect.
Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out only if there are preliminary results of determining glucose on an empty stomach, without load. The glucose content in blood plasma is determined on an empty stomach and 2 hours after a glucose load.
It is necessary to follow a normal diet (with a carbohydrate content of more than 125-150 g per day) and adhere to the usual physical activity for three days before the study. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach after an overnight fast for 12-16 hours (during this time you should not smoke or drink alcohol).
During the study, the patient should lie or sit quietly, not smoke, not be overcooled, and not engage in physical activity.
It is not recommended to conduct research after and during stress, after operations and childbirth, during inflammatory processes, alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis, during menstruation, and in gastrointestinal diseases with impaired glucose absorption.
Before the test, it is necessary to exclude medical procedures and medications (adrenaline, glucocorticoids, contraceptives, caffeine, thiazide diuretics, psychotropic drugs and antidepressants).
Discontinuation of medications is carried out only after preliminary consultation of the patient with a doctor.
A glucose tolerance test is not performed for children under 14 years of age.
For pregnant women, a glucose tolerance test is recommended to be carried out at 24-28 weeks, this allows identifying with accuracy up to 98% of women with gestational diabetes.
Haptoglobin
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude the following drugs: dapsone, methyldopa, sulfasalazine, estrogens, oral contraceptives, tamoxifen, androgens.
Alpha-2-macroglobulin
You must abstain from eating meat for three days before the test.
FibroTest, FibroMax, SteatoScreen
Blood collection is carried out strictly on an empty stomach in the morning. It is not recommended to take ascorbic acid 1-2 days before the test; it is also necessary to exclude medications and foods that cause artificial coloration of the serum (carrots, oranges).
To conduct a FibroMax study, you must indicate your exact weight and height.
Hormonal studies
Blood for hormonal studies must be donated on an empty stomach in the morning, between 8 and 11 am. If this is not possible, blood can be donated for some hormones 4-5 hours after the last meal in the daytime/evening hours (except for those studies for which blood must be donated strictly in the morning). Before taking tests, you should consult a specialist doctor.
1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from the diet; the last meal should not be large. 1 day before the study, psycho-emotional and physical comfort (calm state without overheating and hypothermia) is necessary.
Thyroid hormones
During the initial check of thyroid hormone levels, discontinue medications that affect thyroid function 2-4 weeks before the test (after consultation with your doctor). When monitoring treatment, exclude taking medications on the day of the study and be sure to note this on the referral form (also note information about taking other medications: aspirin, tranquilizers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives).
Sex hormones
In women of reproductive age, the results of hormonal studies are influenced by physiological factors associated with the phase of the menstrual cycle. During the examination for sex hormones, you need to indicate the phase of the menstrual cycle. Hormones of the reproductive system must be taken strictly on the days of the cycle:
- LH, FSH - 2-3 days of the cycle;
- Estradiol - 2-3 or 21-23 days of the cycle;
- Progesterone - days 21-23 of the cycle, with a 28-day cycle. If the cycle is more or less than 28 days, then 7 days before the expected menstruation.
- 17-OH-progesterone, Testosterone - 2-3 days;
- Dihydrotestosterone, Androstenedione glucuronide, Free testosterone, Androstenedione, Sex hormone binding globulin, Anti-Mullerian hormone - on days 2-3 of the cycle.
Prolactin, Macroprolactin
On days 2-3 of the menstrual cycle, donate blood in the morning, at rest; before the examination, avoid palpation of the mammary glands.
Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH/MIS), Inhibin B
For women, the study is carried out on days 3-5 of the menstrual cycle. 3 days before taking blood, avoid intense sports training. The study should not be performed during any acute illness. Do not smoke 1 hour before taking blood.
Adrenaline and norepinephrine
8 days before the study, exclude medications: salicylates, β-blockers. 1 day before the test, you must refrain from heavy physical activity, exclude alcohol, coffee, tea, B vitamins, and bananas.
Renin, angiotensin
Before the study, exclude the use of estrogens (1-2 months before), diuretics (3 weeks before), and antihypertensive drugs (one week before). Blood collection should be carried out in a sitting or standing position.
Aldosterone
In consultation with your doctor, 8 days before the study, discontinue antihypertensive drugs, β-blockers, laxatives, corticosteroids, diuretics, and antidepressants. 3 weeks before the study, discontinue aldosterone antagonists.
ACTH, cortisol
Due to the fact that ACTH and cortisol are stress hormones, you need to calm down and relax for 20 minutes before donating blood. Any stress causes an unmotivated release of these hormones into the blood, which will lead to an increase in this indicator.
The level of these hormones changes cyclically throughout the day, so the most informative results are studies conducted in the morning before 9 o’clock.
Insulin, C-peptide
Donate blood strictly in the morning.
Gastrin-17, Gastrin-17 stimulated, pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, H. Pylori IgG
Blood must be donated for testing on an empty stomach after a 12-hour fast.
1 week before the study, refrain from taking medications that affect gastric secretion: Pepcedin, Zantac, Nizax, Ranimex, Esofex, Losec, Somac, Ranixal, Ranil.
1 day before the study, refrain from taking medications that neutralize hydrochloric acid secreted by the stomach: Alsucral, Balancid, Prepulsid, Metropam, Librax, Gaviscon.
If you have difficulty stopping medications, be sure to inform your doctor.
3 hours before donating blood, refrain from smoking.
Protein C, Protein S, von Willebrand factor
Do not conduct the study during acute periods of illness and while taking anticoagulant drugs (at least 30 days must pass after discontinuation). Biomaterial must be submitted for research on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and blood collection. Women are not recommended to conduct hemostasis tests during menstruation.
PSA (total, free)
After a prostate biopsy and prostate massage, blood can be donated for PSA determination no earlier than 2 weeks later. The post-surgical PSA level is determined no earlier than 6 weeks after the intervention.
CA-125 ovaries
It is more informative to take it 2-3 days after menstruation.
Blood tests for infections
1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from your diet. 2 days before donating blood for viral hepatitis, exclude citrus fruits, orange fruits and vegetables from the diet.
The results of tests for the presence of infections depend on the period of infection and the state of the immune system, so a negative result does not completely rule out infection. At an early stage of the disease, seroconversion occurs (absence of antibodies during the acute period of the disease).
In doubtful cases, it is advisable to re-test after 3-5 days.
A blood test for the presence of IgM class antibodies to infectious agents should be carried out no earlier than 5-7 days from the moment of illness, and IgG and IgA class antibodies no earlier than 10-14 days. This is due to the timing of the production of antibodies by the immune system and their appearance in the blood in the diagnostic titer.
Coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood test
A coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood clotting test helps determine the quantity and quality of prothrombins, as well as their ability to form blood clots and prevent serious blood loss, as evidenced by the rate of formation of blood clots. If clotting rates are reduced, then there is a possibility of extensive bleeding even with minor injuries, which, in turn, can lead to serious health problems. Excessive blood clotting (increased thickness) can lead to the formation of blood clots that can block the most important vessels and arteries. Most often, a coagulogram is prescribed before surgery, for the diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis, during planning of pregnancy or its pathologies, for diseases of the hematopoietic organs, bleeding, diseases of the liver and cardiovascular system. To obtain reliable parameters for this type of study, the patient must follow some rules:
Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, you can drink a glass of plain water without carbon.
Technique for collecting capillary blood from a finger
- Soak a cotton ball (gauze) in an antiseptic.
- With one hand, take the 4th finger of the patient's free hand, massage it lightly, pinching the upper phalanx of the finger with the index and thumb.
- With the other hand, treat the inner surface of the upper phalanx of the patient’s finger with an antiseptic with a cotton ball (gauze) soaked in an antiseptic. Dry the surface of the finger with a dry sterile cloth (cotton ball).
- Place the used napkin (ball) in the consumables tray.
- After the skin has dried, take a scarifier and puncture the skin with a quick movement.
- Place the used scarifier in a puncture-resistant waste container.
- Wipe off the first drops of blood with a dry sterile cloth (cotton ball). Place the used napkin (ball) in the consumables tray.
- By gravity or using a capillary, collect the required amount of blood. The volume of blood drawn must correspond to the mark on the tube.
- Press a napkin (cotton ball) with an antiseptic solution to the puncture site. Ask the patient to hold a napkin (cotton ball) at the puncture site for 2-3 minutes.
- Invert the tube into a vertical position to transfer blood from the capillary to the tube.
- Turn the cap off the tube, remove it, and place it in a puncture-proof container along with the built-in capillary without disassembling it.
- Remove the cap from the base of the test tube, tightly close the test tube or close the test tube with a cap until it clicks (depending on the modification of the test tube).
- Mix the sample thoroughly by inverting the test tube.