Sudden dizziness, loss of balance - probably every adult has experienced these sensations. In most cases, no one attaches importance to these phenomena, although they may signal the onset of the development of a neurological or other disease. If you experience systematic dizziness and loss of balance, you should consult a neurologist to clarify the situation.
In Moscow, patients with dizziness are examined at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic is a modern medical center, where the following areas are represented: neurology, rehabilitation, oncology, a scientific and practical center, a surgical department, and an addiction treatment clinic. The Yusupov Hospital provides examination, treatment and rehabilitation of various neurological pathologies, including dizziness and loss of balance. Highly qualified neurologists who have extensive experience in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases of any complexity work with the patient.
What is unsteadiness of movements?
Unstable movements – permanent or temporary loss of coordination. If they occur systematically, this indicates the presence of abnormal disorders in the body. Extra-systemic indicate that inflammatory processes are occurring in the body.
Most often, unsteadiness of walking manifests itself in combination with other symptoms:
- headache;
- unexplained sudden weakness;
- tingling in the legs;
- dizziness.
To better understand, it is necessary to know why a person may stagger when walking and why this is so important.
Movement is achieved through a healthy bone structure, developed muscles and healthy joints. The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for coordination; it is also controlled by vision and the vestibular apparatus.
Impulses pass through the spinal cord, sending a signal to the lower parts of the body that a movement needs to be performed. Only after this the muscles begin to work.
When these impulses are disrupted, the entire system is disrupted. This is where the gait disorder comes from. A transmission failure causes the legs to become unresponsive.
Failures in the musculoskeletal system lead to exactly the same result. The legs cannot correctly carry out the necessary “commands”.
If the functioning of the cerebellum is disrupted, the impulse itself does not reach, therefore, the command does not arrive at all. Consequently, a person cannot move, his legs do not obey.
Features of the ataxic gait
Due to imbalances, patients with pathological processes in the cerebellum try to increase the area of support, spread their legs widely, stagger and sway randomly when walking.
Movements of the upper and lower extremities lose synchrony. Instability persists in a standing position, regardless of the presence or absence of visual control. With unilateral damage to the cerebellum, one half of the body suffers, and falls on the affected side are possible. When cortical structures are involved, the clinical picture resembles that of cerebellar ataxia. Instability increases when turning, the patient often “falls” in the direction of the lesion, unsteadiness of gait correlates with the severity of the damage to the cortex. In people with damage to the ventrolateral thalamus, unsteadiness and instability occur on the opposite side, and there is a tendency to fall backward or to the healthy side.
Old age
Often, older people (over 60 years old) experience swaying, as well as “floaters” before the eyes.
It is also common to experience tinnitus and dizziness when walking. Headaches appear sharply, and sometimes even fainting occurs. As a rule, all these symptoms are ignored and blamed on age. In some cases, this may indicate problems with the body, so you should consult a doctor. This way you can ensure your usual full life.
One of the reasons is a malfunction of the cardiovascular system of the brain. Atherosclerosis appears (as mentioned above, a disease of the second category).
With age, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is impaired.
Gait disturbance may also be due to heart disease. For example, ischemia can reduce blood circulation in the area of the ear where the organ responsible for balance is located. Also, insufficient blood circulation leads to uncertain movements. Other diseases also have a detrimental effect (arrhythmia, hypertension).
It has a great influence on gait and blood viscosity, because it supplies oxygen to the organs. How quickly it reaches the desired place, including the cerebellum, depends on its speed.
Injuries and diseases of the spine also make it difficult to transmit signals. Therefore, movement disorders are possible. Elderly people are often susceptible to sleep disorders, which leads to diseases of the third category.
The most common occurrence of maladaptation is observed. The person feels extremely insecure, there is a feeling that no one needs him, inexplicable fears and anxiety. As a result, he may skid when walking, become dizzy, have dark vision, and his condition worsens every day. For treatment, you must definitely contact professionals and it is better not to delay, because the consequences can be disastrous.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that many factors can lead to an unsteady gait and they should not be ignored.
If the cause is eliminated, the consequences will also be eliminated. Life will be familiar, fulfilling and healthy. Therefore, it does not matter how old a person is, treatment is necessary regardless of age.
Constant dizziness and its causes
Dizziness is a feeling of uncertainty in determining the position of your body in space. It may be accompanied by a seeming swaying or spinning of the environment or one’s own body, disorientation in space, a feeling of instability, and “floating” of the ground from under one’s feet. In most cases, dizziness can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing, increased sweating, increased heart rate, surges in blood pressure, hearing and vision impairment (nystagmus - involuntary high-frequency oscillatory movements of the eyes). Attacks of uncertainty can last from a few seconds to several hours.
Dizziness and impaired coordination of movements are one of the most common complaints of patients and the most “unloved” symptom for doctors. They can be signs of various diseases: neurological and mental, musculoskeletal and vestibular, diseases of the cardiovascular system or ears and eyes. Therefore, the doctor’s primary task is to clarify the nature of dizziness and correctly diagnose the disease.
Receptors responsible for coordination of movements are located in all extremities of the body, and vision is responsible for orientation in space. Next, all reflex impulses are collected in the brain, where the body’s response is formed. Disruption or distortion of any impulse leads to incorrect information for the brain, and, consequently, a feeling of dizziness.
Systemic dizziness is characteristic of damage to the vestibular apparatus (peripheral or central parts). It is considered normal to have an imbalance after a long ride in vehicles (sickness), swimming or riding on a swing. Some people suffer from such disorders from a very early age.
Causes of constant dizziness
The main causes of dizziness can be:
- Vestibular pathologies of the central or peripheral parts. An apparent sensation of rotation, falling, swaying, tilting of the environment or one’s own body is experienced. As a rule, it is accompanied by nausea, hearing and balance problems, and rapid illusory vibration of surrounding objects.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. There is a feeling of lightheadedness, impending clouding of consciousness, loss of consciousness, and fainting. Quite often accompanied by pale skin, increased heart rate, darkening of the eyes, a feeling of fear, “cold sweat,” and a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
- Neurotic disorders or pinched nerve fibers in the cervical spine. In this case, there is an inability to maintain balance (body balance), instability and unsteadiness of gait, impaired sensitivity of the limbs up to complete paresis (weakening of a muscle or group of muscles due to damage to the pathways of the nervous system and motor centers of the spinal cord and/or brain). Symptoms of dizziness and loss of balance are worse when the body is upright (walking or standing), much less pronounced when sitting, and disappear completely in a horizontal position.
- Cervicogenic disorders. Dizziness and headaches that occur against the background of pain and limited mobility of the cervical segment of the spine. Treatment of headaches and dizziness in this case begins with treatment of the spine and postural disorders (position of the head relative to the entire body).
- Quite often, dizziness precedes migraine attacks. Circulatory disorders in certain areas of the brain associated with the work of the vestibular apparatus cause impaired coordination of movements, irritability, slow reaction and headache. Migraine treatments in many cases relieve all disturbing symptoms.
- Vertebrogenic pathologies. Circulatory disorders or pinched nerve roots caused by osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, herniated intervertebral discs and other diseases of the spine or postural curvature can cause dizziness, pain syndromes, weakness in the limbs and other unpleasant sensations. In this case, it is necessary to consult a vertebrologist, treat spinal diseases, and the disturbing symptoms will subside on their own after proper therapy.
- Traumatic brain injuries, tumors and brain diseases. Accompanied by severe dizziness, headache, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes, poor health, nausea.
Also, the causes of frequent dizziness may be:
- hypertension or hypotension – high or low blood pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- strict diets low iron content in the body, anemia;
- long-term use of certain medications (vasoconstrictors, sedatives, anticonvulsants, psychotropic drugs, etc.);
- diseases of the inner ear (otitis media, etc.);
- constant stressful situations and nervous overstrain.
Quite often, dizziness is accompanied by temporary mental disorders: hysteria, hysteria, panic or anxiety, depersonalization.
First self-help for dizziness
If you experience dizziness or imbalance at home, it is advisable to lie down immediately. At the same time, try to keep your head and shoulders at the same level; place a small cushion under your neck. This will help straighten the spine, release restrictions, if any, and stabilize the blood supply to the brain.
When dizziness occurs on the street, you urgently need to sit down, close your eyes, relax, try not to make sudden movements so as not to lose your balance and fall. If the attack does not go away for more than ten minutes, seek help from others and ask them to call an ambulance.
If attacks of dizziness become a frequent occurrence or last for several days, these are the first signs of serious disorders in the body and you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
This could be a local therapist, a neurologist, a neurologist, a vertebrologist, a doctor who treats the spine, etc. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
When should you sound the alarm?
Impaired coordination in some cases is a consequence of serious illnesses. It is recommended to consult a specialist if:
- stumbling has become more frequent, often occurring even out of the blue;
- falls due to weakness in the legs;
- impaired control of movements;
- unnatural gait;
- after a long walk there is a sudden stop, then there is a feeling that it is impossible to move your leg;
- feeling of “cotton” legs;
- difficulty walking on stairs;
- when moving, most of the weight increasingly moves to the heel area;
- when trying to get up, a person falls;
- difficulty raising a leg or starting to move after a long rest;
- the appearance of dizziness, pounding in the temples, darkening in the eyes.
Often a person begins to be afraid and panic.
It is absolutely impossible to ignore such symptoms, since they indicate the presence of diseases.
Unsystematic sudden dizziness
About 30% of complaints about dizziness and loss of balance are called false, that is, non-systemic. The sensations are not associated with the development of the disease and can occur in the following situations:
- a sharp change in body position when standing up after prolonged sitting or lying, a sharp turn of the head. The feeling of loss of balance lasts seconds and is associated with the redistribution of blood in the vessels;
- the appearance of feelings of fear or anxiety. Dizziness is caused by a psychological factor;
- overwork, lack of sleep;
- lack of nutrients during an irrational diet;
- dizziness during pregnancy may be associated with the development of anemia, fatigue, changes in the body during pregnancy;
- intoxication with medicinal, alcoholic and narcotic substances causes a feeling of loss of balance and dizziness due to the toxic effect on the vestibular apparatus.
Doctor's help
It is impossible to make a diagnosis yourself when it sways from one side to the other. This is done exclusively by specialists. To begin with, doctors monitor the patient’s movements using the following methods:
- observation of movements directed forward with the face and forward with the back;
- doctors watch how the patient moves in a straight line with his right and left sides;
- alternate change of step rhythm;
- comparison of walking with eyes closed and with eyes open;
- watching a person climb stairs;
- movement around an object (for example, a chair);
- making turns while driving;
- It is also suggested to walk on your toes and heels.
Based on the results, the doctor prescribes further examination and treatment:
- undergoing magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray;
- CT scan;
- blood donation (general analysis and biochemical);
- A biopsy of muscle tissue is performed.
In addition, the patient should be examined by other doctors:
- ENT;
- ophthalmologist;
- endocrinologist
After going through all the stages, the doctor can diagnose the patient and prescribe the necessary treatment.
You should turn to traditional medicine only after examination and consultation with a doctor.
Any medications are prescribed only by a certified specialist! All drugs are prescribed based on the individual characteristics of each organism. Medicines that help one person can cause irreparable harm to another.
Who should I contact?
There are often situations when the patient himself understands that he needs the help of a specialist. However, he has no idea which doctor to see. To do this, you need to carefully monitor the symptoms and act in accordance with them:
- Cardiologist. It is worth contacting him if, along with impaired gait, there is also increased blood pressure or in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Neuropathologist. A neurologist is consulted if a person often experiences stress, nervous or other mental disorders.
- Traumatologist/orthopedist. You have been injured, there is pain in the muscles or joints.
- Surgeon. You should see a surgeon if you receive serious injuries.
If it is impossible to identify the symptoms on your own, you should consult a general practitioner.
Often the cause of symptoms is sought using magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method allows you to identify the cause of the development of pathology, as well as make an accurate diagnosis.
Choosing a clinic is easy to do using the service. A single registration center for MRI or CT allows you to select a medical center based on specified parameters: type of examination, metro station, and also sort the search results by price, rating, work schedule.
Patients have access to online registration through the website or telephone registration with a discount on the study in the amount of up to 1,000 rubles.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics are determined taking into account the underlying disease. In case of infectious-inflammatory genesis of ataxic gait, antibiotic therapy or antiviral therapy is indicated. For patients with vascular diseases, depending on the nature of the pathology, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, thrombolytics, angioprotectors, and vasodilators may be recommended. Patients with ataxia and unsteady gait due to intoxication require detoxification therapy.
Pathogenetic therapy for hereditary ataxia has not been developed. The same symptomatic measures are taken as for ataxias of other etiologies. Prescribe B vitamins, anticholinesterase drugs, ATP, piracetam, meldonium. Exercise therapy classes are conducted to improve the general condition and strength of muscles, and reduce the severity of incoordination. Patients are referred for massage.
Surgery
Surgical interventions are required for large processes and circulatory disorders. Taking into account the etiology of the ataxic gait, the following techniques are used:
- Neoplasms
: removal of tumors of the cerebellum, cortex, brain stem. - Abscesses
: drainage, removal along with the capsule. - Hematomas
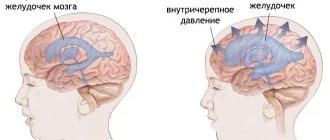
: transcranial and endoscopic removal, stereotactic aspiration. - Occlusive hydrocephalus
: ventriculoatrial and ventriculoperitoneal shunting, external ventricular drainage.