Tachycardia in children and newborns: norms, causes and symptoms
Tachycardia in children and newborns is a rapid heartbeat. Very often this is a physiological phenomenon. The child is usually nervous during the examination. But sometimes tachycardia can be a symptom of a developing disease. Symptoms of tachycardia are sometimes confused with other diseases. Therefore, any alarming symptom should be diagnosed by a cardiologist. Pediatric cardiology specialists deal with diseases of this type. It is worth knowing the norms, causes and symptoms of childhood tachycardia in order to fully take care of the proper development of the child.
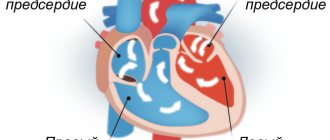
The heart of every child is the most important element of the circulatory system.
This organ works constantly. An accelerated heartbeat can be caused by natural reasons, so-called physiological. But the cause of concern may be an irregular heartbeat that appears without an external reason. In adults, tachycardia is more than 100 beats per minute. For children these norms are different. Tachycardia in the youngest patients in most cases is not a serious threat, but always requires consultation with a doctor.
Recovery prognosis
As a rule, experts give a favorable prognosis for recovery for children with any type of tachycardia. Effective treatment in almost every case will return the child to a normal lifestyle without restrictions.
In adolescents, tachycardia will most likely persist for the rest of their lives, and therefore they will not stop taking medications. In addition, adherence to the recommended diet and exercise will always have to accompany it, otherwise even slight excess weight will put a strain on the heart and provoke the development of various diseases.
Author : Alexander Kulakov
Certified physician. Graduated from the Moscow Medical School. Clara Zetkin, Moscow Medical and Dental Institute named after. Evdokimov. Author med. content of the site tvou-voleyball.ru
Tachycardia in children
Tachycardia in children is a rapid and uneven heartbeat, which can be a sign of heart disease and related ailments. Very often, a child's rapid heartbeat is caused by non-cardiac (non-cardiac) causes. The average "speed" of the pulse in such young patients and the range of values change with age. Therefore, it is difficult to talk about constant values. Children are also very physically active, which creates an ideal environment for increased heart rate and frequent changes in heart rate measurements.
Disorders of regular heartbeat occur in children of any age. They can appear very sporadically or periodically, but sometimes they appear constantly. Currently, it is possible to detect tachycardia in the fetus. This is achieved using CTG testing. This is a method of intrauterine monitoring aimed at identifying symptoms of intrauterine hypoxia when it does not yet cause irreversible changes in the child’s body. If tachycardia occurs in the fetus, doctors usually decide on a caesarean section. Cardiac arrhythmias can also occur in newborns and children.
About
Case from practice
I bring to your attention a very illustrative case where a combination of a number of unpleasant circumstances and mistakes led to serious health problems for a young girl.
Thirteen-year-old K. was sent to a specialized cardiac surgery hospital with complaints of pulling and stabbing pain behind the sternum on the left, not periodic, not associated with the emotional state, physical activity and changes in body position. Painful attacks passed after taking sedatives or on their own. She had been noticing the sensations for a couple of years and came in due to the worsening of her condition.
Anamnesis of life
She was born full-term from the second pregnancy. There are no hereditary complications, bad habits, or professional hazards on the part of the parents. In the first half of pregnancy, the mother suffered from severe toxicosis. No examination for intrauterine infections was carried out.
As she grew older, she suffered from the following diseases:
- 1 year - no pathologies;
- 4 years - scarlet fever;
- 5 years - HES;
- 6 years old - lacunar tonsillitis.
At an older age, I occasionally suffered from ARVI.
Electrocardiography was not performed until the age of ten!
An ENT doctor diagnosed and observed chronic tonsillitis in the compensation stage.
Physically developed in accordance with age standards, harmoniously.
History of the disease
For the first time I felt pain in my heart when I reached the age of ten and addressed these complaints to a cardiorheumatologist.
A month later, the pain returned and began to appear more often. Extrasystole and atrial flutter appeared. This time K. was hospitalized and she was prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs, which, however, did not bring the expected effect. The girl was sent to a cardiac surgery hospital.
The ECG shows sinus arrhythmia, and the EchoCG shows enlargement of the left ventricle. Mitral valve prolapse was also detected, which at that time had not yet led to hemodynamic disturbances. The attending physician prescribed daily ECG monitoring, with the help of which attacks of atrial arrhythmia were detected.
The prescribed drug antiarrhythmic therapy was effective and led to a decrease in heart rate during attacks of atrial arrhythmia and the cessation of relapses of atrial fibrillation.
The child was observed in the clinic for six months. Despite supportive treatment, atrial tachyarrhythmia persisted. Echocardiography revealed enlargement of the right chambers of the heart. Considering that conservative treatment methods failed to achieve either a complete cure or even reliable stabilization of the condition, and the conduction system of the heart was under constant threat of inflammatory changes, it was decided to perform a biopsy of endomyocardial tissue using an intracardiac catheter.
During the examination of the biopsy specimen, tissue degeneration and the presence of a large number of leukocytes were revealed.
Subsequently, the girl was treated with cardioprotectors, antiarrhythmics, and anticoagulants.
Sluggish chronic tonsillitis was treated in order to eliminate the source of pathogenic microflora in the body.
After the entire complex of measures taken, K.’s well-being improved, relapses of arrhythmias were not observed, and the size of the heart returned to normal. However, there is dysfunction of the sinus node, and the patient is being monitored.
Conclusion
The patient came to this difficult situation for several reasons:
- lack of ECG control during periods of life that threaten the development of arrhythmias;
- the presence of an unsanitized chronic source of infection in the body;
- latent, sluggish, difficult to diagnose course of endomyocarditis.
To prevent such cases in other children, you should be more attentive to preventive examinations, observing the principle of overdiagnosis. In doubtful cases, it is better to refer the child for additional examination, which will show the norm, than to miss the pathology!
Tachycardia in a newborn
Tachycardia in a newborn means 200-300 heart beats per minute. It should be remembered that these norms are completely different from the norms for adults. The normal heart rate of a newborn is 140 beats per minute. In an adult, already 100 beats per minute means tachycardia, in a newborn it means a normal heartbeat. Doctors often emphasize that tachycardia in such young children is a physiological and very common phenomenon. This is closely related to the personal characteristics of such young patients, who are usually very nervous and fearful during the examination. This state of anxiety passes and does not pose any danger. Very often, after examination, the newborn's heart does not show any signs of tachycardia. But sometimes the cause of heart problems in newborns can be temporary pathological conditions associated with childbirth.
These include:
- perinatal hypoxia,
- maternal illnesses during pregnancy,
- hypoglycemia ,
- ion Disorders,
- anemia.
In the prenatal period, specific muscle connections are formed between the atria and chambers of the heart. They contribute to the development of paroxysmal arrhythmias in newborns until normal cardiac function has fully developed. Tachycardia can already be detected prenatally by ultrasound of the fetal heart. Early detection of tachycardia may indicate heart disease. Modern medicines and equipment in neonatal units make it easier to determine the level of risk to the baby and provide appropriate treatment.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help reduce the risk of tachycardia and the likelihood of complications after it:
- proper nutrition, following a healthy diet (more fruits, grains, vegetables);
- limited consumption of caffeine, which is found in tea and chocolate;
- prevent your child from gaining excess weight;
- avoiding stress and emotional turmoil;
- playing sports without excessive stress;
- proper daily routine, including proper sleep and rest;
- taking sedatives and vitamins for the heart (if necessary);
- control over blood cholesterol levels;
- regular visits to the doctor.
Causes of tachycardia in children
Tachycardia in children most often has non-cardiological causes, that is, the causes are not purely cardiac.
The most common:
- fever - an increase in temperature in such a small child by 1 degree causes an increase in heart rate by 10 beats per minute,
- dehydration ,
- powerful emotions,
- anxiety
- anemia,
- overexertion (even with prolonged crying),
- medications taken.
Tachycardia in children can also be caused by various diseases. These include:
- hypoxia,
- congenital heart defects,
- respiratory system diseases,
- frequent infections
- myocarditis,
- shock, i.e. immediate allergic reaction,
- paroxysmal increase in heart rate, disproportionate to the child’s activity,
- chest pain,
- loss of consciousness,
- abnormal ECG recording.
About
Fever varies:
- with the flow:
- acute (fever up to 2 weeks),
- subacute (up to 6 weeks),
- chronic (over 6 weeks).
- according to the degree of increase in the indicator:
- subfebrile (increase to +38.0 degrees)
- febrile (from +38.0 to +39.0 degrees),
- pyretic (from + 39.0 to +41.0 degrees),
- hyperpyretic (over +41.0 degrees).
- by type of temperature curve:
- constant (temperature fluctuations during the day do not exceed 1 degree).
- laxative (daily fluctuations up to 2 degrees),
- atypical (oscillations are chaotic, varied and irregular),
- debilitating (a combination of laxative and atypical fever with fluctuations during the day of more than 2-3 degrees),
- intermittent (a combination of short-term periods of increase and decrease in temperature to normal values),
- recurrent (alternating periods of temperature increase with periods of temperature normalization from 2 to 7 days).
According to the recommendation of the WHO (World Health Organization), antipyretic drugs are prescribed to children according to age:
- from birth to 2 months at a temperature of +38.0 degrees,
- children from 3 months to 24 months with a temperature of +38.5 degrees,
- children from 1 to 5 years old with a temperature of +39.0 degrees,
- children over 5 years old at + 39.5- +40.0 degrees.
Norms of tachycardia in children
The norms of tachycardia in children differ from the norms in adults. What is already an adult tachycardia is still normal in a newborn or child. The normal heart rate for a newborn is about 140 beats per minute. Pathological changes reach 200-300 beats per minute. This condition requires a full consultation with a doctor.
The correct heart rate (beat) depending on age is as follows:
- newborn – up to 3 months – 140 beats per minute (in deep sleep from 80 to 140),
- 3 months – 2 years – 130 beats per minute (in deep sleep from 75 to 160),
- 2 years – 10 years – 80 beats per minute (in deep sleep 60-90),
- over 10 years old - 75 beats per minute (in deep sleep 50-90).
Should parents worry?
Regardless of whether the child has complaints, parents should be attentive to the state of his health. Indeed, in the life of a growing organism there are 4 periods of risk for the appearance of arrhythmias, through which everyone goes through:
- newborn;
- from four to five years;
- from seven years to eight;
- from twelve to thirteen years old.
Children of these age groups must undergo mandatory electrocardiographic examination. If a child presents even one cardiogenic complaint, then doctors should prescribe additional types of ECG, various tests and examinations.
If problems are identified, then you need to start treating the child without delay. Most arrhythmias have a favorable prognosis. Clear recommendations on treatment tactics have been developed; in severe cases, surgical interventions are performed. Arrhythmia is not a death sentence; it must be fought and can be defeated, returning the child to a full life.
Symptoms of tachycardia in children
Symptoms of tachycardia in children often differ from those in adults. As a rule, they are uncharacteristic. The child cannot independently determine how he is feeling, say that his heart rate is racing or shortness of breath.
The most characteristic symptoms in children:
- pale skin,
- irritability,
- Poor appetite
- frequent vomiting,
- anxiety
- apathy
- rapid breathing.
Very often, such symptoms are confused with infections and parents cannot always attribute them to tachycardia. Only a cardiologist can make the correct diagnosis. The first signal is always a rapid heartbeat (rapid pulse). Very often it can be assessed by auscultation of the heart. The doctor always conducts a detailed interview with the parents, who must inform them of all the alarming symptoms noticed. Only a pediatric cardiologist decides on the treatment method. Sometimes it is necessary to administer medications for a long time to normalize heart function. Here diagnosis is of great importance. The doctor always evaluates all the symptoms - the child's appearance, nutritional status, heart rate, respiratory effort and pain reactions. Laboratory tests and ECG are an indispensable addition to chests. With proper treatment, tachycardia in children is not a problem.
About
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine can significantly help in the fight against tachycardia, but folk remedies cannot replace drug treatment. Before using any method, you must consult your doctor.
Treatment of tachycardia using traditional medicine involves the following effects:
- general calming effect;
- sleep stabilization;
- normalization of the nervous system;
- decreased myocardial excitability;
- activation of general regulatory processes in the body to protect it.
There are a huge number of recipes with medicinal plants: hawthorn, valerian, chicory, lemon balm, motherwort, honey, etc. The following recipes are most effective:
Calming collection No. 1. Pour a pinch of calendula flowers and motherwort herb into 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, strain and drink warm after lunch.
Calming collection No. 2. Pour a tablespoon of dried white willow flowers into a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. Then strain and divide into 6 portions.
Calming collection No. 3. Add a tablespoon of lemon balm to a glass of hot water and steep like regular tea. Drink the drink up to three times a day.
At the pharmacy you can buy ready-made tinctures of hawthorn, motherwort, and valerian. They should be taken 10-15 drops 3 times a day or if your heart rate increases.