Video
Pain under the shoulder blade. Question answer.
Topic: Questions and Answers
Pain under the shoulder blade
Topic: Encyclopedia of diseases
Title
- Pain under the left shoulder blade
- Pain under the right shoulder blade
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
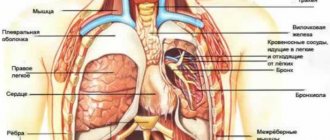
Pain under the shoulder blade is a fairly common complaint among patients and often presents difficulties both for diagnosis and treatment. The pain can be localized both under the left and under the right shoulder blade.
Characteristics of pain
If the pain in your heart radiates to your shoulder blade, don’t panic right away. To begin with, you must clearly understand the nature of the sensations that arise. In 90% of cases, this will allow you to independently understand the cause of the symptom. Substernal discomfort, accompanied by irradiation to some other area of the body, can be:
- sharp or blunt;
- pressing or stabbing;
- cutting or burning.
Having decided on this point, the patient most often himself guesses about the primary source of the pathological symptom. It is equally important to note the area where the pain is spreading. Sometimes it comes from the center and goes to the periphery of the chest. In some cases, it migrates into the interscapular space, and sometimes affects the lower jaw and even the hand.
Pay attention to the duration and strength of unpleasant sensations, to factors that can change their intensity and location. This refers to the use of vasodilators and changing posture.
Prevention of pain in the left shoulder blade
In order to prevent cases when it hurts on the left and radiates to the shoulder blade, you need to:
- engage in physical exercises to strengthen the back muscles;
- eat right to avoid diseases of the digestive system;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid strenuous physical activity;
- maintain posture;
- sleep on a hard surface;
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid stressful situations.
If you have pain on the left shoulder blade for 2–3 days, you should consult a specialist. You should immediately consult a doctor if the pain in your left shoulder blade is very severe and is accompanied by rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, cough, dizziness, nausea or vomiting.
The mechanism of development of pain
How does it happen that the heart hurts, but it stings under the shoulder blade, and most often with the left one? I think the answer to this question interests many readers. To understand the origin of this phenomenon, it is necessary to delve a little into the doctrine of the processes of intrauterine development of the fetus. At the time when our heart takes on its final form, the formation of the neck, back and girdle of the upper extremities, which includes not only the arms themselves, but also the shoulder blades, is completed - all these formations receive nerve fibers from nearby segments of the spinal cord. Therefore, the pain impulse can “jump” from one floor to another. This phenomenon was called irradiation.
This leads to the conclusion: there is no need to go to extremes and attribute a heart attack to yourself before a full medical examination.
How to prevent shoulder pain
To prevent pain from occurring, the following conditions must be observed:
- lead an active lifestyle, move more, engage in feasible sports;
- Avoid prolonged periods with your arms raised above your head, as well as movements associated with unilateral load on the shoulder joint; At risk are weightlifters, tennis players, and miners; If a representative of one of these groups feels persistent pain in the shoulder, perhaps he should change his occupation or at least reduce his exposure to harmful factors as much as possible.
Cardiogenic causes of the symptom
A person with a long history of coronary heart disease is unlikely to be surprised by pain in the scapula area. Occurring against the background of insufficient oxygen supply to myocardial cells, unpleasant sensations can spread to more unpredictable areas of the body. For example, the stomach or lower jaw. As you understand, this is connected with the mechanism described above. An experienced patient knows perfectly well how the pathology will manifest itself and what factors provoke a new attack.
Those who first encountered such a clinic either become scared, and then they start taking pills indiscriminately, or they ignore the symptom and thereby worsen the prognosis of the disease. That is why it is important to distinguish pain from angina pectoris, arrhythmias and heart attack. We will talk about them further.
Angina pectoris
Angina is one of the manifestations of hypoxia of the heart muscle. In this case, a pain syndrome is formed that can often spread far beyond the chest.
The following situations may lead to an attack:
- inadequate physical activity exceeding the body's reserve;
- psycho-emotional tension, simply put, stress;
- rapid change in ambient temperature. For example, when swimming in cold water after leaving the steam room;
- banal overeating;
- sudden increase in blood pressure.
As you understand, an attack is accompanied by pain, often of a pressing nature. Patients, describing it, say that “it was as if someone heavy was sitting on the chest.” It can simultaneously be localized under the shoulder blade and in the heart area, in the arm, and jaw. Sometimes angina manifestations are confused with a heart attack. What will allow us to distinguish these two states?
The pain with incoming myocardial ischemia is short-term: if you do not take a vasodilator, it will go away on its own in about 15 minutes. But with necrosis - the death of cells in a certain area of the heart - taking Nitroglycerin will not help.
You can read more about who gets angina and why, as well as methods of treating it, here.
Myocardial infarction
One of the first places among the causes of sharp pain under the left shoulder blade and in the area of the heart is myocardial infarction. I note that the reasons listed above can lead to it. But changes in cells that develop against the background of oxygen starvation become irreversible. That is why the clinical picture of this condition is brighter than with angina pectoris.
Let's look at the main symptoms of a heart attack, distinguishing it from other pathologies with similar characteristics of unpleasant sensations.
These features are:
- a dagger-like, acute attack of pain that does not stop after taking Nitroglycerin;
- a feeling of approaching death, a person is seized with fear, he panics;
- excessive sweating and pale skin;
- lack of a comfortable body position that would reduce discomfort;
- the appearance of shortness of breath, the patient cannot take a deep breath.
The most unpleasant thing in this situation is the many faces of a heart attack. The disease may debut not with pain in the heart, but, for example, in the jaw or stomach. This significantly complicates diagnosis and worsens the prognosis. To learn how to recognize the disease and treat it correctly, read the article at the link.
Heart rhythm disturbances
Heart rhythm disturbances themselves are not the cause of pain in the heart region, radiating under the shoulder blade. They rather lead to a deterioration in the blood supply to the myocardium and its ischemia, which are accompanied by discomfort. Why is this happening?
Arrhythmias may consist of extraordinary contractions of the atria or ventricles or blockades. In this case, the sequential movement of blood from one section to another is disrupted. The vessels feeding the myocardium are filled from the initial part of the aorta, and if the pressure in it is low or the output is too small, then the cells will not receive the necessary volumes of oxygen. The latter will entail an attack similar to angina pectoris.
What to do
Now we have come to a very important moment - providing the necessary assistance in the event of pain of cardiac origin. You must:
- if possible, calm the patient and provide him with access to oxygen (unfasten the belt, unfasten the collar of the shirt, open the window);
- give the patient “Nitroglycerin” under the tongue, if the sensations do not subside after five minutes, you can take another tablet;
- consult a doctor by calling an ambulance team.
If the drug worked the first time, then you can go to the clinic on your own for an appointment with a local therapist or cardiologist.
Diagnostics
Patients with pain under the left shoulder blade are first referred for consultation to an orthopedic traumatologist. If there are no disorders of the musculoskeletal system, other specialists are involved in the diagnostic search: neurologist, cardiologist, surgeon, etc. To establish the causes of pain, a full range of instrumental studies is prescribed, which includes:
- Radiography.
An X-ray of the scapula in frontal and lateral projections allows one to exclude or confirm traumatic injury. Radiation imaging of the spine is indicated for suspected osteochondrosis, scoliosis, or spondylolisthesis. Plain radiography of the chest cavity allows one to suspect damage to the lungs or heart. - Electrocardiogram.
A standard 12-lead ECG is a screening method, based on the results of which the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and identifies dangerous processes (myocardial infarction, life-threatening arrhythmias). The diagnostic complex is complemented by classical or transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac electrophysiology. - Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
A quick and non-invasive method is used to detect common conditions causing pain in the left shoulder blade. Ultrasound examination shows signs of a stomach ulcer, inflammatory infiltration of the pancreas, and enlarged spleen. To clarify the diagnosis of peptic ulcer, EGD is used. - Additional methods
. To clarify the nature and severity of bone changes, an MRI of the spine is performed. In case of probable bronchopulmonary diseases, bronchoscopy with biopsy and pleural puncture are performed. If there are difficulties in diagnosing abdominal pathology, diagnostic laparoscopy is recommended.
Laboratory examination methods play a major role in making a diagnosis. A clinical blood test shows signs of inflammation or disruption of hematopoietic processes. Indicators of acute phase proteins and proteinograms are informative in case of possible heart damage or an autoimmune process. Specific myocardial markers are assessed for anginal pain.
To diagnose gastrointestinal diseases, a coprogram is performed: the presence of pancreatitis is indicated by a high content of undigested food particles, an increase in the number of striated muscle fibers and starch grains. In case of inflammatory processes of the lungs and pleura, bacteriological seeding of the biomaterial is necessary, followed by a test for the sensitivity of the isolated microorganisms to antibiotics.
Massage of the back and subscapular area
Extracardiac causes of pain
Heart attack and angina are far from the only reasons why pain in the heart area radiates to the shoulder blade or arm. Diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy) and gastrointestinal tract (GERD, acute pancreatitis) can also lead to such a symptom. But most often such discomfort has neurological causes. A banal and, in principle, harmless osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine with a pronounced radicular component can easily imitate an attack of angina pectoris and a heart attack.
Next we will look at reasons not directly related to the heart.
Neurological pathologies
Among conditions accompanied by pain under the scapula and in the heart area, neurological ones occur in 40-45% of cases. It can sometimes be difficult to distinguish them from heart diseases based only on complaints and a quick examination. In any case, you will have to resort to instrumental diagnostics.
True pain in the heart is always combined with changes in blood pressure and pulse. This is what will allow us to differentiate the cause of the symptom at the first stage.
What pathologies of the peripheral nervous system can be misleading with pseudocardiological signs?
| Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine with radicular syndrome | Develops due to malnutrition of the intervertebral discs. The latter become thinner and their outer ring collapses. This leads to leakage of the nucleus and compression of the spinal nerves. Pain appears, most often between the shoulder blades, and due to the close location of the centers responsible for the heart, irritation can spread to them, simulating discomfort in the myocardium. |
| Intercostal neuralgia | Occurs against the background of compression of the nerve by muscles, lipoma, or damage to it after suffering from herpes zoster. If the fibers on the left are involved in the process, then this may well create the illusion of pain in the heart. And the irradiation of the impulse in the opposite direction is accompanied by discomfort under the scapula. |
I can say, based on my experience, that without performing an ECG, in some cases, even a highly qualified specialist will not be able to understand the real reason for the observed clinic.
How to cope with pain
In order not to harm your health and not to blur the symptoms when pain appears in the heart area, which spreads under the shoulder blade, for starters:
- take Nitroglycerin;
- listen to your feelings. If the pill has no effect, but the discomfort is not acute, allows you to breathe calmly, does not cause panic, and loses intensity when you change position, then most likely the cause is a neurological disease.
In this case, an ordinary non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam) can help.
Respiratory system
Pain under the left shoulder blade is not excluded due to respiratory diseases.
With left-sided pneumonia, mild chest pain or under the left shoulder blade is observed - dull, aching in nature, intensifying during movement or with deep breathing. Associated symptoms include fever to critical levels, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, etc.
When necrotic cavities form in the left lung, accompanied by inflammatory processes and the formation of pus, pain is observed in the chest area, in some cases radiating to the scapula. The pathology is accompanied by a cough with purulent sputum, shortness of breath, and lack of air during breathing.
Diagnosis of left-sided pleurisy (accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity) is carried out on the basis of the following symptoms: acute chest pain, sometimes radiating under the shoulder blade, fever, shortness of breath, dry cough and other manifestations.
Important! Almost all diseases of the respiratory system, accompanied by pain, are characterized by a cough of various types.
The occurrence of pain under the left shoulder blade is also possible due to acute bronchitis, tracheitis or tracheobronchitis.
Expert advice
Many people with back pain that develops against the background of osteochondrosis begin to warm the affected area with heating pads, apply alcohol compresses, go to the bathhouse or rub themselves with gels with an irritating effect based on capsoicin. This cannot be done, since the nerve is pinched, inflamed and swollen. Such treatment only worsens the situation. To quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations, take NSAIDs, limit yourself in physical activity and use local anesthetic drugs.
Shoulder Pain Treatment
Treatment of shoulder pain should be carried out strictly individually, taking into account examination data and the established diagnosis. It is performed by an orthopedist-traumatologist or rheumatologist. In case of very severe pain, pain therapy is carried out by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. A specialist will always find something to treat even very severe shoulder pain.
Diagnostics
A correct diagnosis is the path to prescribing adequate treatment and relieving the patient of pain. In diagnosis, examination and clinical examination of the patient by the attending physician using special assessment tests is of particular importance. They allow you to preliminarily determine which structures were damaged. The location of the damage is determined in more detail using functional tests.
Clinical data are confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies that reveal inflammatory reactions, the presence or absence of infectious, autoallergic processes, the degree of destruction of articular and periarticular tissues. In identifying tendonitis and capsulitis, the main instrumental diagnostic methods are ultrasound and MRI.
How to treat shoulder pain
Treatment for shoulder pain begins with limiting the load on the affected limb. The patient is allowed movements that he can perform painlessly. Immobilization of the limb (scarf bandage) is carried out in short courses if the severity of the pain syndrome is very great. Prolonged immobilization contributes to the consolidation of hand dysfunction. Today, for partial gentle immobilization, taping is often used - fixing muscles with adhesive tapes in a certain position to prevent injury. This significantly improves the quality of conservative therapy.
After acute pain in the shoulder has been eliminated, treatment is continued by prescribing courses of physical therapy (physical therapy) and massage. At any stage of the disease, conservative therapy includes physiotherapy and reflexology courses. In case of severe pain, this is electrophoresis with novocaine, then warming procedures, mud and baths.
At the same time, drug therapy is prescribed. We remove pain by prescribing drugs from the NSAID group in tablets, injections, ointments (the drug with the best analgesic properties is Ketorol). For very severe shoulder pain, treatment includes narcotic painkillers (Tramadol) and glucocorticosteroids (GCS - Betamethosone). Sometimes folk remedies are also used.
To restore cartilage, chondroprotectors (Dona, Artra, Structum) are prescribed. Drugs in this group also help restore damaged periarticular tissues - tendons and ligaments, since they have the same origin as cartilage cells.
Surgical assistance will be required for some types of fractures, dislocations, ruptures of tendons and ligaments. If joint function is completely lost, if conservative treatment does not help, the destroyed joint must be removed and replaced with an artificial one (endoprosthesis surgery).
To prevent pain from reoccurring, a complex of rehabilitation measures is carried out using exercise therapy, massage, reflexology courses, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
What injections to give for shoulder pain
Injections are prescribed for severe pain that is not relieved by pills and external means:
- Analgin (Baralgin)
- one ampoule contains 1 ml of solution or 500 mg of active substance - a single dose for an adult; may have a toxic effect on hematopoiesis, so use it with caution; - Ketorolac (Ketorol)
– in one ampoule 30 mg of active ingredient – a single dose for an adult; contraindications: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, increased bleeding.
Blockades are widely used - injections of painkiller solutions into the most painful points.
The Moscow Paramita clinic uses the most modern methods of diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of all diseases that cause shoulder pain syndrome.
If necessary, if the disease threatens the patient’s life, after examination by a doctor, he is urgently sent to the hospital. But we treat most pain syndromes on an outpatient basis. Detailed information about treatment can be found on our website.
Injections for shoulder pain
Clinical case
Patient A., 35 years old, came to the emergency department with complaints of nagging pain in the heart area that radiated to the scapula.
This symptom appeared after sharply leaning to the side with dumbbells while working out in the gym. The patient allegedly heard a click. Objectively, he is calm, his skin is of normal color, dry, his pulse and blood pressure are within normal limits. Palpation of paravertebral points in the interscapular region is painful, muscle tension is detected, more on the left, and lateral movements are also limited. A preliminary diagnosis was made: “Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, pain syndrome.” An ECG and CT scan of the thoracic spine were performed. Changes characteristic of osteochondrosis were found. The ECG revealed no pathology.
The patient was prescribed Meloxicam, Amelotex gel, Tizalud, Milgamma, and L-lysine aescinate. Three days later, his condition improved significantly, and he was discharged for outpatient follow-up treatment.
Have you encountered a similar symptom? What were your actions? Let's discuss this in the comments.
Classification
The reasons underlying pain in the area of the shoulder blades on the left side are quite varied. There may be pain;
- aching;
- like a dull pain;
- with increased intensity;
- sharp, when it takes your breath away;
- pulling;
- burning;
- permanent, not passing;
- piercing (lumbago);
- pressing;
- pulsating;
- pointwise.
Important! Often the cause of pain is prolonged stay of the body in an uncomfortable position, as well as muscle strain due to physical activity. They go away on their own and usually do not require medical intervention.
Prolonged pain syndrome, as well as its systematic nature, makes consultation with a specialist a necessity. Acute pain in the area of the left shoulder blade requires urgent medical intervention, because... the factor does not exclude the manifestation of angina pectoris, exacerbation of stomach ulcers, or activation of inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
Pain affecting the lower part of the left shoulder blade from the back is often a consequence of injuries, diseases of the musculoskeletal system and pathologies of the internal organs.