ECG technique: algorithm
Immediately before the scheduled registration of an ECG, the patient should not eat, smoke, drink stimulating drinks (tea, coffee, energy drinks), or exert any physical stress on the body.
We record in the necessary documentation the patient’s personal data, medical history number, date and time of the ECG.
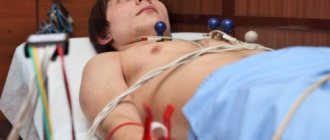
We place the patient on the couch in a supine position. We degrease those areas of the skin where we will apply the electrodes - wipe them with a napkin soaked in an isotonic solution of sodium chloride (0.9%). We apply electrodes: 4 plate electrodes - on the lower thirds of the inner surface of the legs and forearms, and on the chest - chest electrodes equipped with suction cups. For single-channel recording, 1 chest electrode is used, for multi-channel recording, several are used.
We connect wires of a certain color coming from the electrocardiograph to each electrode.
Common markings for electrocardiograph wires:
- red - right hand;
- yellow - left hand;
- green - left leg;
- black - right leg (patient grounding);
- white - chest electrode.
When recording an ECG in 6 chest leads in the presence of a six-channel electrocardiograph, use the following tip markings:
- red - for connection to electrode V1;
- yellow - to V2;
- green to V3;
- brown - to V4;
- black - to V5;
- blue or purple - to V6.
Most often, the ECG is recorded in 12 leads:
- standard (bipolar) leads (I, II, III);
- 3 reinforced unipolar leads;
- 6 chest leads.
Standard (bipolar) ECG leads
Registration of standard limb leads is carried out by connecting electrodes in pairs:
- I standard lead - left hand (+) and right hand (-);
- II standard lead - left leg (+) and right arm (-);
- III standard lead - left leg (+) and left leg (-).
Electrodes are applied to the left arm, right arm and left leg (see markings in the figure). A 4th electrode is placed on the right leg to connect to the ground wire.
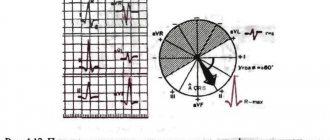
Formation of three standard electrocardiographic leads from the limbs. Below is Einthoven’s triangle, each side of which is the axis of one or another standard lead
Reinforced unipolar limb leads
Unipolar leads are characterized by the presence of only one active - positive - electrode, the negative electrode is indifferent and represents a “combined Golberg electrode”, which is formed when two limbs are connected through additional resistance.
Reinforced unipolar leads have the following designations:
- aVR—right arm abduction;
- aVL - from the left hand;
- aVF - from the left leg.
Formation of three reinforced unipolar limb leads. Below is Einthoven’s triangle and the location of the axes of three reinforced unipolar limb leads.
Chest leads
The chest leads in the ECG are unipolar. The active electrode is connected to the positive pole of the electrocardiograph, and the triple indifferent electrode combined from the limbs is connected to the negative pole of the device. The chest leads are usually designated by the letter V:
- V1 - the active electrode is placed in the IV intercostal space at the right edge of the sternum;
- V2 - in the IV intercostal space at the left edge of the sternum;
- V3 - between the IV and V intercostal spaces along the left parasternal line;
- V4 - in the 5th intercostal space along the left midclavicular line;
- V5 - in the 5th intercostal space along the anterior axillary line;
- V6 - and V intercostal space along the midaxillary line.
Selecting the electrocardiograph gain
When selecting the gain of each channel of the electrocardiograph, it is necessary that a voltage of 1 mV causes a deflection of the galvanometer and recording system of 10 mm. In the “0” position of the lead switch, the gain of the device is adjusted and the calibration millivolt is recorded. If the amplitude of the teeth is too large (1 mV = 5 mm), you can reduce the gain; if it is small (1 mV = 15-20 mm), you can increase it.
ECG registration
An electrocardiogram is recorded while the patient is breathing quietly. First - in standard leads I, II, III, then - in reinforced unipolar leads from the limbs (aVR, aVL, aVF), then - in chest leads V1. V2, V3, V4, V5, V6. At least 4 cardiac cycles should be recorded in each lead.
As can be concluded from the above, with the necessary knowledge and skills, the technique of taking an ECG should not present any difficulties for the nurse.
Basic rules for electrode placement
To record an ECG, you need to install electrodes on special points on the body. This is the only way to correctly record the electrical impulses produced by the heart. It is the correct location of the terminal that ensures a clear recording of the cardiogram. Be sure to lubricate the ECG electrode with alcohol.
If the patient has a lot of body hair, then you need to treat the skin with a soap solution or shave the hair. For better electrical conductivity, you need to lubricate each electrode with gel. If you don’t have the gel at hand, you can take an isotonic solution or gauze pads. But if the study is long, then gauze pads cannot be used.
If stationary ECG devices are used, they must be grounded.
Electrodes are either single-use or reusable. The choice of electrodes depends on the preferences of the healthcare professional performing the ECG.
ecg how to do it correctly
Application
- Determination of frequency (see also pulse) and regularity of heart contractions (for example, extrasystoles (extraordinary contractions), or loss of individual contractions - arrhythmias).
- Indicates acute or chronic myocardial damage (myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia).
- Can be used to identify metabolic disorders of potassium, calcium, magnesium and other electrolytes.
- Detection of intracardiac conduction disorders (various blockades).
- Screening method for coronary heart disease, including stress tests.
- Gives an idea of the physical condition of the heart (left ventricular hypertrophy).
- May provide information about non-cardiac diseases such as pulmonary embolism.
- Allows you to remotely diagnose acute cardiac pathology (myocardial ischemia) using a cardiophone.
- Can be used in studies of cognitive processes, alone or in combination with other methods
How to install electrodes on limbs?
For better memorization, you can use the traffic light rule. Place red on the right hand, yellow on the left hand, green on the left leg and black on the right leg. It is the last electrode that is grounding.
All placement is performed on the proximal part of the limbs. But, be sure to lubricate the place where the terminals are applied with gel. If there is no gel, you can take an isotonic solution or a gauze pad. If one of the limbs is missing, you need to install clamps on the stump. For better contact, you need to secure the terminals with rubber bands.
correct application of electrodes
Carrying out an ECG using Neb
To carry out Neb diagnostics, it is first necessary to correctly position the electrodes. There are three of them in total, painted in different colors. To improve the contact properties between the electrode and the patient’s skin, a special paste with a slightly thick consistency, made from baby soap and plain water, is used. To avoid staining the sheet that is placed under the body of the subject, you need to use oilcloth.
The connection occurs as follows:
- The first to attach is the electrode, which is active and yellow in color. Using a special flat electrode plate, it is installed under the left shoulder blade in its lower corner. Installation in the V7 position is allowed - it was noticed that in this position the result is more accurate. In addition, this method greatly facilitates the diagnosis of bedridden patients.
- The next one is a red electrode, which, unlike yellow, is passive. It is attached using a pear-shaped suction cup. The location of this electrode is the second intercostal space on the right side of the chest.
- The last electrode is painted green and is attached to the body, like the red one, using a suction cup. Unfortunately, it is often the green conductor that is not fixed where it is needed. Its correct location is at the apex of the heart. The correct place can be determined by palpation - apical impulses are felt in the right place. Often the location is determined incorrectly and the electrode is installed in the fifth intercostal space, on the left side of the clavicular line.
After connecting all the electrodes, you can determine the triangle with the heart inside. The ECG procedure occurs by switching a toggle switch to connect various axes in series:
- the first axis is formed from the red and yellow electrodes. This lead is parallel to the back of the heart. This standard position is written with the letter “D” and is considered the most accurate indicator for determining the presence of cardiac pathologies, and more precisely, for myocardial infarction associated with the left ventricle;
- the second position is indicated by the letter "A". The axis, which is formed when the toggle switch is switched for the second time, is located on the side of the front wall of the organ. The data that needs to be taken at this stage does not greatly affect the originally obtained values;
- the third switch remains similar to axes V2 and V3, the only difference is the location of the heart organ in the chest. The results of the third switch are written with the letter “I”, but they also do not greatly affect the data obtained during the first switch.
So, we can draw the following conclusion - the most accurate and important data in diagnostics is obtained when the toggle switch is first switched and the axis with the letter “D” is formed.
The ECG showed distinctive signs, which consisted of the ST line. It can be raised and have a hump-shaped shape, which directly indicates myocardial infarction, or it can be lowered and imply hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart. When analyzing the results, it is also important to pay attention to the shape of the tooth - it can be negative symmetrical and negative asymmetrical.
Preparatory stage
The ECG is performed in a separate room, where satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions are established to ensure complete patient comfort. This room may contain additional structures intended for stress tests or bicycle ergometry.
Patient preparation consists of the following manipulations:
- The person is calmed down and completely relaxed;
- The forearms, shins and upper body are exposed;
- The areas where the electrodes are installed are degreased and moistened with a special gel to improve electrical conductivity;
- The essence of the study is explained to the patient.
Kleten lead
Since 1968, in the practice of cardiological teams of emergency medical services in Yekaterinburg, an additional lead according to Kleten has been used, which, for brevity of recording and ease of pronunciation, is designated in the work of the KSSP by one letter - “ K ” [1]. For recording, the wire from the right hand (red) is installed above the manubrium sterni (manubrium sterni). To do this, you can use a chest electrode (suction cup). Lead switch on the second standard lead – II. This lead resembles aVF, but is 2/3 higher than it. This is explained by the fact that during registration, the right hand is excluded, i.e., a conductor with high resistance, therefore the voltage of this lead is higher.
We (together with O.R. Okulsky) [4] studied the information content of this lead in comparison with others, reflecting changes in the posterior wall of the left ventricle. In all cases where myocardial infarction of the posterior wall was diagnosed, changes pathognomonic of this pathology (ST segment elevation, pathological Q wave) occurred in the lead under discussion. In the case of myocardial infarction of anterior localization, ST segment depression occurred in lead “K”. A total of 130 call cards were analyzed. The analysis data allows us to recommend to emergency doctors in case of extreme lack of time in combination with the patient’s severe condition (severe anginal attack, cardiogenic shock collapse, acute heart failure, recording an ECG in the car, etc.) - instead of recording leads II, III, III a, aVF, K - it is permissible to limit ourselves to recording lead “K”. In this case, it is necessary to justify the reason for the shortened examination in the call card.
Reinforced leads
In standard leads (I, II, III) only large changes are visible, so they came up with enhanced limb leads.
Lead aVL is responsible for the lateral wall. If there are changes in lead I and are duplicated in lead aVL, then these are changes along the anterior wall. If the changes are only in aVL - the side wall.
aVF is responsible for the back wall, the changes will be more reliable.
aVR - gain of lead II. Is negative because The negative pole of the dipole always faces it.
Rice. 2. Reinforced limb leads
Decoding the results
The interpretation is performed by a functional diagnostics doctor. The subject of his consideration is a tape with a cardiogram on which the teeth are depicted. The specialist evaluates the intervals, height and makes a diagnosis about the condition of the heart muscle.
As indicated, lead D is the most informative of the three considered. The presence of ischemic changes is indicated by three main indicators on the cardiogram:
- increased voltage in the QRS complex;
- non-compliance with the norm of the ratio of the amplitudes of the Q and R waves;
- expansion of the Q wave (also fixed in the second switching).
It is impossible to independently determine the condition of the heart using a cardiogram. Wait for a consultation with a specialist from the NEARMEDIC clinic or with your attending physician if you are undergoing examination and treatment in another clinic.
The information value of the method becomes higher when used in addition to recording electrocardiography in 12 leads and other techniques (according to Arrighi, in orthogonal leads). In addition to the ECG, data on the condition of the heart are provided by electrocardiography, color circulation and ultrasound with Dopplerography. In difficult cases, several techniques are used.
Historical reference
The study of biocurrents created by the heart muscle was actively carried out back in the 19th century. At the same time, the first device was created that made it possible to record these impulses and use them to evaluate the work of the heart. Thus, the world's first electrocardiograph was created, thanks to which it is possible to record data on the contraction of the heart muscle and the conduction of an electrical impulse along special paths. Since then, the medical field has continued to improve and every year the accuracy of reading biocurrents when recording an electrocardiogram increases.
Recording an ECG in children and pregnant women
Electrocardiography is performed on pregnant women and even newborn children. There are no contraindications to the study, but certain difficulties will arise with people with serious mental disorders. The difference in recording an ECG in an adult and a child is only in the size of the electrodes, which can also be purchased on the Avicena-med medical consumables resource.
Some nuances arise when taking an ECG in people with dextracardia. In such patients, the heart is on the right side, so the results of the study will be exactly the opposite of normal. If the patient is aware of his peculiarity, he is obliged to warn the medical professional.
Lead registration
When registering standard leads, the location of the electrodes should be as follows:
- First standard lead: right hand (-), left hand (+).
- Second standard lead: right arm (-), left leg (+).
- Third standard lead: left leg (+), left arm (-).
The patient should be at rest. The specialist asks him not to be nervous and not to move. Then the ECG is recorded in leads I, II and III, followed by recording in the enhanced and chest leads. In this case, at least 4 cardiac cycles are recorded in each lead.
How to interpret an ECG?
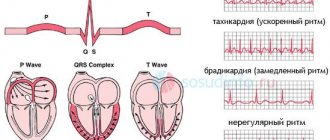
One of the purposes of electrocardiography is to obtain an electrocardiogram, a special graphic image with a broken curve and sharp peaks. The peaks (or spikes) are located above the horizontal line on the graph.
They indicate the depth and frequency of rhythm changes. When deciphering the results of ECG registration, the spaces between these teeth are of great importance. They are designated in the electrocardiogram by letter combinations: “TP”, “QRST”, “TP”.
The recovery phase between muscle contractions is designated “T” on the graph. Atrial excitation and depolarization are indicated by the letter “P”, the recovery cycle of the ventricles is indicated by the letter “U”, and ventricular excitation is indicated by the letters “S”, “Q”, “R”.
Cardiogram of a healthy patient
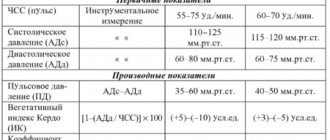
The specialist focuses on the established standards and compares them with the indicators of the obtained cardiogram. If the patient’s health is good, the cardiogram should display the following parameters:
- QT – no more than 450 milliseconds.
- P – positive.
- EOS – not rejected.
- S – negative, below the R wave.
- T – positive.
- Q – negative.
- Heart rate – from 60 to 80.
- QRS is about 120 milliseconds.
Possible deviations
The specialist must determine the distance from one R wave to the other.
- If there are differences in distance between the R waves, this may indicate that the patient has a cardiac arrhythmia.
- Low heart rates may indicate bradycardia.
- If there is no P wave, the pacemaker has changed.
- If the heart rate is rapid, tachycardia is suspected.
- If the number of gastric complexes is above 105, this is a sign of tachycardia.
- But if the number of gastric complexes is below 60, then this is a sign of bradycardia.
Recommendations for patients
Before undergoing an ECG, patients are advised to:
- Remove foods that affect the cardiovascular system from your diet;
- Stop taking certain medications (only with your doctor's approval);
- Avoid strenuous physical activity;
- Do not apply creams or lotions to your arms, legs, or chest.
If there is severe shortness of breath in a patient in a supine position, it is allowed to record an electrocardiogram while sitting. But in this case, the nurse must more carefully monitor the electrode attachments so that they do not slip.