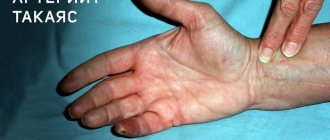
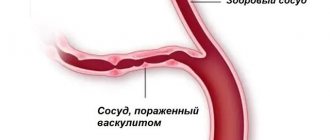
Raynaud's syndrome is a serious condition that is caused by spasm of peripheral blood vessels. Because of it, blood flow in the small vessels of the legs (at the level of the feet) and hands is disrupted. This syndrome is usually one of the symptoms of many other diseases. For example, it occurs in rheumatism, endocrine disorders, psychopathy, etc. Only sometimes it is impossible to determine the underlying disease, so Raynaud's disease may be considered independent.
Most often, this syndrome affects young and mature women, as well as residents of regions with cold climates.
Provoking factors
The underlying causes of Raynaud's syndrome have not been identified, but there are a number of factors that, according to doctors, contribute to its development. These include:
- hereditary tendency;
- permanent injury to fingers and toes;
- endocrine system disorders: diabetes, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, etc.;
- disorders associated with hematopoietic functions;
- constant contact with cold water;
- some diseases of the spine;
- alcohol dependence, drug addiction;
- unstable mental state;
- heavy metal intoxication;
- serious stress;
- constant contact with chemicals;
- certain autoimmune diseases.
The disease in an advanced state can manifest itself even without provoking factors - then they talk about spontaneous attacks of Raynaud's syndrome.
Causes of Raynaud's disease
It is believed that the cause of excessively pronounced vasospasm in response to provoking stimuli is a defect in the central and local mechanisms of regulation of vascular tone. Among these factors, vascular endothelial, intravascular and neurovegetative disorders are important. In secondary SR, structural changes in blood vessels are also a significant factor.
Factors that provoke vasospastic reactions are low ambient temperature and/or emotional stress.
Symptoms, manifestations
Symptoms of Raynaud's disease include:
- whitening of the skin on the fingers;
- feeling of coldness, numbness;
- burning, pain, feeling of fullness;
- swelling, cyanosis;
- formation of ulcers and necrosis (over time);
- nail dystrophy;
- curvature of fingers.
The attacks begin with the skin turning white, then the situation gradually worsens. The attacks themselves become longer, and the damage becomes more obvious. This depends on the stage of Raynaud's syndrome.
Are you experiencing symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Raynaud's syndrome: symptoms and treatment, features of the disease and its prevention
The primary syndrome requires less treatment effort than the secondary one. For patients whose phenomenon is not aggravated by other diseases, doctors recommend completely giving up smoking, avoiding the slightest hypothermia and stress, and regularly moisturizing the skin with special medicinal cosmetics. Secondary Raynaud's syndrome, the treatment of which is carried out as part of the treatment of other pathologies, requires individual and thoughtful therapy. In its absence, the risk of tissue damage and trophic disorders increases: blood flows poorly to them, causing ulcers, necrosis and even gangrene.
Raynaud's syndrome, the treatment of which is prescribed by a doctor, requires accurate diagnosis. It is important to correctly determine the type of phenomenon in a particular patient and select the therapy he needs. The medical clinic is equipped with equipment for conducting research of varying complexity. At your initial appointment, the center’s doctors will explain to you in detail how Raynaud’s syndrome manifests itself. The symptoms and treatment of its two varieties, as you know, differ from each other. Experienced doctors will determine which one is worth talking about in your case. Sign up for a consultation, dispel all your doubts and fears!
Stages
At the angiospastic stage, the patient experiences slight tingling, goosebumps, and chilliness. The skin becomes pale, sensitivity in the fingers is lost, and an aching sensation of pain may appear. After this, hyperemia occurs - that is, the vessels become overfilled with blood, slight swelling and redness appear.
At the angioparalytic stage, exacerbations occur that last longer, cyanosis (blue discoloration) and severe swelling occur. The pain gets worse. Often the patient may experience a fever, cold sweats, and even a feeling of fear and anxiety.
In the third, trophoparalytic stage, the pain becomes less, but if Raynaud's disease is not treated, the consequences for the fingers are much worse. These are the appearance of ulcers, areas of necrosis - the fingers are literally destroyed, and the patient becomes disabled. The condition is serious both from a physical and psychological point of view.
It is the third stage that is truly dangerous, and the first two only lead to it. But treatment and observation by a doctor should begin as early as possible in order to prevent complications.
Amen's test
1) Amen's test to detect occlusion of the branches of the radial artery or ulnar artery distal to the wrist. The patient clenches his fist to force the blood out of the hand. The doctor clamps the ulnar and radial arteries. The patient unclenches his fist, the hand remains pale. The doctor stops compressing the radial artery while continuing to compress the ulnar artery. If the radial artery distal to the site of clamping is patent, the hand quickly turns pink. If the patency of the radial artery is impaired, the hand remains pale. The patency of the distal branches of the ulnar artery is examined in the same way.
Diagnostics
As a rule, diagnosing Raynaud's disease is not particularly difficult for professionals, but a comprehensive examination is still required. After examination, cold tests and history taking, patients are prescribed:
- blood biochemistry;
- hemogram;
- coagulogram;
- general urine analysis;
- immunogram;
- Ultrasound – examination of internal organs;
- spine tomography;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels, as well as some other studies.
An important goal is to rule out other diseases that may cause similar symptoms.
In our clinic we perform:
- Microsurgical bypass of the arteries of the leg and foot
The Innovative Vascular Center has been developing technology for microsurgical operations for obliterating endarteritis for more than 10 years. Given the poor condition of the vascular bed and the lack of target arteries for bypass surgery, these operations are labor-intensive and not as successful as for atherosclerosis. However, our clinic has developed original approaches to include 3rd-4th order arteries into the bloodstream using 25-40x optical magnification and special surgical instruments. Our surgeons manage to restore blood circulation and preserve the leg in 80% of patients with gangrene of the fingers against the background of obliterating endarteritis.
- Transplantation of a feeding flap on a vascular pedicle
In approximately 40% of patients with Buerger's disease, target arteries for bypass grafting cannot be found in the foot. Until 2011, we, like most vascular surgeons in the world, considered such cases hopeless from the point of view of restoring blood flow. However, in 2011, our center began to develop methods of plastic microsurgery to improve blood supply to tissues. The idea is to transplant a complex of tissues onto a vascular pedicle. In a certain area, a section of tissue is taken that receives blood supply through the feeding vessels. This tissue complex is then transplanted onto the lower leg or foot of a patient with endarteritis.
Since this flap receives independent nutrition, it begins to grow into surrounding tissues with poor blood circulation. During the growth of this flap, new vessels grow into the ischemic tissue, improving nutrition. This unique method allows you to restore blood circulation, eliminate the symptoms of critical ischemia and save the leg for most patients with Buerger's disease. In Russia, such operations are performed only at the Innovative Vascular Center. The greater omentum, radial or thoracodorsal flap can be used as a donor tissue complex. The choice of flap for transplantation depends on the degree of damage to surrounding tissues and the shape of the wound defect. It is very important to prepare the wound defect for flap transplantation, which is carried out using modern wound cleansing technologies.
Treatment
Since stress, as the diagnosis of Raynaud’s syndrome shows, is one of the possible factors in the development of the disease, treatment will be aimed both at working directly with the vessels and at improving the overall quality of a person’s life.
To restore physical condition, vasodilators, antispasmodics, glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics and other medications are used. If medication and additional recommendations do not give the desired result, surgery is prescribed. The endoscopic method makes the operation more gentle when it comes to correcting the functioning of blood vessels. But in extreme cases, patients may require amputation of a limb or part of it.
At the same time, as already mentioned, other methods of work are used to treat Raynaud's syndrome:
- psychotherapy. It aims to reduce stress levels, as well as discover the hidden causes of suppressed stress, if any;
- different types of physiotherapy. These are magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin baths, etc.;
- physiotherapy;
- mud treatment;
- a diet focused on healthy eating;
- special massages and much more.
As an aid, after consultation with a doctor, for Raynaud's syndrome, you can use some folk recipes, for example, pine baths.
Treatment, as a rule, is long-term, and therefore requires patience from the patient and strict adherence to all recommendations of the attending physician.
Traditional treatment of endarteritis in Russia
Treatment of obliterating endarteritis of the vessels of the lower extremities (Buerger's disease) is a very difficult task.
This disease primarily affects the small vessels of the extremities, blocking blood circulation at the level of the arteries of the leg and foot. The pathological process consists of inflammation of the vascular wall, the development of connective tissue inside, which leads to narrowing of the lumen and subsequent thrombosis. Insufficiency of arterial circulation leads to the appearance of conditions that contribute to fatigue in the calf muscles, and then there is excruciating pain in the legs, feet and fingers, intermittent claudication, and pain when walking. In advanced stages, formidable symptoms of severe arterial insufficiency develop - trophic ulcers of the skin of the legs and ischemic gangrene of the fingers, constant excruciating pain. All this ultimately leads to amputation at the level of the leg or thigh. Unhappy young people with obliterating endarteritis hope to receive treatment in vascular departments, but despairing of results, they turn to traditional medicine methods, but do not find healing anywhere. Until now, Russian medicine considers obliterating endarteritis of the vessels of the lower extremities to be a disease, the prevention and treatment of which cannot be effective. But the Innovative Vascular Center strongly disagrees with this. We know how to treat obliterating endarteritis!
Prevention
To make the consequences of Raynaud's syndrome less likely to affect you, you should think about prevention, which includes:
- protection of hands and feet in the cold season. It is also necessary to avoid regular contact with cold water;
- rejection of bad habits. Smoking has a particularly strong effect on the functioning of blood vessels;
- careful health monitoring, timely treatment of any diseases;
- a healthy lifestyle, including adequate and balanced nutrition;
- avoiding any injury. This also applies to the correct choice of shoes - they should not be small, they should not rub or injure the foot;
- proper skin care. You should avoid aggressive liquid soap, lubricate your hands and feet with nourishing, moisturizing creams, and also protect your hands when working with household chemicals;
- reduction of stress factors. A calm life without unnecessary worries is also an important component for health.
If a person observes all of the above, and is also treated for all the diseases that have already been detected in him, there is a high chance of not encountering the symptoms of Raynaud's disease.
What is offered for obliterating endarteritis in regular vascular clinics?
- To give up smoking
The disease most often develops in smokers. More than 80% of patients with Buerger's disease smoked for more than 5 years; for those who continued to smoke, amputation was usually performed 3 years after diagnosis. Those who quit smoking in the early stages of the disease have hope - amputation was required in only 15% of cases. One conclusion follows from this: the best treatment for Buerger's disease is to quit smoking!
- Intravenous administration of vascular drugs
Vasaprostan is a prostaglandin drug that can affect blood flow in an ischemic limb. It affects platelet aggregation, some blood clotting factors, and reduces spasm of the vascular wall. However, clinical experience has shown that many hours of infusions of vazaprostan twice a day are not effective enough to relieve pain and do not stop the development of the disease in later stages. According to our data, the use of vazaprostan was effective in only 10% of patients with critical ischemia due to thromboangiitis obliterans. Other proposed drugs include antispasmodics such as no-spa, nicotinic acid, vitamin B12 and B6. At an advanced stage of obliterating endarteritis, such therapy has no clinical effect and is empirical in nature. It is necessary to look for vascular surgeons who can solve the problem of blood flow in Buerger's disease, eliminate its symptoms and pathogenetic treatment.
- Hormonal pulse therapy
Knowledge about the inflammatory nature of vascular damage in endarteritis has made it possible to propose hormonal anti-inflammatory therapy for its treatment. The administration of hormones in high doses in short courses allows for greater suppression of the active autoimmune inflammatory process and promotes clinical improvement and pain reduction. However, in case of critical ischemia, hormonal therapy does not stop the development of gangrene and reduces immunity. In our clinic, pulse therapy is used as preoperative preparation before vascular surgery, in order to relieve the acute inflammatory process. The effectiveness of hormonal therapy is assessed using the CIC (circulating immune complexes) test. This blood test shows the activity of the inflammatory process in the body. With exacerbation of endarteritis, the level of CEC increases sharply. A decrease in the level of CEC after treatment allows us to expect a decrease in changes in the vascular wall and the achievement of complete remission.
- Lumbar sympathectomy
During this operation, the lumbar sympathetic nodes are isolated through an incision or puncture and removed. Sympathectomy causes redness of the affected limbs, an increase in skin temperature occurs, this is what the expanded lumen of the small skin vessels of the legs leads to. The effect on small vessels in the initial stages of the disease contributes to the disappearance of the pain syndrome: small ulcers on the fingers of the lower extremities healed. Capillaroscopy shows an increase in blood flow in the area of the fingernails without pulsation in the arteries. Before the development of microsurgical treatment methods, sympathectomy was the main surgical method for improving blood flow in endarteritis. But the effectiveness of sympathectomy turned out to be small. Only 40% of patients noted real improvement. In our clinic, sympathectomy is sometimes used as an auxiliary treatment technology.
- Angioplasty of the tibial arteries
The development of endovascular surgery technologies gave hope for the possibility of restoring blood flow in Buerger's disease. However, accumulated clinical experience has shown that the arteries of the leg restored after angioplasty very quickly close again. A large number of studies have shown that angioplasty is ineffective for this diagnosis. The attending physician still has hope for the appearance of balloons with a special medicinal coating that reduces inflammation.