Causes
Depending on what caused the development of inflammation, the following types are distinguished:
- Bacterial (infectious). Occurs due to exposure to microorganisms such as coccus, tuberculosis and other bacteria. Possible consequences of late treatment and late treatment: impaired renal function, heart disease, spread of inflammation to nearby organs.
- Immune. The antigen complex deposited in the heart walls provokes the development of the disease. It is this type of inflammatory process that most often develops with rheumatism and chronic connective tissue diseases.
- Traumatic. Develops as a result of injury or malignant neoplasm.
- Reactive. The development of inflammation occurs as a result of myocardial infarction, radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer.
Detection of the disease in the early stages: diagnosis of rheumatism
Timely diagnosis of rheumatism becomes possible by analyzing the main symptoms. In addition, the disease is determined by a blood test: in children, this study reveals a high content of leukocytes and an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and antibodies to streptococci are detected.
Heart rhythm disturbances that accompany its inflammation, caused, in turn, by rheumatism, are detected using an electrocardiogram. In order to timely diagnose and begin treatment of heart valve damage, echocardiography is performed.
Symptoms of inflammation development
Each disease has its own symptoms. The following signs are the reason to seek help from specialists at SANMEDEXPERT clinics:
- Endocarditis. This is the cause of deformation of the valve leaflets and the formation of heart disease within six months or two years. Inflammation can be rheumatic or infectious. In the latter case, the symptoms are more pronounced: profuse sweating, chills, fever, rash, nausea, kidney damage, decreased hemoglobin, muscle pain.
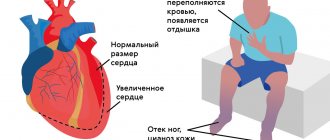
- Myocarditis. The mild form is characterized by shortness of breath and increased heart rate even with minor physical exertion. Heart rhythm disturbances, enlargement of the heart muscle and liver are signs accompanying severe forms.
- Pericarditis. There are dry and exudate forms of inflammation. In the first case, patients complain of dull pain in the cardiac region. In the second, inflammation is manifested by shortness of breath even at rest, heaviness in the area of the heart muscle. In the chronic form, there is an increase in blood pressure, an increase in liver size, swelling of the lower extremities, and ascites.
Inflammatory heart diseases
| Inflammation of the heart | 111 |
| Endocarditis | 1555 |
| Myocarditis | 2130 |
| Pericarditis | 1243 |
The inflammatory process can affect various membranes of the heart. In this regard, they distinguish:
- Endocarditis – damage to the internal connective tissue membrane, endocardium;
- Myocarditis – inflammation of the heart muscle;
- Pericarditis - the outer connective tissue membrane, the pericardium, is inflamed, represented by two layers, external and internal;
- Pancarditis is inflammation of all three linings of the heart.
Why do inflammatory heart diseases occur?
The main reason is the direct effect of viral infection (herpes virus, cytomegalovirus), bacterial (staphylococcus, streptococcus), and in rare cases, fungal in nature. Sometimes the introduction of an infection (mainly streptococcal) triggers the so-called. an autoimmune mechanism in which the heart muscle is damaged by circulating immune complexes consisting of microbial toxins and antibodies to them. The autoimmune pathway is characteristic of cardiac pathology in systemic collagenoses - rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus.
In addition, inflammatory lesions of the heart lead to:
- Allergic reactions;
- Certain medications;
- Chest injuries;
- Conditions after cardiac surgery;
- Severe burns;
- Gout;
- Tuberculosis;
- Chronic renal failure.
- Frequent and recurrent acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, sore throats
How does heart inflammation manifest?
Inflammation of the heart by :
- Increase in heart size. The heart expands in all directions - the so-called. bull's heart.
- A decrease in myocardial contractility - mainly with myocarditis.
- Formation of valve defects in the form of valvular insufficiency or stenosis. More often observed with endocarditis.
- Accumulation of liquid effusion in the cavity between the pericardial layers.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
The severity of all these manifestations is not the same in each individual clinical case. But together they mutually burden each other and lead to heart failure.
In addition to general weakness and dizziness, it is accompanied by pale skin and shortness of breath. Sometimes the temperature rises to subfebrile levels. In advanced stages of heart failure, swelling appears in the legs, the liver enlarges, and free fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory heart diseases in the clinic at Barclay LLC MED-City
During diagnosis, a wide range of studies is used: ECG, ultrasound of the heart, Holter monitoring, immunological tests. Treatment is aimed at eliminating not only the cause, but also the consequences of heart inflammation - heart failure.
If you experience discomfort in the heart area, be sure to consult a specialist. You can make an appointment right now by calling + 7-495-979-99-82; +7-495-978-78-67
Diagnosis and treatment
Due to the fact that inflammatory heart diseases are one of the causes of the development of heart disease, after the first symptoms appear, you should immediately contact experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic.
Diagnostic methods used:
- Laboratory research
- Electrocardiography
- Echocardiography
- X-ray
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is admitted to the hospital. The intensity and course of treatment depend on the severity of the inflammatory process:
- In mild cases, a ward regimen, a special diet with a limited amount of salt and water, and medication are indicated.
- The average form requires strict bed rest and dietary rules.
- In especially severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
The duration of treatment depends on many factors, the main one of which is the timeliness of treatment. Be attentive to your health!
Symptoms of pericarditis
The onset of pericarditis, symptoms and first signs are quite characteristic. The main reason to see a doctor is chest pain. The pain syndrome in this disease can be quite pronounced and persistent. But there are times when fever comes first in severity. Its combination with shortness of breath and chest pain is often mistaken for pneumonia.
The pain syndrome in this cardiac pathology can radiate, as with angina pectoris, to the left arm and shoulder blade. But the hallmark of pain with pericarditis is the lack of connection with physical activity. The pain is almost constant and intensifies when changing body position or taking a deep breath.
In addition to pain, pericarditis is always accompanied by additional symptoms: general weakness, increased body temperature, shortness of breath with little physical exertion, interruptions in heart function, and decreased blood pressure. Unlike angina, nitrate-based medications do not provide relief.
If you notice similar symptoms in yourself or your loved ones, you need to urgently consult a doctor, because the price of delay can be human life. Only a professional cardiologist, having examined the patient and prescribed an immediate instrumental examination, will be able to accurately diagnose and recommend adequate treatment.
Otherwise, if medications are not prescribed in a timely manner, a terrible complication inevitably arises - cardiac tamponade. With tamponade, a large amount of exudate accumulates in the pericardial cavity. The consequence is that the heart muscle is literally compressed and cannot fully contract.
The result of such compression is acute cardiovascular failure, cardiac arrest and death of the patient. In this case, the usual methods of resuscitation rarely have a positive effect, and only the release of the pericardium from the excess amount of exudative fluid can make the heart beat again.
Prevention
There are two types of preventive measures:
- Primary. It is aimed at comprehensively strengthening the immune system by maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, hardening procedures and timely treatment of foci of infection (caries, sinusitis, and so on).
- Secondary. After completing the course of treatment and discharge, the patient is registered with a dispensary for constant monitoring and prevention of relapses. A change in work regime is necessary, since a person needs to work in a comfortable environment with a minimum amount of physical activity.
Effective treatment of rheumatism
Effective treatment of rheumatism should be aimed not only at suppressing streptococcal infection, but also at preventing relapse and suppressing inflammation, especially in the heart and joints. You need to know that getting rid of this serious disease must necessarily be accompanied by limiting the patient’s physical activity, which negatively affects the condition of tissues damaged by inflammation. In order to recover, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest.
If streptococcal tonsillitis is detected, the patient is prescribed internal penicillin, which is prescribed for ten days. Residual infection in a sick child is eliminated by injections of penicillin. To eliminate pain and inflammation, non-steroidal drugs, including aspirin, are prescribed.
A child who suffered from rheumatism in childhood should receive penicillin internally or intramuscularly until the age of eighteen. This is necessary in order to prevent relapse of the disease. If a person has suffered heart damage during the course of his illness, then throughout his life the patient must take an antibiotic before any operation (even tooth extraction).
Diet and cardiovascular disease
Making small changes to your diet is one of the easiest and most effective ways to reduce your risk of heart disease. You can do it like this:
- Reducing fat in your diet, especially saturated fat and trans fat
- More fruits and vegetables, whole grains and soluble fiber
- Drinking alcohol in moderation
- Reducing salt to maintain lower blood pressure
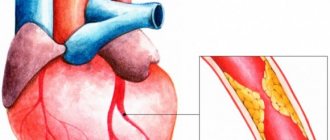
Cholesterol and cardiovascular disease
Because there is a proven direct link between high blood cholesterol and your risk of heart disease, reducing the amount of fat in your diet, especially saturated fat, can help lower your blood cholesterol. According to the official recommendations of the European Society of Atherosclerosis, “normal” levels of fatty fractions in the blood are: 1. Total cholesterol - less than 5.2 mmol/l. 2. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) - less than 3-3.5 mmol/l. 3. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) - more than 1.0 mmol/l. 4. Triglycerides - less than 2.0 mmol/l. People with average energy expenditure should consume no more than 70g of fat per day and less than 20g of saturated fat.
Risk factors for cardiovascular disease
Some risk factors for cardiovascular disease are potentially reversible or can be changed. They include:
- Smoking cigarettes
- Elevated LDL (low density) cholesterol levels
- High triglyceride levels in the blood
- Low HDL (high density) cholesterol
- Overweight
- Large waist circumference (“apple shape”)
- High blood pressure
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Diabetes
4.Treatment
Therapy for inflammation of the heart muscle, as well as symptoms, depends on the causes, pace, severity of the pathological process, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases (especially infectious foci that require immediate treatment) and the general somatic condition of the patient. Treatment is etiopathogenetic in nature, i.e. is aimed at eliminating the immediate causes - if and to the extent possible.
Thus, for infectious lesions, antibiotic, immunostimulating, and restorative treatment is prescribed; in the presence of an allergic component, antihistamines and desensitizing drugs are prescribed. According to indications, antiarrhythmic therapy is prescribed, measures are taken to relieve symptoms of acute heart failure, prevent and/or treat complications. If necessary, specialists from related fields (infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, allergist, etc.) are involved in the diagnostic and treatment process.
Accordingly, the prognosis is also purely individual; In this regard, the timeliness of seeking specialized help is important. Today, the possibilities for its effective provision are very wide, and in many cases, inflammation can be eliminated completely, without any consequences or significant complications, however, in more severe situations, the outcome may be disability or even death of the patient.
Therefore, at the slightest symptoms of cardiac dysfunction, especially those progressing against the background (or after) of an acute viral or bacterial infection, it is necessary to be examined by a cardiologist.
2. Reasons
There are several main factors that can cause inflammation of cardiac structures:
- infections, and the pathogenic agent can be both bacteria and viruses. Infectious and inflammatory processes of the heart are extremely dangerous (even fatal) due to their complications: the formation of acquired heart disease, the development of severe renal failure, etc.;
- metabolic disorders (metabolic disorders);
- toxic damage;
- combined infectious and allergic reactions;
- systemic autoimmune diseases;
- injuries;
- oncopathology.
The last two factors in the vast majority of cases lead to pericarditis.
As for toxic or infectious-allergic inflammation, a particular (and quite common) case is bacterial invasions - waste products of pathogenic microorganisms can cause both intoxication and an acute allergic reaction from the muscle tissue of the heart.
Visit our Cardiology page