Diabetic foot is a broad concept that refers to the destruction of the skin, bones and nerves in the feet that develops in patients with diabetes and can lead to the death of the limb.
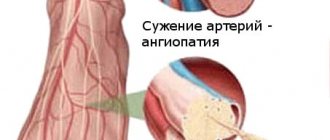
The main cause of diabetic foot syndrome (DFS) is damage to blood vessels by atherosclerotic plaques and mediocalcinosis (hardening of the vessel walls), characteristic of diabetes mellitus. Blood flow is disrupted, ulcers and gangrene develop, and wounds may not heal at all.
In addition, diabetics develop peripheral nerve damage (neuropathy), which reduces the sensitivity of the skin of the legs and the secretion of sweat. Patients with neuropathy do not feel pain from minor injuries and may not notice them until the wounds turn into trophic ulcers.
A dangerous factor for complications in diabetes is severe immunodeficiency. It promotes the unlimited spread of infection through soft tissues and the development of general blood infection - sepsis.
Only a comprehensive impact on all factors of the syndrome can successfully prevent amputation and death of these patients.
How does diabetic foot develop?
Diabetes mellitus leads to the destruction of peripheral nerve fibers and a decrease in the sensitivity of the limbs. The patient may not notice the injury, burn, or frostbite in time. Damage does not heal for a long time and becomes a source of development of bacterial infections: staphylococci, streptococci, anaerobic microbes.
The pathogenesis of DFS involves damage to blood vessels and reduced blood flow to the extremities. Insufficient blood circulation makes it difficult for wounds to heal and fight infections. This leads to the fact that injuries, calluses, cracks and fungal diseases can cause ulcers and gangrene of the foot. If life is threatened, amputation is possible.
The disease occurs in 8-10% of patients with diabetes. In type 1 disorder, it manifests itself 7-9 years after the onset of the disease. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, it occurs from the onset of the disease.
How to improve blood circulation in the legs?
To prevent diabetic foot complications, it is important to maintain good blood circulation in the extremities.
To do this, do leg exercises daily and maintain general physical activity:
- wiggle your toes throughout the day;
- make movements in the ankle joints, pull the toe away from you and towards you, rotate clockwise and counterclockwise;
- Walk more, swim, ride a bike, if there are no contraindications.
If you have a sedentary job, try to get up and walk around a little every hour. While you are sitting, keep your legs in a position that does not impede blood circulation. To do this, space them out slightly. At the same time, your feet should be completely on the floor, wiggle your toes. If possible, elevate your legs, for example by placing them on a stool. Never sit cross-legged for long periods of time. This way you compress the vessels and further reduce blood flow to the feet.
Smoking poses a major threat to your feet. If you suffer from this bad habit, be sure to quit. If you can’t quit on your own, seek professional help from a psychologist. Smoking has a bad effect on the entire cardiovascular system, reduces blood flow to the legs, and contributes to clogged arteries. Accelerates damage to small blood vessels in the feet and legs. Statistically, many people with diabetes who need amputation are smokers.
Diabetic foot forms
The syndrome has different pathogenesis and causes of development. According to the classification proposed by the Diabetic Foot Consensus in 2011, there are 3 forms of pathology:
- neuropathic - 60-75% of cases;
- ischemic - 5-10%;
- neuroischemic - 20-30%.
Neuropathic diabetic foot
caused by a disorder of the nervous system of the limb. Signs of the disease: deformation of the leg bones, fractures, loss of sensitivity, cracks, calluses and ulcers with swollen edges. Develops in areas subject to the greatest load. If you have problems in the field of neurology, you will need to consult a specialized specialist - a neurologist.
Cause of ischemic form
is vascular damage. With this pathology, fatigue increases, lameness, swelling and pain appear when walking. Calluses appear on the lateral surfaces of the foot, heels, and ankles, and then purulent ulcers covered with a dark scab.
In mixed form
Both nervous and vascular disorders are present. The pathology is typical for patients who have been ill for 10 years or older.
Types of disease
Depending on whether the nerves or blood vessels are affected, the following classification of diabetic foot is accepted in medicine:
- Neuropathic. With this type, nerve endings are damaged (polyneuropathy), their sensitivity decreases, and the pain and temperature threshold decreases;
- Ischemic. With this type, vascular damage occurs. Due to the thickening of the walls, the clearance decreases, blood supply and nutrition to the legs decrease. In diabetes, macroangiopathy and microangiopathy develop. With macroangiopathy, large vessels are affected, and the progression of atherosclerosis in the vessels of the heart and lower extremities is accelerated. With microangiopathy, capillaries are damaged;
- Neuroischemic, simultaneous damage to nerves and blood vessels. This type manifests itself as a combination of the previous two.
In practice, neuropathic (66% of cases) and neuroischemic forms are more common.
Causes of diabetic foot, who is at risk
Damage to limb tissue is caused by metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus. Factors that increase the risk of developing the syndrome:
- chronic high blood sugar;
- alcoholism, smoking;
- kidney diseases;
- foot deformities;
- excess weight;
- uncomfortable shoes;
- hyperkeratosis;
- blockage and narrowing of the main arteries;
- decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities;
- history of ulcers and amputations.
40-50% of diabetics are at risk; the disease is more common among women.
Diabetic foot symptoms
Signs of pathology may vary among patients. Symptoms that require you to see a doctor:
- loss of sensation in the foot;
- numbness or tingling;
- blisters, ulcers, calluses;
- swelling;
- hair loss on the lower extremities;
- fast fatiguability;
- lameness;
- dry skin;
- change in skin color, redness;
- chills;
- poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
If alarming symptoms appear, you need to make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor will conduct a preliminary examination and refer you to specialists. The causes of diabetic foot are treated by an endocrinologist. Timely treatment will save the patient from complications.
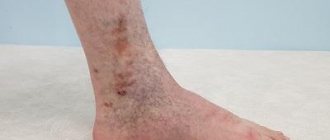
What does a diabetic foot look like, signs
All patients diagnosed with diabetes require a daily foot examination to detect the disease at an early stage. According to Wagner's classification, diabetic foot syndrome is divided into 6 stages:
- Changes in bone structure.
- The appearance of ulcers on the skin.
- Destruction of soft tissues.
- Inflammation of bone tissue.
- Gangrene of fingers.
- Gangrene of the foot and leg.
Patients with DFS complain of long-term non-healing wounds of the lower extremities. As can be seen in the photographs of patients, ulcers appear on the skin that spread deep and along the perimeter of the foot. A bacterial and fungal infection is added. The wounds involve tendons and joints. In the final stages, bones and joints are involved and tissue death occurs.
Basic rules for foot care
Diabetic feet need to be cared for daily, following simple rules of prevention:
- careful hygiene, including the interdigital space;
- treatment of keratinized areas with pumice;
- moisturizing dry skin with cream;
- Regularly changing socks. Socks and stockings must be made of natural fabric and selected exactly in size so that folds and gathers do not form and the tissues of the foot and lower leg are not compressed;
- wearing loose, comfortable shoes.
In addition, it is important to carefully trim your nails in a straight line, not to use medicinal products without a doctor’s prescription, to do daily exercises to improve blood flow, and to undergo regular medical examinations.
What not to do:
- walk barefoot even after all ulcers and other injuries have healed;
- be exposed to hypothermia;
- warm your feet by rubbing, steaming and using a heating pad;
- cover the damage with a band-aid without consulting a doctor. You should only use special dressings prescribed by your doctor.
Medical examination
Patients with diabetes mellitus and signs of DFS can be examined by an endocrinologist in Sergiev Posad at the Paracelsus clinic.
The center is equipped with expert-class ultrasound equipment. Our own laboratory quickly produces accurate results on the day of testing.
Reception is conducted by highly qualified endocrinologists with 11 years of experience in the specialty. In the department of endocrinology, appointments are conducted by a doctor of medical sciences with 37 years of experience in the specialty.
Patients at high risk of developing diabetic foot should be observed not only by an endocrinologist, but also by a vascular surgeon and orthopedic traumatologist. It is important to conduct self-examination for diagnosis, the purpose of which is to early detect signs of diabetic foot: changes in skin color, dryness, swelling and pain, crooked toes, fungal infections.
At the Paracelsus clinic, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, based on the results of which the doctor will select treatment. In the clinic, you can examine arteries and veins, identify vascular damage at an early stage and determine the state of blood flow.
Competent treatment from our doctors will prevent the development of complications. The doctor will help you adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Flow
When the development of diabetic foot begins, diet and control of sugar levels, proper foot care, periodic examination of the feet and timely monitoring by a doctor are extremely important. In this case, complications rarely develop. In European countries where podiatry services are developed, the development of diabetic gangrene is very rare. The number of amputations due to diabetes in Europe has decreased tenfold, but in Russia diabetic gangrene is the main cause of high amputation rates.
Treatment of diabetic foot
Treatment of DFS consists of basic and additional measures.
The main ones include:
- normalization of glucose, lipid, blood pressure levels;
- elimination of the causes of the disease - treatment of blood vessels and nerve fibers;
Additional methods:
- antibacterial therapy;
- offloading to relieve pressure on painful areas of the foot.
- anesthesia;
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; self-administration of medications can be dangerous.
Surgical treatment of diabetic foot
In 80% of cases of patients with diabetic foot syndrome, surgical treatment is required.
The indications are:
- chills, fever;
- the presence of rapidly progressing infection, foot necrosis or gangrene;
- need for emergency surgery.
The surgeon chooses surgical tactics based on the clinical picture and form of infection.
Vascular surgery helps normalize blood flow, preserve a limb, and stop tissue necrosis. For the ischemic form of diabetic foot, endovascular dilatation and stenting of peripheral arteries, thromboembolectomy, popliteal foot bypass, arterialization of the veins of the foot, etc. are used.
Treatment of foot ulcers can be performed surgically to remove necrotic areas, which prevents further bacterial growth and infection.
Physiotherapy for diabetic foot
Physiotherapy is often used at the rehabilitation stage.
Modern methods:
- magnetic therapy - stimulates the immune system, provides tissues with nutrition, anesthetizes and strengthens blood vessels;
- phonophoresis - activates tissue restoration, relieves inflammation, eliminates pain;
- amplipulse therapy - improves blood circulation, nutrition and tissue regeneration;
- phototherapy - promotes healing of wounds and ulcers;
- UHF increases blood flow, has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and trophic effect.
Treatment of diabetic foot syndrome involves diet, foot skin care and therapeutic exercises.
Folk remedies for diabetic foot
At home, DFS can be treated only in the early stages, treating wounds and ulcers without infection. When treating SDS with traditional methods, it is important to remember that these remedies do not replace a visit to the doctor, a course of medications, and, if necessary, surgery.
Alternative medicine methods are possible only as an addition to the main therapy and after agreement with the attending physician. The use of unconventional methods without visiting a doctor in severe stages is unacceptable - it threatens the life and health of the patient.
Alternative Treatments for Diabetic Foot
Alternative treatment tactics - leeches, homeopathy, dietary supplements, either do not have official scientific evidence or are not effective enough. You should not experiment, as this may have negative consequences: amputation of a limb or death.
How to Avoid Diabetic Foot Surgery
Timely diagnosis and prevention of complications of diabetes mellitus have reduced the number of amputations by almost 50% over the past 10 years. The patient needs regular medical examination, monitoring of sugar levels and treatment prescribed by an endocrinologist.
Nutrition for diabetic foot
Diet is an important component of the treatment of DFS. Principles of nutrition for diabetes:
- exclude fast carbohydrates and foods with a high glycemic index;
- do not eat fatty foods and processed foods;
- divide food into small parts, eat at least 5 times a day;
- count grain units;
- eat more vegetables.
You should select a diet individually, taking into account medications, under the guidance of a doctor.
Shoes for diabetic feet
Wearing orthopedic shoes will reduce the risk of injury, calluses, and foot deformities. The special sole has shock-absorbing and anti-slip properties, reducing the likelihood of falls. Shoes for diabetics contain a minimum of seams and are equipped with comfortable fasteners. All materials are elastic and will protect against the appearance of calluses. When choosing, take into account:
- possibility of installing orthopedic insoles;
- the presence of adjustable clasp;
- ease of dressing;
- the heel is small, with a beveled front edge, or a solid low platform;
- hard, wide, stable sole;
- Elastic and breathable upper.
Shoes are selected by an orthopedic traumatologist. When purchasing, fitting is important, so it is better not to order shoes from online stores.
Foot Care - How to Treat Diabetic Foot Wounds
If you have diabetes, it is important to follow the basic rules: wash your feet every day with warm water, pat dry with a soft towel, apply moisturizer and always wear comfortable shoes and socks. Trimming manicure is not acceptable, only careful filing. The patient needs a daily foot examination; if poor vision or excess weight makes this difficult to do, then you should ask family members or a medical professional about it.
When a wound appears you will need:
- disinfection with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine;
- spend the next day at rest;
- Consult a doctor if the damage has not healed within 3 days.
For treatment, do not use iodine, brilliant green, or alcohol: these products dry the skin and interfere with healing.
Therapeutic exercises for diabetic feet
Physical activity for diabetes improves the condition of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, helps maintain normal body weight and reduces glycemic levels.
Special exercises for the legs will restore blood flow to the feet and strengthen muscles and joints.
Recommendations before exercise:
- consult a doctor before training;
- do not inject insulin immediately before training;
- 10-15 minutes before class, increase your blood sugar level by eating a fruit (for example, an apple);
- the indicator should not exceed 15 mmol/l;
- blood pressure - no more than 140/90, pulse before training - up to 80 beats, during - up to 140.
An example of one of the exercises:
- Lie on the mat and raise your legs vertically up. Bend your knees and perform movements in a circle left and right 15 times.
- Without getting up from the mat, raise your legs and try to close your feet. Place your feet on the floor. Repeat 15 times.
- Lie on the floor, raise your legs and straighten them as much as possible. Hold this for 1-3 minutes. Then sit on the bed so that your legs hang down.
Therapeutic exercises should be performed 3-4 times a week.
Lifestyle with diabetic foot
People at risk should give up smoking and alcohol, follow a diet, lead an active lifestyle, and treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner. Patients should undergo regular medical examinations and adhere to the recommendations of the endocrinologist.
Features of hygienic care
Patients with diabetes should pay increased attention to the quality of hygienic care and avoid increased physical activity. Sports should be as safe as possible, without the risk of injury and muscle strain.
It is recommended to comply with the following rules and restrictions:
- give up uncomfortable shoes that compress the limbs, cause circulatory problems, and increase signs of ischemia;
- make sure that shoes do not rub the skin, since any damage due to diabetes can lead to infectious complications, the development of sepsis and the appearance of gangrene;
- if it is necessary to cut off rough areas on the feet or remove calluses, it is better to contact a cosmetologist who carries out such procedures in compliance with all infection safety rules;
- nails are cut without injury, without removing the nail plates in the corners;
- refuse trimmed manicures, especially those done at home;
- You should not walk barefoot at home or on the street, as this leads to injuries and increases the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory processes;
- if you play sports, regularly walk long distances, choose the most comfortable shoes made from natural materials that allow air flow;
- Wrap your feet with warm water and soap several times a day, without using rough abrasives or hard washcloths;
- Avoid taking excessively hot baths, do not use alcohol compresses or perform other aggressive procedures that can cause redness and damage to the skin.
If even minor injuries occur in the leg area, high-quality antiseptic treatment is carried out. Most often, doctors prescribe antibacterial ointments and agents that prevent the development of an infectious process. For dry skin, use moisturizing creams or special medicinal cosmetics designed to care for the skin of patients with diabetes.
With severe necrosis and the development of gangrene, the leg is amputated, since even modern vascular operations cannot give the desired effect. The extent of surgical intervention depends on the degree of skin damage. The toes die first. If they are removed in time, the limb can be preserved with all its functions. It is important to monitor the patient’s condition after such surgery to prevent relapse of the disease and further spread of gangrene to the preserved tissue.
Complications of diabetic foot
Against the background of weak sensitivity, pain from injuries is not felt. Even an ulcer under a dry scab on the plantar surface of the foot can go unnoticed for a long time. The bottom of the ulcer can be bones and tendons.
Wound defects in diabetic foot do not respond well to conservative therapy and require long-term local and systemic treatment. With the development of a foot ulcer, amputation is required in 10-24% of patients, which is accompanied by disability and increased mortality from developing complications. The problem of diabetic foot dictates the need to improve the level of diagnosis, treatment and medical examination of patients with diabetes.
Effect of diabetes on feet
If blood glucose levels are consistently high for 5-10 years, metabolism is disrupted. This leads to the formation of trophic changes in the bones, skin, muscles, blood vessels, and tendons. The legs suffer first - diabetes is often accompanied by excess weight and varicose veins.
Also, patients with diabetes have reduced immunity, as a result of which wounds, scratches, and ulcers take months to heal. The pathology is accompanied by a violation of the nerve conduction of the skin, as a result of which a person simply does not feel damage to the skin. All this leads to the development of diabetic foot. Untimely treatment can lead to serious complications, leading to serious consequences: from amputation to death.
Treatment by an endocrinologist at the Paracelsus clinic, Sergiev Posad
At the Paracelsus Medical Center, patients are treated by endocrinologists with at least 11 years of experience.
You can be examined and treated by a doctor of medical sciences with 37 years of experience in endocrinology.
We invite you to our medical center for diagnosis and treatment if alarming symptoms of diabetic foot syndrome appear.
Diagnosis of diabetic foot
The process of making a diagnosis begins with a conversation with a doctor, collecting complaints, and medical history data. Then inspect the changes. At the initial consultation stage, the doctor will determine the need for consultation with other specialists - orthopedic traumatologist, vascular surgeon, neurologist, surgeon.
In medicine, an integrated approach is used to treat complex diseases. The patient will be able to get advice from all the necessary specialists in our center.
Diagnosis is carried out using laboratory and instrumental methods. The laboratory diagnostic plan includes:
- clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- analysis of the amount of hormones;
Instrumental diagnostics at the Paracelsus clinic are carried out using expert-class equipment. An ultrasound examination will be performed to assess the condition of blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the specialist conducts an examination and prescribes a comprehensive examination. Diagnosis can be carried out not only by an endocrinologist, but also by a podologist, as well as a vascular surgeon and orthopedist. In our clinic, you will be referred to the right specialist so that the doctor can conduct a high-quality and comprehensive examination. The clinic is equipped with high-quality equipment for laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
It is extremely important to assess the patient’s general health in order to make a definite prognosis for recovery and identify concomitant disorders and diseases that require additional correction. The doctor also determines further measures aimed at correcting the disorder and preventing adverse health consequences.
Examination of patients includes the following procedures and techniques:
- collecting anamnesis, careful examination of the skin, identifying characteristic changes, signs of swelling and increased pain, curvature of joints;
- determination of the ankle-brachial index, reflex activity;
- assessment of tactile, temperature, vibration sensitivity;
- Doppler ultrasound of leg vessels;
- angiography with contrast, CT arteriography;
- radiography.
Specialists also study the results of laboratory procedures and pay increased attention to blood glucose levels, cholesterol levels, determination of ketone bodies and sugar levels in urine.