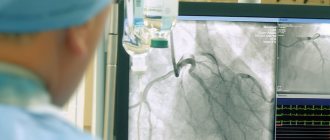
Coronary angiography is the “gold standard” for diagnosing coronary heart disease. This procedure is performed to determine the extent of damage to the coronary arteries of the heart using high-quality contrast.
Coronary angiography is performed under local anesthesia (the catheter insertion site in the area of the femoral fold is numbed). The essence of the method is that a thin probe is inserted through the femoral artery, which is accessed in the area of the femoral fold, through which a catheter is inserted. The entire procedure is carried out under X-ray control. When the catheter reaches the desired level, a radiopaque substance is injected into the bloodstream and a series of x-rays are taken, which will subsequently give a complete picture of the condition of the patient’s blood vessels.
At the NT-Medicine clinic, coronary angiography is performed in a modern cath lab using the innovative third-generation angiographic system Veradius Unity (Philips), which allows obtaining high-definition images at a frequency of 30 frames per second.
Indications for coronary angiography
- examination of men aged 45–65 years and women aged 55–75 years without established cardiovascular diseases;
- an established diagnosis of coronary artery disease to clarify the degree of risk of heart attack and prognosis of the course of the disease;
- diabetes mellitus in men 45–65 years old and women 55–75 years old without established cardiovascular diseases;
- lipid metabolism disorders in patients with an established diagnosis of coronary artery disease, as an additional diagnostic test to decide on the initiation or change of drug therapy;
- chest pain of unknown etiology, episodes of arrhythmia;
- assessment of the condition of coronary stents, aortic and mammary coronary bypass grafts.
- anomalies of the development of the coronary arteries.
- ambiguous load test results.
What is coronary angiography?
Coronary angiography is a modern invasive method of checking the vessels that carry oxygen to the heart muscle. This method is radiological. Thanks to it, after introducing a contrast agent into the vessels, various pathologies of the heart and blood vessels feeding the organ can be detected.
Coronary angiography is a method widely used in therapy, cardiology and cardiac surgery in modern times. Thanks to this method, doctors are able to not only detect defects in the functioning of the organ in a timely manner, but also eliminate them in a timely manner by performing an operation in real time. By injecting a contrast agent into the vessels, doctors can fully assess the patient's blood flow and accurately localize blockage or reduction in the lumen of the coronary artery.
Coronary angiography is a modern method that provides specialists with a large amount of information about the patient’s health. This is an invasive method, so it is carried out in a special operating room prepared for the procedure and having all the necessary equipment.
Indications for use
Everyone knows that diagnostic measures, like treatment, should be prescribed only to people who need it. Therefore, for their implementation there is a list of indications and contraindications, which allows us to determine the main group of patients allowed for the study.
Today, the main indications for coronary vascular examination are:
- Acute pathologies of the heart muscle;
- Suspicion of blockage and damage to the coronary veins and arteries;
- Stenosis of arteries by plaques;
- Myocardial infarction in the acute stage, as well as suspicion of its presence;
- Coronary heart disease in the chronic stage and suspected disease;
- Angina pectoris of all types and stages;
- The appearance of atypical pain behind the sternum;
- Congestive heart failure;
- Presence and suspicion of infectious and inflammatory processes in the heart - endocarditis, myocarditis;
- Recent chest injuries.
In addition, coronary angiography is also performed on completely healthy people to diagnose the condition of the heart and blood vessels. This procedure is used for early diagnosis of diseases in persons exposed to dangerous and harmful production, heavy physical labor, and also living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Indications for diagnosing the heart and blood vessels using this method include preventive examinations immediately before surgery of any complexity, to determine the possibility of surgery at a given time.
How to prepare for coronary angiography?
A prerequisite for the procedure is a preliminary consultation with a cardiologist, whose task is to determine the presence of indications or contraindications for this type of study, the need to prescribe additional diagnostic methods, prescribe corrective therapy, etc.
- The day before the test, exclude foods that provoke fermentation from the diet (juices, fresh fruits and vegetables, rye bread), and refrain from overeating. You can drink non-carbonated water in unlimited quantities, at least 1.5 liters.
- Before the study, it is necessary to warn the doctor about any chronic diseases and possible reactions to medications, allergies to iodine preparations and local anesthetics.
- On the day of the study, breakfast is excluded, but you can continue to take medications prescribed by your doctor.
- After the procedure, you need to drink plenty of fluids, at least 2 liters of water, for 6-8 hours.
How is coronary balloon angioplasty and coronary stenting performed?
Special miniature instruments can be passed through the catheter into the vessels of the heart. A special catheter balloon, which is very thin when folded, is brought to the site of narrowing and straightened out, thereby expanding the section of the artery. This is how angioplasty is performed. After this, the balloon is deflated and removed from the artery. To ensure the restoration of the blood vessel, control angiography is performed. Then, in most cases, coronary stenting is performed - a stent is additionally installed at the site of narrowing of the artery, which from the inside supports the vessel in a straightened state. The stent remains in the artery forever.
Coronary angiography is the gold standard in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease
Coronary angiography is a radiopaque research method that evaluates the condition of the arteries of the heart. Coronary angiography is the most accurate and reliable way to diagnose coronary heart disease, which allows you to decide on the patient’s treatment tactics in each specific situation, for example, the possibility of continuing treatment with medications, the need for such treatment procedures as angioplasty and stenting or coronary artery bypass grafting. This procedure is invasive, which involves the introduction of a special catheter in an operating room and can be performed both for diagnostic purposes and to monitor the condition of blood vessels after operations already performed.
Coronary angiography is a radiopaque research method, which is the most accurate and reliable way to diagnose coronary artery disease, allowing you to accurately determine the nature, location and degree of narrowing of the coronary artery. This method is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and allows us to decide on the choice and scope of further treatment procedures such as balloon angioplasty and coronary bypass surgery.
Objectives of coronary angiography:
- determine the location and anatomical structure of the coronary arteries;
- identify the presence and degree of stenosis of the artery lumen;
- determine the exact location of the lesion and extent;
- determine the diameter of the artery lumen (unchanged and at the site of stenosis);
- establish the presence and severity of collateral vessels.
Indications for coronary angiography
- high risk of complications according to clinical and non-invasive examination, including asymptomatic IB;
- ineffectiveness of drug treatment for angina pectoris;
- unstable angina pectoris, not amenable to drug treatment, occurring in a patient with a history of myocardial infarction, accompanied by left ventricular dysfunction, arterial hypotension or pulmonary edema;
- post-infarction angina;
- inability to determine the risk of complications using non-invasive methods;
- upcoming open heart surgery (for example, valve replacement, correction of congenital heart defects, etc.) in a patient over 35 years of age.
Stages of coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is performed both routinely and urgently. Indications for coronary angiography are determined by your attending physician, who will prescribe the necessary tests and studies necessary to perform the procedure.
At the first stage , patients are selected for a diagnostic procedure, and the necessary additional examinations are carried out.
Indications for coronary angiography:
- identified or suspected ischemic heart disease;
- pain in the chest, suspicious for angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- planned surgery for heart defects;
- heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias.
Indications for coronary angiography are determined by the attending physician in accordance with accepted criteria. In preparing the patient for coronary angiography, the necessary tests and studies are performed. In addition to these, additional studies may be prescribed. The second stage of outpatient CAG angiography procedure itself . The patient is admitted to the day hospital ward. After assessing the stability of his condition, premedication is administered and he is transported to the cath lab, where the coronary angiography procedure is performed. After anesthetizing the access area, research begins - a special catheter is passed through the artery of the forearm into the lumen of the coronary arteries . Using a catheter, a radiopaque substance is injected into the blood, thanks to which the lumen of the vessels becomes visible on a special device - an angiograph. During coronary angiography, the degree and size of damage to the coronary vessels is determined, which determines further treatment tactics. This procedure is low-traumatic, which allows it to be performed under local anesthesia without the use of general anesthesia. The duration of the procedure, as a rule, does not exceed 20 minutes. From the operating room, the patient, accompanied by medical personnel, is taken to the day hospital ward. The third stage of outpatient coronary angiography is observation of the patient in a day hospital ward for 4-5 hours after the study. In the ward, the patient can drink water or juices without restrictions and have lunch. If there are no complications, the patient is sent home. On the day of outpatient coronary angiography, the patient receives a conclusion with recommendations on further treatment tactics and a disk with the results of coronary angiography. If complications arise during coronary angiography or during the control period, patients are hospitalized in the intensive observation unit of the hospital.
FAQ:
Question: I am 56 years old and have coronary heart disease. The cardiologist recommends a coronary angiography. I don't quite understand what this is? Answer : Coronary angiography is a study of the vessels of the heart, which, like a crown, surround the heart, supplying it with oxygen-rich blood. They are called coronary arteries. Narrowing of the coronary arteries leads to a decrease in blood supply to the heart, which leads to oxygen starvation, i.e. to cardiac ischemia. It is very important to know the condition of the arteries of the heart, because... the obstruction to blood flow can be eliminated, radically relieving the person of the symptoms of coronary heart disease. Question: How is coronary angiography performed? Answer : Coronary angiography is an x-ray examination in which a special contrast agent is injected into the vessels of the heart using a flexible thin probe. As the contrast agent passes through the vessels, short-term x-rays are taken with significant magnification using high-resolution equipment. The slightest changes in the coronary bed are visible “at a glance.” The results are recorded in digital format and are available for viewing on any personal computer. Question: Is coronary angiography performed under anesthesia? Answer : No general anesthesia is required. The pulse is determined in the groin area or on the wrist, and a probe or catheter is inserted into the lumen of the artery under local anesthesia. The subject does not feel how the catheter moves through the vessels, because There are no sensory nerve endings inside the arteries. There is no pain, the patient is fully conscious and, together with the operator, monitors the progress of the study on the monitor. The duration of the procedure is no more than 15-20 minutes. Further monitoring of the patient for several hours is necessary. In the department, coronary angiography is performed exclusively through the radial artery (at the wrist). Immediately after the examination, the patient can get up and walk, the bandage on his arm does not limit him in any way (see ambulatory coronary angiography). After 4 hours the patient is discharged home. If the examination is carried out through the groin, then bed rest is necessary and the period of stay in the clinic is extended to a day. Question: If coronary angiography does not reveal narrowing in the vessels of the heart, then there is no coronary heart disease? Answer : Yes, the absence of changes in the coronary arteries practically excludes the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. In rare cases, ischemia of the heart muscle can occur in the presence of “normal” coronary arteries, but the absence of damage to the arteries of the heart is the most reliable predictor of a good prognosis. This is very important information for choosing the right patient management tactics. Question: At what age is coronary angiography performed, what are the contraindications to coronary angiography? Answer : Coronary angiography is performed at any age, in all cases when there is a need for it, namely if the patient has angina pectoris after myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography, in the first hours of myocardial infarction, makes it possible to determine where the blockage of the vessel is causing the heart attack and immediately eliminate it. Coronary angiography is necessary for all adults with heart defects before surgery, before “major” vascular operations. Some patients at high risk of coronary heart disease, such as diabetes, may not have symptoms of the disease. In this case, coronary angiography is, in fact, the only reliable way to exclude or confirm coronary disease.
List of documents and tests required for coronary angiography
- general blood analysis,
- blood type,
- Rh factor,
- tests for hepatitis B and C viruses, HIV, RW,
- ECG in 12 leads,
- Echo-KG.
If necessary, additional studies can be carried out. The patient can undergo examinations both in the clinic at his place of residence and in the clinic where he will undergo coronary angiography.
After hospitalization, you are examined by the attending physician and, if necessary, specialists from other specialties are involved. The condition at the time of coronary angiography is clarified, the essence and possible results of the procedure are explained.
The patient is taken to the X-ray endovascular surgery office.
The procedure is low-traumatic - the patient remains conscious during the entire procedure. After local anesthesia, the examination begins - a special catheter is passed through the femoral artery and the upper part of the aorta into the lumen of the coronary arteries. In some cases, the catheter is inserted through the artery of the forearm, which reduces the observation period after coronary angiography. A radiopaque substance is injected through the catheter, which is carried by the bloodstream through the coronary vessels. The process is recorded using a special installation - an angiograph.
The result is displayed both on the monitor and placed in a digital archive. During coronary angiography, the degree and size of damage to the coronary vessels is determined, which determines further treatment tactics. If necessary, after agreement with the patient, it is possible to perform simultaneous balloon dilation and (or) installation of vascular endoprostheses - stents. After the examination, the specialist shows the patient a recording of his coronary angiography and explains the extent of damage to the coronary vessels and recommends further treatment tactics. After the examination, the patient is given a written conclusion and a recording of coronary angiography on a CD. This allows the recording to be used for study by specialists in any medical institution, on any computer, when determining the dynamics of the disease.
Coronary angiography is routinely performed free of charge for the patient at St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution GB No. 40, as well as subsequent treatment methods, according to indications - balloon angioplasty with stenting of the coronary arteries and coronary artery bypass grafting.
Consultations with a cardiologist to determine indications for coronary angiography and set a date for this procedure are held in the rehabilitation building of St. Petersburg State Budgetary Institution of Healthcare No. 40 on Tuesdays and Thursdays from 14:00 to 16:00 in room 426 on the 4th floor.
For consultation you need:
- passport, medical insurance;
- referral from the clinic where you are being seen;
- medical examinations, which should include an ECG, the result of an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart), the result of Holter ECG monitoring.
Balloon angioplasty and stenting of the coronary arteries are carried out routinely according to the federal quota, which is issued in our institution (this type of treatment is also free for the patient) if the patient has:
- passports;
- medical policy;
- SNILS.
____________________________________________
Consultations with a cardiologist to determine indications for coronary angiography and set a date for this procedure are carried out in the rehabilitation building of St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution GB No. 40
on Tuesdays and Thursdays from 14:00 to 16:00 in room 426 on the 4th floor.
For any questions you may have, you can contact the following numbers:
437-30-88,
← Back