- Treatment of retinal diseases
Retinal diseases are considered the most dangerous among pathologies of the visual system, since if they are not treated in time, they can lead to complete blindness.
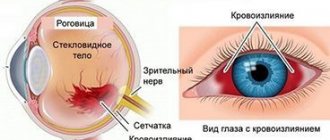
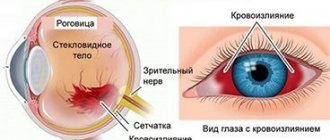
One of the serious disorders that requires immediate consultation with a doctor is hemorrhage in the retina. Retinal hemorrhage or retinal bleeding occurs due to deterioration of the blood vessels. This often happens with retinal vascular thrombosis, when the vessels become blocked and rupture, resulting in blood entering the retinal tissue. Ophthalmologists have all the capabilities for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment and prevention of various pathologies of the retina. Therefore, if you experience any visual discomfort, contact a professional.
The causes of retinal hemorrhage can be:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure);
- Diabetic retinopathy (with complications of diabetes mellitus);
- Blockage or thrombosis of the retinal veins, atherosclerosis;
- Inflammatory diseases of the eye;
- High myopia;
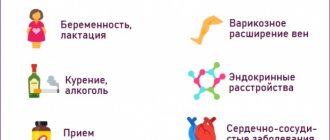
Also, the cause of hemorrhage in the retina can be mechanical factors: in newborns - shaking, in adult patients - severe coughing, blows to the head or face, etc. In addition, hemorrhages in the retina occur in women during childbirth, which is why it is so important during pregnancy see an ophthalmologist to maintain good vision.
Prevention
Retinal hemorrhages may recur. To prevent such complications, mandatory medical examination and limitation of physical activity are recommended for 2-3 months after discharge from the hospital. For diabetic patients, therapy of the underlying disease, correction of the diet, as well as working and rest conditions are necessary.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic provides consultations to children from 4 years old. We are open seven days a week and work daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment for identified pathologies.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure or make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 and 8 (499) 322-36-36 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00) or using the online registration form .
Manifestations and symptoms of retinal hemorrhage
When a vascular rupture occurs and blood enters the retina, this may often be outwardly unnoticeable to a person, but the condition itself is quite dangerous. It all really depends on the location of the rupture of the vessel.
If the hemorrhage occurs somewhere on the periphery of the retina and does not affect its central part - the macula, then this condition may have virtually no effect on the quality of vision and is detected only during a comprehensive vision diagnosis with examination of the fundus.
If the bleeding occurs in the center of the macula, then this condition is very dangerous and can lead to complete loss of vision.
Retinal damage
As you know, the retina of our eye is responsible for the perception of light and the transmission of nerve impulses to the brain, and therefore is the most important structure providing visual perception of the surrounding world.
The retina tissue consumes more glucose and oxygen per unit of its weight than any other tissue in our body, so it requires a good blood supply. However, with diabetes, pathological changes occur in the blood vessels that supply the retina, which leads to the development of a specific lesion of the retina - diabetic retinopathy (more about this disease: https://www.okomed.ru/diabet.html). This disease develops gradually and is poorly diagnosed in the early stages. In addition, it is difficult to treat and can result in blindness. The need for retinal surgery in diabetes is often due to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
What are the signs of retinal hemorrhage:
- A growing cloudy spot appears before the eyes;
- Vision begins to deteriorate sharply
- “Flies” flash before the eyes;
- Feeling of pressure in the eyes;
- Double image
Any discomfort in the organ of vision requires examination and consultation with an ophthalmologist and retinologist. All these services can be obtained at a specialized ophthalmological clinic.
Since all visual receptors are concentrated in the retina, even the slightest hemorrhage can be dangerous and lead to retinal detachment, otherwise there is a risk of blindness.
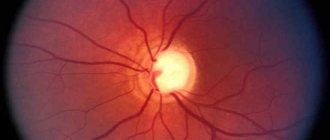
Retinal diseases
The retina is the thinnest inner layer of the eye, adjacent throughout its entire length from the inside to the vitreous body, and from the outside to the choroid of the eyeball. The retina is responsible for image perception and is sensitive to light.
Major retinal diseases:
- retinitis
- retinal hemorrhage
- retinal detachment
- retinal tumor
- retinal dystrophy
- macular degeneration and macular degeneration
- diabetic retinopathy
- retinal tear
- retinal degeneration
- hypertensive retinopathy
- retinal angiopathy
Main “risk groups”
- people with moderate and high myopia
- pregnant women
- elderly people with diabetes.
Inflammatory disease of the retina - retinitis
Retinitis is an inflammatory disease of the retina, which can be either unilateral or bilateral. This inflammatory disease of the retina can be either infectious or toxic-allergic in nature. Retinitis can occur due to a number of infectious diseases. For example, such as: AIDS, syphilis, viral and purulent infections, etc.
Symptoms of retinitis depend on the location of the process on the retina. But the main one is a decrease in visual acuity and a change in the field of vision. There are cases where retinal damage is initially limited to small areas, which then enlarge, leading to progressive loss of vision. treated with medication.
Retinal hemorrhage
Hemorrhages in the retina are more often related to vascular diseases and lead to decreased visual acuity, retinal detachment, secondary glaucoma, retinal dystrophy and other diseases.
The causes of retinal hemorrhage may be associated with hardening of blood vessels in old age, due to thrombosis (blockage) of the central retinal vein or one of its branches. Also, retinal hemorrhage can be caused by diabetes mellitus, heart defects, blood diseases, skin burns, bruises, etc.
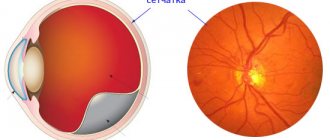
Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is the separation of the retina of the eye from the choroid. When the retina ruptures, the intraocular fluid penetrates under it and peels off from the choroid. If retinal detachment occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, as delay may result in blindness.
Typically, retinal detachment is treated surgically . This can be extrascleral ballooning or filling (the purpose of such treatment is to achieve adherence of the retina to the choroid), then laser coagulation and vitrectomy are performed (used to remove scars and blood from the vitreous). Surgical treatment methods usually require restriction of visual work and physical activity.
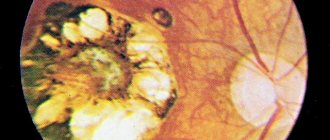
Retinal tumor
Retinal tumors are neoplasms of the retina that can be malignant or benign. Most often, tumors develop in childhood: in the first months of life in 20% of cases, in the first years in 55%. In 25% of patients, the process affects both eyes. The most common of retinal tumors are gliomas, which arise from the outer layer of the retina.
In the early stages, thickening of the retina occurs and this can only be determined by examining the fundus and ultrasound of the eye. After some time, the tumor takes up most of the eye. Due to the development of the tumor, the eyeball protrudes and its mobility is limited. Vision disappears.
The occurrence of the disease has a certain hereditary connection according to the incorrect dominant type.
Retinal tumors must be treated as soon as possible and in specialized ophthalmology departments of hospitals. If treatment is delayed, it can lead to irreversible consequences . Of the modern treatment methods for retinal tumors, the most effective are low-temperature (cryogenic) therapy and photocoagulation. Surgical treatment methods are organ-preserving.
Retinal dystrophy
Retinal dystrophy is usually caused by disorders in the vascular system of the eye. It mainly affects older people, whose vision gradually deteriorates. Very often, degenerative changes in the retina accompany moderate and high degrees of myopia. The fact is that usually in this case the size of the eyeball is increased, and the retina lining its back surface is stretched, which leads to dystrophy.
Modern treatment of this condition, as well as other types of dystrophies (many inflammatory and vascular diseases of the retina lead to dystrophies), occurs using an argon laser. The main goal of this treatment is to strengthen and, in the case of retinal detachment, to postoperatively limit the retinal tear.
The principle of treatment is based on the fact that laser exposure leads to a sharp increase in temperature, which causes coagulation (clotting) of the tissue. Thanks to this, the operation is bloodless. The laser has very high precision and is used to create fusions between the retina and choroid of the eye (i.e. strengthening the retina).
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
The most common cause of vision loss in people over 50 years of age. In VMD, the central part of the retina, the so-called macula macula, is affected.
The main risk factors for developing AMD are:
- Age over 50
- Cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, hypertension)
- Genetic predisposition
- Gender (more common in women)
In the initial stages, the disease occurs unnoticed by the patient and can only be detected during an appointment with an ophthalmologist. With the progression of AMD and its transition to the so-called neovascular form, the patient may notice decreased vision, a feeling of curvature of lines, blurred and disappearing areas. If these symptoms occur, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. Treatment: administration of angiogenesis inhibitors.
Diabetic retinopathy
In diabetes, the vessels of the retina are affected, which leads to a disruption in the supply of oxygen to the tissues and the development of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy usually develops 5-10 years after the onset of diabetes. In type I diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent), diabetic retonopathy proceeds rapidly and proliferative diabetic retinopathy .
This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of new vessels that grow from the retina into the vitreous body and cause hemorrhages in it, and also enhance scarring processes in the vitreous body and can cause the development of retinal detachment. In type II diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent), changes mainly occur in the central zone of the retina. Diabetic maculopathy occurs , often cystic, which leads to decreased central vision.
Another form of diabetic retinopathy is background retinopathy , in which pathological changes occur only in the retina of the eye. Due to disturbances in the area of the capillary vessels of the retina, small hemorrhages, deposits of metabolic products, and retinal edema occur. This form primarily affects older diabetics and eventually leads to gradual deterioration of vision.
Treatment methods for diabetic retinopathy:
- laser coagulation of the retina,
- intravitreal or intraocular administration of drugs,
- operation - vitrectomy.
Retinal tear
Retinal tears most often occur in nearsighted people due to mechanical tension of the pathologically altered vitreous body. Patients note black threads in front of the affected eye, as well as light flashes. First, the edge of the tear in the retina begins to peel off, which later leads to retinal detachment.
To eliminate this, at the stage of holes or breaks, areas of the healthy retina are fixed using laser photocoagulation. Scarring occurs at retinal coagulation points. As a result, a strong connection between the retina and the choroid occurs. The coagulation technique involves applying 2-3 rows of coagulates around the hole or rupture.
Retinal angiopathy
Angiopathy is a lesion of blood vessels, the cause of which is most often general diseases (vegetative-vascular dystonia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc.). Most often, angiopathy is caused by lesions of blood vessels and is expressed by spasms and paresis of blood vessels. Also, among the problems that can arise with the retina are injuries, burns, and retinal swelling .
This condition is extremely dangerous and can cause low vision and blindness.
Diagnosis of retinal hemorrhage
In ophthalmology, the diagnosis of retinal diseases is carried out using the most modern equipment, which makes it possible to identify the disease long before its manifestation, namely:
— Laser optical scanning tomograph (OST) – studies the structure of the retina throughout its depth.
— Fluorescent antigraph – for accurate and effective diagnosis of diseases of the retina, optic nerve and choroid.
Also, in order to identify the cause of hemorrhage in the retina, the ophthalmologist prescribes a general blood test, a blood sugar test and an ECG.
Treatment
Treatment of retinal hemorrhages is carried out only in an ophthalmological hospital, where patients are required to be hospitalized.
As a conservative therapy, in the treatment of retinal hemorrhages, corticosteroids (subconjunctival injections), angioprotectors, antioxidants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, vasodilators and antihistamines are prescribed. Osmotherapy and laser coagulation are carried out (for large volumes).
The duration of treatment is usually 14 days, after which the hemorrhage will resolve and vision will improve.
Retinal surgery for diabetes
Today, the most effective and reliable method of stopping the development of pathological changes in the retina caused by diabetes is laser coagulation of the retina. Such an operation does not require the patient to stay in the hospital, the intervention is carried out in 1 or 2 stages (depending on the degree of damage to the fundus). The operation is painless and local anesthesia is sufficient to perform it.
The essence of laser coagulation of the retina is to apply therapeutic burns (coagulates) to the retina using a medical laser with a certain radiation spectrum. Depending on the location and severity of the pathological process, the following types of operation are distinguished:
- local photocoagulation - the doctor applies pinpoint coagulates in the area of maximum retinal detachment;
- barrier photocoagulation - therapeutic burns are applied parallel to the paramacular area in several rows;
- panretinal laser coagulation - during the treatment process a large number of cauterizations are performed over almost the entire area of the retina (excluding the macular area of the optic nerve), this technology is used in cases of massive retinal damage and a pronounced proliferative process.
AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION (AMD)
The most common cause of vision loss in people over 50 years of age. AMD affects the central part of the retina, the so-called macula.
The main risk factors for developing AMD are:
- Age over 50
- Cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, hypertension)
- Genetic predisposition
- Gender (more common in women)
In the initial stages, the disease occurs unnoticed by the patient and can only be detected during an appointment with an ophthalmologist. With the progression of AMD and its transition to the so-called neovascular form, the patient may notice decreased vision, a feeling of curvature of lines, blurred and disappearing areas. If these symptoms occur, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Currently, the most effective method of treating AMD is intravitreal (i.e. inside the eye) administration of LUCENTIS, EYLEA (AFLIBERCEPT) - drugs that block the growth of new vessels under the retina. LUCENTIS, EYLEA (AFLIBERCEPT) can not only preserve, but also improve the vision of a patient with AMD. Treatment methods for AMD also include laser photocoagulation and photodynamic therapy.
Damage to the vitreous
The clear, gel-like substance that fills the eyeball is called the vitreous. This structure of the eye has a special structure and composition, which can be disrupted when exposed to various factors (diabetes mellitus is one of these negative factors). In this case, experts talk about destruction of the vitreous body.
With destructive changes in the vitreous body, opaque particles appear, which are perceived as spots and “floaters” floating before the eyes. In addition, changes in the structure of the vitreous body can lead to mechanical effects on the retina and cause its detachment. That is why all people with diabetes are advised to immediately consult an ophthalmologist if they have any visual impairment.
Treatment methods for the retina and vitreous body in diabetes
The choice of specific methods of helping a patient suffering from ophthalmological complications of diabetes depends on the type of pathology and the stage of its development. The OkoMed Clinic offers patients the following main methods of treatment for diabetic damage to the retina and vitreous body:
- intraocular injections of drugs that slow down the formation of new blood vessels;
- laser coagulation of the retina - allows you to ensure tight fusion of the retina with the underlying choroid using a laser, which makes it possible to stop the process of retinal detachment in 85 percent of cases;
- vitrectomy, that is, removal of the vitreous body and its replacement with a transparent substance.