Cardiac surgery is a branch of medicine devoted to the surgical treatment of the heart. In case of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, such intervention is a last resort. Doctors try to restore the patient’s health without surgery, but in some cases only cardiac surgery can save the patient. Today, this field of cardiology uses the latest advances in science to return the patient to health and a full life.
Briefly about the treatment method
The use of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) as an emergency treatment for myocardial infarction is urgent.
The goal of primary PCI is to open the artery as quickly as possible, preferably within 90 minutes. The treatment method is very effective, often without complications, but, unfortunately, not everywhere patients have the opportunity to seek help on time or get to the hospital on time. Another type of emergency surgery for myocardial infarction is coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), which is usually performed to simultaneously treat mechanical complications such as papillary muscle rupture or ventricular septal defect accompanied by cardiogenic shock. In uncomplicated MI, mortality can be high when surgery is performed immediately after the infarction.
What types of valves are there?
Three types of elements can be used to replace an unhealthy valve:
- Biological. They suggest recreating a new valve from the patient’s own tissues. Such a valve will last about 10-15 years, after which the operation will need to be repeated. This is due to the gradual wear and tear of the element and its inevitable degenerative changes. With this approach, anticoagulants need to be taken only for the first six months after surgery.
- Mechanical. Such a valve is manufactured in a laboratory and requires constant use of anticoagulants (for the entire life of the patient). Such prostheses are installed mainly in patients who have not reached old age.
- Donor. This option is used only in extreme cases, as there is a risk of rejection of donor tissue by the patient's body. The outcome of such an operation is difficult to predict, and the possibility of complications cannot be excluded. In order for the valve to take root, doctors need to carry out therapy that suppresses the recipient’s immunity so that the immune system does not begin to fight the foreign element. As with the installation of an artificial valve, the patient is advised to take lifelong anticoagulants to exclude the possibility of thrombus formation.
- Available: doctor’s appointment from 1500 rubles
- Convenient: open daily from 8:00 to 21:00
- Quickly: we will carry out all the diagnostics at the first appointment
- Complete: has all the necessary equipment
Indications and contraindications for the treatment method
Indications for stenting are:
- Myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation.
- Unstable angina and myocardial infarction without ST segment elevation.
- Stable ischemic heart disease.
There are no absolute contraindications to stenting of coronary arteries. The main contraindication is the impossibility of prescribing antiplatelet therapy.
Relative contraindications: acute renal failure, chronic renal failure, ongoing gastrointestinal bleeding, fever of unknown origin, possibly infectious, untreated active infectious process, acute stroke, severe anemia, malignant uncontrolled arterial hypertension, severe electrolyte disturbances, lack of contact with the patient due to with a psychological condition or serious illness, severe concomitant pathology in which coronary angiography can complicate the course of the disease, patient refusal of necessary further treatment (coronary angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting, valve replacement), digitalis intoxication, documented anaphylactic reaction to a contrast agent, severe illness peripheral vessels, impeding access to the vascular bed, decompensated congestive heart failure or pulmonary edema, severe coagulopathy, aortic valve endocarditis.
How the treatment method works
Coronary artery stenting for myocardial infarction includes the following steps:
- A stent is inserted into the narrowing of the coronary artery using a special balloon catheter. A stent is a stainless metal tube with many cells of various configurations.
- When the balloon is inflated, the stent expands in diameter and is pressed tightly into the artery wall, increasing the lumen of the narrowed vessel, which allows blood to flow freely to the heart.
- The balloon is deflated and removed, while the stent remains permanently in place at the site of narrowing or blockage.
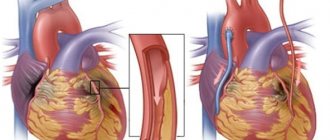
Coronary artery bypass grafting is performed on an open heart. The idea is to create a bypass (shunt) from the aorta to the coronary artery, bypassing the site of blockage or narrowing. Usually the material for the shunt is the person’s own vein; sometimes it is necessary to use artificial material. Your attending physician will tell you in more detail about the stages of coronary artery bypass surgery itself.
HOW THE HEART VESSELS ARE TREATED WITHOUT A SINGLE INCISION IN THE CHEST
Doctors at the Presidential Clinic are improving methods of treating heart vessels together with a famous cardiologist from Switzerland: they will perform surgery on a patient who, under other circumstances, would not be allowed to go on the operating table. We went straight to the scene and talked to interventional surgeons at the Presidential Clinic about how they treat the blood vessels of the heart and keep it beating.
But before the operation itself, let’s go through a short educational program on medical terms. The interventional surgeon at the Presidential Clinic, Alexander Zemlyansky, explains:
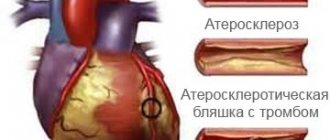
“Every organ has vessels that feed it. The heart vessels are called coronary arteries. If they are clogged with blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques, then the gaps in the vessels narrow, close, thrombose, blood flow decreases and the heart receives insufficient nutrition. It is this lack of blood flow into our organ that is called ischemia.”
However, the diagnosis of a patient who has already been prepared for surgery sounds even more complicated: coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, functional class three. In professional translation, all these terms indicate a lack of blood supply to the heart, which is most often treated surgically.
“In this regard, there are two main types of treatment for coronary heart disease -
Alexander Viktorovich continues,
“an open or traditional surgical operation, when the chest is opened and the cardiac surgeon creates an anastomosis, or bypass vessel.
Thus, this damaged area is excluded from the blood flow chain by another vessel. This standard coronary artery bypass surgery is performed by all cardiac surgeons, and our Center performs a lot of such operations. You could say that this is the daily work of a cardiac surgeon .
«But there is a second method of surgical treatment of blood vessels, ours, endovascular, -
says interventional surgeon Alexander Zemlyansky -
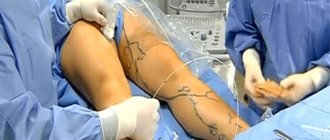
when treatment is carried out without an incision in the chest, through a small puncture in the area of the femoral or radial artery.
Using guides and a catheter, which serves as a delivery system for instruments and is a thin tube, we penetrate the blocked area of the vessel and expand it from the inside with a balloon. It swells and enlarges the area obstructing blood flow. Next, we secure the result with a stent: it, in the form of a frame, supports the vascular wall from the inside.” For each type of operation, according to the doctor, there are indications: open intervention is performed if all three coronary vessels that supply the heart are blocked. When they are less affected, interventional surgeons get to work. In the first case, during an open operation, doctors stop the heart, and in the meantime the function of the pump is taken over by the heart-lung machine. With the second, endovascular (intravascular) method, the entire manipulation takes place on the working heart, and the patient, as a rule, is conscious all the time.
But there is also a third type of treatment - a backup plan for doctors and salvation for those who would have been denied surgery in the first two cases.
“Today we had the same situation: there is a category of patients who have a problem with the vessels, that is, their complete occlusion - blockage. But for this patient, for example, due to concomitant illness or age, it is impossible to undergo open heart surgery, which is usually performed with such a diagnosis, since he will not tolerate it,”
notes Alexander Zemlyansky, introducing us to the new terminology. The third way surgeons will operate on the patient is a variation of traditional endovascular (intravascular) surgery, also called retrograde coronary recanalization.
However, in order not to remember complex combinations of words, we are recommended to understand the essence: surgeons will make their way to the blocked area through the vessels connecting the coronary arteries of the heart to each other - they are called the collateral system. Through the gaps of such collaterals, doctors plan to carry out the necessary instruments to the damaged area. The operation has begun.
Patient: An elderly lady, seventy-nine years old. As they would have said before, this is a rather delicate age to undergo any kind of manipulation, especially on the heart. But not now. She will spend the entire operation conscious, and the recovery process itself will not take much time. This is the success of modern medicine, notes an invited specialist from Switzerland upon leaving the operating room. Dr. Olaf Franzen is an interventional cardiologist. His track record includes the first operation in the world to replace the mitral valve of the heart with a bioprosthesis, performed without opening the chest, using an endovascular (intravascular) method.
Dr. Franzen talks about the development of technology - the first closed operations lasted seven hours, now they are performed in less than an hour; the growth of cardiovascular diseases in the world - he calls them the main “killers” of humanity today, and also notes how to take care of the heart and its vessels with age:
“90% of heart and vascular diseases can be prevented if you watch your lifestyle. All we need is to control risk factors, this includes quitting smoking, eating healthy, exercising every day, controlling blood cholesterol and blood pressure. In some countries, too many deaths occur due to heart and vascular diseases, and these deaths could not have happened, all because people themselves find it difficult to control their own habits. Everything revolves around the lifestyle you lead. It is not expensive at all compared to the treatment you will need if you get sick. Preventive measures are much cheaper.”
At the same time, in the professional sphere, Dr. Franzen summarizes, it is also important to develop useful habits, only this time - regarding the constant exchange of experience. In medicine, the doctor is sure, there is no superior side, since everyone learns all the time:
“We call it a master class and therefore it seems to us that someone will teach, but in reality it is always a mutual exchange of knowledge, we are constantly learning from each other. We doctors need to work together more and more and understand that the patient is at the center of our concerns. We must work as a team, because the activity and will of hospital management in this regard is becoming increasingly important. They need to create an atmosphere that will inspire doctors to work together, because one discipline cannot cure a patient. If we are treating a heart vessel, we need echocardiograms, the help of cardiac surgeons, cardiologists, and they must make decisions together. This is a new challenge for doctors and I like that your Hospital sees this and works on existing problems.”
One of these tasks is to show that such operations are available to citizens of the country: in our case, a rare manipulation of the heart vessels for Kazakhstan was performed by Hospital surgeons on a patient from Kostanay as part of a highly specialized medical care program. In simple terms, according to quota.
Observation program after treatment method
Cardiac rehabilitation aims to optimize function and quality of life in those suffering from heart failure. Exercise is an important part of rehabilitation after a myocardial infarction, which has beneficial effects on cholesterol levels, blood pressure, weight, stress and mood. Some patients are afraid of exercise because it can cause another heart attack. But you need to understand that the doctor, upon discharge, indicates the required dosed physical activity. The risk of another heart attack is reduced with strict blood pressure control and lifestyle changes, mainly smoking cessation, regular exercise, a sensible diet for heart disease patients, and limiting alcohol consumption. Drugs are typically prescribed after a myocardial infarction to prevent secondary cardiovascular events, such as further myocardial infarctions, congestive heart failure, or cerebrovascular disease.
Possible complications:
Coronary stenting rarely causes complications, but there are certain risks associated with it:
- Repeated narrowing of blood vessels (stent restenosis). If angioplasty is performed without stent implantation, the probability of restenosis reaches 30-40%. Installation of a bare metal stent reduces the possibility of relapse to 20%, and drug-coated stents - to 1%.
- The occurrence of blood clots. After some time, blood clots can form inside the stents, which are dangerous because they lead to a heart attack. To reduce the likelihood of their occurrence to a minimum, we recommend taking antiplatelet medications prescribed by your doctor: Plavix, aspirin, etc.
- Bleeding from the catheter site (arm or leg). In most cases, there will only be a slight bruise, but there is still a risk of serious bleeding.