Aspirin is a popular drug in the category of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is also used for the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system. There is one persistent myth that aspirin thins the blood and is indicated for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. However, this is not entirely true. Aspirin affects blood clotting and, as a result, the process of thrombus formation. But the thickness of the blood is affected by the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells. The lower their value, the more liquid the blood in the body.
In this article we will consider in detail the drug aspirin cardio. How does it differ from the usual simple aspirin, what effect does it have on the body and cardiac activity in particular.
Medicine aspirin cardio
In addition to the fact that the drug belongs to the category of NSAIDs and has an antipyretic effect and analgesic effect, aspirin cardio is used in the primary prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system and in the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction. Reduces the risk of developing the disease with unstable angina. The drug is prescribed for cardiovascular pathologies due to its antithrombotic effect.
The main difference between the drug and regular aspirin is that aspirin cardio is coated with a special enteric coating. Due to this, it is used for long courses in cardiology. This coating allows the active substance to be released in the intestines, thereby minimizing one of the main side effects of aspirin - damage to the gastric mucosa.
Composition of the drug
The active ingredient of the drug is acetylsalicylic acid.
Excipients include corn starch and cellulose powder.
The enteric coating contains polysorbate, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc and other compounds.
Thus, when prescribing the drug, individual intolerance to the components of the composition should be taken into account.
Release form and dosage
The drug aspirin cardio is available only in the form of enteric-coated tablets in dosages of 100 mg and 300 mg.
The number of tablets in a package can be: 20 pcs., 28 pcs., 56 pcs.
In a shell or without?
Coated aspirin tablets are designed to pass through the stomach without disintegrating until they reach the intestines. The protective coating is thought to allow aspirin tablets to be gentler on the stomach lining, and may be useful for people with a history of gastritis or ulcers who take aspirin daily.
However, some researchers believe there is no evidence that coated aspirin reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Moreover, there are a number of publications that such aspirin is less effective for preventing heart attacks.
Indications for aspirin cardio
- Primary prevention of acute myocardial infarction, taking into account aggravating risks - hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, smoking.
- Prevention after a heart attack.
- Stable and unstable angina (including suspicion of acute myocardial infarction).
- Prevention of stroke (including in patients with transient cerebrovascular accident).
- Prevention of cerebrovascular accidents.
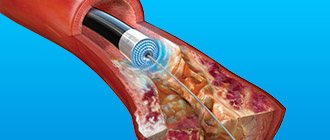
- Prevention of thromboembolism after operations on blood vessels and arteries (bypass surgery, endarterectomy, angioplasty and stenting).
- Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches (including long-term immobilization as a result of extensive surgery).
Methods of application
The method of administration and dosage regimen of the drug depend on its release form and other factors. The optimal dosage regimen is determined by a specialist based on specific indications. It is advisable to take aspirin cardio tablets orally before meals with plenty of liquid, preferably at the same time, once a day.
The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor. The usually recommended dose is 100 mg 1 time per day, but the approach to the dosage regimen is individual. Depending on the indications, it may increase to 300 mg/day.
Primary prevention of acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors: 100 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
- The recommended dosage for the prevention of recurrent infarction is 100-300 mg/day.
- For unstable angina, as well as the onset of myocardial infarction, the initial dose is 100-300 mg. In this case, the first tablet is chewed to speed up absorption. The drug should be taken as soon as possible at the slightest suspicion of danger. For a month after the attack, a maintenance dose of 200-300 mg/day is recommended. Further, all treatment recommendations are prescribed by a specialist based on the patient’s vital signs.
- Prevention of stroke and cerebrovascular accident: 100-300 mg/day.
- Prevention of thromboembolism after vascular surgery: 100-300 mg/day.
- Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: 100-200 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
The compliance of the dosage form of a particular drug with the indications for use and dosage regimen should be strictly observed.
How do you know that the benefits outweigh the harm?
The doctor, with your help, will collect and analyze many factors and then make a decision. You yourself can try to assess your risks using an online calculator developed by American cardiologists.
Remember that arterial hypertension itself is not an indication for prescribing aspirin if the patient does not have a diagnosis of coronary heart or brain disease! On the contrary, poorly controlled, high blood pressure is often a contraindication to the use of aspirin, since sudden increases in blood pressure increase the risk of intracerebral bleeding, and aspirin can significantly increase it.
In addition, aspirin may reduce the effectiveness of some drugs used to treat hypertension, such as enalapril, captopril, lisinopril, perindopril, and beta blockers.
If taking preventative aspirin turns out to be unreasonably dangerous for you, your doctor will suggest other prevention options, such as lifestyle changes or taking statins.
Currently commercially available are predominantly low-dose enteric-coated aspirin tablets. The outer shell “dissolves” only in the small intestine, protecting the stomach from irritation. These tablets must be swallowed whole without chewing.
There are also combination preparations containing the additive magnesium hydroxide. It is believed that magnesium in this combination reduces the harmful effects of acetylsalicylic acid on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
And don't use aspirin if the tablets smell strongly of vinegar—the medicine has probably gone bad!
In order for aspirin to effectively protect your blood vessels, it is prescribed for daily long-term, usually lifelong use. Most likely, you will not feel any changes in your body after starting treatment - but this does not mean that aspirin does not work!
Contraindications
Express contraindications include:
- allergy to the active substance and components of the drug,
- Gastrointestinal diseases, including erosions, ulcers in the acute stage,
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system
- hemorrhagic diathesis,
- pregnancy and lactation (the 1st and 3rd trimesters are considered especially dangerous)
- aortic aneurysm
- renal or liver failure
- and children under 15 years of age.
Overdose
Signs of a moderate overdose include:
- Hearing impairment
- Headache
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Noise in ears
If you reduce the dose of the drug, these symptoms will disappear.
In case of severe overdose, the following occurs:
- Ketosis
- Fever
- Respiratory failure
- Severe hypoglycemia
- Cardiogenic shock
With such symptoms, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital.
Special Recommendations
Aspirin cardio and chronic diseases
Particular caution should be exercised when taking aspirin for persons suffering from diseases of the respiratory system. The fact is that taking aspirin causes a narrowing of the bronchi, which can cause so-called aspirin asthma, or provoke asthma, which is in remission.
Aspirin cardio and childhood
When taken in its pure form in children, due to their young age, the concentration of glucose in the plasma can sharply decrease, in parallel with this, the level of ketone bodies in the blood increases, plasma acidification occurs, and fatty acids accumulate in the liver. These metabolic disturbances lead to swelling of tissues and organs.
Children become more than just lethargic. Aggravating symptoms such as cramps, diarrhea, rapid breathing and palpitations may occur. Up to loss of consciousness and severe muscle hypotension. Such conditions in children can be life-threatening, so the drug is contraindicated for them.
Aspirin cardio and alcohol
The combined use of alcohol and aspirin is not recommended. Alcohol and alcohol-containing products are known for their vasodilating properties. But in combination with aspirin, the effect can be most unexpected. The risks of bleeding increase, including in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, exacerbation of liver diseases or the occurrence of any acute symptoms associated with this organ.
Aspirin cardio and pregnancy
The active substance freely and easily penetrates the placental barrier, which can lead to negative consequences for the fetus.
When used in the first trimester, it leads to the development of a “cleft palate” (cleft palate); in the third trimester, it causes inhibition of labor, premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, disruption of the functioning of the pulmonary vessels and hypertension in the pulmonary circulation.
Acetylsalicylic acid is also excreted in breast milk, which increases the risk of bleeding in the baby due to impaired platelet function. Therefore, the advisability of using the drug during pregnancy and lactation should be justified by the specialist making the decision on the prescription.
Drug interactions with daily aspirin therapy
The combination of taking aspirin with anticoagulants can significantly increase the risk of serious hemorrhagic complications. Such concomitant therapy should be carefully discussed with your doctor.
Some medications may also increase the risk of bleeding. Medicines that may interact with aspirin include:
- Heparin
- Ibuprofen (if taken regularly)
- Corticosteroids
- Clopidogrel
- Some antidepressants (clomipramine, paroxetine, etc.)
Taking certain dietary supplements may also increase the risk of bleeding. These include:
- Blueberry
- Capsaicin
- Cat claw
- Evening primrose oil
- Ginkgo
- Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil)
Aspirin after a hangover
To achieve optimal results, you must follow the instructions, which indicate the algorithm for taking the drug and its dosage. Taking pills in random order is unacceptable, so it is important to remember the harmful effects of the elements of the drug on the body.
- Before use, you must read the instructions and the permissible dose.
- For an effective effect, the drug is taken a couple of hours before the feast and 6 hours after it.
- People with ulcerative lesions of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract or with metabolic peculiarities should consult a doctor before use.
- Aspirin is taken in moderation, so regular use of the drug is prohibited for “alcoholics” and people who frequently drink alcohol.
conclusions
Does aspirin help with hangovers—yes, it does. But for this it is necessary to create optimal conditions for the body and reduce the likelihood of side effects. Aspirin is an almost ideal option, but only in cases of uniform use. In large quantities with regular use, it can cause irreparable consequences that will have to be eliminated with medications that contribute to the emergence of new problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is important to be aware and careful when taking any medications, otherwise you can harm your own body.
Features of drugs when interacting with alcohol
In home medicine cabinets you can sometimes find many medications that are applicable in certain cases. But there are a number of pharmaceutical substances that are strictly incompatible with alcohol and alcoholic products. The main drugs not recommended for use in such cases are divided into groups:
- sleeping pills group of drugs;
- antidepressants;
- tranquilizers;
- antipyretic group based on paracetamol;
- analgesics;
- painkillers.
note
Medicines containing acetylsalicylic acid are not recommended due to possible internal bleeding. They arise from the interaction of gastric juice, alcohol and drug substances. As a result, the reaction can significantly damage the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and aggravate the condition of erosions, if any.
The main criterion in selecting a remedy that helps with a hangover is the composition and form of action of the drug. Therefore, no matter what pharmacological group the medicine belongs to, in the presence of ulcers and lesions of the stomach this is an unacceptable mistake. For those who do not suffer from such gastrointestinal diseases, there is a high risk of erosive spots appearing as a result of the interaction of acids.
Effect of the drug on the body
Given the controversial effectiveness of aspirin, it is important to remember that the determining role is played by the person’s condition, the characteristics of his body and the presence of any internal injuries and diseases. The illusory effectiveness of this medicine for such people can result in irreversible processes that can lead to death. The main positive aspects when taking medications of different pharmacological groups:
- improving blood circulation and providing oxygen to cellular structures;
- aspirin relieves any manifestations of pain and inflammatory processes;
- thins the blood and stimulates free circulation;
- reduces blood pressure;
- Acetylsalicylic acid does not cure, but alleviates the human condition.
Objective use of the drug is achieved thanks to the correct sequence and dosage, which was established by the attending physician. Many people take the pill the day before the upcoming feast. This allows you to significantly reduce the impact of alcohol on the body, prevent the appearance of hangover symptoms and provide yourself with a “morning without consequences.”