Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Prevention of addictions
- Prevention of alcoholism
- Smoking prevention
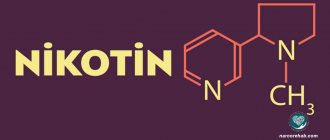
— Smoking prevention — Nicotine: disgusting, pleasant, dangerous
A drop of nicotine not only “kills the horse”, but also helps prevent the development of Alzheimer's disease. A click of a lighter, a few puffs - and after just 7 seconds, the molecules of the substance overcome the blood-brain barrier and begin to act on the brain. The effect of nicotine is not only the appearance of relaxation and high spirits. The substance also affects sleep and wakefulness rhythms, appetite, pain perception, digestion and the cardiovascular system.
Regular smoking leads to the formation of a dependence syndrome and chronic changes in tissues and organs.
Content:
- Circulatory problems caused by smoking
- How does the body react to the intake of tobacco smoke?
- How does nicotine affect blood vessels?
- Features of blood circulation in the brain during smoking
- Nicotine and blood vessels of the lower extremities
- How to prevent the effects of nicotine on blood vessels
Tobacco smoking has a particularly pronounced effect on the cardiovascular system. Some believe that the main ingredient contained in tobacco, nicotine, constricts blood vessels. Others think that it expands them, or does not affect vascular tone at all. What's really going on?
Why nicotine is harmful to the brain
Smoking and cerebral blood vessels are our worst enemies. Nicotine contained in tobacco smoke causes vasoconstriction. At the same time, the amount of nutrients and oxygen entering the neurons of the brain sharply decreases. Neurons die from oxygen starvation. This increases the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
But neuronal degeneration is only one of the consequences of how smoking affects the blood vessels of the brain. The most dangerous result of many years of inhaling tobacco smoke is cerebral ischemia and stroke.
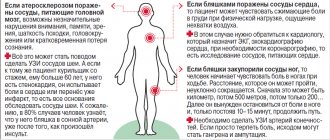
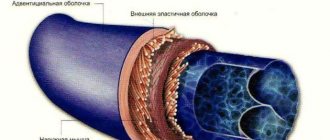
When blood vessels narrow, the heart begins to work at an accelerated pace. The heart rate increases by 20-30 beats per minute. Increased pressure makes blood vessels less elastic. Over time, irreversible damage appears in the vessels - microcracks. Protein and lipid metabolism is disrupted, resulting in cholesterol accumulation on the walls of blood vessels. This disease is called atherosclerosis.
Circulatory problems caused by smoking
Long-term smoking, in addition to addiction, causes pathological changes in almost all organs and systems. The blood vessels and heart are especially affected.
A smoker has:
- Higher increase in blood pressure for your age group.
- Increased heart rate by 10-12 beats.
- Persistent spasm of arterioles.
- Deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the inside of blood vessels after destruction of the vascular wall.
- Danger of thrombosis and blood clot rupture.
- Increased blood viscosity due to adhesion (gluing of platelets) and changes in rheological properties.
- Disruption of metabolic processes that enhance thrombus formation and sclerosis of the vascular bed.
- Reducing the content of prostacyclin, which dilates arteries and capillaries.
All these deviations sooner or later become the causes of many diseases that require long-term treatment and the use of expensive drugs. Acute and chronic pathologies significantly worsen the quality of life of patients and lead to premature aging.
Bad habits (smoking) with varicose veins
Statistics show that varicose veins are one of the most common diseases diagnosed in people aged 30–45 years. In the overwhelming majority of cases, varicose veins affect the lower extremities and a process of irreversible stretching of the veins is observed. At the initial stage, the disease does not have pronounced symptoms; spasms and heaviness in the legs are periodically felt. Later other symptoms appear:
- Swollen veins that enlarge after exercise;
- Severe swelling of the legs by the end of the day;
- Regular attacks of acute pain, convulsive syndrome;
- Nodular formations, itching of the skin, trophic ulcers.
What is the etiology of the disease? Normally, the blood flow should go from bottom to top, overcoming gravity, which is ensured by the work of the leg muscles and venous valves, as well as the pressure of blood from the arteries. But a number of factors can cause a functional failure, resulting in stagnation, pressure increases excessively, and the venous walls begin to deform. The following causes of varicose veins are identified:
- Lifestyle. Being forced to sit or stand for long periods of time, which is common in many modern jobs, can impair blood flow. Muscle pumps, designed to move blood to the heart, become numb and stop working actively;
- Genetic predisposition. People with unfavorable heredity are most susceptible to varicose veins. Scientists have proven that congenital valve insufficiency is passed on from generation to generation;
- Overweight. Obesity provokes hormonal changes in the body, and this negatively affects the condition of the venous walls and their elasticity. The situation is also complicated by increased load on the lower extremities, which causes circulatory problems;
- Pregnancy. The growing uterus and fetus compress the veins, creating obstacles to normal blood circulation. Increasing weight puts additional stress on the legs, superficial veins stretch and thin;
- Bad habits. An unbalanced diet - consuming large amounts of fatty, salty and spicy foods - significantly increases blood viscosity, slowing down its flow. Alcohol dehydrates the body and destroys the membrane of red blood cells, which leads to the formation of blood clots.
Often patients do not pay due attention to protruding veins because they do not experience discomfort. Experts are unanimous: there is no point in delaying examination and treatment, the disease will gradually progress. At the first signs of varicose veins, you should pay attention to a number of contraindications, compliance with which will help avoid worsening the condition:
- Physical inactivity, excessive physical activity (heavy lifting);
- Visiting baths, saunas, beaches and physiotherapy;
- Taking medications that thicken the blood;
- Wearing high heels.
Separately, it is necessary to mention the dangers of smoking for varicose veins. Constant consumption of substances containing nicotine in large doses reduces the level of vitamin C, which plays an important role in the synthesis of collagen and elastin, which form the connective tissue of venous walls and valves. The toxic chemicals that make up cigarettes destroy the venous walls, which can lead to the development of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities. In combination with factors such as obesity, hereditary predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, smoking can accelerate the course of the disease and lead to serious consequences.
, Phlebofa is successfully used to treat varicose veins on the legs.
. This is a unique medicine based on diosmin, a bioflavonoid obtained from plants of the rue family. The drug has a pronounced angioprotective property and solves several problems at once: it enhances blood microcirculation and lymphatic drainage, increases the tone of the veins, and fights stagnation. "Phlebofa" is indicated for use in cases of varicose veins, capillary fragility, lymphovenous insufficiency and hemorrhoids. Contraindicated for persons with hypersensitivity to the components, children under 18 years of age, pregnant and lactating women.
Read the instructions for the drug “Phlebofa”
Find out the price of "Flebof"
How does the body react to the intake of tobacco smoke?
Once in the lungs, toxic ingredients are absorbed into the alveoli into the capillary network and are carried by the bloodstream throughout the body. Penetrating through the blood-brain barrier into the control center of the cardiovascular system, nicotine causes a narrowing of blood vessels and a failure of metabolic processes. The blood stops receiving enough oxygen. As a result, all organs begin to experience oxygen deficiency - hypoxia .
The functionality of the entire body is impaired. Cells that are especially sensitive to the lack of oxygen die. Smoking poses a serious problem for pregnant women. Nicotine causes constriction of blood vessels in the placenta, endangering the baby's health. Pregnant women should be clear about the level of responsibility they have. If they smoke during the fetal development of the child, then he is highly likely to develop serious diseases.
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system
Smoking contributes to the rapid wear and aging of the cardiovascular system, the development of hypertension, coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, obliterating endarteritis, etc. Once in the blood, the toxic substances contained in tobacco smoke are carried through the tissues within 21- 23 seconds (time of complete blood circulation); those. almost instantly poison the entire body.
After smoking 2-3 cigarettes, small blood vessels go into a state of spasm, which lasts 20-30 minutes! For those who smoke a pack of cigarettes a day, the blood vessels are constantly in a state of spasm. As a result, the lumen of small arteries decreases, since nicotine causes a narrowing of blood vessels. As a result, the normal nutrition of many body tissues is disrupted.
When smoking, arteries lose their elasticity, become dense, brittle, and fragile. Over the years, the lumen of smokers' blood vessels narrows more and more, and this can end in disaster.
Constant spasm of blood vessels caused by smoking is a significant factor in the occurrence of hypertension, coronary heart disease and obliterating endarteritis. Under the influence of nicotine, brain vessels also wear out faster, their lumen narrows, and elasticity decreases. Blood flows in smaller quantities, which leads to impaired cerebral circulation and hemorrhages in the brain.
While smoking, the pulse increases by about 20 beats per minute, as the heart works under increased load. In this case, the function of the heart is impaired due to spasm of the small blood vessels that supply the heart muscle. As a result of spasm of the coronary vessels, smokers experience attacks of palpitations, pain in the heart area, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
The effect of nicotine on increasing blood pressure has been established. The general narrowing of blood vessels and high blood pressure lead to the fact that the number of smokers with hypertension is much greater than among non-smokers, especially in young and middle age. “Tobacco hypertension” leads to early “tobacco sclerosis” of blood vessels.
Smoking is an important cause of coronary heart disease, as it contributes to the development of the atherosclerotic process.
The main role in the mechanisms of development of coronary heart disease under the influence of smoking belongs to carbon monoxide. Nicotine causes an increase in blood pressure and heart rate, and carbon monoxide causes cardiac failure.
Cardiac vasospasm is the most common complication of smoking. The result of such a spasm can be a myocardial infarction - the death of a section of the heart muscle due to a violation of its nutrition. Death of a large area of the heart muscle leads to death. It is no coincidence that the mortality rate from myocardial infarction among smokers aged 40-50 years is 3 times higher than among those who do not smoke.
Smoking promotes earlier development of atherosclerosis, especially sclerosis of the coronary vessels of the heart, which can lead to angina pectoris (angina pectoris).
Smoking leads to vascular spasms, in particular of the coronary arteries of the heart, manifested by attacks of angina. Due to the development of coronary heart disease, angina pectoris occurs 2 times more often in smokers, and sudden death 4 times more often than in non-smokers.
If you stop smoking when angina attacks occur, the signs of the disease gradually disappear.
Nicotine also promotes fatty degeneration of the heart muscle, reducing the performance of the heart. Often with excessive smoking, dizziness and vomiting are observed, which are explained by spasm of cerebral vessels.
Smoking is the main cause of another very serious vascular disease of the lower extremities - intermittent claudication. This disease is associated with obliterating endarteritis of the arteries of the lower extremities, which can lead to gangrene (death) of the foot and leg and often require their amputation.
Passive smoking, which is the inhalation of smoke coming from a person's cigarette, is also harmful to the health of the heart and blood vessels, as it is also smoking to some extent. It has been proven that secondhand smoke contains almost all the chemical compounds that smokers inhale as a result of smoking. In some cases, secondhand smoke harms people even more than people who smoke and increases the risk of heart attack and death in adults.
Passive smoking is very harmful for children and adolescents, as it tends to increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease in the future. This is because inhaling cigarette smoke increases blood pressure and damages heart tissue, and also reduces levels of high-density lipoproteins, called “good cholesterol,” which reduces the risk of atherosclerosis.
The risk of secondhand smoke is especially high for premature babies who have respiratory distress syndrome, as well as children with asthma.
Cardiologists believe that quitting tobacco smoke is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of heart disease. You should not start smoking, but if this habit is already present, you need to give it up, regardless of your smoking history.
It is also important to avoid secondhand smoke. To do this, it is enough not to visit places where smoking is allowed, and also ask friends and family members not to smoke in the car or in the house.
Quitting smoking significantly reduces the possibility of developing heart disease, in some cases leading to death , reduces the risk of blood clots and the development of atherosclerosis, as well as the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, recurrent heart attack and death as a result of other chronic diseases.
Researchers studying heart disease and the impact of smoking on the development of heart disease have found that in countries that have banned smoking in public places and at work, the number of heart attacks has decreased significantly .
Scientists explain this fact as a result of a decrease in active and passive smoking.
How does nicotine affect blood vessels?
Experienced smokers claim that the process itself has undoubted benefits, since at the moment of inhaling, in addition to pleasure, they receive relief.
They observe:
Disappearance of pain in the heart and head.- Appearance of appetite.
- Normalization of the gastrointestinal tract.
With a more detailed study of the effect of nicotine on blood vessels, the improvement in the condition of heavy smokers becomes quite clear.
The mechanism of action of this substance includes 2 stages:
- Short-term, based on the activation of cholinergic receptors of the nervous system. Under their influence, the muscular wall of the arteries and especially the small network of arterioles relaxes. Against this background, the lumen of blood vessels increases and the heart rate slows down. Blood pressure decreases, and the person feels pleasantly relaxed and feels better. It is on this effect that the myth about the benefits of smoking is based.
- Phase of pathological changes. It begins against the background of excess production of neurotransmitters: adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine. Excessive amounts of these substances lead to increased heart rate, increased cardiac output, spasm of the vascular wall, narrowing of the lumen with a subsequent increase in blood pressure.
Description of the mechanism of action allows us to definitively answer the question of what is the effect of nicotine on blood vessels.
Cardiac ischemia
The combined effects of tobacco smoke and carbon monoxide cause aging of the arteries. They narrow, and as a result, the normal functioning of the heart is disrupted, which leads to the development of coronary artery disease, often progressing to myocardial infarction.
Myocardial infarction
Carbon monoxide prevents the transfer of oxygen from the blood to tissues, including the heart. At the same time, smoking leads to vasoconstriction, and blood transportation becomes even more difficult. If we add to this the fact that inhaled toxic substances from tobacco smoke increase blood clotting, thereby provoking the formation of blood clots, the risk of myocardial infarction increases 4-5 times (compared to non-smokers), and more often in young people, which is explained primarily early start of smoking. People under 40 years of age are most at risk in this regard.
Moreover, all this applies not only to active, but also to passive smoking.
The choice is yours…
Answer
- Victoria Rumyantseva
- Smoking
Features of blood circulation in the brain during smoking
The cells of the central nervous system are the most sensitive to thickened blood and low oxygen content.
Against this background, patients develop:
- Headache.
- Noise in ears.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Memory loss.
- Weakness and decreased performance.
All these signs are a consequence of hypertension and thrombotic complications.
Over time, symptoms intensify and patients develop:
- Transient cerebrovascular accidents.
- Strokes.
- Encephalopathy.
- Dementia.
Nicotine and blood vessels of the lower extremities
Regular smoking causes one of the most terrible complications - obliterating endarteritis . With this disease, persistent spasm of small arterioles develops, accompanied by impaired circulation in the tissues supplied by these vessels. Spasmodic attacks at the beginning of the disease are reversible. But over time, they become more frequent and lengthen until they become persistent. The toes are the first to be affected.
The disease manifests itself:
- Whitening of the skin, feeling of cold, tingling and numbness in the extremities.
- Pain and cramps during physical activity.
- Intermittent claudication with periodic stops to normalize blood circulation.
- Increasing fatigue.
Over time, atrophy and gangrene develop, requiring immediate amputation.
You can check the condition of your arteries yourself.
Sit cross-legged. If pain appears in the calf muscle of the upper leg, and there is numbness and “goosebumps” in the fingertips, it means that not all is well with you.
Raise both legs up - the sole of the one with damaged arteries will turn pale. If the skin on your legs has turned ivory, pain is felt not only in the lower leg, but also in the hips, buttocks and lower back, and you, along with other troubles, are at risk of impotence (Leriche syndrome).
How to prevent the effects of nicotine on blood vessels
Taking timely measures will help avoid problems in the future.
For circulatory disorders caused by tobacco smoke, you must:
- Immediately get rid of the painful habit.
- Do breathing exercises and exercises that restore normal blood flow.
- Regularly douse yourself with cold water or take a contrast shower.
- Provide yourself with a balanced diet high in vitamins.
Compliance with these simple rules will return blood vessels to health and patients to a normal life.
Varicose veins when smoking: what to do to avoid the development of the disease?
If you are not yet able to cope with a bad habit, but do not want to face the problem of varicose veins, you can use the following tips:
- Do not smoke after exercising, playing sports, having sexual intercourse, climbing stairs, or while walking. This way you can reduce the negative effects of nicotine on blood vessels.
- Women who smoke are not recommended to wear high-heeled shoes and tight-fitting trousers, as such clothing and shoes provoke the development of varicose veins.
- If you have a sedentary lifestyle (sedentary work, frequent car trips), it is recommended to perform at least a couple of exercises once every 2-3 hours to normalize blood circulation. Roll from your heels to your toes, while lying down, lift your legs up (exercise “birch tree”), alternately rotate your right and left legs, first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- During sleep, smokers are recommended to place a special orthopedic pillow under their lower limbs.
- Go swimming. This sport not only helps fight varicose veins, but also perfectly tones the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, the organs of which suffer the most from smoking.
Prevention of varicose veins when smoking
- If you already have signs of varicose veins caused by smoking, consult a phlebologist regarding the use of compression hosiery - tights, stockings, golf.
- Take a contrast shower. Alternating exposure to warm and cold water helps strengthen the blood vessels in the legs.
Contrast shower as a prevention of varicose veins when smoking
- Periodically perform self-massage of the lower extremities. However, it can only be done at the stage of formation of spider veins. If you have already developed varicose veins, it is not recommended to do massage yourself: it is better to trust a professional massage therapist in this matter (and only as prescribed by a phlebologist).
Methods for preventing varicose veins from smoking: self-massage
- If you are unable to give up smoking, at least try to say goodbye to other bad habits.
!
Reduce alcohol consumption, stay hydrated and eat right, focusing on foods that strengthen the vascular wall and prevent the development of varicose veins.
An excellent preventative measure that improves blood circulation and the condition of the vessels of the lower extremities with varicose veins is the use of Normaven® Leg Cream. It contains natural ingredients, the action of which is aimed at getting rid of the feeling of heaviness and fullness in the legs, reducing spider veins and generally improving the appearance of the legs. The active components of the product - chestnut extract, green tea, ginkgo biloba, lingonberry, arnica and wormwood, menthol, lemon oil, panthenol and vitamin complex - have a pronounced venotonic, antihypoxic and antioxidant effect.
Literature:
- Tobacco smoking: harm, ways to quit: recommendations for those who smoke and want to get rid of tobacco addiction / Ovchinnikov B.V., Dyakonov I.F., Zobnev V.M., Dyakonova T.I.; under general ed. V. K. Shamrey. - St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2012. – 45 p.
- Fundamentals of medical knowledge: textbook. manual for pedagogical students. universities: textbook. manual for university students / O. G. Gureeva and others; Ministry of Education and Science of Russia. Federation, Omsk. state ped. univ. - Omsk: Omsk State Pedagogical University Publishing House, 2004. - 255 p.
- Bad habits and their prevention: textbook / comp. Gorskaya I.Yu., comp. Gubareva N.V. - Omsk: Publishing house SibGUFK, 2010. - 212 p.
Modern means of combating nicotine addiction
In developed countries, every year half of smokers try to quit their bad habit, but only 2% of them succeed. This low success rate is due to the fact that smokers usually decide to quit suddenly and try to do it without resorting to auxiliary means.
The most popular way to treat nicotine addiction is nicotine replacement therapy (NRT). It is based on the idea that taking nicotine in controlled and constantly decreasing doses will ultimately lead to recovery from addiction. The first NRT drug was nicotine chewing gum released in 1971 by the Swedish company Nicorette. Today, pharmacies sell dozens of drugs from different companies based on the “wedge by wedge” principle: nicotine patches, inhalers, lollipops, sprays and, of course, chewing gum. A number of studies have shown that NRT is twice as effective as placebo [20] and could help an additional three percent of smokers quit.
Much less known are other, sometimes much more effective, anti-smoking medications.
One such drug is cytisine, a broom alkaloid. This plant has been known in traditional medicine for centuries, and during World War II, people began to consider it as a substitute for tobacco. Cytisine appeared on the market even earlier than nicotine chewing gum - in 1964 it began to be produced in Bulgaria under the Tabex brand.
Cytisine, like nicotine, can bind to nicotinic receptors in the brain. But, firstly, it binds to them more tightly, that is, it does not allow nicotine to approach them, and secondly, it activates them weaker. Thus, cytisine interferes with the reinforcement of addiction, even if the person continues to consume nicotine. If a person has stopped smoking and experiences discomfort, then cytisine stimulates the pleasure center enough to eliminate withdrawal symptoms, but not enough to form a new addiction.
This drug is not widely used outside Central and Eastern Europe [21]. According to 2011 data, cytisine is 3.5 times more effective than nicotine replacement therapy drugs [22]. However, it is worth considering that in general less research has been carried out on cytisine than on other drugs, which actually hinders its spread throughout the world.
Varenicline, a drug from the largest pharmaceutical corporation Pfizer, produced since 2006, has a similar mechanism of action. Varenicline has undergone rigorous clinical trials and is sold worldwide. Its effectiveness during long-term therapy is slightly greater than that of NRT, while the drug itself is noticeably more expensive than nicotine gum and cytisine [23].
Another common treatment for nicotine addiction is bupropion. This drug has been produced since 1989 and is positioned primarily as an antidepressant. Its ability to make smoking cessation easier is only a side effect: bupropion binds to nicotinic receptors in the brain, but does not activate them. The effectiveness of this substance is comparable to nicotine replacement therapy [24].
Figure 3. Nicotine is chemically similar to acetylcholine (one of the substances that transmit nerve impulses between neurons) and imitates its action. Modern medications for nicotine addiction are structurally similar to nicotine, but have a different effect on the nicotinic receptors of neurons, easing withdrawal symptoms.
The action of all the described drugs is based on the binding of nicotinic receptors in the brain. In recent years, there has been active development of a fundamentally different approach to the treatment of nicotine addiction - nicotine vaccination.
As with conventional vaccination, this therapy produces antibodies in the patient's body. Antibodies bind nicotine, thereby preventing it from entering the brain and depriving it of physiological activity.
Vaccines of this kind can help not only against nicotine, but also against any other chemical addiction (except alcohol). The body typically does not produce antibodies against small molecules of psychoactive substances, so vaccines combine these molecules with larger proteins that trigger an immune response.
There have already been successful trials of nicotine, methamphetamine, cocaine and opiate vaccines. With vaccination, the side effects of treatment are much weaker, and the effect is more stable than with drug therapy. But there are also disadvantages: vaccination has no effect at all on a quarter of addicts. In addition, anti-nicotine vaccination can be frightening due to its duration: the course consists of 4-5 injections over three months [25].
Recently, the genetic approach to the study of nicotine addiction has become extremely popular. Thanks to massive research into the genome of smokers, thousands of mutations have already been identified that affect the likelihood of starting or quitting smoking and determining the severity of nicotine addiction. The data obtained can help in the creation of new tools for quitting smoking or help select the most effective of those already available [26].