Becoming a mother and having a healthy child is a great happiness! However, complications during pregnancy can occur in any woman, even a completely healthy woman. That’s why it’s so important to see a good specialist from the earliest stages of pregnancy (see pregnancy management).
The following complications of pregnancy are distinguished:
- toxicosis;
- gestosis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- miscarriage (spontaneous abortion);
- frozen (non-developing pregnancy).
1
Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
2 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
3 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
Toxicoses
Toxicosis occurs in the first half of the term and is manifested by dyspeptic disorders and disorders of all types of metabolism.
In almost 90% of cases, early toxicosis in the first half of pregnancy is manifested by nausea and vomiting. If pregnancy is proceeding normally, then nausea or vomiting may occur no more than 2-3 times during the morning, more often on an empty stomach. These disorders do not require treatment and should go away on their own after 12-13 weeks.
Toxicosis is a condition in which nausea and vomiting occur at any time of the day, regardless of meals, and are accompanied by decreased appetite, exhaustion, weakness and weight loss.
How does capillary toxicosis manifest itself?
The symptoms of this disease are quite varied, and generally there is a predominance of one or more syndromes. The disease always has an acute onset with an increase in body temperature.
Abdominal pain is a common accompanying symptom of the disease.
The following syndromes may occur:
Cutaneous
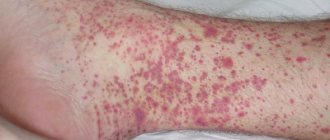
– occurs in absolutely all patients and manifests itself in the initial period of the disease. In this case, maculopapular hemorrhagic elements of different sizes form on the skin, which do not disappear with pressure. Sometimes a urticarial rash may be noticed. The rashes are located symmetrically, in the lower part of the legs, on the thighs and buttocks, near large joints, and sometimes on the arms and torso. Often the abundance of the rash is associated with the severity of the disease. If the degree is severe, necrosis is observed in the center of the rash element, followed by the formation of an ulcer. During the period of resolution, the rash ends in hyperpigmentation, which persists for a long time.
Articular
– occurs in 65-80% of patients. The lesions may be short-term in nature, such as minor arthralgia, or persist for a couple of days with severe pain, swelling, redness and disturbances of movement in the affected joints, characteristic of arthritis. The knee and ankle joints are usually affected. This syndrome occurs regardless of the time that has passed since the onset of the disease, has a transient nature and does not cause joint deformation.
Abdominal
– sometimes precedes or accompanies skin and joint manifestations. Abdominal pain occurs, varying in intensity. Sometimes patients are unable to indicate a specific location of pain. Nausea and vomiting, stool disturbances occur. Pain can occur several times a day and go away on its own, or disappear on the first day after treatment. In more severe cases, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting with blood, and diarrhea mixed with blood may occur.
Renal
– the least common and occurs in less than 30% of patients. Accompanied by symptoms of glomerulonephritis and hematuria of varying degrees, some patients experience nephrotic syndrome. Although rare, kidney damage is the most persistent symptom of capillary toxicosis and can cause renal failure.
Symptoms associated with damage to other organs are practically non-existent. However, if they occur, these include myocarditis, hemorrhagic pericarditis, shortness of breath, cough with blood streaks, dizziness, headache, hemorrhagic stroke.
After the rash heals, areas of hyperpigmentation remain on the skin for some time.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia develops in the second half of pregnancy (after 20 weeks) and poses a great danger not only to the pregnancy itself, but also to the health of the woman and her child. Typically, gestosis is manifested by the occurrence of edema (hydropsis of the pregnant woman).
The next stage of gestosis - preeclampsia - is accompanied by increased blood pressure and the appearance of protein in the urine. This indicates changes in the biochemical composition of the blood, deterioration of blood circulation in the capillaries and small vessels (and in the placenta too). As gestosis progresses, eclampsia may occur with a critical decrease in cerebral circulation, cerebral ischemia and cytotoxic cerebral edema. Convulsions appear and coma is possible.
Preeclampsia ranks third among the causes of death in pregnant women, perinatal mortality with preeclampsia is 18-30%.
Therefore, it is so important for all pregnant women to be observed by an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist, who can promptly detect and prevent such complications during pregnancy.
About hemorrhagic vasculitis and its causes
Henoch-Schönlein disease is one of the most common hemorrhagic pathologies today. In general, it is allergic in nature, but with damage to capillaries, small venules and arterioles.
In children it can be found between the ages of 4 and 14 years, and the average number of sick children varies between 25 people per 10 thousand.
Causes that have a provoking effect include:
- viral diseases;
- bacterial diseases;
- parasites;
- vaccination;
- the presence of drug or nutritional allergies;
- hypothermia.
Pathology can be provoked even by a banal ARVI
Many authors of medical works emphasize that the development of hemorrhagic vasculitis under the influence of specific causes is possible only in the presence of a genetic predisposition. The mechanism of development of capillary toxicosis lies in the formation of immune complexes.
During circulation in the blood, they are deposited on the internal surfaces of the walls of small vessels and their subsequent damage, accompanied by an aseptic inflammatory process. When the walls become inflamed, their permeability increases and fibrin and thrombotic masses are deposited in the lumen of the vessel.
It is these processes that hemorrhagic vasculitis owes its main pathological symptoms - microthrombosis and hemorrhagic syndrome.
Capillary toxicosis can have different sizes
Ectopic pregnancy
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fetus does not develop in the uterus, but in the cervical canal, fallopian tube, abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Normally, when an egg leaves the ovary, it enters the opening of the fallopian tube. Moving with the help of special cilia that cover the fallopian tube, after a few days the egg reaches the uterus. In normal cases, the process of fertilization of the egg occurs in the tube, then the cell appears in the uterus.
In the case of infectious obstruction of the tube or other pathology, the egg freezes in place or moves very slowly, never having time to reach the uterus. This is how an ectopic pregnancy occurs.
A blood test for hCG helps in establishing the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy.
HCG is human chorionic gonadotropin. HCG contains alpha and beta units. Using blood tests to detect an increase in hCG levels, the presence of pregnancy can be accurately determined. So, during a normal pregnancy, the hCG level increases by 65% every two days. But with an ectopic pregnancy, this dynamics is not obvious.
In a normal pregnancy, hCG rises until the 10th week, then begins to decline. Stopping the increase in hCG levels may be a consequence of a missed or undeveloped pregnancy.
Methods for diagnosing capillary toxicosis
If you suspect hemorrhagic vasculitis, you should consult a rheumatologist. At the appointment, age is taken into account, anamnesis is collected, indicators of clinical and laboratory research methods are studied, and the presence of other diseases is excluded.
In the CBC of patients with hemorrhagic vasculitis, leukocytosis and a slight increase in ESR, increased platelet and eosinophil content can be observed.
In addition to OAC, the following studies are prescribed:
- OAM;
- coagulogram;
- biochemical urine analysis;
- Zimnitsky's test;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- gastroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- stool occult blood test;
- skin biopsy.
The price of blood and urine tests in general is not high and allows you to provide the doctor with accurate data if you contact a medical facility in a timely manner. In addition, differential diagnosis is carried out with leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic vasculitis, Still's disease, acute glomerulonephritis and thrombocytopenic purpura.
Blood tests are necessary for an accurate diagnosis
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy, independent of the woman’s will, at up to 22 weeks. The phenomenon is quite common. Every fifth pregnancy in women can end in spontaneous miscarriage.
The symptoms of miscarriage in the early stages (6-8 weeks) may not be very noticeable. There may be a delay in menstruation, a change in the nature of bleeding during menstruation, and moderate lower back pain. According to statistics, about 80% of all miscarriages occur before 12 weeks.
A miscarriage in late pregnancy is accompanied by symptoms such as nagging pain in the lower back, abdomen and sacral area, brown or scarlet spotting from the vagina. If treatment is not carried out, then the detachment of the fruiting body from the wall of the uterus and its expulsion begins. In this case, bleeding may increase and intense cramping pain may occur. A miscarriage can result in the release of the entire fruiting body or its parts getting stuck in the uterus (in such a case, medical intervention will be required).
A recurrent miscarriage is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy (up to 22 weeks), which is repeated with each pregnancy.
If a woman has had 2 or more spontaneous miscarriages, doctors can diagnose “recurrent miscarriage.”
1 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
2 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
3 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
Types of capillarotoxicosis
In the clinical development of the disease, there is an acute phase (onset of the disease or exacerbation) and a subsiding phase (period of improvement).
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, the doctor may classify one of the forms:
- simple;
- articular;
- abdominal;
- lightning fast.
In addition, the disease can occur in acute (about 2 months), protracted (up to 6 months) and chronic forms. In addition to its forms, Henoch-Schönlein disease has certain degrees of severity that affect the course of the disease.
- Mild degree. In this case, the patient's condition is satisfactory, the rash is not profuse, and arthralgia is observed.
- Average degree. The condition is defined as moderate severity, the rash is profuse, arthralgia is accompanied by changes in the joints like arthritis, periodic pain in the abdomen and microhematuria occur.
- Severe degree. The condition is severe, the rash is significantly widespread, with areas of necrosis. Nephrotic syndrome, angioedema, gross hematuria, gastrointestinal bleeding, and in some cases acute renal failure are observed.
Important! Despite the fact that the disease in childhood occurs in children aged 4-5 years and older, there are cases of capillary toxicosis in younger children. Therefore, it is important to take any rash in your child seriously.
The disease has several degrees of severity
Premature birth
Preterm labor is the onset of labor before 37 weeks. Premature birth can occur suddenly or follow an existing threat of miscarriage.
The process can begin with uterine hypertonicity, isolated contractions and moderate abdominal pain. Another scenario is rupture of the membranes and rupture of amniotic fluid. Sometimes premature labor can begin with bleeding. This happens with placenta previa or placenta abruption.
In any case, urgent hospitalization of the pregnant woman is necessary, in which all necessary measures will be taken to maintain the pregnancy.
In case of critical placental abruption and rupture of the amniotic sac, emergency delivery may be performed.
Frozen pregnancy
Frozen pregnancy (or non-developing pregnancy) is one of the types of miscarriage. We can talk about miscarriage in situations where the beginning of pregnancy complied with all medical standards, and then there was a complete stop in the development of the fetus and its death.
In addition, pregnancy failure can occur in the case of successful conception, when the egg is fertilized and has time to attach to the uterus, in the complete absence of embryo development. This is called an “empty fertilized sac” - all extra-embryonic organs are formed, but the embryo is missing from the egg.
Quite often, a non-developing pregnancy is diagnosed in the early stages of pregnancy.
Signs of a non-developing pregnancy may be erased. More often, scanty blood discharge from the genital tract occurs with or without nagging pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, an ultrasound scan is necessary. With a fertilized egg size of 20 mm, an embryo with a heartbeat should be visualized. If the period is shorter and the average internal diameter of the ovum is less than 20 mm, and there is no pain, then the doctor prescribes a control ultrasound after 7-10 days (based on the results of the study, the diagnosis of a non-developing or frozen pregnancy is finally established or refuted).
1 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
2 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
3 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
Causes of miscarriage
The reasons for a non-developing pregnancy in the early stages are quite similar to the general situation when a woman cannot bear a child.
There are many reasons why a pregnant woman may lose her baby:
- the presence of infectious diseases (bacterial, fungal and viral diseases lead to inflammation of the endometrium, and this prevents the fetus from gaining a foothold in the uterus and developing);
- sexually transmitted infections (herpes, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia);
- endocrine diseases, which can lead to hormonal imbalance and, as a result, miscarriage;
- mental, physical and emotional exhaustion;
- lack of female hormones, such as progesterone, which can lead to termination of pregnancy;
- chromosomal and other fetal abnormalities;
- congenital and acquired pathology of the uterus (for example, as a result of abortions and miscarriages in the past);
- Rh conflict (a negative Rh factor in the mother and a positive Rh factor in the father can lead to a conflict of antibodies, as a result of which the mother’s body perceives the fetus as a foreign body and tries to push it out of the body);
- the presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman (smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs, which leads to intoxication of the body;
- unfavorable environmental conditions, radiation.
1 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
2 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
3 Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
Early toxicosis in pregnant women: treatment options
Until now, a unified understanding of the etiology and pathogenesis of toxicosis has not been formed. Only one etiological point is not discussed - the presence of pregnancy (fertilized egg). There are many theories explaining the mechanism of development of early toxicosis: reflex, neurogenic, hormonal, allergic, immune, corticovisceral. In the pathogenesis of early toxicosis, a leading role is played by disruption of the functional state of the central nervous system. In the early stages of pregnancy, symptoms of early toxicosis are manifested by gastrointestinal dysfunction. Food reflexes are associated with the autonomic centers of the diencephalic region of the brain. Afferent signals arriving in this area from peripheral receptors may be perverted in nature (either due to changes in the uterine receptors or in the pathways); disturbances are also possible in the centers of the diencephalic region themselves, which can affect the nature of the response efferent impulses. When the sensitivity of the diencephalic region is impaired, changes in reflex reactions and disturbances in nutritional functions quickly occur: loss of appetite, nausea, salivation (salivation), vomiting [1].
There are common (nausea and vomiting of pregnant women, dizziness, drooling) and rare forms of early toxicosis (dermatoses of pregnancy, tetany, osteomalacia, bronchial asthma of pregnant women).
Vomiting of pregnancy (emesis gravidarum) occurs in approximately 50–60% of pregnant women, but no more than 8–10% of them require treatment. The earlier vomiting during pregnancy occurs, the more severe it is. Depending on the severity of vomiting, three degrees of severity are distinguished: I - mild, II - moderate and III - severe.
With stage I vomiting of pregnancy, the general condition of the patient remains satisfactory. Vomiting is observed up to 5 times a day, often after meals, sometimes on an empty stomach. This reduces appetite and depresses the mood of a pregnant woman. The patient loses no more than 3 kg in weight, body temperature remains within normal limits. The humidity of the skin and mucous membranes remains normal, the pulse rate does not exceed 80 beats/min. Blood pressure does not change. Clinical urine and blood tests showed no pathological changes.
In degree II, the woman’s general condition is noticeably impaired: vomiting is observed from 6 to 10 times a day and is no longer associated with food intake, body weight loss ranges from 2 to 3 kg in 1.5–2 weeks. Possible low-grade fever. The moisture content of the skin and mucous membranes remains normal. Tachycardia - up to 90–100 beats/min. Blood pressure may be slightly reduced. Acetonuria is observed in 20–50% of patients.
With grade III severity (excessive vomiting), the woman’s general condition deteriorates sharply. Vomiting occurs up to 20–25 times a day, sometimes with any movement of the patient. Sleep is disturbed and adynamia develops. Body weight loss reaches up to 8–10 kg. The skin and mucous membranes become dry, the tongue is coated. Body temperature rises (37.2–37.5 °C). Tachycardia - up to 110–120 beats/min, blood pressure decreases. Pregnant women do not retain food or water, which leads to dehydration and metabolic changes. All types of metabolism are disrupted. Daily diuresis is reduced, acetonuria, and often protein and casts in the urine are observed. Sometimes the hemoglobin content in the blood increases, which is associated with dehydration. A biochemical blood test reveals hypo- and dysproteinemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and increased creatinine.
The main symptoms characterizing the severity of vomiting are presented in the table.
Manifestations of early toxicosis in pregnant women must be differentiated from a number of diseases in which vomiting is also observed (foodborne toxic infection, gastritis, pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, stomach cancer, neuroinfection, etc.).
Ptyalism (salivation) is a very common symptom of early toxicosis. Saliva loss reaches 1 liter per day. Ptyalism is characterized by dehydration and hypoproteinemia. The disorder is accompanied by a depressed mental state. The pathogenesis factors are the same as for vomiting during pregnancy. Drooling can occur either with vomiting during pregnancy or on its own. Daily salivation can reach 1 liter or more. With severe salivation, maceration of the skin and mucous membranes of the lips occurs, appetite decreases, and health worsens. The pregnant woman is losing weight and sleep is disturbed.
Treatment of mild to moderate symptoms of early toxicosis in pregnant women is carried out on an outpatient basis. Treatment of severe, uncontrollable vomiting may require hospitalization.
Standard approaches to the treatment of symptoms of early toxicosis. Rational nutrition for pregnant women is of great importance in treatment. Food should be varied, easily digestible, and contain a large amount of vitamins. It should be taken chilled, in small portions every 2-3 hours while lying down. Mineral non-carbonated alkaline water is indicated in small volumes 5-6 times a day. Drug therapy includes the prescription of antiemetics (Cerukal, Torekan, etc.), herbal mixtures and herbal infusions, artichoke extract (Hofitol), multivitamins, antihistamines (Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine), B vitamins, Droperidol, etc.
When prescribing therapy, the following must be taken into account: a) possible harmful effects on the developing fetus; b) side effects when using drugs that require subsequent corrective therapy. Often in the pharmacotherapy of a pregnant woman, what is important is not the high efficiency, but the greatest safety of the drug for the pregnant woman and the fetus.
In recent years, homeopathic treatment methods have become especially popular and the pharmaceutical market has been replenished with various homeopathic drugs. Efficiency, safety, absence of side effects, high compliance, financial accessibility, and the possibility of combining with allopathic medicines make homeopathic medicines indispensable for use in children, pregnant women, the elderly, and patients prone to allergic reactions. The popularity of homeopathy continues to grow rapidly both among patients and among doctors, although homeopaths in both Russia and the West still face distrust in their activities.
We have studied the effectiveness of the homeopathic drug Cocculin in patients suffering from early toxicosis of pregnancy. The drug Cocculin, produced in France since 1969, has established itself as a highly effective remedy against kinetosis (motion sickness). The drug contains several homeopathic components: Cocculus Indicus, Nux Vomica, Tabacum Nicotiana and Petroleum. Being an exclusively homeopathic remedy, Cocculin does not have sedative activity: it does not cause daytime drowsiness, does not reduce activity and performance. Cocculin has no contraindications, so adults, children, pregnant women, and the elderly can take it. The drug is compatible with any other medications. In particular, Cocculin does not enhance the effect of hypnotics and sedatives [2].
Total in medical in 2006–2007. Cocculin was prescribed as monotherapy to 98 patients with early toxicosis (mild to moderate severity). Patients filled out questionnaires that indicated the severity of the main clinical symptoms of toxicosis (hypersalivation, nausea, vomiting in the morning, vomiting after eating, loss of appetite, changes in taste sensations). The patients took Cocculin 2 tablets 3 times a day for a week, assessing the dynamics of toxicosis. If the effect was absent or insignificant, the drug was discontinued and standard treatment with antiemetics (metoclopramide, etc.) was prescribed. The degree of toxicosis intensity was assessed in points (from 0 to 3). When analyzing the questionnaires received from patients, it was revealed that in 27% of patients the symptoms of toxicosis completely ceased, and in another 31 (32%) there was a significant improvement. 29 (30%) patients indicated a lack of clinical effect. In 11 patients, progression of disease symptoms was observed during treatment with Cocculin. In general, the treatment was well tolerated. No side effects were observed. 9 out of 11 patients whose condition worsened during treatment suffered from early toxicosis of moderate severity.
The comparison group included 103 patients with early toxicosis who received standard treatment - metoclopramide (Cerucal), artichoke extract (Hofitol), herbal remedies, etc. A retrospective analysis of outpatient records revealed that in 24% of patients the symptoms of toxicosis ceased, in 36% - improvement in condition was noted. 18 patients in this group were hospitalized in the hospital due to worsening of the disease.
In general, the effectiveness of Cocculin was comparable to standard methods.
Most patients who noted the good effect of Cocculin continued to take it independently throughout the first trimester.
The data obtained confirm the possibility of using the complex homeopathic drug Cocculin as a starting monotherapy for early toxicosis in pregnant women.
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
Literature
- Kharkevich O. N., Kanus I. I., Buyanova A. N., Malevich Yu. K., Mukhachev B. V. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of gestosis. Minsk, 2001.
- Zamergrad M. E. Motion sickness // Difficult patient. 2006. No. 4. pp.31–34.
O. P. Dubskaya L. A. Bondarenko G. A. Chernykh Medical, Moscow region
Diagnosis of complications during pregnancy
Diagnosis of pregnancy or its complications begins with a visit to a gynecologist. The doctor pays attention to the woman’s complaints, which include weakness, malaise, delayed menstruation, the appearance of toxicosis, engorgement of the mammary glands, etc.
A home test for determining pregnancy based on the level of the hCG hormone in the urine is indicative (a study of the morning urine sample is especially informative).
A gynecological examination can reveal an enlarged uterus and other signs of pregnancy.
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs up to 10-11 weeks of pregnancy is carried out in cases where the attending physician needs to determine the location of pregnancy (uterine or ectopic) or exclude a frozen pregnancy.
Then tests are prescribed to determine the level of hCG in the blood, blood and urine tests for infections such as herpes simplex virus and type 2, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, etc.
To prevent pregnancy complications, consultations are held with related specialists: ophthalmologist, therapist, ENT doctor, dentist, etc.