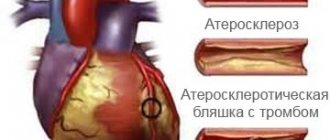
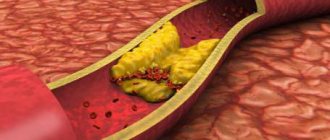
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of narrowing of the arteries, leading to oxygen starvation (ischemia) of tissues. If the arteries of the heart (coronary arteries) are affected by atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease develops. When the cerebral vessels are damaged, coronary artery disease occurs, and when the arteries supplying the lower extremities are damaged, the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted, leading to gangrene. Bypass surgery is considered a radical treatment for coronary artery disease. The operation is associated with major surgical trauma (anesthesia, opening of the chest, artificial circulation, postoperative resuscitation) and a long period of rehabilitation.
The team of cardiovascular surgeons and cardiologists at our clinic can offer a complete alternative to surgery - minimally invasive treatment - angioplasty and stenting of narrowed arteries:
- without anesthesia,
- without opening the chest,
- through a small puncture on the wrist.
The duration of stenting is determined by the condition of the patient’s vessels (presence of calcium in plaques, anatomical features) and the complexity of the intervention. On average, angioplasty lasts about 40 minutes. After stent implantation, the patient is under the supervision of a cardiologist for 24 hours and, as a rule, is discharged the next day. Thus, hospitalization in a hospital for angioplasty usually takes 1-2 days.
What is angioplasty
With atherosclerosis, dense plaques of cholesterol form on the walls of the arteries of the lower extremities. They block and narrow the lumen, disrupt the blood supply to the legs, leading to complications: oxygen starvation of tissues, brain, heart muscle, necrosis, trophic ulcers.
The main signs of the disease at stages 3–4 (“critical ischemia”):
- aching or sharp pain in the leg when walking and physical activity;
- numbness, tingling in the calves;
- pale skin;
- reduction of the fat layer, muscle fiber atrophy;
- excessive hair loss;
- change in the shape of nails, keratinization on the heels and toes;
- the appearance of non-healing ulcers.
Surgical angioplasty is a minimally invasive operation that restores the lumen of a damaged vessel. The method is endovascular and does not require long-term hospitalization of the patient in a hospital. Cardiac surgeons have developed several methods to normalize blood flow without painful incisions.
Carotid angioplasty
Angioplasty with stenting of the carotid arteries is one of the most promising and complex areas in endovascular surgery to restore blood supply to the brain.
Surgery of the carotid arteries is indicated when the carotid arteries are narrowed by 60% or more in the presence of symptoms such as transient ischemic attacks, syncope, or a previous stroke. If the carotid arteries are narrowed by more than 70%, even in the absence of obvious symptoms, surgical treatment is indicated.
Indications for angioplasty
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities often develops in old age due to diabetes, obesity, smoking or poor nutrition. At stages 3 and 4, diabetic foot and dry gangrene often develop due to reduced blood flow. The situation requires urgent care, surgery or even amputation.
Main indications for endovascular surgery:
- narrowing of the vascular bed (stenosis);
- severe swelling;
- anemic condition;
- atherosclerotic lesion of the iliac artery;
- leg cramps;
- trophic ulcers.
Indication for stent installation is a narrowing of the lumen by 75%, a high risk of amputation of the foot due to gangrene. After this procedure, in 95% of cases, the healing of trophic ulcers is accelerated, the blood supply to the muscles is normalized, and tension pain disappears.
Why do they trust us and choose the CELT clinic?
- Our clinic is an expert level of cardiovascular surgery at the level of the best cardiology clinics in Europe and the world. Cardiology and cardiovascular surgery are one of the key areas of CELT.
- We have in stock almost all stents currently available on the market in Russia.
- Highly qualified doctors have more than 20 years of experience in performing endovascular operations of varying severity.
- Our specialists were the first to implant a stent in Russia - in 1993, and for a long time they were evangelists of endovascular surgery in our country, consistently proving to the cardiological community the advantages of stenting over coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for a wide range of indications. This is now a generally accepted fact. Most cardiovascular surgeries in Russia, as well as throughout the world, are performed using endovascular techniques.
- Many of our patients choose CELT for angioplasty and stenting operations as an alternative to treatment in Germany, Israel or the USA, not only because of the cost, which is several times lower, but also because of higher quality. It's hard to believe, but it's true!
- We perform operations even on those patients who, due to the severity of their condition, were denied coronary artery bypass grafting.
Method of operation
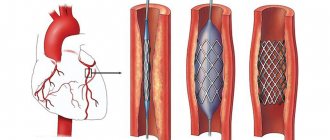
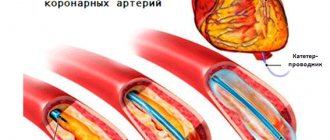
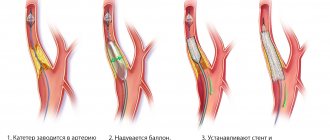
The official name of the method is percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty, or stenting. During the operation, a special device with a miniature balloon is inserted into a vessel affected by atherosclerosis through a thin catheter. Under pressure, air enters it, the stent expands, increasing the lumen.
After inflating the balloon, the surgeon carefully removes the catheter, leaving the stent securely in place in the artery. The procedure does not remove atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels, but reduces the risk of new deposits in the operated areas. The speed and volume of blood flow increases, nutrition of soft tissues, bones, and leg joints is restored.
Stenting of the lower extremities is carried out in a minimally invasive way: the surgeon makes punctures on the skin no more than 1 cm in diameter in the groin area. The catheter easily passes through the iliac artery through the thigh to the lower leg. At the same time, using diagnostic equipment, the patient’s condition and the location of the stent are monitored.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, which is important for older people. The patient does not experience pain or discomfort and recovers quickly after the end of stenting.
Treatment in the Department of Vascular Surgery
Vascular pathologies primarily affect parts of the body located furthest from the power source - that is, the heart. For this reason, the vast majority of vascular lesions occur in the lower extremities.
A responsible patient should contact vascular surgeons and phlebologists when symptoms of the disease are first detected. Long-term obliterating and occlusive lesions of veins or arteries are fraught with severe complications, including loss of limbs and forced immobilization with disability.
Complex treatment of the lower extremities in the department of vascular surgery includes:
- Carrying out planned or emergency surgical intervention for various purposes (dissolution of blood clots, removal of atherosclerotic plaques, artificial dilation of the lumens of blood vessels, replacement of the affected vessel, etc.);
- Conservative (medicinal) treatment with the aim of accelerating the patient’s recovery after surgery, as well as preventing further complications and / or relapses;
- Rehabilitation measures (selection of current physical procedures);
- Dynamic monitoring of the patient's condition.
Modern vascular surgery offers patients a variety of minimally invasive and atraumatic techniques that are equal or superior in effectiveness to full-fledged outdated operations.
Main types of angioplasty
Depending on the symptoms and degree of damage to the large arteries, an effective and safe surgical method for humans is selected:
- Transluminal angioplasty - a special balloon is used that is inflated, preventing stenosis. It compresses the plaques on the walls, but after removal there remains a risk of relapse.
- Stenting – a metal structure in the form of a spring creates a strong frame and prevents the artery from decreasing in diameter. After removing the balloon, the stent remains fixed and blocks the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques. The shape and size of the device are selected individually.
- Laser angioplasty is the newest method in which a quartz thread is inserted into the vessel. Laser beams act on the skin through the skin and increase the temperature, melting cholesterol deposits.
For atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, stenting is most effective. During physical activity, the device supports blood vessels from the inside, controls stretching, blood pressure, and removes swelling in the ankles and cramps in the legs.
Types of angioplastic stenting of the lower extremities:
- Reconstruction of an artery in case of complete blockage by atherosclerotic plaques, installation of an artificial vessel. It starts the blood flow bypassing the affected area.
- An operation to strengthen the stretched artery wall. The stent forms a mesh that restores firmness and elasticity, prevents stenosis, spasms, and thrombosis.
- Standard balloon angioplasty of the iliac artery.
- Administration of drugs simultaneously with the stent for the treatment of atherosclerosis, inflammation, systemic lupus.
When choosing a method, the patient’s age, the presence of contraindications, and general health are taken into account.
Risk groups and concomitant diseases for atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities:
- male gender (distribution of disease: 85% men, 15% women);
- age 50 years and older, although the disease is getting younger;
- hereditary factor;
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- high cholesterol (infatuation with fatty foods);
Signs (symptoms) and stages of the disease
The main symptom signaling the onset of blockage of the arteries of the lower extremities is the so-called “intermittent claudication.”
When walking, pain appears in the muscles of the legs, which is characterized as “fettering”, “squeezing”, the leg seems to “go wooden”. The pain intensifies when running or climbing stairs. The location of the pain zones depends on the location of the compressed (affected) areas of the arteries. The most common pain is in the calf muscles. But pain can also occur in the muscles of the thighs and buttocks, which indicates damage to large arteries: the iliac, abdominal aorta. The extent to which circulation is impaired can be understood by the distance that the patient travels before the first attacks of pain appear.
Stages 1 and 2 : pain in the lower extremities after 500-1000 meters of walking, the toes go numb, the leg is cold, the skin of the lower leg and foot turns pale.
Stage 3 : pain occurs when walking short distances, up to 100 meters, hair loss on the lower leg, foot and toes, the skin acquires a purplish-bluish tint, wounds heal poorly, nail growth slows down, and deformation occurs.
Stage 4 : the legs hurt at rest, in a horizontal position, the pain temporarily subsides when lowering the legs down, then intensifies. Necrosis and tissue necrosis begin, non-healing trophic ulcers appear. Men experience impotence.
Stage 5 : gangrene of the leg develops, starting from the foot. Only surgical intervention and limb amputation can help save the patient’s life.
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities occurring against the background of diabetes mellitus is especially dangerous. The disease progresses rapidly and leads to necrotic lesions and gangrene in just a matter of days and even hours.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities in our Center
Only comprehensive diagnostics using modern diagnostic systems provides reliable information on what stage of the disease the patient is at and what forms and methods of treatment will be most effective.
During the initial free consultation, the patient is interviewed and examined, complaints are listened to, visible changes in the skin are noted, and lesions are identified.
Further diagnosis of arteries is carried out using non-invasive painless methods: ultrasound scanning (ultrasound duplex scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities).
The walls of blood vessels are examined and assessed by a specialist, the speed of blood flow is established, and obstacles that disrupt healthy circulation are identified.
In severe forms of the disease, tests and additional diagnostic methods are prescribed (CT angiography of leg vessels, measurement of partial pressure of oxygen in tissues) in order to assess the patient’s condition in detail before surgery.
Modern treatment of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
In the initial stages, it is possible to combine the use of medications and the use of physiotherapy, which includes a set of exercise therapy exercises and dosed (short) walking.
If there is a slight partial narrowing of the artery section, stenting is used: the affected artery is punctured, a catheter with a stent is inserted, which, using a compressed air cylinder, opens, expanding the narrow section and is fixed, thereby restoring blood circulation.
In case of serious disruption of blood flow, when the blocked areas of the vessels are prolonged, surgical methods are used to restore blood circulation:
- prosthetics or bypass surgery with a synthetic prosthesis (alloprosthesis);
- prosthetics or bypass with an autologous vein: using your own vein, a bridge is created, a bypass from the proximal to the distal end, that is, bypassing the blocked area;
Profundoplasty is a surgical correction effective in terms of clinical results, which is performed for patients with occlusion of the superficial femoral artery and stenosis of the deep femoral artery with chronic ischemia of the lower extremities of severe stages. For this, endarterectomy from the deep femoral artery and angioplasty with a patch are used, which can be the patient’s vein or artery or special artificial synthetic substitutes. Today, profundoplasty is a method with highly proven effectiveness, which can be used to reduce the degree of ischemia and reduce the risk of limb amputation.
What to do for atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
The first thing you need to know. Atherosclerosis is not a death sentence. Despite the fact that the vessels cannot be restored to their original form, with timely access to a vascular surgeon, the patient has every chance to continue to live and work fully. But even with serious changes and lost time, there are great hopes for the successful finalization of the process, which consists of preserving the lower extremities while following the doctor’s simple recommendations in the postoperative period. In our clinic, qualified vascular surgeons literally rescue people from the other world who were rejected by other medical institutions. We urge you not to be indifferent to your health, get free consultation, and, if necessary, stop atherosclerosis using modern methods of vascular surgery. Your operation can be performed free of charge, as it is high-tech assistance and is subject to quotas from budget funds.
Main advantages and disadvantages of stenting
Surgery has many indications and is recommended for patients with allergies to anesthesia.
Unlike a standard operation, the advantages of a closed procedure are:
- average duration – from 40 minutes to 3 hours;
- rapid restoration of blood flow in the first minutes after installation of the structure;
- prevention of thrombosis, myocardial infarction, cerebral or pulmonary stroke;
- blood loss is excluded, there are no incisions, scars, scars;
- short rehabilitation period (after 4 days the patient is sent for home treatment);
- postoperative complications develop only in 4−7% of cases;
- possibility of treating patients up to 75 years of age with minimal risk.
Stenting is a gentle method that allows you to avoid surgery under general anesthesia, amputation and distal prosthetics for diabetic feet.
Among the contraindications to angioplasty:
- acute pulmonary failure;
- endocarditis;
- exacerbation of chronic joint diseases;
- liver failure;
- hemocoagulation disorder;
- hypertensive crisis;
- severe infections of the genitourinary tract and respiratory organs.
The procedure is not recommended if you are intolerant to the components of the contrast agent, which is administered to monitor the movement of the catheter. During stent installation, computed tomography is used, so the operation is not performed during pregnancy at any stage.
Coronary angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty is used to restore the patency of the coronary arteries and normal functioning of the heart, both in angina pectoris and in acute myocardial infarction
We can speak of a successful angioplasty procedure if, according to angiography after the intervention, the residual stenosis in the affected vessel was 20% and blood flow in the artery was completely restored, the procedure was completed without serious complications, and the signs and symptoms of ischemia decreased after the patient recovered from the operation.
Preparing for surgery
Before stenting the lower extremities, the doctor must properly prepare the patient.
The following diagnostic procedures are preliminarily prescribed:
- determination of blood clotting using a coagulogram;
- clinical blood test;
- X-ray scanning of the vessels of the legs with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of blood vessels, liver;
- duplex ultrasound scanning to assess the condition of the arteries.
For chronic diseases, it is recommended to additionally visit your doctor and adjust the dose of daily medications. If you are prone to allergies, the anesthesiologist may prescribe a contrast test.
How is the operation performed?
Patients are rarely hospitalized first: diagnosis can be done on an outpatient basis. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is administered, the patient is positioned on the operating table, and changes into a disposable gown. At the same time, the X-ray equipment is set up.
The contrast agent is administered intravenously in small doses during surgery. An incision is made with a scalpel on the inner thigh or groin to provide access to the iliac vein. A small-diameter catheter with a metal stent is slowly passed through the vessel to the blocked area.
When operating on the arteries of the lower extremities, a coronary stent system from is often used. The cobalt alloy design features an innovative RESOLUTE INTEGRITY zotarolimus coating made from a biocompatible polymer.
Its advantages:
- high degree of flexibility;
- the polymer is released within 6 months, protects the vessel from inflammation and infection;
- tight fit to the walls;
- safety in diabetes.
There is a miniature balloon inside the stent. After insertion and inflation for several minutes, the doctor monitors blood pressure readings to ensure improved blood flow.
After removing the catheters, the puncture is gently clamped for 15-20 minutes, which accelerates blood clotting. The patient is transferred to a regular ward under the supervision of a doctor.
Possible complications
Iliac vein rupture is a rare complication associated with the difficulty of overcoming a blocked vein. Treatment can be carried out endovascularly - by pressing the tear site with a balloon, open vein ligation, conservative wait-and-see tactics.
Rethrombosis of the reconstructed segment rarely develops during the intervention. If during control duplex scanning of the veins within 7 days after the intervention no thrombosis occurs, then the patency of the vein has been restored for a long time.
Bleeding from the access site is rarely a serious problem, since the vein is well pressed with a pressure bandage.
Pulmonary embolism is a theoretically possible complication of vein stenting due to acute venous thrombosis, but when a temporary vena cava filter is used for protection, the likelihood of thromboembolism is minimal.
Recovery after angioplasty
If there are no contraindications, the patient is recommended to get up the next day, perform simple exercises, and take a few steps around the room. He is given vasodilators and painkillers that dissolve atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels.
Rehabilitation at home helps reduce the risk of relapse:
- daily performance of a complex of physical therapy;
- method of dosed walking “health path” for training the blood vessels of the legs;
- taking medications to control blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Proper and nutritious nutrition plays an important role. During recovery, it is recommended to completely avoid salty and fried foods and animal fats. The basis of the menu should be products enriched with microelements, potassium, magnesium, vitamins A and E for the elasticity of blood vessels.
What should you expect after angioplasty and stenting?
After the operation, hospitalization is required for at least a day. During this time, specialists will monitor your health, especially your blood pressure and heart rate. It is very important not to move the limb where the puncture was made, as this may cause bleeding. Usually there are no complications, but in extreme cases the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Pallor of the limb.
- Acute pain syndrome.
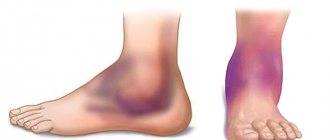
- Hematoma and swelling in the puncture area.
- Bleeding.
- Numbness and freezing of the limb.
If complications occur, you should immediately notify medical personnel.
During the rehabilitation period, it is advisable to drink more water to cleanse the body. Aerobic and anaerobic exercise is completely prohibited. You can only perform physical therapy and a narrow range of exercises prescribed by your doctor. In addition, blood thinners are taken (this is necessary to prevent the formation of blood clots). It is advisable to regularly undergo a general blood test and coagulogram during recovery to avoid serious complications.
Results after angioplasty
Restoring the iliac artery without anesthesia is guaranteed to relieve leg cramps and pain for 5-10 years. The patency of the blood vessel is maintained at 80−85%, which allows you to lead an active lifestyle and reduces the risk of dangerous complications for the body.
To prevent relapse, you need to visit a vascular surgeon annually, having previously undergone the following procedures:
- ultrasound examination of the arteries and veins of the lower extremities;
- tomography using a contrast agent.
Angioplasty of the lower limb artery is the only way to preserve blood circulation in the foot, prevent gangrene and the development of trophic ulcers. Installing a stent using a gentle method in combination with diet and physical activity gives a long-lasting effect and returns the ability to move without pain and restrictions.
Possible complications of vascular stenting
- bleeding;
- damage to the artery wall;
- hematoma formation at the puncture site;
- artery blockage;
- disorders of the kidneys;
- thrombosis and restenosis in the stent area.
Vascular stenting brings a pronounced positive effect, and complications and contraindications to this procedure are quite rare.
A short rehabilitation period and low invasiveness make stenting one of the most popular operations in vascular surgery.