Generally accepted norms of indicators
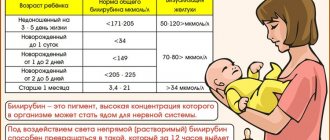
The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age is different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborns, in the initial stages of life, up to 200 µmol/l, this is due to the period of adaptation of the newborn’s gastrointestinal tract to the digestion of mother’s milk. The acceptable level of bilirubin concentration for each age will be different. The highest concentration of the substance in the blood is observed in newborn children, in the initial stages of life. In one-year-old children and children under 13 years of age, a satisfactory indicator of the concentration of indirect pigment is considered to be up to 20.3 µmol/l, for direct pigment up to 5.2 µmol/l.
The degree of concentration of the substance for adults should not cause concern if the survey analysis shows a level of up to 19.9 µmol/l for indirect, and 4.9 µmol/l for direct bilirubin, since such measurements are satisfactory for people of the adult age category.
Clinical manifestations
Jaundice
A characteristic and striking clinical sign is yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera (whites of the eyes). In fact, all biological fluids of the body turn yellow, except saliva and tears. Yellowness of the skin is associated with the impregnation of tissues with bilirubin due to its high content in the blood.
Cholestasis
Cholestasis is the cessation of bile secretion into the intestines. It remains in the ducts, accumulates there and is eventually absorbed back into the blood. All together this leads to the following manifestations:
- In the blood, in addition to an increase in bilirubin content, there is also an increase in the content of cholesterol, lipids, and cholates. In addition, the activity of some enzymes increases, for example, alkaline phosphatase, GGTP, etc.
- Cholemia. Bile acids entering the bloodstream have a toxic effect, which is accompanied by a decrease in heart rate, a decrease in blood pressure, patients are drowsy and irritable, they may show signs of depression. Due to the toxic effect on nerve endings, itching develops, which is difficult to stop. The entry of bile acids into the urine leads to a change in the properties of surface tension, which causes it to foam during urination. Together with the dark brown coloration, this sign is called “beer urine.”
Acholia
Acholia is a symptom complex that develops when bile does not enter the intestines. This leads to indigestion. First of all, fat digestion suffers. They are not absorbed and are excreted along with feces. This condition is called steatorrhea. The metabolism of proteins and vitamins, especially fat-soluble ones, including vitamin K, which is necessary for the synthesis of blood clotting factors, is also disrupted. This, in turn, leads to bleeding. Also, normally, bile has a bactericidal effect. Accordingly, in its absence, the ratio of intestinal flora begins to be disrupted towards the predominance of anaerobes.
Bile has a stimulating effect on intestinal motility. Accordingly, in its absence, constipation occurs, which is replaced by foul-smelling diarrhea due to the dilution of intestinal contents by putrefactive microflora. The absence of bile pigments in stool leads to its discoloration - acholic stool.
Discholia
Stagnation of bile in the ducts leads to the fact that it changes its physical and chemical properties, which ultimately contributes to the formation of stones.
Causes of increased bilirubin in the blood
The source of the pathological condition is caused by disruption of the liver, resulting in improper outflow of bile, which causes the occurrence of viral lesions and hepatitis.
symptoms of increased bilirubin
The cause of increased bilirubin in the blood may be:
- Chronic or autoimmune hepatitis.
- Non-benign neoplasms in the liver area.
- Incorrect functioning of the pancreas.
- Intoxication of the body through poisoning can also cause an increase in bilirubin.
By the way, any of the above reasons is pathological and requires immediate medical intervention and long-term treatment
Why does obstructive jaundice develop?
Malformations of the hepatobiliary system:
- Atresia and hypoplasia of the biliary tract.
- Bile duct cysts.
- Diverticula of the duodenum.
Non-inflammatory and inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder:
- Cholangiolithiasis is gallstones that obstruct the lumen of the bile duct.
- Strictures and stenosis of the bile ducts.
- Cholangitis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Cysts of the head of the pancreas.
Tumors:
- Cancer of the bile or hepatic ducts.
- Liver cancer.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Metastatic liver damage.
- Benign tumors - papillomatosis of the bile ducts.
Parasitic infestations:
- Echinococcus.
- Alveococcus.
Symptoms indicating increased bilirubin
There are symptoms the presence of which in a person means that the percentage of bilirubin in the blood is too high:
- The whites of the eyes began to turn yellow.
- The skin color becomes more jaundiced.
- Itching of the skin, which intensifies at night.
These symptoms are an important indicator that the body is undergoing internal bile poisoning; ignoring these problems can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the body.
The often manifested bitter taste in the mouth is also one of the symptoms of increased bilirubin in the blood.
treatment of direct bilirubin in the blood
A rapid increase in this substance provokes the darkening of the urinary fluid to a brown color, and solid bowel movements take on a white color. All of the above symptoms are accompanied by severe weakness, high fever and enlarged liver. If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately seek help from the nearest hospital.
What does bilirubin level indicate in adults?
10.09.2021
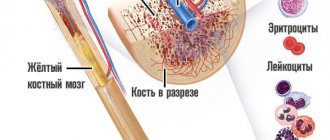
Bilirubin is a substance that is formed as a byproduct after the breakdown of hemoglobin (the protein that colors blood
red and helps carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body) and old red blood cells.
The process of creating and destroying red blood cells is constant, and a number of by-products are released as waste products.
Bilirubin is also produced as a product that is excreted from the body through the digestive system and is
part of the bile secreted by the liver . It is this pigment that gives the yellow color to urine , feces and bruises.
Bilirubin levels are usually low in the body. When bilirubin levels in the body increase, it may be a cause for concern.
as it indicates the presence of health-related disorders, especially the liver .
Triggers that increase bilirubin levels
An accumulation of bilirubin in the body can be a sign of a diseased liver , which can lead to unwanted complications if left untreated .
In addition, high levels can be caused by the following reasons:
- Bilirubin levels can skyrocket when the liver's to process this byproduct is impaired.
- Antibiotics and medications such as flurazepam, phenytoin, diazepam and indomethacin can increase bilirubin levels in the body.
- An allergic reaction to blood received during a transfusion, called a transfusion reaction, can increase bilirubin levels.
- Blood -related disorders such as sickle cell anemia, an inherited disease that causes rapid destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis), are also responsible for increased bilirubin levels.
- Tumors affecting the liver , bile ducts or gallbladder are heralds of increased bilirubin in humans.
- Diseases such as gallstones ( or gallstones ) and pancreatic cancer obstruct and cause damage to the bile ducts.
- An infection in the gallbladder , called cholecystitis , is another causative factor for high bilirubin levels in adults.
- Increased conjugated bilirubin or Dublin Johnson syndrome, where there is a decrease in enzymes produced by the liver .
- Diseases that increase bilirubin in adults are cirrhosis , severe hepatitis, and Gilbert's syndrome. They affect the processing of bilirubin in the liver .
Symptoms of elevated bilirubin
Increased levels can be detected by monitoring body signals. Timely detection of such signals can prevent the exacerbation of this condition.
- Changes in skin color, eye , nausea and vomiting. Dark amber or brownish-yellow urine .
- High fever is accompanied by chills, itching, pale stools, abdominal and swelling .
- Fatigue and general malaise, loss of appetite.
Treatment of elevated bilirubin
To determine bilirubin levels, a person must undergo regular medical examinations.
urine test is done to check the level of bilirubin in the body.
High levels in adults can cause liver , which can be life-threatening.
Drinking barley water throughout the day is an effective home remedy and helps treat this disorder.
The patient should refrain from using tobacco and alcohol.
To avoid any complications, it is necessary to take medications that will help fight liver disorders and restore health.
Published in Laboratory research Premium Clinic
Treatment of elevated direct bilirubin
You can influence the high concentration of bilirubin in the blood by following a diet and doing physical exercise. After undergoing a biochemical examination of the blood, based on the tests obtained, the doctor prescribes the patient a set of treatment and recommendations aimed at establishing the proper functioning of the liver and the outflow of bile. Even with the slightest discrepancy with the norms, the doctor is obliged to prescribe treatment to correct the functioning of metabolic processes; you can often undergo such a course of treatment at home, while following all the recommendations. In this case, the examination results show a disappointing picture; if necessary, surgical intervention is required, followed by hospitalization in a hospital.
If bilirubin is elevated during pregnancy
The appearance of jaundice can occur during all stages of pregnancy. If the analysis reveals an excess of bilirubin, this may be associated with the following diseases:
- viral hepatitis in acute form;
- intrahepatic cholestasis;
- acute fatty liver degeneration.
It is viral hepatitis that is the main cause of jaundice in pregnant women - it accounts for up to 50% of identified cases. Symptoms of the disease are varied. The pathology begins to manifest itself with weakness, fever, joint pain, skin rashes, and changes in the color of urine and feces. In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor, take a blood test and other tests.
The second most common cause of abnormal bilirubin levels in pregnant women is intrahepatic cholestasis (another name is hepatosis). It accounts for up to 25% of identified cases. The main symptoms are;
- frequent itching of the skin;
- moderate jaundice;
- darkening of urine;
- stool lightening;
- rarely – prolonged, repeated vomiting.
As a rule, the described signs progress during the 3rd trimester, less often they appear at earlier stages. When taking an analysis, it turns out that bilirubin exceeds the norm by 4-5 times.
Finally, jaundice may also be associated with acute fatty degeneration. This pathology is much less common - 1 in 13,000 births. It manifests itself as a complication, more often in primiparous women in the last stage of pregnancy. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established.
Treatment
The choice of treatment regimen is made by the doctor taking into account the identified pathologies. When making a diagnosis, the nature of the enzyme deviation from the norm (increased or decreased value) is taken into account.
There are no special pharmacological agents that lower bilirubin. In cases where the provoking factor is medications or toxic substances, it is necessary to stop taking them. If we are talking about vital medications, the doctor selects safe substitutes.
When the enzyme level is too high, the following methods are used:
- the use of drugs that activate the outflow of bile (Allahol, Hofitol);
- cleansing droppers with glucose (stimulating the elimination of indirect toxins);
- phototherapy (irradiation with special lamps, under the influence of light the molecules of indirect bilirubin and other substances bind together);
- taking pharmacological agents that accelerate metabolic functions (Mezim, Festal, Pancreatin);
- dietary diet.
Treatment of jaundice
Obstructive jaundice requires surgical treatment. At the first stage, drug therapy is carried out aimed at reducing the toxic effect of bilirubin. The following technologies are used as part of surgical treatment:
Minimally invasive interventions
When the duct is obstructed by stones, lithotripsy is used - destruction and removal of stones from the lumen of the ducts. For this, endoscopic technologies, laser, electrohydraulic, or ultrasonic crushing of stones can be used.
If there is obstruction due to stenosis, stricture, or tumor compression, stenting, bougienage, or balloon dilatation of the narrowing site is performed. The choice of treatment method depends on the causes of the obstruction.
These measures are carried out endoscopically through the duodenum. If this is not possible, percutaneous transhepatic drainage of the bile duct is used, in which a drainage catheter is installed into it, draining the bile into a special receiver. After stabilizing the patient's condition and eliminating the toxic effects of hyperbilirubinemia, an attempt is made to establish normal passage of bile to the duodenum. For this purpose, full-fledged operations are used.
Gilbert's syndrome
One of the reasons for the deviation of the enzyme indicator from the norm is Gilbert's syndrome. Many people know nothing about this disease. His symptoms are mild, and the course of the disease is chronic. Among the few signs:
- muscle weakness, pain;
- bowel dysfunction;
- bloating;
- destabilization of the psycho-emotional background;
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
Genetic pathology disrupts bilirubin metabolism, resulting in test results that are abnormal. The syndrome is inherited in the form of a defect of the second chromosome. Some patients learn about the disease only after donating blood, when an altered enzyme level is detected.
Therapy is aimed at combating symptomatic manifestations and complications. The patient is also recommended to follow a strict diet for life.
Jaundice may develop against the background of Gilbert's syndrome. The pathology is treated with medication.
How is a biochemical blood test performed?
A biochemical blood test is a common type of diagnosis that doctors prescribe to assess the condition of the patient’s body. This is a quick and informative method that allows you to identify signs of asymptomatic diseases.
To obtain accurate data, the patient is recommended to prepare before going to the laboratory. Failure to follow the rules may result in incorrect diagnosis.
Basic requirements for the preparatory process:
- biochemistry is carried out in the morning (8-00 - 11-00);
- you need to come to the laboratory on an empty stomach (the period of fasting should be at least 8 and no more than 12 hours);
- the day before the test, you should not eat heavy food, you are allowed to drink only purified water;
- if the patient is taking medication, first check with the doctor whether a break is required;
- 1 hour before going to the clinic you should stop smoking;
- one day before the procedure, you should avoid outbursts of emotions and physical activity;
- It is recommended to sit directly in front of the door to rest for about 15 minutes.
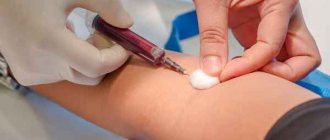
The process of drawing blood involves applying a tourniquet and placing it above the elbow. The puncture site is treated with cotton wool soaked in an antiseptic. This is necessary to prevent infection. After inserting the needle, the nurse checks that the vein is full of blood. Next, the biomaterial is collected. When taking tests, the patient's body must remain motionless.
If it is not possible to take blood from the ulnar vein, the collection is carried out from other veins available for the procedure. The biomaterial is poured from the syringe into a test tube and sent to the laboratory along with the referral.
Complications of jaundice
High hyperbilirubinemia and jaundice are life-threatening conditions and can lead to death, even after eliminating the causes that caused it.
When hepatocytes are destroyed, a large amount of toxic substances are released into the blood, which have a systemic effect. Functional disorders increase, and renal-hepatic syndrome develops. Bilirubin penetrates the blood-brain barrier and causes disruption of the brain (hepatic encephalopathy), which is accompanied by stunned consciousness, even coma.
A toxic effect of bilirubin on surfactant, an important component of the lungs, has also been noted. When it is damaged, respiratory failure develops. Impaired production of blood coagulation factors leads to the development of DIC syndrome.