The best specialists in the industry work in cardiology at the IMMA medical center. An individual approach to each patient ensures a reliable collection of the clinical picture of a dangerous heart disease – myocarditis. In their work, cardiologists are guided by evidence-based medical practice, the principles of evidence-based medicine and the recommendations of the WHO of the Russian Federation. Which together gives high efficiency and a positive prognosis of therapy. The use of modern equipment for diagnostic measures makes it possible to accurately determine the presence or absence of myocarditis.
In our clinics you can:
- Get a consultation with a cardiologist;
- Take an ECG and get a professional interpretation of the results;
- Complete the ABPM procedure;
- Undergo Holter monitoring;
- Take advantage of other services of our clinics.
For more details and any questions, please contact the number listed on the website
Myocarditis - basic definition
Inflammation of the heart muscle that is not associated with impaired blood circulation in the coronary arteries is called myocarditis. The disease affects the middle layer of muscle tissue - the myocardium. The causative agents are specific infections and viral pathologies. In some cases, inflammation can be triggered by allergic, autoimmune diseases and acute intoxication. According to the World Health Organization, myocarditis is diagnosed in 10% of cases of all heart diseases.
The main danger of the pathology is the absence of an age threshold. Myocarditis can develop in both children and the elderly. Although the prognosis for most cases is positive, the disease is highly unpredictable. Without timely diagnosis and treatment, a sudden disturbance in heart rhythm may occur - arrhythmia, which causes extremely serious consequences, including death.
Infectious myocarditis
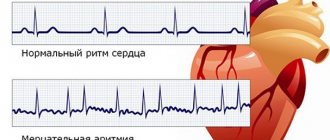
Myocarditis begins against the background of infection or shortly after it with malaise, sometimes persistent pain in the heart, palpitations and interruptions in its work and shortness of breath, and occasionally pain in the joints. Body temperature is normal or slightly elevated. The onset of the disease may be unnoticeable or hidden. The severity of symptoms is largely determined by the prevalence and severity of the progression of the process. The size of the heart increases early. Important, but not constant signs are disturbances of the heart rhythm (tachycardia - its increase, bradycardia - its decrease, atrial fibrillation, extrasystole) and conduction (various blockades): palpitations, interruptions in the heart, a feeling of “fading”, “stopping”. Myocarditis can be complicated by the development of heart failure. Infectious myocarditis can occur in two forms: infectious-toxic, in which signs of heart damage appear during a period of severe intoxication; infectious-allergic, in which signs of heart damage usually occur 2-3 weeks after the onset of an acute or exacerbation of a chronic infectious disease.
Types of myocarditis depending on the causes
The classification of the disease according to the ICD is based on the cause-and-effect factor that causes myocarditis. Depending on the provocateurs, the disease takes the following forms:
- Infectious myocarditis
Infectious diseases of various origins, in severe manifestations, cause complications on the myocardium - inflammation develops. The cause may be all kinds of herpes, influenza, and hepatitis viruses. Bacterial diseases. Fungal pathologies of Candida and Aspergillus. Parasitic organisms. Diphtheria bacillus, chlamydia, streptococcus.
- Rheumatic myocarditis
It is a derivative of infectious myocarditis. Develops against the background of a depressed immune system. The main reason is hemolytic streptococcus, which causes pathologies on the mucous membranes.
- Allergic myocarditis
The disease develops against the background of an allergic reaction. In this case, the factors can be very different. Burns that provoke the release of large amounts of toxic substances into the blood. Organ transplantation, transplantation leading to implant rejection and myocardial damage. Allergy to drugs, as a result of which the drugs cause inflammation of the heart muscle.
- Toxic myocarditis
Alcohol poisoning, kidney failure, which results in increased uric acid levels, and heavy metal vapors can cause inflammatory processes in the myocardium.
- Symptomatic myocarditis
The consequence of chronic diseases can be myocarditis. As a rule, these are autoimmune diseases - lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, which have an extremely negative effect on all internal organs, including the heart.
- Idiopathic myocarditis
A disease with unknown etiology. It is characterized by partial damage to the myocardium and a severe form of the course. Most often it becomes the cause of death. This is due to the current impossibility of establishing the causes of development.
Based on the classification of the disease, most existing infections can cause an inflammatory process in the heart muscle. Therefore, even a seemingly banal cold can give impetus to the inflammatory process in the myocardium. A preventive examination after a viral illness is the best way to prevent myocarditis.
Important! A timely detected and fully treated infection minimizes the risk of complications affecting the heart muscle.
Publications in the media
Almost any term in Latin with the ending “it” means inflammation: bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi, tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, etc. Myocarditis is inflammation of the muscle tissue of the heart. Similar to inflammation of any skeletal muscle after a sprain or hypothermia, which is manifested by pain, impaired muscle function, local swelling and redness, pain and decreased contractility also occur in the heart muscle. Due to inflammation, the current of impulses through the conduction system of the heart slows down - blockade and heart rhythm disturbances develop.
Myocarditis can occur with any acute or chronic indolent infectious disease. Most often, myocarditis develops due to viral infections. Non-infectious factors that cause myocarditis include some medications, including antibiotics, sulfonamides, etc., as well as vaccines and inoculations. In addition, myocarditis often accompanies systemic connective tissue diseases, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and vasculitis. Among the causes of myocardial inflammation, a special place is given to rheumatism, in which myocarditis is one of the main and leading manifestations of the disease along with endocarditis and pericarditis - inflammation of the inner and outer lining of the heart, respectively.
There is also idiopathic (that is, without an obvious known cause) myocarditis, which is called Abramov-Fiedler. Moreover, in the classic course of the disease, examination and blood tests do not reveal the infection that provoked myocardial inflammation.
According to the course, acute, subacute and chronic myocarditis are distinguished. In a chronic course, depending on the frequency of relapses, cardiac function can significantly decrease and chronic heart failure develops.
Quite often, myocarditis is not accompanied by significant symptoms of the disease and is recognized only during an instrumental examination, sometimes performed for another reason. Complaints may be limited to general weakness, chest discomfort, palpitations, a slight increase in body temperature - nonspecific complaints, for which not everyone goes to the doctor, and almost no one comes to the cardiologist.
In typical, clinically pronounced cases, there are complaints of prolonged pain in the heart area not associated with physical activity, weakness, increased fatigue, shortness of breath and palpitations even at rest, and interruptions in cardiac function. Body temperature is often subfibrile: 37-37.90C.
Myocarditis begins against the background of an acute infectious disease or shortly after it. The malaise intensifies and the above complaints appear. Sometimes the pain in the heart is persistent and long-lasting. Body temperature is normal or slightly elevated. The severity of symptoms is determined by the prevalence of the inflammatory process in the myocardium - how much of the heart muscle is involved in inflammation and begins to work worse - to contract. Due to a decrease in myocardial tone, the size of the heart increases, the normal functioning of the valves is disrupted, and cardiac output decreases. Myocarditis can be complicated by the development of acute heart failure - a reason for emergency hospitalization and intensive care.
Myocarditis can occur in two clinical forms: infectious-toxic (heart lesions appear during a period of severe intoxication against the background of infection) and infectious-allergic (the infectious agent triggers an excessive immune response of the body and the body’s own immune cells begin to fight and destroy their own cells in different organs , including hearts, which in a number of ways are a little similar to bacteria and viruses. Therefore, the immune system cannot distinguish body cells from harmful microbes. That is why infectious-allergic myocarditis can occur and continue after the end of the infectious process that caused it.
Idiopathic myocarditis
Idiopathic myocarditis, in which there is no clearly established cause for the development of inflammation in the myocardium, is characterized by a more severe, sometimes fulminant course with the rapid development of a large “flabby” heart and heart failure. Without timely help, most often, such myocarditis is fatal or requires an urgent heart transplant, which in our country, unfortunately, is not always possible. In a large heart, blood flow slows down significantly, valve function is disrupted, and cardiac output decreases. The walls of the heart are stretched so much that even after successful treatment, changes in the myocardium can be irreversible. In idiopathic myocarditis, both rhythm disturbances and the formation of blood clots inside the heart due to its expansion and turbulent blood flow, which can enter the brain and lungs, leading to fatal thromboembolic complications - pulmonary infarctions, strokes, etc., are deadly in idiopathic myocarditis.
Myocarditis in children
Myocarditis in a child, as well as in an adult, occurs as a result of an infectious factor. In children, due to the failure of the immune response to a number of bacteria and viruses that adults are more “familiar” with, even a mild infection can lead to generalization - complications in other organs, most often the heart and kidneys. Children are characterized by the presence of two types of myocarditis:
1. Congenital - in this case, from the day of birth, the child exhibits lethargy, pallor, shortness of breath, changes in the ECG, low blood pressure, weak sucking reflex, etc. The child does not gain weight. Jaundice prolongs due to insufficient blood supply to the liver. The situation requires immediate treatment. Most often, this condition is associated with an intrapartum infection - then antibiotics are quite effective and the process is reversible. If congenital myocarditis is associated with impaired immunity and occurs as part of an autoimmune process, treatment is more complex, the prognosis is worse, and death is possible.
2. Purchased. This type of myocarditis, as in adults, is divided into acute, subacute and chronic, and is most often a consequence of ARVI. The child's appetite decreases, anxiety occurs during the day and sleep disturbances at night, episodes of cyanosis (blue face) and shortness of breath, increased body temperature. In this case, examination and observation by a cardiologist is mandatory.
Instrumental examination methods
In a blood test, the level of inflammation indicators increases - leukocytes, ESR, C-reactive protein, etc., but, unlike a banal infection, with myocarditis the level of enzymes in the blood increases - MB-CPK and troponin. These enzymes are normally found inside the muscle cells of the heart. During inflammation, which leads, among other things, to disruption of the integrity of cell membranes, enzymes enter the blood and their level is proportional to the number of damaged cells. This happens when the myocardium becomes inflamed or damaged during a heart attack.
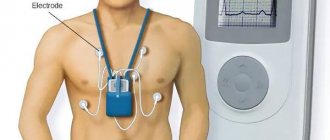
The ECG records certain changes that are characteristic specifically of myocarditis, although often difficult to distinguish from ischemic ones. Almost always, with myocarditis, ECG reveals disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction.
Ultrasound of the heart - decreased myocardial contractility, expansion of the cavities of the heart, accumulation of fluid around the heart and other specific changes.
Forecast
With Abramov-Fiedler myocarditis, myocarditis against the background of sepsis (severe generalized infection and damage to almost all organs), the prognosis for life is unfavorable - mortality up to 50-60%.
With infectious myocarditis, with timely and adequate treatment, in most cases, myocarditis is asymptomatic and ends with complete recovery. Occasionally, changes in ECG or cardiac ultrasound data will persist for a long time. Most often, there are no signs of previous myocarditis 2-3 months after the end of the disease. Other forms of myocarditis with an acute and subacute course in at least 1/3 of cases result in complete recovery, and mortality in Russia reaches 5-10%.
Prevention
Prevention is the prevention and timely effective treatment of infectious diseases. If signs of infection appear, you should consult your doctor. Of course, a runny nose can be treated at home, but without a doctor and a basic examination you will not be able to distinguish between a “lingering” runny nose and the onset of an inflammatory process in the heart. It is also important to treat infectious diseases. Do not stop therapy prematurely, including antibiotics, even if nothing bothers you anymore.
If you have had myocarditis, you need to be examined and treated with greater care and attention for any, even “harmless” infection. If you are planning to undergo any surgical intervention, including tooth extraction, warts or skin papillomas, etc., be sure to undergo antibiotic prophylaxis under the supervision of a doctor.
Indications for hospitalization
In this matter everything is extremely simple. Suspicion of acute myocarditis or exacerbation of chronic myocarditis is an undeniable indication for hospitalization. Myocarditis is not treated at home, no matter how severe it is. Severe arrhythmias and acute heart failure can develop suddenly, and you will miss the moment to begin adequate treatment.
Treatment of myocarditis is carried out exclusively in a hospital under the dynamic supervision of a doctor. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, including hormonal ones, are prescribed, the pulse rate is reduced and, if necessary, drugs are prescribed against disturbances in heart rhythm and conduction.
Cardiologist, Ph.D. Zaikina Alexandra
Symptoms
The signs of myocarditis are extensive and completely depend on the form, course and degree of development of the pathology. The development of the disease is divided into several groups:
- According to the form of the course: acute, chronic and rapid.
- By localization: focal and diffuse.
- By severity: light, medium and severe.
With any type of myocarditis, patients have several similar symptoms: chronic fatigue, general weakness, pain in the chest and under the left shoulder blade, increased sweating, shortness of breath.
An expanded group of signs indicates the presence of a certain type of myocarditis:
• Minor symptoms are characteristic of infectious-allergic myocarditis. The patient experiences slight weakness, perceived more as a consequence of fatigue than as a symptom of a dangerous disease. Taking vitamins and aspirin, a person does not even think about the fact that dangerous inflammatory processes are occurring in the body.
• Idiopathic or rheumatic myocarditis is manifested by acute, burning pain in the heart and left arm. The clinical picture is similar to ischemic heart disease - lethargy, limited motor function, constant lack of air, and in some cases, night fever.
• Diffuse localization of the inflammatory process affecting the entire myocardium is characterized by acute heart failure and its characteristic symptoms. Swelling appears, bruises under the eyes, limbs go numb and acquire a bluish tint.
• Bacterial myocarditis is characterized by disruption of the circulatory system. There is a high risk of blood clots forming in the main arteries of the heart. It manifests itself as a change in the color of the skin, shortness of breath, even during rest, and constant aching pain behind the sternum.
The severity of the pathology is completely reflected in the appearance of the patient. At the initial stages of the inflammatory process, no visible changes are observed. The patient may complain to the attending physician about general weakness. As the disease worsens, the patient's lips become blue, the limbs become pale, and swelling occurs under the eyes. In the severe form, swollen veins in the neck and arms, a painful dry cough, and shortness of breath are clearly visible, interfering with the usual activities.
Important! If any of these signs appear, you should immediately seek medical help. It is especially important to do this after suffering from infectious diseases.
Myocarditis - how is diagnosis done?
At the first signs, immediately contact a clinic where competent doctors work. They will conduct a targeted examination and give directions for further, detailed examination. But, there are stages of diagnostics:
- External examination of the baby . An experienced cardiologist immediately diagnoses that the heart muscle is inflamed. A blue tint to the face, swollen legs, swollen veins, hard breathing, all this makes it clear to the specialist that it is necessary to check the functioning of the heart as a whole.
- Percussion . At this moment, the doctor “tapping” and accurately determines the boundaries of the expansion of the heart muscle.
- Using a phonendoscope, the doctor listens to the frequency and rhythm of the heartbeat;
But, unfortunately, not every pediatrician is able to make a correct and clear diagnosis, so most likely you will be referred for a thorough examination using special devices that will give a complete picture of the child’s condition. Myocarditis and its diagnosis require increased attention from parents ; some notice manifestations quite late, which significantly aggravates the situation.
Treatment
The main attention in the conservative treatment of myocarditis is paid to etiotropic therapy - elimination of causes and complications. In the first stages, hospitalization occurs, a strict diet is prescribed, bad habits are eliminated, and inflammation is relieved.
The standard scheme of therapeutic measures is as follows:
- Strict bed rest in a hospital for at least four weeks;
- Limiting physical activity;
- Supportive complex therapy;
- Taking a wide group of anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs;
- Antibiotic treatment for specific viral pathologies;
- Prescription of hormonal drugs - glucocorticosteroids (GCS). It is used in severe cases to suppress the hormone cortisone, which is responsible for the development of inflammatory processes;
- Immunomodulation. Maintaining and restoring the body’s protective function;
- Correction of metabolic processes. To enrich the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients;
- Preventive vitamin course.
Compliance with basic treatment standards is the key to successful treatment. Therefore, self-medication of heart pain is strictly contraindicated. This can lead to irreparable complications, the mildest of which will be myocardial infarction. The patient is only required to be attentive to his own health - to listen to the first alarm bells of the body and undergo a timely examination. Only a cardiologist can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment after a complete history collection.
Complications
The consequences of advanced myocarditis are negative processes in the heart muscle. Depending on the course and form of the disease, irreversible changes may appear in the myocardium, which lead to disruption of the normal functionality of the heart muscle - blood pumping. In extreme cases, the lesions are so severe that they lead to cardiac arrest and sudden death.
Long-term myocarditis leads to abnormal enlargement of the heart muscle. The process is irreversible, so in such cases the patient is advised to undergo long-term therapy and a complete overhaul of their lifestyle.
The most severe consequences are considered to be giant cell myocarditis. Most patients with this diagnosis require heart transplantation. Otherwise, cardiologists give an unfavorable prognosis for life. According to WHO, approximately 90% of patients die within 4-5 years if a heart transplant is not performed.
The inflammatory process in the myocardium contributes to scarring of muscle tissue, which in turn completely disrupts the heart rhythm and blood supply. This leads to the development of heart failure and, as a rule, ends with ischemic heart disease.
But in most cases, normal heart function is restored, although it requires long-term preventive treatment and lifelong monitoring by a cardiologist.
Myocarditis in children
Myocarditis in a child, as well as in an adult, occurs as a result of the action of viruses and bacteria. Children are characterized by the presence of two types of myocarditis:
-Congenital - in this case, the child suffers from lethargy, pallor, and shortness of breath from the day he is born. Gets tired quickly when feeding and does not gain weight. This type of disease is characterized by a significant expansion of the boundaries of the heart, tachycardia.
- Acquired. This type of myocarditis is divided into acute, subacute and chronic. Acute myocarditis is a consequence of acute respiratory viral infection. Initial signs: lack of normal appetite, restlessness and night moans of the child, attacks of cyanosis (blue discoloration) and shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting. In the case of subacute and chronic myocarditis, both significant and minor symptoms are noted. Minor ones include hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), tendency to faint, and vomiting. Significant - cyanosis, cardiac hump (change in the shape of the chest above the heart area in the form of a hump), tachypnea (increased breathing).
Who is at risk
The most common cause of myocarditis is viral pathologies of various origins. Therefore, the risk group includes every person who has had herpes, hepatitis B, C, rubella, chicken pox, measles, diphtheria and even influenza. Since most people have been diagnosed with some kind of viral disease, everyone must undergo a preventive examination in order to exclude the presence of inflammatory processes in the heart. This can subsequently save lives.
The risk of developing myocarditis increases in proportion to the presence of infectious pathologies. Listening to your heart is recommended for everyone who has suffered or is a carrier of diseases caused by the following pathogens:
- Bacteria that provoke the development of tuberculosis, chlamydia, staphylococcus.
- Fungal genus Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida. They cause such common diseases as tonsillitis, laryngitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis, candidiasis, etc.
- Parasitic worms - roundworms, echinococci, trichinella, lamblia, toxocariasis.
- Diabetes mellitus in any degree.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Autoimmune pathologies – rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, vasculitis.
The risk group includes people whose professional activities involve working in enterprises with hazardous working conditions, where there is a possibility of heavy metal poisoning. Taking certain medications can cause inflammation of the myocardium. For example, antiallergic cephalosporins or antidepressants have an extremely negative effect on cardiac activity. Social factors play an important role for the myocardium. Abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking and other dangerous and harmful addictions contribute to the development of myocarditis.
Causes
There are two types :
- congenital;
- acquired.
The development of the disease is influenced by a certain number of aspects, among which are:
- Infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal, etc.).
- Helminthic infestations (echinococcosis, trichinosis).
- Factors of a toxic or chemical nature (insect bites, snake bites, exposure to chemicals on the body, drugs or alcohol).
- Aspects of physical health (overwork, overheating).
- The influence of drugs and other means (vaccination, antibiotics).
- Allergic reactions.
From the above reasons, it becomes clear that the disease can mainly manifest itself in children who have had viral or bacterial infections ; in addition, such children are susceptible to allergic reactions. Therefore, it is a good idea for parents to limit the consumption of foods to which the baby is allergic. Otherwise, you can only aggravate the situation and only cause harm.
Read also: Ultrasound of the child’s heart (echocardiography)
Consultation and examination with a cardiologist
IMMA medical clinics have modern equipment and their own laboratories to accurately determine myocarditis in the initial stages. The full range of studies includes an initial examination by a qualified cardiologist, clarifying tests, and diagnostic measures using modern technologies. Diagnosis and treatment of myocarditis in children and adults takes place in equipped clinics, trained by experienced personnel, under the guidance of leading cardiologists.
To make an appointment, use the contacts listed on the website. The professional staff of the clinic will provide all possible information support.