Some symptoms of multiple sclerosis cannot be ignored immediately. For example, those relating to pain and spasms, vision, and the ability to move. But whether the disease has affected cognitive functions - attention, thinking, memory - is not always clear. This usually happens gradually. It is important to note that thinking quickly, remembering and multitasking has become much more difficult. Cognitive problems are the most common reason people with multiple sclerosis leave their jobs. To protect yourself from this prospect, you need to take care to maintain your intellectual tone for as long as possible.
Cognitive activity includes [1]:
- attention, ability to concentrate;
- memory - remembering and remembering;
- thinking, including figurative and spatial, analytics and intelligence;
- synthesis - the ability to draw conclusions and make decisions, plan and organize;
- visual, auditory, etc. perception, analysis of these signals by the brain;
- speech, the ability to select the right words, to express a thought coherently.
Cognitive impairment is not found in all people with multiple sclerosis (MS). Researchers estimate the occurrence of this symptom in completely different ways: from 10 to 93% [3–5]. Apparently, a lot depends on the subjective attitude of the patient himself and on how noticeable the dysfunction is.
The most common cause for concern is the inability to think as quickly as before and perform multiple tasks at the same time. It becomes more difficult for someone to remember where things are or what he wanted to say. Someone has problems with orientation in space. Many people become afraid that thinking problems will intensify and lead to troubles at work and in relationships [2].
There are three types of cognitive disorders [4–5]:
- Mild to moderate impairment reduces the function of one or more cognitive domains. The degree of the disorder is not severe, so it often escapes the attention of the doctor and is not recorded by the patient.
- Monofunctional - when there is a significant impairment in one of the cognitive areas, such as speech or memory, or it noticeably dominates the others. This is usually associated with damage to a specific area of the brain.
- Dementia is a serious degradation of several functions of the mind at once. As a result, it leads to disadaptation in society and distortion of personality.
General information
Sclerosis is a medical term used to define the process of replacing organ parenchyma with denser connective tissue.
Sclerosis is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of other underlying ailments. The reasons for this phenomenon in the body can be a variety of processes: blood circulation disorders, inflammation, changes that occur in the human body due to age.
Sclerosis can develop in different organs. Thus, with cardiosclerosis, changes occur in the heart, with atherosclerosis - in the walls of blood vessels, with nephrosclerosis - in the kidneys, with pneumosclerosis - in the lungs, etc.
Diet for cerebral sclerosis
Diet No. 10C is prescribed, which consists of reducing the intake of animal fat, easily digestible carbohydrates and cholesterol, as well as salt to 5–7 grams per day. It is recommended to eat plant foods and seafood. The diet should include ingredients that contain B vitamins and vitamin C, dietary fiber, potassium, magnesium (vegetable oils, vegetables and fruits, seafood, cottage cheese). Ready meals should be fresh. Boiled food is preferred, sometimes baking is allowed. The food temperature is normal. Approximate composition of KBZHU: 2200-2600 kcal, proteins - 90-100 g (50% animal), fats - 70-80 g (40% vegetable), carbohydrates - 300-350 g (50 g sugar). Low numbers are recommended for comorbid obesity. Consume up to 1.2 liters of water per day, table salt - up to 7 g.
It is prohibited to consume any types of fatty, salty and spicy foods: fatty meats, fish, poultry, canned food, sausage, caviar, smoked and salted fish, butter and puff pastry, fatty dairy products, rice, semolina, pasta, various salty and spicy foods. snacks and sauces.
A sample menu for one day would look like this:
First breakfast: low-fat cottage cheese with a small handful of nuts and dried apricots, a protein omelet, weak tea.
Second breakfast: fresh apple.
Lunch: fresh cabbage soup, steamed meat balls (chicken), vegetable sauté, compote.
Snack: rose hip decoction, apple or pear.
Dinner: tomato and seaweed salad, baked fish and boiled potatoes, tea with lemon.
At night: a glass of 1% kefir.
Causes of multiple sclerosis
The exact causes of the development of multiple sclerosis are still not known. Experts talk about the autoimmune nature of the disease. It is the central nervous system that controls the functioning of all systems and organs of the human body. It consists of the brain and spinal cord. Due to the autoimmune nature of the disease, the immune system attacks the body's own cells. Consequently, in multiple sclerosis, cells in the spinal cord and brain are affected.
But there are other theories about the occurrence of this disease in humans. Consequently, doctors tend to consider multiple sclerosis as a polyetiological disease . This means that the cause of the disease is a combination of several factors. We are talking about a malfunction of the immune system, external influences, infectious diseases, as well as genetic disposition.
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are prescribed. Our specialists at the Yusupov Hospital will select the most suitable combination based on your medical history and examination.
- statins;
- antiplatelet agents;
- nootropics to improve cerebral circulation;
- antihypertensive drugs and drugs that lower blood sugar (if there is a concomitant pathology).
Statins are drugs that reduce certain fractions of lipids (in particular low- and very low-density lipoproteins), which are deposited on the walls of blood vessels. Antiplatelet agents increase blood clotting to prevent the accumulation of red blood cells on the atherosclerotic plaque. Thus, these two groups of drugs protect against recurrent sclerosis and the risk of stroke.
Nootropic drugs, in turn, have a stimulating effect on the integrative function of the brain. By regulating energy processes in cells, they fight hypoxia and also improve blood supply to the central nervous system. Taking nootropics improves the trophism of nervous tissue, which leads to increased brain activity, activation of operational and long-term memory and restoration of hemodynamics after a stroke or brain injury.
Antihypertensive therapy aims to lower blood pressure below 140/90 to prevent complications.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
The symptoms of multiple sclerosis are varied, and different combinations of them are possible. Speaking about the symptoms of the disease and explaining to the patient what it is, doctors identify more than 50 different signs of the disease that can manifest themselves in each individual case. Depending on certain features of the course of the disease and the person’s conditions ( pregnancy , concomitant illness), the severity and duration of such symptoms are determined.
When diagnosing the disease, most often the most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis are determined. We are talking about a depressive state, constant fatigue, a feeling of numbness or tingling in the arms and legs. Bladder and bowel dysfunction , various sexual dysfunctions , dizziness , periodic tremors and pain , ataxia , cognitive impairment , and vision problems are also noted . However, all these signs may indicate other diseases, so it is impossible to diagnose a patient with “multiple sclerosis” solely on the basis of identifying symptoms.
The life expectancy of people with this disease directly depends on timely diagnosis and the correct approach to treatment. If the patient does everything strictly according to the doctor’s recommendations, then his life expectancy is normal.
Why do cognitive impairments occur?
The main reason is organic. Cognitive functions are impaired when their material carrier, the nerve chain, is damaged. It consists of nerve cells - neurons, their processes and contacts - synapses with which they communicate with each other. The long extension of a neuron—the axon—conducts a signal over a distance. Its terminal section branches and forms synapses for communication with other neurons.
The pathological processes of multiple sclerosis can disrupt nerve chains [6]:
- Damage to myelin , the insulating substance of nerve fibers.
Along perforated pathways, impulses travel slower and require more energy. Cognitive processes associated with these pathways also slow down. Myelin can be restored, but connective tissue often “puts a patch” faster than it. The fiber regains physical integrity, but its function is not corrected. Plaques prevent the axon from conducting signals and forming nerve connections. - Atrophy of the axon axis may occur following the destruction of its membrane, as it becomes more vulnerable and its nutrition is disrupted. In cognitive terms, this means that existing connections may be disrupted, and potential ones may not be formed.
- Atrophy of gray matter - the neurons themselves and supporting cells - also entails cognitive impairment. They are associated with a decrease in brain volume in general and with thinning of the gray matter of the cortex. The fluid-filled ventricles in the brain, on the other hand, enlarge. Depending on the type of multiple sclerosis, different areas are identified, damage to which most often leads to problems in cognition [7]. The mechanisms of atrophy may be associated with the destruction of fiber myelin, or may have other reasons [8].
- Impaired cerebral blood supply is detected in the early stages of the disease, regardless of the type of course. Affects both foci of demyelination and apparently normal areas. It often precedes brain atrophy in MS. Some researchers have linked deterioration in brain metabolism and cognitive impairment [9].
Scientists disagree about which areas of the body are damaged and lead to dementia and other cognitive disorders. It is more or less accurately possible to link monofunctional disorders and certain parts of the brain. For example, if there are areas of demyelination or atrophy in Broca's area, there is a high likelihood that speech problems will arise. Some researchers believe that memory impairment is primarily associated with the destruction of myelin in the areas of the corona radiata, insula, and hippocampus. Still, it is believed that the severity and nature of cognitive impairment are associated not so much with the location of the lesions, but with their size and number [3–5].
Multiple sclerosis and cognitive impairment are linked by the following patterns [10]:
- As the duration of the disease , foci of damage in the nervous tissue accumulate and expand. At the same time, cognitive dysfunction also increases.
- The degree of disability with a decrease in the speed of thinking and attention span. Time spent on completing tasks increases.
- During exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, a person is more likely to make mistakes at work. Often, exacerbation is accompanied by vision problems. This also affects the number of errors.
- Cognitive impairments are detected even at the stage of a clinically isolated syndrome. They are most pronounced in patients with primary progressive and progressive forms with exacerbations [3].
The brain is able to adapt and restore neural connections with the help of neighboring neurons. The more extensive the neural network is, the easier it is to establish communications. The cerebral reserve, which compensates for damaged circuits, is greater in people with high intelligence and those accustomed to mental work [7].
In addition to pathological processes, other factors also contribute to the functioning of the brain in MS [4]:
- Age - over the years, neurons that are used less intensively are increasingly destroyed. As a result, the cerebral reserve is depleted. In areas of the brain such as the memory center - the hippocampus - neurons continue to renew into old age. However, the blood flow no longer feeds them as actively, so fewer nerve connections are formed. In addition, in old age, one patient may experience two cerebral diseases simultaneously.
- Low intellectual activity increases the risk of cognitive impairment in MS. Education, the intensity of mental work, and initial thinking abilities also matter.
- Psycho-emotional disorders - depression, anxiety, chronic fatigue, insomnia, etc. affect brain processes. Cognitive impairment often occurs as a consequence of these problems. The temporary factor is stress .
- Vascular pathologies , including arterial hypertension, previous strokes and various heart diseases, can disrupt the microcirculation of the brain and cause cognitive impairment. Diabetes mellitus, especially type II, may act through vascular or molecular mechanisms [7].
Diagnosis of cognitive impairment
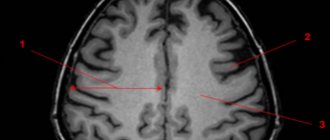
The severity and nature of cognitive problems do not always depend on physical damage to the brain. You can't judge them based on MRI results alone. Moreover, white and gray matter may appear normal, but neural connections may be disrupted [10].
Cognitive disorders largely determine aspects of personality: character, subjective attitude, predisposition to a particular mental state [4].
The first step in diagnosis is to listen to yourself. Pay attention to the slightest changes in mental activity. If you have suspicions, but you are not sure, ask your loved ones to watch you from the side. Pay attention to other symptoms of MS: depression, anxiety, apathy, insomnia, fatigue.
Share the results with your neurologist. If necessary, he will refer you to a clinical psychologist for evaluation. In addition to the symptoms you notice, age, length of illness, the presence of vascular disorders, psycho-emotional disorders, and relapses of MS will be taken into account [11].
Medical diagnosis of cognitive impairment in MS may include tests [12] *:
- MoCA (Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale) is a 10-minute test to identify dysfunction in various cognitive domains [13];
- PASAT is part of the MSFC test. Attention, information processing speed and working memory are assessed in 15 minutes;
- oral SDMT - measures the same as the PASAT. The test takes about 5 minutes. As an analogue, the two-minute PST test is used;
- Stroop test - determines the stability and selectivity of attention. Requires 5 minutes;
- BRB-NT, MACFIMS and BICAMS methods are used for more detailed diagnostics.
The tasks given are varied. They are asked to perform some action, such as cutting paper or combing their hair. Tests include tasks for counting, drawing, choosing figures, memorization, orientation in space and time. It is required to give objects a name, repeat a phrase, and build an associative series [12–13].
Diagnostics
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis is not easy, as its symptoms are common to many other diseases. There is currently no diagnostic method for accurately determining multiple sclerosis. Therefore, if there is a suspicion of this disease, a complex of research methods is used. First of all, the doctor studies the medical history and conducts a neurological examination. The patient is prescribed an MRI and lumbar puncture. To exclude other diseases, a laboratory blood test is practiced.
Treatment
When discussing the treatment of multiple sclerosis, patients are primarily interested in how curable multiple sclerosis is. Currently, there is not a single case of complete cure for this disease. But the use of preventive therapy makes it possible to delay the development of new symptoms, and also significantly reduce the number and frequency of relapses of the disease. In this case, immunomodulatory agents, monoclonal antibody drugs, and chemotherapy are actively used.
When determining a plan for how to treat multiple sclerosis in an individual case, the doctor takes into account the specific symptoms of the disease and prescribes exactly the medicine for multiple sclerosis that can alleviate their manifestation. However, for symptoms of multiple sclerosis, not only pills for a specific manifestation are used. If the patient goes to a specialized medical center, he is also prescribed physiotherapeutic methods of therapy, as well as a specially designed diet . Supportive treatment with folk remedies can also be practiced. Thanks to the constant work of researchers on the problem of treating multiple sclerosis, something new in the treatment of the disease regularly appears.
When the disease relapses, patients are often prescribed large doses of corticosteroids, which reduces the duration of the relapse.
Doctors are very careful about making predictions about the course of multiple sclerosis. But there are statistics that indicate that the prognosis is more favorable if the disease began before the age of 35; a woman is sick; the intervals between illnesses are long; After relapses, complete recovery occurs.
With multiple sclerosis, it is important to avoid infections, since even an acute respiratory infection can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. Patients should not be allowed to overheat, become overtired , or eat too much. Stress also has a negative impact on the patient's condition.
Treatment of cognitive impairment
It is not always possible to fully restore cognitive function. In most cases, therapy is aimed at compensating for an existing deficiency and adapting the patient. It is important to prevent serious cognitive impairment in time and prevent dementia from developing. Therefore, the main role is given to timely diagnosis [4].
The next stage is adequate treatment. The decision to select the pharmacological group of a drug and the course of treatment is very important, since many factors must be taken into account. It is taken by the attending physician.
Drug therapy for cognitive functions is aimed at [4,14–17]:
- Slowing down the pathological processes of multiple sclerosis .
The most obvious protection of nervous tissue in MS is provided by DMTs. Because nerve circuits can be repaired by other neurons, it is important to reduce nerve tissue destruction and inflammation in the brain. This creates the ground for compensation processes and reduces the rate of development of cognitive impairment. But there is also a downside. Although DMTs prevent severe cognitive impairment, they may have side effects and partially impair mental performance through other mechanisms. However, the benefits of taking DMTRS are incomparably higher, and side effects should not serve as a reason for discontinuing the drug on your own. If they appear, you should discuss the issue of symptomatic treatment with your doctor [14]. - Treatment of depression, anxiety, insomnia and other psycho-emotional disorders that worsen cognitive functions. Antidepressants, sedatives, anxiolytics, stimulants, etc. are used.
- Elimination of imbalance of neurotransmitters - dopamine, glutamate, acetylcholine. For correction, drugs of various groups are used, including donepezil, memantine, choline alfoscerate, glycerophosphate. The course of treatment is usually long, lasting six months or more. It is important to observe regularity and be under medical supervision [4, 15].
- Restoration of cerebral circulation , which is especially important in the presence of vascular disorders. Much attention is paid to improving metabolism , in particular replenishing energy reserves.
- Protecting nervous tissue from the negative influence of various molecules, increasing the safety margin. Drugs are used to strengthen the membranes of nerve cells (phosphatidylserine [16]), eliminate free radicals (thioctic acid [17]), and reduce the need for oxygen in conditions of its deficiency.
The doctor may prescribe a drug with a complex effect. Some drugs combine both protective and metabolic properties. The drugs can simultaneously improve blood flow to the brain and improve the balance of neurotransmitters. Many of them belong to the group of nootropics.
Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate (Mexidol), polypeptides of the cerebral cortex of cattle (cortexin) [16], piracetam, ginkgo biloba extract [15], cerebrolysin, citicoline [17], etc. have a complex effect.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is also called motor neuron disease. This is a disease of the nervous system that has a progressive chronic nature, during which central and peripheral motor neurons are selectively affected. In this condition, a person experiences increasing weakness of the shoulder and pelvic girdle, bulbar muscles, trunk and abdominal muscles, while the extraocular muscles and sphincters of the pelvic organs are affected to a lesser extent. Treatment of the disease is carried out continuously, in courses.
As a rule, the disease occurs sporadically; familial cases occur rarely. A person can get sick at any age, but more often the disease develops in people after 50 years of age.
It is believed that the disease is caused by a virus. The disease develops slowly, sometimes a person does not notice its onset. First of all, weakness of the distal parts of the arms gradually develops, and difficulty speaking may occur. Later, the specialist discovers the presence of atrophy and paresis of the small muscles of the distal segments of the arms. Gradually, there is a progression of paresis and atrophy, which can spread to the muscles of other parts of the body. In addition to these signs, the patient has symptoms that indicate damage to the pyramidal system.
Over time, the patient develops problems with swallowing, articulation, and phonation. They gradually become more pronounced. The tongue has limited movement and atrophy. The patient does not have a pharyngeal reflex; constant salivation occurs due to the inability to swallow saliva.
If there is weakness in the neck muscles, the patient's head may droop and movement is limited. Over time, facial and chewing muscles weaken. A person has a lower jaw and it becomes difficult for him to chew. Involuntary laughter and crying are also possible.
Doctors distinguish three types of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: bulbar , cervicothoracic , lumbosacral . The disease is always progressive.
Diagnosis of the disease includes determining the presence of characteristic symptoms. The patient also undergoes electromyography, the data of which can confirm damage to the cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord. To clarify the diagnosis, MRI of the cervical spine and myelography are performed.
Existing methods of therapy to this day do not completely cure the disease. Patients should be regularly monitored by several doctors of different specialties. Patients are prescribed to take riluzone , vitamin E , and B vitamins . Treatment with nootropic drugs , ATP , and anabolic hormones . To improve neuromuscular conduction, treatment with dibazole , prozerin , and oxazil . The use of other drugs and light massage sessions of the limbs is also practiced.
The disease can last from two to ten years, and the prognosis is unfavorable. The patient dies from paralysis of the respiratory center, exhaustion, and intercurrent infections. If a person also has bulbar disorders, he can live no more than two years.
How to increase cerebral reserve
Mental activity, fine motor skills and physical activity will help with this. Such measures are especially effective in preventing cognitive impairment [11,18–19].
Try to read more, solve crosswords, puzzles, and sometimes play computer games. Organize your vacation so that intellectual activity takes place there. It is known that during times of stress, most people find it more difficult to think. It's good if you manage to find an activity that would keep your mind in good shape, but would not cause stress. With such training it will be easier for you to cope with real mental loads. For example, you can install counting, memory, and word search games on your smartphone.
Study and work itself supports cerebral reserve. You should not indulge in idleness and take long breaks unnecessarily. In old age, you should also not neglect intellectual activity. If cognitive function is compromised, maintaining mental tone should be a priority.
Intelligence can also be developed through the body. Both fine and gross motor exercises improve cognitive function [18]. The mechanism of their action differs in many ways; different neural networks are involved. However, there is something in common.
During one or another physical action, a person also performs cognitive tasks. He orients himself in space, makes decisions, counts, analyzes, and remembers. Physical activity reinforces these processes with the release of pleasure mediators - endorphins, dopamine, serotonin. This way, successful actions are encouraged, and motivation is established not only to move, but also to think.
Handicrafts, drawing, writing or typing, and playing musical instruments help develop fine motor skills. Massage and finger exercises also stimulate the nervous system, including the cognitive departments.
Experts recommend that people with multiple sclerosis engage in sports on a regular basis. Coordination exercises, dancing and walking work well. The main thing is that the person likes them and is able to fulfill them [19]. Regular training is best for improving working memory [18].
Sclerosis of cerebral vessels
Sclerosis of cerebral vessels ( cerebral atherosclerosis ) is a disease that occurs relatively frequently. In the process of its development, damage to vessels of the muscular-elastic type occurs. In this case, pockets of lipid deposits gradually form in the inner lining of blood vessels in the brain. They can be either single or multiple. As the disease develops, the vessel gradually becomes deformed and narrows. Sometimes complete obliteration of the vessel occurs. As a consequence, there is a chronic, slowly increasing lack of supply to the organ that is fed through the brain vessel affected by sclerosis.
Most often, the symptoms of this disease, as well as damage to the blood vessels of the lower extremities, appear in people after the age of twenty, but the disease is most common among people over the age of 50.
As a rule, the manifestation of the disease is determined by a hereditary factor. However, the disease begins to develop under the influence of factors that stimulate its manifestations. These are too frequent psycho-emotional stress , diabetes mellitus , arterial hypertension , alimentary obesity , physical inactivity , and smoking .
Symptoms of the disease can be different and depend on where the disease is localized and where the process spreads. Diagnosis is based on the presence of damage to individual vessels.
To treat the disease, methods are used to stop the progression of the disease, as well as to activate the development of circulatory blood flow pathways.
As a therapy, it is practiced to ensure regular muscle activity, for which special exercises are used. Particular attention is paid to the patient’s nutrition. His diet should contain equal amounts of vegetable and animal fats, since weight gain with this disease is undesirable. If a person already has excess weight , then he should get rid of it.
In addition, it is important to provide systematic treatment of diseases that accompany sclerosis. A sharp drop in blood sugar, as well as a drop in blood pressure, should not be allowed.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis (from the Greek athera - mush and sclerosis) is a chronic disease in which the walls of the arteries thicken and lose elasticity, which leads to a narrowing of their lumen, and therefore to obstruction of blood flow.
Atherosclerosis (from the Greek athera - mush and sclerosis) is a chronic disease in which the walls of the arteries thicken and lose elasticity, which leads to a narrowing of their lumen, and therefore to obstruction of blood flow.
Victims of atherosclerosis are usually middle-aged and elderly people. However, atherosclerotic changes are found, in some cases, in children and even newborns. They also say that atherosclerosis is mainly a disease of people with high intelligence.
Atherosclerosis is more often observed in men over 35 years of age who are exposed to frequent stress. The hereditary factor also plays a role. Diabetes mellitus, obesity, gout, cholelithiasis, etc. contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. A diet with an excess amount of animal fat plays a significant role as a factor predisposing to atherosclerosis, but not as the root cause of atherosclerosis. Low physical activity plays a significant role in the development of atherosclerosis. An important reason should be considered psycho-emotional stress, traumatic to the nervous system, the influence of a busy pace of life, noise, some specific working conditions, etc.
In healthy people, blood flows freely through the arteries to all parts of the body, supplying them with oxygen and other nutrients. Excess cholesterol in the blood is deposited on the inner surface of blood vessels, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
An atherosclerotic plaque is a formation consisting of a mixture of fats (primarily cholesterol) and calcium.
On the surface of this “growth” on the inner lining of the vessel, a thrombus begins to be deposited - an accumulation of cells, mainly platelets (blood elements involved in the coagulation process) and blood proteins.
The thrombus, firstly, further narrows the lumen of the artery, and secondly, a piece can come off from it, which is carried further along the vessel by the blood flow until the diameter of the latter becomes so small that the thrombus gets stuck. In this case, a severe circulatory disorder occurs: blood simply stops flowing to any organ (or part of it) and it may die. The latter situation occurs in the following diseases: blockage of intestinal arteries, leg arteries, kidney infarction, spleen infarction, etc. If the vessels supplying the heart are damaged, a heart attack develops, and if atherosclerosis affects the arteries supplying the brain, the risk of stroke increases many times over.
The disease develops over several years, slowly but surely capturing still intact vessels. Starting from the moment when the lumen of the artery narrows by more than half, a person begins to feel the first signs of a lack of blood supply to a tissue or organ.
How and where atherosclerosis manifests itself depends on where it develops. For example, atherosclerosis of the aorta is affected by gradually increasing arterial hypertension, and in the worst case scenario, the development of a dissecting aortic aneurysm is possible - in this case, the aortic wall is thinned to the limit, and blood clots press on it from the inside - this threatens to rupture the aorta at any moment, which leads to death outcome.
Atherosclerosis of the branches of the aortic arch leads to insufficient blood supply to the brain, which causes dizziness, fainting and can lead to stroke. And atherosclerosis of the coronary (coronary) arteries of the heart leads to the development of coronary heart disease.
Atherosclerosis of the mesenteric arteries, that is, the arteries that supply the intestines, can lead to:
thrombosis (blood clotting in the lumen of the vessel) of arterial branches, resulting in necrosis (tissue death) of the intestinal wall and mesentery;
abdominal toad is attacks of colic-like abdominal pain that occurs soon after eating, often with vomiting and bloating. By the way, such attacks are relieved by fasting.
Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries disrupts the blood supply to the kidneys, leading to persistent arterial hypertension that is difficult to treat. The outcome of this process is nephrosclerosis and chronic renal failure. And atherosclerotic damage to the vessels of the penis due to smoking, diabetes mellitus or hypertension is one of the most serious factors of erectile dysfunction.
Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities manifests itself as chronic pain in the calf area, appearing when walking and disappearing when stopping. Pain in various leg muscles when walking forces a person to stop often. This phenomenon is called intermittent claudication.
Diagnosis
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels can occur for quite a long time without any manifestations, but modern examination methods make it possible to detect this disease in the early stages - for this purpose, the Doppler ultrasound method has been developed. Such a study is necessary because there are methods to reduce the risk of developing cerebrovascular accidents - strokes. To study the condition of blood vessels, the method of coronary angiography is used - specially taken x-rays allow one to determine the exact location of atherosclerotic plaques and the degree of narrowing of the lumen. In general, at the first episode of cerebrovascular accident, an examination by a cardiologist is simply mandatory.
Treatment
Currently, very effective surgical methods are used to treat atherosclerosis and its consequences - expanding the lumen of a narrowed vessel using a balloon, removing atherosclerotic plaques, replacing part of the affected vessel or creating a new path for blood flow. Also in recent years, there has been active development of new methods for treating atherosclerosis.
But in addition to radical methods, you can try to maintain your health on your own. For example, if you have pain in your legs, you should still walk for at least an hour a day. Naturally, when pain appears, you need to stop, and after the pain goes away, go again, but at a slower pace. Walking helps to open reserve, collateral vessels, and often a person’s condition noticeably improves.
It is useful for patients with atherosclerosis to eat seaweed, peas, peeled fried and stewed eggplants, cauliflower, strawberries, figs, raisins, walnuts, onions, cherries, grapefruits, watermelons, and vegetable oil. You should sharply limit your consumption of animal fats in any form.
Source: www.media.ru
Subchondral sclerosis
Subchondral sclerosis is a disease that affects the joints. As the disease progresses, articular cartilage degenerates, resulting in changes in the articular surface. The incidence of the disease increases markedly with age. Subchondral sclerosis is divided into primary and secondary forms. In the first case, the cause of the disease is severe overload of the spine, while the disease develops in healthy cartilage. In the second case, the disease develops on previously injured cartilage, which has been negatively affected due to injury, arthritis or the influence of other disorders.
Subchondral sclerosis of the endplates of the vertebral bodies often occurs when a person develops osteochondrosis or spondylitis . It is important to conduct a competent diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment for the disease. Various methods of therapy are practiced, but if the disease is too advanced, the doctor may decide on surgical intervention.
Sclerosis of the prostate, lungs
In addition to the types of sclerosis described above, patients are often diagnosed with sclerosis of the prostate or lungs . In the first case, there is a gradual sclerotic degeneration of the prostate gland, which develops as a result of the inflammatory process. During the development of this disease, elasticity is lost and the patency of the vesico-urethral segment is impaired. This, in turn, leads to chronic urinary retention. In most cases, this disease is preceded by chronic prostatitis. The disease relatively often affects young men.
Pulmonary sclerosis ( pneumosclerosis ) is the process of proliferation of connective tissue in the lungs, which ultimately leads to impaired lung function. The disease often develops as a consequence of tuberculosis, acute and prolonged pneumonia. Cardiogenic pneumosclerosis is distinguished, which is diagnosed in people suffering from prolonged congestion due to damage to the myocardium, aorta, and heart defects.
Tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis is also called Bourneville's disease . The name of the disease contains the Latin word tuber, which means “growth”, “tumor”. This is a rare disease of a genetic nature, during the development of which benign formations appear in various organs. Due to the very wide range of varied symptoms, the disease is multisystem in nature. If tumors arise in the brain, the patient may develop epilepsy and decrease in intelligence. When internal organs are damaged, a variety of signs of the disease appear. When making the initial diagnosis, the appearance of characteristic neoplasms in the fundus and facial skin is important.
As a rule, this disease manifests itself in children in the first year of life. They experience skin lesions, epileptic seizures and intellectual impairment. Often these signs are also accompanied by hydrocephalus . As the child ages, seizures become more frequent, and the decline in intelligence progresses. Patients with this diagnosis live no more than 25 years. After the diagnosis is established, they are prescribed symptomatic therapy, aimed mainly at stopping epileptic seizures. It is important to ensure a continuous treatment process.
In common parlance there is also the expression “ senile sclerosis ”. It is used when talking about a variety of memory impairments in older people. But in fact, there is no such disease, and the expression, obviously, comes from the term “cerebral atherosclerosis,” that is, atherosclerosis of the brain vessels, in which dementia in older people.
List of sources
- Schmidt T.E., Yakhno N.N. Multiple sclerosis. M.: MEDpress-inform; 2010;
- Korkina, M.V. Mental disorders in multiple sclerosis / M.V. Korkina, Yu.S. Martynov. G. F. Malkov. - M.: Publishing house UDN, 1986;
- Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases. Ed. E.I. Guseva, I.A. Zavalishina, A.N. Boyko. M.: Miklos. 2004;
- Gusev E.I., Boyko A.N. Multiple sclerosis: from studying immunopathogenesis to new treatment methods. M. 2001;
- Yakhno N.N., Shtulman D.R. Diseases of the nervous system: a guide for doctors in 2 volumes. M.: Medicine, 2001.