Useful articles / August 8, 2019
People are accustomed to blaming unhealthy food and stress for the occurrence of gastritis and ulcers, although in fact most problems with the gastrointestinal tract are due to the insidious bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
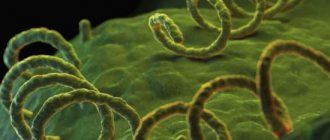
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped parasitic bacterium that can penetrate the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. It produces toxins that affect the mucous membrane of these organs and cause pathological changes. The peculiarity of Helicobacter pylori is that the aggressive acidic gastric environment is a very comfortable habitat for it. And, if most bacteria die in such an aggressive environment, then Helicobacter adapts well to it. According to statistics, more than 80% of the Russian population is infected with this bacteria.
To accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment for gastrointestinal problems, the patient must be tested for the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body . What laboratory diagnostic methods exist today and how accurate are they?
Detailed description of the study
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that affects the gastric mucosa due to its resistance to acidic environments.
It is assumed that infection with this infection occurs at an early age and is transmitted to children from parents or in preschool institutions. The most likely route of infection is considered to be the fecal-oral route of infection when living with an infected person in the same house, as well as during a long stay in a large group.
In addition, the oral route of transmission of infection through saliva and kissing has been recorded. There have been suggestions about the possibility of Helicobacter pylori infection during fibrogastroscopy - an examination through an endoscope that has been insufficiently treated with disinfectants.
After penetration into the stomach, Helicobacter pylori colonizes its mucous membrane, causing gastritis of the antrum of the stomach. The bacterium is protected from exposure to an aggressive acidic environment by producing alkali (ammonia) and some other substances that damage the gastric mucosa.
In response to Helicobacter pylori entering the body, the immune system produces antibodies. Initially, antibodies of class A and M are formed, they are soon replaced by immunoglobulins of class G. In most cases, the body is not able to completely defeat this infection, which predetermines the preservation of a high level of class G antibodies to it.
When combined with other unfavorable conditions, such as stress, poor diet, and infection with this bacterium, it leads to the formation of erosions and stomach ulcers. The following symptoms are noted:
1. pain in the upper abdomen (on an empty stomach);
2. nausea;
3. belching air;
Some people are asymptomatic when infected with Helicobacter pylori. Long-term damage to the gastric mucosa by this bacterium leads to the development of atrophy and decreased acid production. The risk of developing stomach cancer and lymphoma increases. A particularly high risk of developing cancer is observed in those whose relatives suffered from it.
Determining the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the body is important for early diagnosis of gastric pathology. Class G antibodies are produced several weeks after infection and are detected throughout life in the presence of bacteria in the body.
This test is relevant, in combination with other antibodies (IgA, IgM), as a primary diagnosis of this infection, but is not recommended for assessing the effectiveness of treatment, because IgG may persist for a long time even after successful therapeutic measures.
How is the Helicobacter test interpreted?
If the research is qualitative, then there can be only two results - “positive” or “negative”. If a quantitative method is used, the analysis standards will depend on the specific laboratory, and only a doctor can interpret them.
How can you become infected with Helicobacter pylori?
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is called an intrafamilial infection and it occurs in 80% of the Russian population. The main modes of transmission: fecal-oral, oral-oral, household. This could be kissing, sharing utensils, eating insufficiently clean vegetables and fruits, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules... Most often, infection occurs in childhood through household contact. If, for example, parents have the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in their bodies, then it is passed on to their children. Another question is in what period of a person’s life it will manifest itself. Do not forget that most diseases of the upper digestive tract occur precisely because of this bacterium. Gastroenterologists warn that 100% of people with Helicobacter develop gastritis over time. Therefore, it is important to detect it and undergo treatment on time.
References
- Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Abdulganieva D.I., Alekseenko S.A., Ivashkina N.Yu., Korochanskaya N.V., Mammaev S.N., Poluektova E.A., Trukhmanov A. S., Uspensky Yu.P., Tsukanov V.V., Shifrin O.S., Zolnikova O.Yu., Ivashkin K.V., Lapina T.L., Maslennikov R.V., Ulyanin A.I. . Practical recommendations of the Scientific Community for Promoting the Clinical Study of the Human Microbiome (NSOM) and the Russian Gastroenterological Association (RGA) on the use of probiotics for the treatment and prevention of gastroenterological diseases in adults. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2020
- GuevaraB, CogdillAG. Helicobacter pylori: A Review of Current Diagnosticand ManagementStrategies. DigDisSci. 2020
- Choi IJ, Kim CG, Lee JY. Family History of Gastric Cancer and Helicobacter pylori Treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020
Blood and stool tests
20–30 days before stool examinations, you should stop taking antibiotics, and three days before, you should stop using coloring products. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach. One day before, you need to eliminate fatty foods from your diet.
The results of stool tests are released the next day. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test is just as quick, but a Western blot test, which requires more time and more complex equipment, can take up to six days.
A stool test only shows the presence or absence of infection. Blood tests provide more accurate results and reveal the presence or possibility of developing peptic ulcers.
How does the procedure work?
The study allows you to determine the level of antibodies in the blood against bacteria, including Helicobacter pylori. The basis of the method is donating blood for analysis. Basically, serum is required, which is collected from a vein.
The biomaterial is collected in a container with a coagulant gel. With its help, plasma is released that is used in further research.
The only complication during the procedure is the occurrence of bruises when a vein is punctured. To make the hematoma resolve faster, it is enough to apply a dry, warm object.
The immunoglobulin G test result can be obtained 24 hours after blood collection. To study the IgA type indicator, an additional 8 hours will be required.
The price for the procedure ranges from 340 rubles for one specific antibody to 900 rubles for all three types.
Contraindications for carrying out
ELISA analysis should be abandoned in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- with possible convulsions;
- with damage to the skin or subcutaneous fat;
- with phlebitis of the vein.
Indications for testing
It is difficult to imagine that a person who does not have symptoms of the disease would go for a full-scale examination unnecessarily.
Symptoms predisposing to testing for Helicobacter pylori:
- Gastralgia (pain in the stomach and intestines) of varying intensity. Appear during or after meals, caused by enzyme deficiency and impaired digestion of food and its stagnation in the stomach.
- "Hunger pains." They appear 2-3 hours after eating and disappear during meals. Due to damage to the mucous membrane, its sensitivity worsens, the patient feels how food and water pass through the digestive tract.
- Intense heartburn. It occurs due to the backflow of aggressive gastric juice into the esophagus that is not intended for this, and with frequent repetitions it is a symptom of pathology.
- A feeling of heaviness that occurs even after taking minimal portions of food. The patient has a feeling of a full stomach.
- Frequent nausea not caused by objective reasons (for example, toxicosis of pregnancy).
- A combination of stomach pain with vomiting and inability to eat and drink.
- Slight discomfort in the projection of the stomach, loss of appetite, mild heaviness. Often appear at the initial stage of heliobacteriosis.
- The presence of mucus in the stool.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor for examination and treatment.
Decoding the analysis results
Despite the fact that the decoding of the indicators should be entrusted to the doctor who referred for the examination, all patients want to find out their results on their own.
How much is the norm for Helicobacter pylori? The norm of bacteria content when testing venous blood: 0-0.9 units/ml .
Interpretation of other meanings:
- 0.9-1.1 units/ml – the likelihood of Helicobacter pylori infection is doubtful;
- More than 1.1 units/ml – bacteria are definitely present in the body. High risk of developing stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
The norm for the urease test is the absence of crimson color in the color of the material. The norm for bacterioscopic examination is the absence of pathogens.
Urease breath test
Analysis for Helicobacter pylori using the urease test is associated with the synthesis of the urease enzyme by the bacterium. It is this that allows the microorganism to exist in the gastric juice, breaks down urea to the level of ammonia and carbon dioxide, which is exhaled through the lungs. The technique has 3 modifications:
- with urea labeled with radioactive carbon isotopes;
- 13C – urease test;
- helic test.
Modern test systems are equipped with special protection of the breathing tube from saliva
Option with urea isotopes - at the beginning of the study, the patient simply breathes into a tube, and two air samples are taken from him. 15 minutes after ingestion of the labeled urea solution, 4 more samples are taken. When breathing, it is important to promptly swallow accumulated saliva; if it gets into the samples, it spoils the results and the test has to be repeated.
The 13C urease test is the most common in gastroenterological diagnostics. In this embodiment, non-radioactive urea labeled with the 13C isotope is used. The patient only has to take 2 samples of exhaled air in special bags: the first on an empty stomach in the morning, the second 30 minutes after taking the diagnostic solution.
The advantages of the method are:
- accurate diagnosis;
- safety in the absence of the use of radioactive materials;
- The duration of the study is within 40 minutes, which is convenient for the patient.
Breathing helic test - a modification uses urea. It is characterized by a large flow of released gas after taking the urea mixture. The content in the initial air sample and after exposure to urea is compared.
The test is considered safe and is suggested for use in diagnostics for children and pregnant women. But experts do not confirm its sufficient accuracy, so they rarely use it. In conclusion, after the urease test, the activity will be indicated:
- if detected, a positive result;
- if not, negative.
The indicators are determined quantitatively using a special apparatus (mass spectrometer). It is customary to evaluate the analysis for Helicobacter depending on the level of the isotope or its substitute in the exhaled air mixture:
- a mild degree of contamination is considered 1–3.4%;
- average - 3.5–6.4;
- severe - 6.5–9.4;
- extremely severe - any indicators above 9.5%.
It is important to remember that the urease breath test can give a false-negative result if the day before the patient took drugs that reduce the secretory activity of the gastric glands. These medications block the action of bacterial urease, then urea stops breaking down.
[node:field_field_doprekl2]
How is the urease rapid test performed?
Helicobacter can be determined by the activity of urease not only in exhaled air, but also directly in a piece of tissue from the gastric mucosa obtained during fibrogastroscopy. It is inoculated on a special medium, which, in the presence of urease and the release of ammonia, begins to become alkalized. The use of a yellow indicator is accompanied by a replacement with a crimson color.
The assessment is carried out according to the number of pluses (+) depending on the time required to change the color:
- + — it took at least 24 hours (infection is minor);
- ++ — the process took up to three hours (moderate prevalence);
- +++ - color changed within an hour (significant infection).
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori
The endoscopic examination method is considered the most accurate test. A biopsy of the gastrointestinal tract reveals not only the presence or absence of bacteria, but also determines the stage of the disease, and also allows you to immediately find out whether the organs are affected or not.
This study is carried out using a gastroscope (a long tube inserted into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth and equipped with a camera and a device for taking a tissue sample). In addition to taking biomaterial for biopsy, the gastroenterologist visually examines the condition of the walls of the duodenum and stomach.
Two hours before the biopsy, you should not smoke or drink, and your last meal should be 12 hours before.
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori can be performed under anesthesia. The procedure lasts about twenty minutes. The doctor will determine the ulcer, if any, during the examination, and the patient will receive the test results the next day.
Our clinic has the opportunity to conduct FGDS with Helicobacter pylori and other studies.
Preparing for analysis
To obtain objective indicators, you need to carefully prepare for testing for Helicobacter pylori.
Necessary preparations:
- Complete smoking cessation the day before the test. Nicotine negatively affects the gastric mucosa, distorting test results.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol. The reason is the same.
- Prohibition on drinking tea and coffee, which negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Temporary restriction on food intake for 8 hours before analysis.
Since blood for Helicobacter testing is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, you can take some food and water with you to the clinic.
Biopsy method with cytological examination
The most accurate method of detection is the examination of cytological material in the form of mucus smears obtained during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The possibility of false results is virtually eliminated. Difficulties depend only on the training and experience of the personnel.
Helicobacter under a microscope has a very characteristic appearance with flagella
A negative result is assessed as the norm for Helicobacter (not detected); the detection of even single bacteria is considered positive.
For quantitative assessment, use the designation of contamination pluses or the number of microorganisms in the field of view:
- (+) or weak - noted when up to 20 bacteria are detected in the field of view of the microscope;
- (++) or moderate - 20–40 microorganisms;
- (+++) high - over 40 bacteria.
Who needs to be tested?
An analysis to detect Helicobacter in the body is prescribed for the following indications:
- if a person often feels discomfort in the intestines in the form of incomprehensible pain, increased gas formation, grumbling, a tendency to diarrhea or constipation, intolerance to some food;
- against the background of complete health, but in the presence of a sick person in the family to identify bacterial carriage, even a minimal number of bacteria in conditions of reduced immunity can very quickly cause severe damage to the stomach;
- one cannot ignore such a sign as rapid intoxication from small doses of alcohol with a pronounced hangover; Helicobacter bacteria disrupt food processing processes and the action of enzymes for the absorption of alcohol;
- with incomprehensible pain in the epigastric region, a feeling of heaviness, heartburn;
- deterioration of health after eating fatty and fried foods, spicy dishes;
- The patient experiences attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Quantitative confirmation of stomach contamination with Helicobacter is necessary:
- to select a treatment method for gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- detection of infection in the postoperative period of patients with a removed stomach tumor, lymphoma;
- monitoring the effectiveness of the targeted use of medicines.
More than 140 years have passed since the discovery of Helicobacter. Modern scientists are working on proposals for reliable rapid tests. Life requires the introduction of a quick examination method at the clinic level.