Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 36 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
Lymph flow is no less important for the body than the functioning of the circulatory system. Therefore, any disturbances in the structure of the lymphatic system immediately make themselves felt with noticeable external signs. Among them is lymphostasis, or lymphodema, associated with impaired drainage of lymph from internal organs or limbs. The result is noticeable swelling with darkening of the skin at the site of stagnation of lymphatic fluid, which can only be dealt with by contacting a qualified specialist. Today, about 10 million people suffer from lymphostasis, mainly women, whose stagnation of lymph in the body is associated with physiological and hormonal reasons.
Types of lymphostasis
Depending on the cause of the development of lymphodema, there are:
- primary, or congenital form;
- secondary, or acquired form of the disease.
Congenital pathology develops against the background of disturbances in the formation of the lymphatic system during intrauterine development. In rare cases, a hereditary factor may influence lymph flow disturbances. Cases of primary lymphostasis account for about 6% of the total number of patients with this disease.
The acquired form of lymphodema occurs under the influence of unfavorable external factors. The first symptoms often make themselves felt in childhood and adolescence, and later intensify during pregnancy and lactation, which is due to hormonal changes in the body during puberty and gestation. A sharp progression of lymphostasis is possible after pregnancy or severe injury.
How does the lymphatic system work?
There are many lymphatic capillaries in all human organs and tissues.
They are closed at one end and unite into larger lymphatic vessels. As blood flows through small arteries, some of its liquid part, plasma, leaks into the tissues. Tissue fluid is partially absorbed into small veins and partially into lymphatic capillaries. Thus, it does not accumulate in tissues. All lymphatic vessels empty into lymph nodes. Here the lymph is filtered and cleared of foreign agents. Lymphocytes, the cells of the immune system, are formed in the lymph nodes. Usually many small afferent vessels flow into the lymph node, and only 1-2 efferent vessels exit.
Lymphatic vessels unite into larger ones and form two main ducts: the thoracic and right lymphatic. They flow into the right and left subclavian veins, respectively. Thus, the lymphatic system cleanses tissue fluid and returns it to the bloodstream.
Causes
In most cases, the development of lymphoma is caused by the patient having the following diseases:
- infectious diseases that cause inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- chronic venous insufficiency syndrome with thrombophlebitis and varicose veins;
- damage to the lymph nodes and narrowing of the pathways;
- injuries and burns affecting the subcutaneous layer of cells;
- oncological diseases treated with radiation therapy;
- neoplasms in soft tissues;
- penetration and development of parasites in the structure of the lymphatic system;
- heart and kidney diseases that cause persistent tissue swelling.
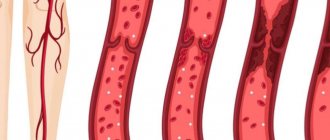
The impact of one or more of these factors in combination with the anatomical features of the patient’s body leads to disruption of the conductive and contractile function of the lymphatic vessels. They lose the ability to circulate lymph throughout the body, which causes stagnation. This condition is especially dangerous for the lower extremities, where lymphatic fluid enters in large quantities under the influence of its own gravity, but does not have the opportunity to rise up through the contracting vessels.
With prolonged stagnation of lymph, proteins, mucopolysaccharides and other organic substances are released from it. They saturate the walls of blood vessels and disrupt their natural structure. Connective tissue quickly grows inside the pathways, narrowing the lumen and making it impossible for lymph to move within the body.
Primary and secondary lymphedema
Lymphostasis is caused by lymphedema, classified as primary and secondary.
Primary lymphedema is considered a hereditary disorder that appears primarily during puberty and only sporadically. It is a direct consequence of genetically determined insufficiency of lymphatic vessels. Secondary lymphedema is provoked by related pathologies.
The following diseases contribute to the development of secondary lymphedema:
- Tumors and neoplasms of the lymphatic system (benign and malignant);
- Mechanical damage to blood vessels and lymph nodes due to injuries (burns, fractures, bruises, dislocations);
- Staphylococcal, fungal, bacterial and parasitic infections;
- Metastatic block of lymphatic tracts and nodes;
- Permanent disorders of the systemic circulation due to chronic cardiovascular diseases;
- Heart failure;
- Severe pathologies and kidney dysfunction;
- Hypoproteinemia;
- Venous insufficiency;
- Obesity;
- Tuberculosis;
- Postthrombophlebitic syndromes.
In some cases, lymphedema develops due to surgical removal of lymph nodes during the treatment of cancer. This can also happen due to irradiation of the lymph nodes for therapeutic purposes.
Symptoms
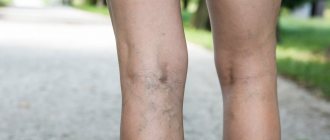
The first sign of the disease is severe swelling that rises from the toes along the ankle joint to the lower leg and thigh. For this reason:
- the limb loses its natural shape and becomes like a column;
- the skin becomes stretched, causing the patient unpleasant pain;
- joints become less mobile;
- the pattern of veins on the limbs disappears, the skin noticeably becomes rougher and darker, and its structure becomes similar to an orange peel.
Signs of lymphostasis at different stages of the disease
Depending on the severity of symptoms, the following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- at the first stage, edema occurs only under the influence of external unfavorable factors: prolonged sitting or standing, increased volumes of water drunk, heat, etc. More often, edematous phenomena appear in the late afternoon;
- the second stage of lymphedema is said to occur when swelling occurs more frequently and the patient begins to feel severe pain and heaviness in the legs. When you press on the skin, a noticeable dent remains, which gradually levels out. The patient’s body weight increases due to edema, and the skin noticeably becomes rougher, losing its natural elasticity;
- at the third stage, the joints of the limb become immobilized, it loses its natural shape, and signs of trophic ulcers appear on the skin, which can lead to sepsis and the gradual development of tissue necrosis.
Complications
In the absence of medical control and treatment, lymphedema can cause:
- hyperkeratosis;
- skin fistulas;
- tissue phlegmon;
- erysipelas, etc.
With a long course of the disease, signs of lymphangiosarcoma may appear.
Are you experiencing symptoms of lymphedema?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Diagnosis of edema
At the MedicCity clinic you will be provided with highly qualified medical care for lymphostasis and other phlebological diseases. Within one clinic, you can get advice from a vascular surgeon and, if necessary, doctors from other areas, as well as undergo a full examination.
Studies that need to be completed for lymphostasis:
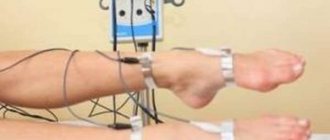
- Ultrasound of blood vessels of the lower extremities;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- biochemical blood test, urine test;
- lymphography and lymphoscintigraphy to determine the patency of blood vessels (if necessary, as prescribed by your doctor).
1 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
2 Vascular ultrasound in MedicCity
3 Vascular ultrasound in MedicCity
Currently, every tenth inhabitant of the Earth suffers from fluid retention in the lower extremities. If the treatment of lymphostasis is left to chance, then such unpleasant diseases as eczema, erysipelas and trophic ulcers may be added to lymphostasis. Due to lymphostasis, a person can become disabled and walk on crutches.
Treatment
Conservative treatment of lymph flow disorders is effective only in the early stages, when soft tissues have not yet received irreversible damage. While taking medications, the patient is recommended to:
- wear compression knitwear;
- engage in physical therapy;
- review your diet in favor of dietary dishes for weight loss;
- take a course of lymphatic drainage massage;
- drink medications with a diuretic effect, phleboprotectors, compounds to improve the circulation of fluids in the body, and vitamin C;
- follow a diet for lymphostasis;
- sign up for physiotherapy treatments.
Prices for treatment and doctor's appointments in our center
| Basic services | price, rub. |
| Consultation with a doctor, lymphology specialist | 3 000 |
| Consultation with the head physician | 4 000 |
| Chiropractor consultation | 3 000 |
| Price of decongestant therapy | from 2500 per procedure |
| Taking measurements for the production of compression hosiery | 2 000 |
| Compression jersey | >Price, rub. |
| Jobst Basic circular knit compression socks | 4 000 |
| Jobst Basic circular knit compression tights | 6 500 |
| Jobst Basic Circular Knit Compression Stockings | 6 100 |
| Bandage system for arm and leg | From 100 euros for 1 segment |
| Custom-made compression socks and flat knit socks | Without additional options from 90 euros |
| Massages | price, rub. |
| Manual lymphatic drainage | From 2500 per procedure |
Make an appointment
What it is?
Lymphostasis is a lesion of the entire lymphatic system and a violation of the outflow of lymph. It simply stops circulating and accumulates in the tissues. This is why the legs swell a lot, and the skin becomes very dense over time. The problem does not go away on its own and develops into a more serious form, when a person can hardly move due to severe thickening of the legs.
This phenomenon is popularly called elephantiasis due to its external similarity to the limbs of this animal. Similar stagnation of lymph can develop on one leg or two, and can also affect the arms. From an aesthetic point of view, such a sight is very unpleasant, and it is quite difficult to hide it. On the Internet you can see photos showing examples of this disease.
Preventive measures
Patients will be able to prevent the development and accelerate treatment of lymphostasis of the upper extremities by:
- regular physical activity, special exercises for lymphostasis of the hands;
- lymphatic drainage self-massage skills;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- reviewing the diet to reduce the amount of dishes high in fat and salt;
- avoidance of tight clothing and jewelry that pinches the hands;
- compliance with safety precautions to prevent overheating or skin burns;
- treating wounds and ulcers on the hands to prevent infection;
- weight control.
Additional recommendation: during sleep, it is better to place the limb on a pillow in an elevated position.
Choosing the right compression sleeve will help you cope with the disease at the initial stage. It is advisable to give preference to products from a well-known manufacturer, which guarantees the quality and safety of the ordered product.
Prevention
Preventive measures play an important role. Among them we note:
- Avoiding heavy physical activity;
- Proper balanced nutrition;
- Active lifestyle, swimming, performing special exercises;
- Avoiding overheating;
- Extremity skin care;
It is also important to promptly contact a specialist regarding the use of compression hosiery if symptoms of pathology occur.
The Onco.Rehab Integrative Oncology Clinic tells you that a lot in avoiding the disease depends on you.
Stages of lymphedema
Lymphedema is a chronic disease for which there is no cure. However, there are ways to keep the fluid under control. The severity of lymphedema, according to the International Society of Lymphology, is graded from stage 0 to stage III.
Stage 0
- latent or subclinical lymphedema, which may be present several months before the clinical picture.
Stage I
- early fluid accumulation.
Stage II
- development of tissue fibrosis.
Stage III
- lymphostatic elephantiasis of the limb.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely medical care, the patient may develop:
- severe pain caused by compression of nerve endings;
- deep skin damage with multiple trophic ulcers and inflammatory processes;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- depression;
- compaction of lymphatic vessels.
About the benefits of exercise therapy
In addition to massage, physical exercise is very important for lymphostasis of the lower extremities. They are included in the treatment of this disease. Of course, it is necessary to develop a special complex that needs to be done 2 times a day. You should devote only a quarter of an hour to classes. In this case, a compression bandage must be present on the sore leg.
What exercises can be included in the complex?
- Bicycle with a sore leg;
- Flexion and straightening of toes;
- Rotate your feet in different directions alternately;
- “Drawing” a figure of eight with your feet.
The exercises are very easy, but the important rule is to do them daily.
Features of care for lymphedema at the Ilyinsky Hospital
We use an intermittent pneumatic compression device. The device is programmed and performs compression in a special sequence. This allows lymph to be evacuated in one direction.
In the Ilyinsky hospital, in case of resistant lymphedema, interventional treatment methods are also used. One of them is thoracic sympathetic blockade at the level of Th-3 (third thoracic vertebra) under X-ray control. It is the thoracic section of the sympathetic system that is responsible for the vascular tone of the limb, and blockade of the nerve plexus allows the outflow collaterals to open. Thanks to this procedure, we have good results in cases of difficult-to-resolve lymphostasis. This is essentially one small injection. The procedure is safe and easily tolerated.
We avoid the use of physical therapy treatments such as laser and electrical stimulation due to insufficient evidence of their effectiveness for lymphedema.
We also help restore and control balance in various pain syndromes and in the event of peripheral neuropathies.
In case of increased fatigue, we evaluate the factors that can lead to this condition and teach the technique of “conserving / conserving daily energy”.
For patients undergoing surgical treatment at the Ilyinskaya Hospital, rehabilitation doctors evaluate hand function before surgery. Physical therapy exercises begin on the first day after surgery with easy restoration of the angles of movement of the limb. We recommend such passive exercises under the supervision of a physical therapist during the first week after surgery. Then, in the second week, or when the drainage is removed, patients can begin active movements on their own. This phase lasts 6 to 8 weeks until shoulder function is fully restored. At the same time, you can massage the scar (with the help of a massage therapist or after receiving instructions for self-massage). Between 4 and 6 postoperative weeks, you can do light weight exercises.
If you develop signs of lymphedema, it is very important to take proper skin care to reduce the extent of lymph node dissection, avoid trauma, weight gain, vaccinations, insect bites, and venous access to the involved limb. And immediately resolve the issue of antibiotic therapy in case of signs of infection.
Causes of lymphostasis in the legs, arms and other parts of the body
The causes of primary lymphostasis are disturbances in intrauterine development of the fetus. There are many reasons for the secondary form. Failure in lymph circulation can occur in the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- heart failure;
- glomerulonephritis and other kidney pathologies (causes of leg lymphostasis);
- hypoproteinemia – lack of protein in the blood;
- arteriovenous fistulas – pathological passages between arteries and veins;
- lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- lymphangitis – inflammation of the lymphatic vessels;
- extended mastectomy in women - removal of the mammary gland (lymphostasis of the arm occurs after mastectomy);
- cancer of the prostate gland in men
Causes of development of lymphostasis of the upper limb
The root cause of the development of edema of the upper limb after a mastectomy, as well as radical resection of the mammary gland, is the removal of axillary lymph nodes, which are regional to the mammary gland. Thus, the natural outflow of lymph is disrupted, and its restoration may be impaired due to the formation of scar connective tissue and its subsequent compression of both lymphatic and blood vessels in the operated area.
Other components of complex treatment for breast cancer (radiation therapy, chemotherapy) carried out after surgery can also provoke the development of lymphostasis or intensify existing edema. Other factors that can provoke the development of lymphostasis may be infectious processes, increased physical activity on the upper limb on the operated side, and obesity.
Help for Lemphedema
The most effective way is complex decongestant therapy
.
Complex decongestant therapy includes two stages (phases):
- the first stage is reducing the volume of liquid,
- the second stage is long-term self-control to maintain the achievements of the first phase.
During the first phase, a massage is performed, due to which a reduction in the volume of lymph is achieved. This effect can last from 3 to 8 weeks, until fluid contraction reaches a plateau and massage no longer helps reduce volume.
One of the main components of Phase I is manual lymphatic drainage, which removes fluid through the subepidermal fluid channels that form after the lymphatic channels are damaged. Technically, lymphatic drainage massage is a superficial skin massage performed by a lymphedema physical therapist. The goal is to mobilize fluid from areas of congestion into lymphatic vessels that function properly.
Phase I also includes a gradient compression bandage to mobilize fluid. We use short and long elastic bandages. Short elastic bandages can stretch 40 - 60% of their original length. Long bandages stretch more than 140%. Short bandages are applied with little tension, with a large number of layers in the distal part of the limb. The pressure inside the dressings is low when the patient is at rest. When a person works with a limb, muscle contraction increases the pressure of the intercellular fluid, thereby creating the so-called working pressure. Alternating cycles of tension and relaxation create an internal “pump” that pumps lymph back into the bloodstream.
The overall goal of Stage I is to evacuate accumulated fluid into the circulatory system. Short bandages also help prevent tissue fibrosis. They should be worn even during exercise, as lymph flow may increase during muscle contractions.
Phase II – maintaining the achieved volume. To do this, we select a stocking according to size or order an individual one in case of unevenness in the shape of the limb.