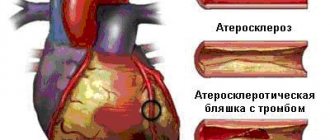
Atherosclerosis of the heart vessels (atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels) is a chronic pathology that develops with the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the coronary arteries. Cholesterol plaques appear due to impaired lipid (fat) metabolism. The artery wall thickens, elasticity is lost, the vessel is deformed with a narrowing of its internal lumen, which interferes with normal blood flow to the heart. When the lumen of a vessel is completely blocked by a plaque, some of the cells die, causing acute myocardial infarction.
Causes of vascular atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries can develop under the influence of endogenous and exogenous factors.
In total there are about 200 of them. The most common causes of pathology are:
- Increased cholesterol levels.
- Smoking.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity.
- Alcoholism.
- Age and gender. Men over 35-40 years of age are more susceptible to coronary artery pathologies. In women of reproductive age, the disease is quite rare. This is due to the synthesis of estrogens, which protect the arteries.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Diabetes.
- Poor diet with a lot of animal fats.
Classification
There are several stages of damage to the coronary arteries:
- Initial. At this stage, there is a slowdown in blood flow and the appearance of microcracks in the vascular endothelium. Such changes lead to lipid deposition and the formation of greasy stains.
- Average. As the pathology develops, clear plaques are already observed. Blood clots may also form. Their danger is that they can come off and close the lumen of the artery.
- Heavy. At this stage, the plaques thicken as calcium salts are deposited in them. Therefore, the coronary artery is deformed, and its lumen narrows.
Technique for stenting coronary arteries (with professional jargon)
“We install the introducer”
To get to the heart vessels, the doctor needs to get into the patient’s arterial system. For this purpose, one of the peripheral arteries is used - the femoral (in the groin) or the radial (on the forearm). Under local anesthesia, a puncture is made in the artery and an introducer is installed - a special tube, which is the “entry gate” for all the necessary instruments.
"Let's put a guide"
Then a special thin-walled tube about a meter long - a guiding catheter (“guide”) is passed through the patient’s arteries and stops, slightly short of the heart, in the aorta. It is from the aorta that the coronary arteries that supply the heart depart. The tips of the catheters are curved in such a way that it is convenient for the doctor to enter one of the coronary arteries, right or left. By controlling the catheter, the doctor “enters” one of the coronary arteries. Half the job is done.
“Starting a conductor”
But how to get to the point of maximum narrowing in the artery? To do this, we need a “rail” along which all our tools will “ride”. This rail is the coronary guidewire - a thin (0.014 inch = 0.35 mm) metal “lint” with a soft tip (so as not to “scratch” the artery during the operation). Sometimes it is quite difficult to place a guidewire behind the site of narrowing; the tortuosity of the artery, the angle of departure of the branches of the artery, or pronounced narrowing due to the presence of plaques interfere. You can take a “harder” or “slipperier” conductor. Well, or just a favorite, because every doctor has his own preferences. One way or another, the guide ends up behind the site of narrowing on the periphery of the artery that we want to stent.
"Ballooning"
The first instrument that gets to the site of narrowing of the artery is a coronary balloon with a diameter most often from 1 to 3.5 mm and a length of 10-20 mm. The balloon is put on the conductor and moves along it to the point of maximum narrowing where it inflates. The pressure inside the cylinder reaches 15-20 A
Next, along the conductor, to the place that was narrowed before the balloon was inflated, the same balloon is inserted, on the surface of which a stent is fixed in a folded state. The balloon is inflated, the stent is expanded and “pressed” into the artery wall. The stent does not always expand perfectly and then the final stage of the procedure is needed - postdilatation (in simple terms - re-inflation).
"Let's blow it out"
A rigid balloon is placed inside the implanted stent and inflated with high pressure (up to 25 atmospheres). Most often, after this, the stent straightens and adheres well to the walls of the artery.
Symptoms
In the early stages, the pathology occurs in a latent form.
The first signs of the disease include:
- pain in the chest area, radiating to the left shoulder and back;
- shortness of breath at the onset of pain;
- dizziness;
- nausea.
None of the listed symptoms are specific. Therefore, the disease is often confused with other pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
With further progression, the following are noted:
- Angina pectoris. This condition is characterized by pain in the chest, which appears after emotional or physical stress.
- Arrhythmia. This condition develops when the myocardium is damaged and the passage of impulses in the heart is impaired.
- Cardiosclerosis. The pathology causes disruption of the contractile function of the heart muscle. It develops when areas of fibrosis form.
- Heart attack. In this condition, the cholesterol plaque ruptures and interferes with normal blood flow.
The pathology is dangerous because it can provoke acute and chronic heart failure. With acute deficiency, the risk of heart attack increases, which often leads to death. Atherosclerotic lesions also contribute to stroke and transient ischemic attacks.
Hemostasis
What to do with a hole in an artery?
If the intervention was carried out through the radial artery (on the arm), a special bracelet with a cushion (hemostatic cuff) is put on the wrist, which will put pressure on the injection site and prevent bleeding. Depending on the situation, the cuff will remain on the arm from 3 to 12 hours.
In case of femoral access, there are 2 main options:
- Manual (manual) hemostasis. After the introducer is removed, the doctor presses with his hands on the injection site for 15 minutes. Then apply a pressure bandage for 6-8 hours. The patient should lie on his back with his leg straight.
- Closure devices are special “plugs” that allow you to close the artery from the inside. In this case, there is no need to put pressure on the leg and a pressure bandage is not needed. A special patch is applied to the injection site and several hours of bed rest are recommended.
Stenting is completed.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of coronary vessels is carried out comprehensively and includes:
- Examination by a cardiologist. On it, the doctor records the patient’s complaints and conducts primary diagnostics, which boils down to listening to the rhythm, measuring blood pressure and an ECG.
- Stress scintigraphy. This study allows us to determine the location of lipid formations and the degree of their severity.
- Ultrasound with Doppler. Allows you to identify changes in the arteries, determine the thickness of their walls, evaluate hemodynamics and other important indicators.
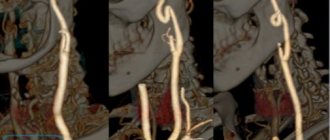
- Coronary angiography. This study is conducted with contrast. It allows you to determine damage to the vascular walls and the degree of narrowing of the arteries of the heart.
- Pristress-ECHO. This study allows us to identify transient disorders of cardiac muscle contractility.
How to choose between stenting, bypass surgery and drug therapy?
This is the task of your cardiologist, who takes into account the following data:
- The severity of symptoms, namely: the severity of angina pectoris, the severity of shortness of breath, in other words, how much ischemic disease “interferes with the life” of the patient.
- Objective evidence of myocardial ischemia (lack of blood). Most often this is a stress test, ideally stress echocardiography, which should be performed by qualified doctors in a center with a large number of such studies.
- Coronary angiography data. With widespread severe damage to all three coronary arteries, the results of bypass surgery are better.
- Accompanying illnesses. If a patient has diabetes mellitus and multivessel disease of the heart arteries, for example, coronary bypass surgery is usually indicated.
Treatment of atherosclerosis
The treatment tactics are determined by the stage of the pathology, the patient’s condition and concomitant ailments.
When carrying out any manipulations, the patient should first of all:
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Normalize weight.
- Make time for regular moderate physical activity.
- Normalize nutrition. It is important to avoid fried, fatty and sweet foods. The diet should be supplemented with fresh vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products and water-based cereals.
Specialists use techniques that allow:
- Adjust blood pressure levels.
- Restore lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Slow down pathological changes in the blood vessels of the heart.
- Reduce the oxygen demand of the heart muscle.
- Reduce the severity of ischemia.
In advanced cases, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries can only be treated surgically.
Today, the following methods are used for effective treatment:
- Coronary artery bypass surgery. This technique allows you to create a bypass for blood flow. The affected area is not involved in blood circulation.
- Coronary stenting. This technique involves inserting a stent with a rigid frame into the affected artery. It allows you to expand the vascular bed and ensure the free passage of a sufficient amount of blood with oxygen and nutrients necessary for the heart muscle.
- Balloon angioplasty. This technique is one of the safest and most effective. A special catheter is inserted into the femoral artery. It is brought to the problem area. Then, at the site of the blockage of the artery, a balloon is inflated, which expands the existing lumen.
Modern methods of treating coronary atherosclerosis make it possible not only to eliminate the symptoms of the pathology, but also its causes. The choice in favor of a certain method should only be made by an experienced doctor. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances!
Contact our clinic in Moscow! We provide all services on the most favorable terms and at the best prices. The estimated cost of specialist consultation and examinations is indicated on the website. You can find out exact prices from specialists. Our medical center adheres to a loyal pricing policy. Thanks to this, therapy for any disease is available to all patients!
What is coronary artery stenting?
More than 2 million stents are implanted annually. And this is understandable, because stents are used to treat one of the most common diseases - coronary heart disease.
Coronary angioplasty and stenting is an intravascular treatment for coronary heart disease. The basis of coronary heart disease is the narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the heart (coronary arteries) by cholesterol plaques. Stenting allows narrowed arteries to widen. To do this, a special balloon is placed inside the artery and inflated, thus “flattening” the cholesterol plaque and restoring blood flow through the artery. After this, a metal frame—a stent—is implanted into the narrowing site to “fix” the result. In this case, there is no need to open the chest and all manipulations are carried out through a small puncture in the artery in the arm or groin.
Disease prevention
Like any other disease, it is easier to prevent than to treat.
General preventive measures include:
- Elimination of existing risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
- Prevention of any foot injuries.
- Preventive and hygienic foot care.
- Wearing comfortable shoes.
Patients with various pathologies of the cardiovascular system require systematic courses of therapy.
If an obstruction has already been detected, reconstructive surgery should be performed as soon as possible. It will allow you to save the limb. By using the help of specialists, you can significantly improve the quality of your life.
Important! Any prevention will be effective if you carry it out under the constant supervision of your doctor. Often a whole group of specialists (surgeons, therapists, cardiologists, phlebologists) is involved in the manipulations.
Who is indicated for cardiac stenting?
Stenting of cardiac vessels is indicated for patients with severe angina pectoris, after myocardial infarction and pre-infarction conditions, patients with proven ischemia (lack of blood to the heart) based on the results of stress tests. In this case, the decision on stenting is made only based on the results of coronary angiography - a contrast study of the heart vessels. Coronary angiography, like stenting, is performed in the cath lab. Often coronary angiography “transitions” into vascular stenting because performed through the same puncture in the artery.